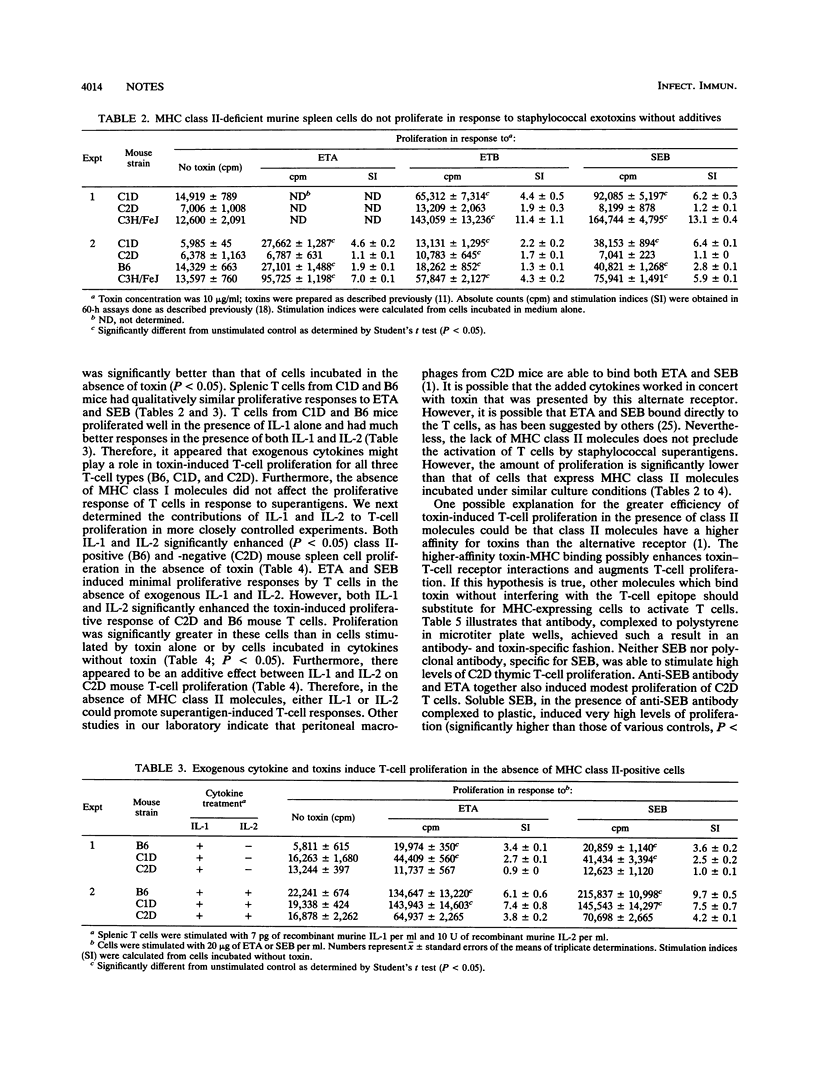
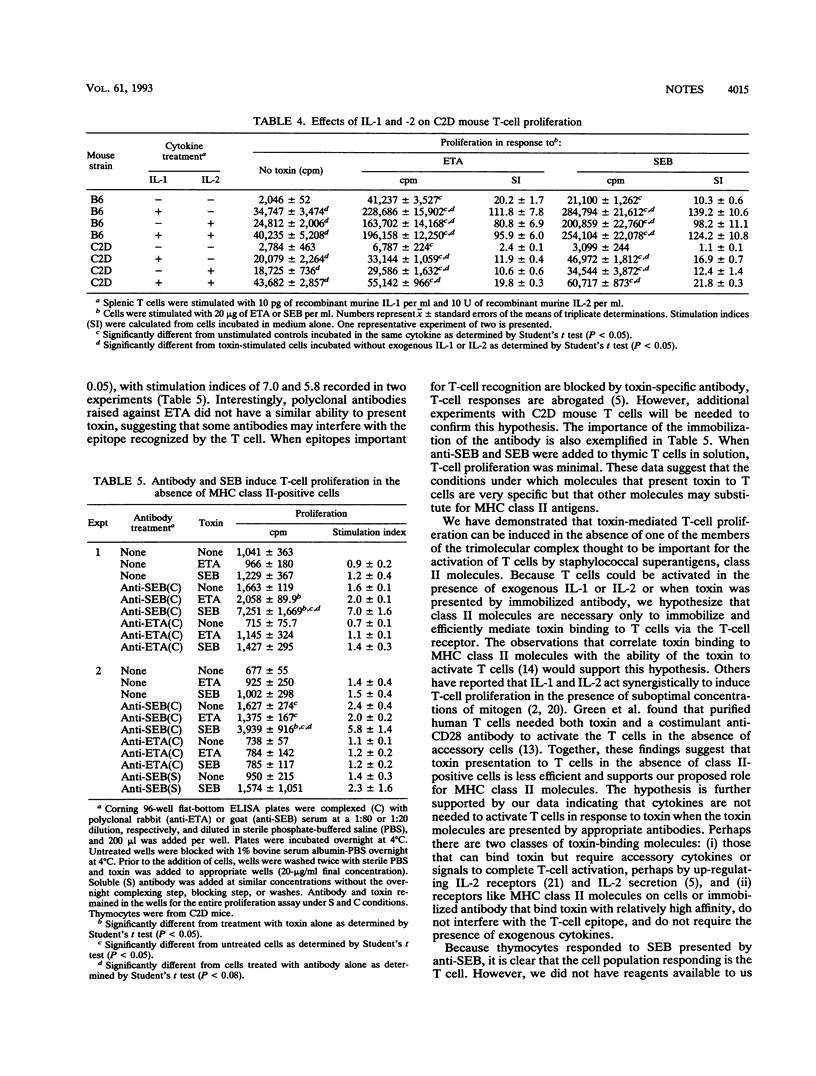
Abstract
We used major histocompatibility complex class II antigen-deficient transgenic mice to show that in vitro natural killer cell cytotoxicity and T-cell activation by staphylococcal exotoxins (superantigens) are not dependent upon the presence of major histocompatibility complex class II molecules. T cells can be activated by exotoxins in the presence of exogenously added interleukin 1 or 2 or in the presence of specific antibody without exogenously added cytokines.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackman M. A., Lund F. E., Surman S., Corley R. B., Woodland D. L. Major histocompatibility complex-restricted recognition of retroviral superantigens by V beta 17+ T cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Jul 1;176(1):275–280. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.1.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bödeker B. G., van Eijk R. V., Mühlradt P. F. Mitogenic effects of partially purified interleukin 2 on thymocyte subpopulations and spleen t cells of the mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Sep;10(9):702–707. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlow D. A., Payne U., Hozumi N., Roder J. C., Czitrom A. A. Class I (H-2Kb) gene transfection reduces susceptibility of YAC-1 lymphoma targets to natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Apr;20(4):841–846. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson R., Fischer H., Sjögren H. O. Binding of staphylococcal enterotoxin A to accessory cells is a requirement for its ability to activate human T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2484–2488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunnick J. E., Sakamoto K., Chapes S. K., Fortner G. W., Takemoto D. J. Induction of tumor cytotoxic immune cells using a protein from the bitter melon (Momordica charantia). Cell Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;126(2):278–289. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90321-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellabona P., Peccoud J., Kappler J., Marrack P., Benoist C., Mathis D. Superantigens interact with MHC class II molecules outside of the antigen groove. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1115–1121. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90388-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Hedlund G., Segren S., Lando P. A., Herrmann T., Kelly A. P., Kalland T. Human major histocompatibility complex class II-negative colon carcinoma cells present staphylococcal superantigens to cytotoxic T lymphocytes: evidence for a novel enterotoxin receptor. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1229–1233. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Hartwig U. T-lymphocyte stimulation by microbial superantigens. Chem Immunol. 1992;55:36–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Mittrücker H. W. Evidence for T cell receptor-HLA class II molecule interaction in the response to superantigenic bacterial toxins. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1331–1333. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming S. D., Iandolo J. J., Chapes S. K. Murine macrophage activation by staphylococcal exotoxins. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4049–4055. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4049-4055.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. D. Superantigen data. Nature. 1992 Dec 3;360(6403):423–423. doi: 10.1038/360423b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. M., Turka L. A., June C. H., Thompson C. B. CD28 and staphylococcal enterotoxins synergize to induce MHC-independent T-cell proliferation. Cell Immunol. 1992 Nov;145(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90308-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman A., Croteau G., Sekaly R. P., Kappler J., Marrack P. HLA-DR alleles differ in their ability to present staphylococcal enterotoxins to T cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):709–717. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman A., Labrecque N., Thibodeau J., Marrack P., Kappler J. W., Sekaly R. P. Identification of the staphylococcal enterotoxin A superantigen binding site in the beta 1 domain of the human histocompatibility antigen HLA-DR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9954–9958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson K. R., Robinson H., Fraser J. D. Two adjacent residues in staphylococcal enterotoxins A and E determine T cell receptor V beta specificity. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):175–184. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höglund P., Glas R., Ohlén C., Ljunggren H. G., Kärre K. Alteration of the natural killer repertoire in H-2 transgenic mice: specificity of rapid lymphoma cell clearance determined by the H-2 phenotype of the target. J Exp Med. 1991 Aug 1;174(2):327–334. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopydlowski K. M., McVey D. S., Woods K. M., Iandolo J. J., Chapes S. K. Effects of antiorthostatic suspension and corticosterone on macrophage and spleen cell function. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Aug;52(2):202–208. doi: 10.1002/jlb.52.2.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao N. S., Bix M., Zijlstra M., Jaenisch R., Raulet D. MHC class I deficiency: susceptibility to natural killer (NK) cells and impaired NK activity. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):199–202. doi: 10.1126/science.1853205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel A. L., Mehta S. R., Ford R. J., Lachman L. B. Effect of interleukin 1 on human thymocytes and purified human T cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):470–475. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männel D. N., Mizel S. B., Diamantstein T., Falk W. Induction of interleukin 2 responsiveness in thymocytes by synergistic action of interleukin 1 and interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3108–3110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisini R., Matricardi P. M., Fattorossi A., Biselli R., D'Amelio R. Presentation of superantigen by human T cell clones: a model of T-T cell interaction. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Aug;22(8):2033–2039. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. K., Pontzer C. H., Johnson H. M. Both alpha-helices along the major histocompatibility complex binding cleft are required for staphylococcal enterotoxin A function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7228–7232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salamon F. T., Fayen J. D., Leonard M. L., Finegan C. K., Rich E. A. Accessory function of human mononuclear phagocytes for lymphocyte responses to the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Cell Immunol. 1992 May;141(2):466–484. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90164-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub D. D., Rogers T. J. Direct activation of murine T cells by staphylococcal enterotoxins. Cell Immunol. 1992 Apr;140(2):267–281. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90195-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



