Abstract
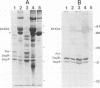
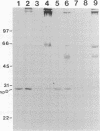
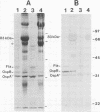
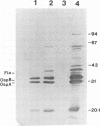
Borrelia burgdorferi produces extracellular vesicles which contain some of the outer surface proteins of the bacterium (e.g., OspA and OspB). Borrelial vesicles, isolated by differential centrifugation and filtration, were tested for the ability to bind to cultured human umbilical vein endothelial (HUVE) cells in culture. The recently described lipoprotein OspD was expressed on vesicles. Vesicles exhibited differential expression of OspB and OspD in a relationship with passage number and medium serum supplement type, respectively. Qualitative immunoblotting analyses demonstrated dose-dependent, passage number-dependent adsorption of vesicles by HUVE cells. This adsorption was demonstrated to be dependent upon a borrelial component of the vesicle and not due to the presence of minor contamination with intact spirochetes. Quantitative experiments examining inhibition of B. burgdorferi-HUVE association as a function of prior vesicle-HUVE association demonstrated dependence upon (i) a borrelial component(s) in the vesicle, (ii) low passage number, and (iii) vesicle protein concentration. However, vesicle pretreatment of the HUVE cell monolayer was not requisite for this inhibition. Vesicles from highly passaged borrelias were noninhibitory for B. burgdorferi-HUVE cell association, regardless of the serum used to supplement the medium. The use of vesicles as a tool for studying B. burgdorferi pathogenesis and/or physiology is proposed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F. Biology of Borrelia species. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):381–400. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.381-400.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Heiland R. A., Schrumpf M. E., Tessier S. L. A Borrelia-specific monoclonal antibody binds to a flagellar epitope. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):549–554. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.549-554.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Laboratory aspects of Lyme borreliosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Oct;1(4):399–414. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.4.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Coleman J. L., Garcia-Monco J. C., Deponte P. C. Biological activity of Borrelia burgdorferi antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:115–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comstock L. E., Fikrig E., Shoberg R. J., Flavell R. A., Thomas D. D. A monoclonal antibody to OspA inhibits association of Borrelia burgdorferi with human endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):423–431. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.423-431.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comstock L. E., Thomas D. D. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi invasion of cultured endothelial cells. Microb Pathog. 1991 Feb;10(2):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90074-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorward D. W., Huguenel E. D., Davis G., Garon C. F. Interactions between extracellular Borrelia burgdorferi proteins and non-Borrelia-directed immunoglobulin M antibodies. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):838–844. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.838-844.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorward D. W., Schwan T. G., Garon C. F. Immune capture and detection of Borrelia burgdorferi antigens in urine, blood, or tissues from infected ticks, mice, dogs, and humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jun;29(6):1162–1170. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.6.1162-1170.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duray P. H., Steere A. C. The spectrum of organ and systems pathology in human Lyme disease. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):169–178. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Monco J. C., Fernandez Villar B., Szczepanski A., Benach J. L. Cytotoxicity of Borrelia burgdorferi for cultured rat glial cells. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1362–1366. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.6.1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garon C. F., Dorward D. W., Corwin M. D. Structural features of Borrelia burgdorferi--the Lyme disease spirochete: silver staining for nucleic acids. Scanning Microsc Suppl. 1989;3:109–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habicht G. S., Beck G., Benach J. L., Coleman J. L., Leichtling K. D. Lyme disease spirochetes induce human and murine interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3147–3154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katona L. I., Beck G., Habicht G. S. Purification and immunological characterization of a major low-molecular-weight lipoprotein from Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):4995–5003. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.4995-5003.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaul R., Wenman W. M. Cyclic AMP inhibits developmental regulation of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):722–727. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.722-727.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre R. B., Perng G. C., Johnson R. C. The 83-kilodalton antigen of Borrelia burgdorferi which stimulates immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG responses in infected hosts is expressed by a chromosomal gene. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1673–1675. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1673-1675.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Y., Sturrock A., Weis J. J. Intracellular localization of Borrelia burgdorferi within human endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):671–678. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.671-678.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. C., Isa S., Vannier E., Georgilis K., Steere A. C., Dinarello C. A. Live Borrelia burgdorferi preferentially activate interleukin-1 beta gene expression and protein synthesis over the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):906–912. doi: 10.1172/JCI115966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Carter C. J., Howell J. K., Barbour A. G. Low-passage-associated proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi B31: characterization and molecular cloning of OspD, a surface-exposed, plasmid-encoded lipoprotein. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4662–4672. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4662-4672.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V., Brandt M. E., Isaacs R. D., Thompson P. A., Beutler B. Lipoproteins of Borrelia burgdorferi and Treponema pallidum activate cachectin/tumor necrosis factor synthesis. Analysis using a CAT reporter construct. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1968–1974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley B. S., Oppenheimer-Marks N., Hansen E. J., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Virulent Treponema pallidum activates human vascular endothelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;165(3):484–493. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.3.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W. Antigenic changes of Borrelia burgdorferi as a result of in vitro cultivation. J Infect Dis. 1987 Nov;156(5):852–853. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.5.852-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E. Cases of Lyme disease in the United States: locations correlated with distribution of Ixodes dammini. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Nov;91(5):730–733. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-5-730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczepanski A., Furie M. B., Benach J. L., Lane B. P., Fleit H. B. Interaction between Borrelia burgdorferi and endothelium in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1637–1647. doi: 10.1172/JCI114615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sădziene A., Rosa P. A., Thompson P. A., Hogan D. M., Barbour A. G. Antibody-resistant mutants of Borrelia burgdorferi: in vitro selection and characterization. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):799–809. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Comstock L. E. Interaction of Lyme disease spirochetes with cultured eucaryotic cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1324–1326. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1324-1326.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitmire W. M., Garon C. F. Specific and nonspecific responses of murine B cells to membrane blebs of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1993 Apr;61(4):1460–1467. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.4.1460-1467.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]