Abstract
The present study evaluated the effect of a novel anti-lipid A monoclonal antibody, termed SdJ5, on the in vitro production of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-1 beta by endotoxin- or lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-challenged human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (hPBMC). In addition, the present study determined whether SdJ5 could neutralize the in vivo toxicity of LPS. SdJ5, at a concentration equal to or greater than 3 micrograms/ml, specifically inhibited TNF-alpha and interleukin-1 beta production by hPBMC stimulated with every type of LPS and lipid A assessed. SdJ5 also showed a significantly greater inhibition of cytokine production than a nonrelevant human immunoglobulin M myeloma control. The SdJ5-mediated inhibition of TNF-alpha production was rapid, as the simultaneous addition of the SdJ5 and LPS still resulted in a marked decrease in hPBMC cytokine synthesis. The ability of SdJ5 to neutralize in vivo toxicity was also determined by using LPS from four different strains of gram-negative bacteria. LPS, when preincubated with SdJ5, resulted in a significant decrease in the 24-h mortality rate compared with that for the control. These studies show that the anti-lipid A monoclonal antibody SdJ5 can modulate LPS-induced cytokine production in vitro and increase the survival rate of rats challenged with lethal doses of LPS.
Full text
PDF
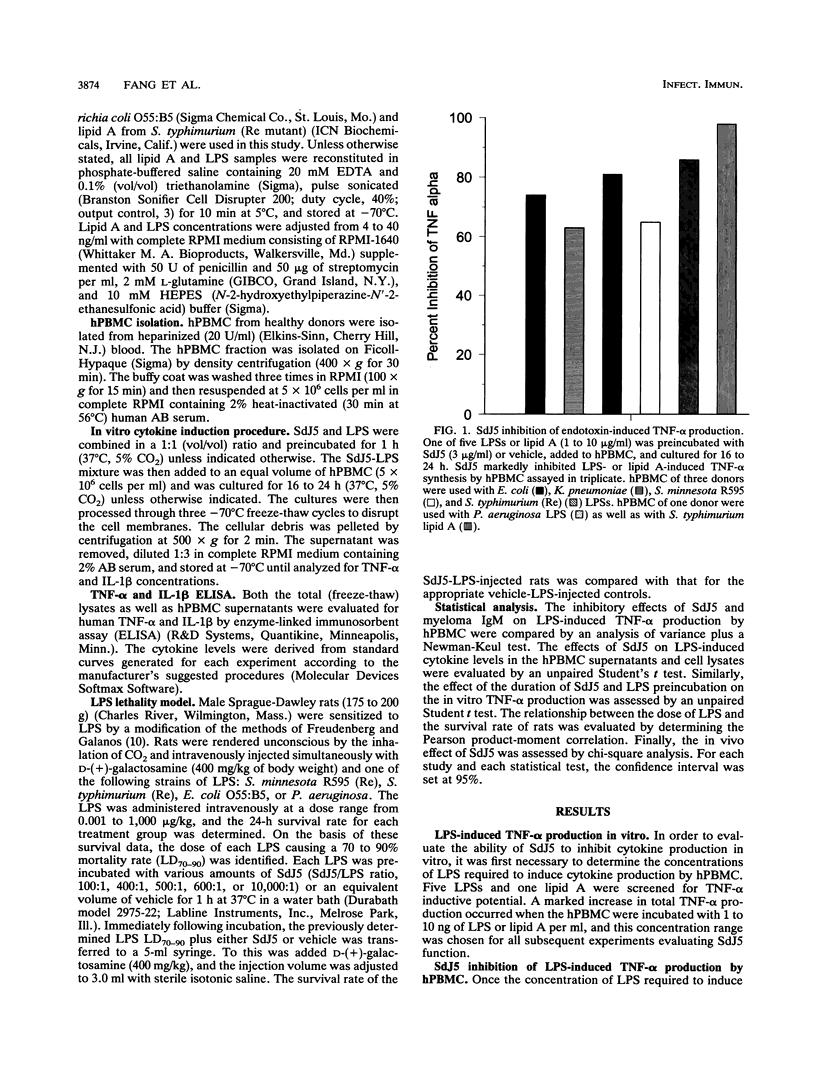
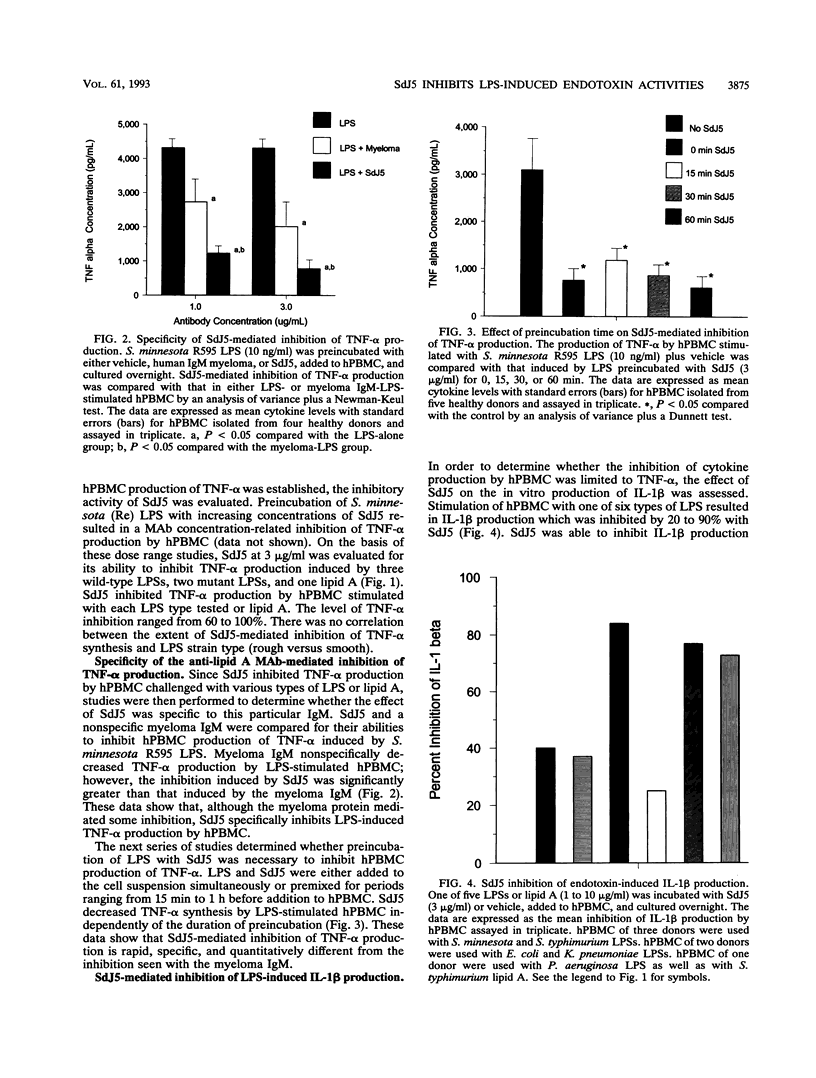
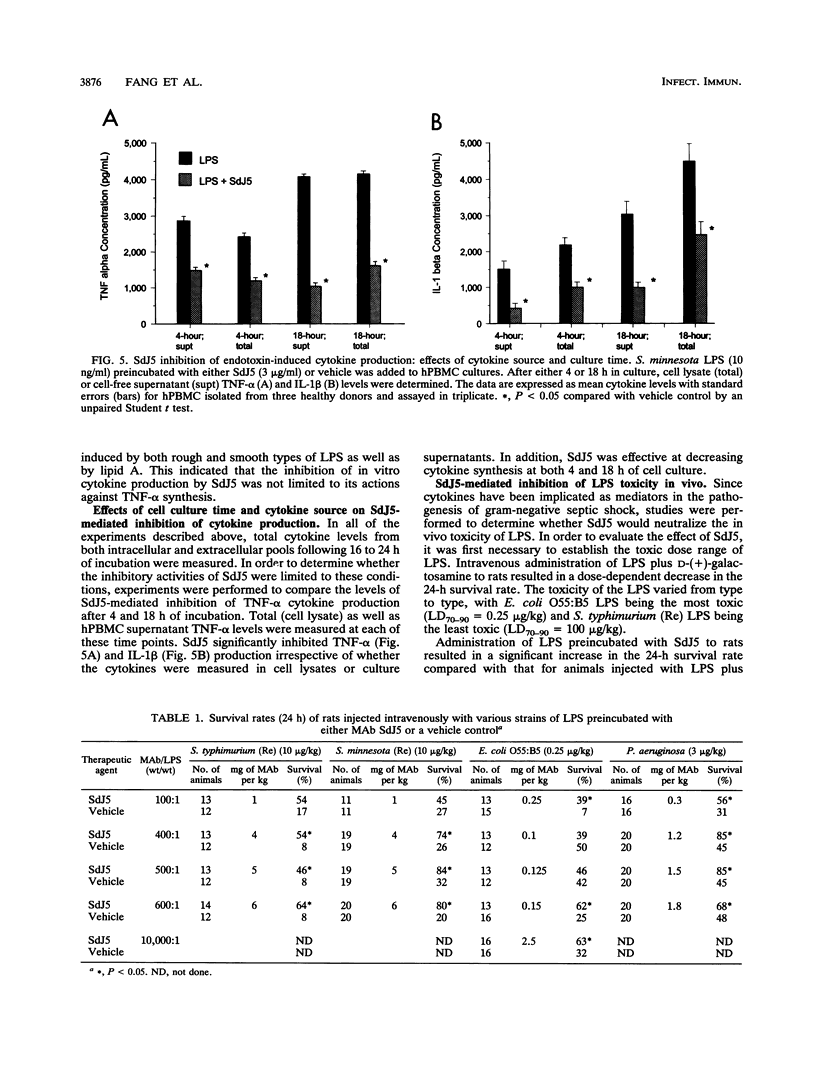


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander H. R., Doherty G. M., Buresh C. M., Venzon D. J., Norton J. A. A recombinant human receptor antagonist to interleukin 1 improves survival after lethal endotoxemia in mice. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):1029–1032. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner J. D., Heumann D., Gerain J., Weinbreck P., Grau G. E., Glauser M. P. Association between protective efficacy of anti-lipopolysaccharide (LPS) antibodies and suppression of LPS-induced tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 6. Comparison of O side chain-specific antibodies with core LPS antibodies. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):889–896. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 12;316(7):379–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702123160705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavaillon J. M., Haeffner-Cavaillon N. Signals involved in interleukin 1 synthesis and release by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated monocytes/macrophages. Cytokine. 1990 Sep;2(5):313–329. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(90)90061-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chia J. K., Pollack M., Guelde G., Koles N. L., Miller M., Evans M. E. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-reactive monoclonal antibodies fail to inhibit LPS-induced tumor necrosis factor secretion by mouse-derived macrophages. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):872–880. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and its biologically related cytokines. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:153–205. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60642-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorai H., Bubbers J. E., Gillies S. D. Cloning and reexpression of a functional human IgM anti-lipid A antibody. Hybridoma. 1992 Oct;11(5):667–675. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1992.11.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y., Moldawer L. L., Marano M., Wei H., Tatter S. B., Clarick R. H., Santhanam U., Sherris D., May L. T., Sehgal P. B. Endotoxemia elicits increased circulating beta 2-IFN/IL-6 in man. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2321–2324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Zeller W. P., Hurley R. M., Jong J. S., Lee C. H. Prophylaxis and treatment of newborn endotoxic shock with anti-lipid A monoclonal antibodies. Circ Shock. 1991 Sep;35(1):60–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R. N., Wilson K. M., Kunz A. Y., Wedel N. I., Gorelick K. J. Observations using antiendotoxin antibody (E5) as adjuvant therapy in humans with suspected, serious, gram-negative sepsis. Crit Care Med. 1992 Jun;20(6):730–735. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199206000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenman R. L., Schein R. M., Martin M. A., Wenzel R. P., MacIntyre N. R., Emmanuel G., Chmel H., Kohler R. B., McCarthy M., Plouffe J. A controlled clinical trial of E5 murine monoclonal IgM antibody to endotoxin in the treatment of gram-negative sepsis. The XOMA Sepsis Study Group. JAMA. 1991 Aug 28;266(8):1097–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw L. B., Tekamp-Olson P., Chang A. C., Lee P. A., Taylor F. B., Jr, Murray C. K., Peer G. T., Emerson T. E., Jr, Passey R. B., Kuo G. C. Survival of primates in LD100 septic shock following therapy with antibody to tumor necrosis factor (TNF alpha). Circ Shock. 1990 Mar;30(3):279–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiener P. A., Marek F., Rodgers G., Lin P. F., Warr G., Desiderio J. Induction of tumor necrosis factor, IFN-gamma, and acute lethality in mice by toxic and non-toxic forms of lipid A. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):870–874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn H. M., Brade L., Appelmelk B. J., Kusumoto S., Rietschel E. T., Brade H. Characterization of the epitope specificity of murine monoclonal antibodies directed against lipid A. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2201–2210. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2201-2210.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Chensue S. W., Phan S. H. Prostaglandins as endogenous mediators of interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):186–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann V., Freudenberg M. A., Galanos C. Lethal toxicity of lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor in normal and D-galactosamine-treated mice. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):657–663. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okusawa S., Gelfand J. A., Ikejima T., Connolly R. J., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin 1 induces a shock-like state in rabbits. Synergism with tumor necrosis factor and the effect of cyclooxygenase inhibition. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1162–1172. doi: 10.1172/JCI113431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peel J. E., Voirol M. J., Kolly C., Gobet D., Martinod S. Induction of circulating tumor necrosis factor cannot be demonstrated during septicemic salmonellosis in calves. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):439–442. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.439-442.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semeraro N., Biondi A., Lorenzet R., Locati D., Mantovani A., Donati M. B. Direct induction of tissue factor synthesis by endotoxin in human macrophages from diverse anatomical sites. Immunology. 1983 Dec;50(4):529–535. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva A. T., Appelmelk B. J., Buurman W. A., Bayston K. F., Cohen J. Monoclonal antibody to endotoxin core protects mice from Escherichia coli sepsis by a mechanism independent of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6. J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):454–459. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva A. T., Bayston K. F., Cohen J. Prophylactic and therapeutic effects of a monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor-alpha in experimental gram-negative shock. J Infect Dis. 1990 Aug;162(2):421–427. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.2.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell R. J., Parrillo J. E. Cardiovascular dysfunction in septic shock. Chest. 1991 Apr;99(4):1000–1009. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.4.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strunk R. C., Whitehead A. S., Cole F. S. Pretranslational regulation of the synthesis of the third component of complement in human mononuclear phagocytes by the lipid A portion of lipopolysaccharide. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):985–990. doi: 10.1172/JCI112099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The HA-1A monoclonal antibody for gram-negative sepsis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jul 25;325(4):279–283. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199107253250411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tune B. M., Hsu C. Y., Bieber M. M., Teng N. N. Effects of anti-lipid A human monoclonal antibody on lipopolysaccharide-induced toxicity to the kidney. J Urol. 1989 Jun;141(6):1463–1466. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)41347-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vacheron F., Mandine E., Lenaour R., Smets P., Zalisz R., Guenounou M. Inhibition of production of tumor necrosis factor by monoclonal antibodies to lipopolysaccharides. J Infect Dis. 1992 May;165(5):873–878. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.5.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi G., Gelfand J. A., Burke J. F., Thompson R. C., Dinarello C. A. A specific receptor antagonist for interleukin 1 prevents Escherichia coli-induced shock in rabbits. FASEB J. 1991 Mar 1;5(3):338–343. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.3.1825816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Matsushima K., Oppenheim J. J., Leonard E. J. Neutrophil chemotactic factor produced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated human blood mononuclear leukocytes: partial characterization and separation from interleukin 1 (IL 1). J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):788–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Gascon R., Alam S., Bermudez L. E. Monoclonal antibodies for treatment of gram-negative infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Nov-Dec;11 (Suppl 7):S1564–S1571. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_7.s1564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler E. J., Fisher C. J., Jr, Sprung C. L., Straube R. C., Sadoff J. C., Foulke G. E., Wortel C. H., Fink M. P., Dellinger R. P., Teng N. N. Treatment of gram-negative bacteremia and septic shock with HA-1A human monoclonal antibody against endotoxin. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The HA-1A Sepsis Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1991 Feb 14;324(7):429–436. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199102143240701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


