Abstract
The major outer membrane protein (MOMP) of Chlamydia trachomatis was expressed in Escherichia coli. To assess whether it assembled into a conformationally correct structure at the cell surface, we characterized the recombinant MOMP (rMOMP) by Western immunoblot analysis, indirect immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation with monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) that recognize contiguous and conformational MOMP epitopes. Western blot analysis showed that most of the rMOMP comigrated with authentic monomer MOMP, indicating that its signal peptide was recognized and cleaved by E. coli. The rMOMP could not be detected on the cell surface of viable or formalin-killed E. coli organisms by indirect immunofluorescence staining with a MAb specific for a MOMP contiguous epitope. In contrast, the same MAb readily stained rMOMP-expressing E. coli cells that had been permeabilized by methanol fixation. A MAb that recognizes a conformational MOMP epitope and reacted strongly with formalin- or methanol-fixed elementary bodies failed to stain formalin- or methanol-fixed E. coli expressing rMOMP. Moreover, this MAb did not immunoprecipitate rMOMP from expressing E. coli cells even though it precipitated the authentic protein from lysates of C. trachomatis elementary bodies. Therefore we concluded that rMOMP was not localized to the E. coli cell surface and was not recognizable by a conformation-dependent antibody. These results indicate that rMOMP expressed by E. coli is unlikely to serve as an accurate model of MOMP structure and function. They also question the utility of rMOMP as a source of immunogen for eliciting neutralizing antibodies against conformational antigenic sites of the protein.
Full text
PDF

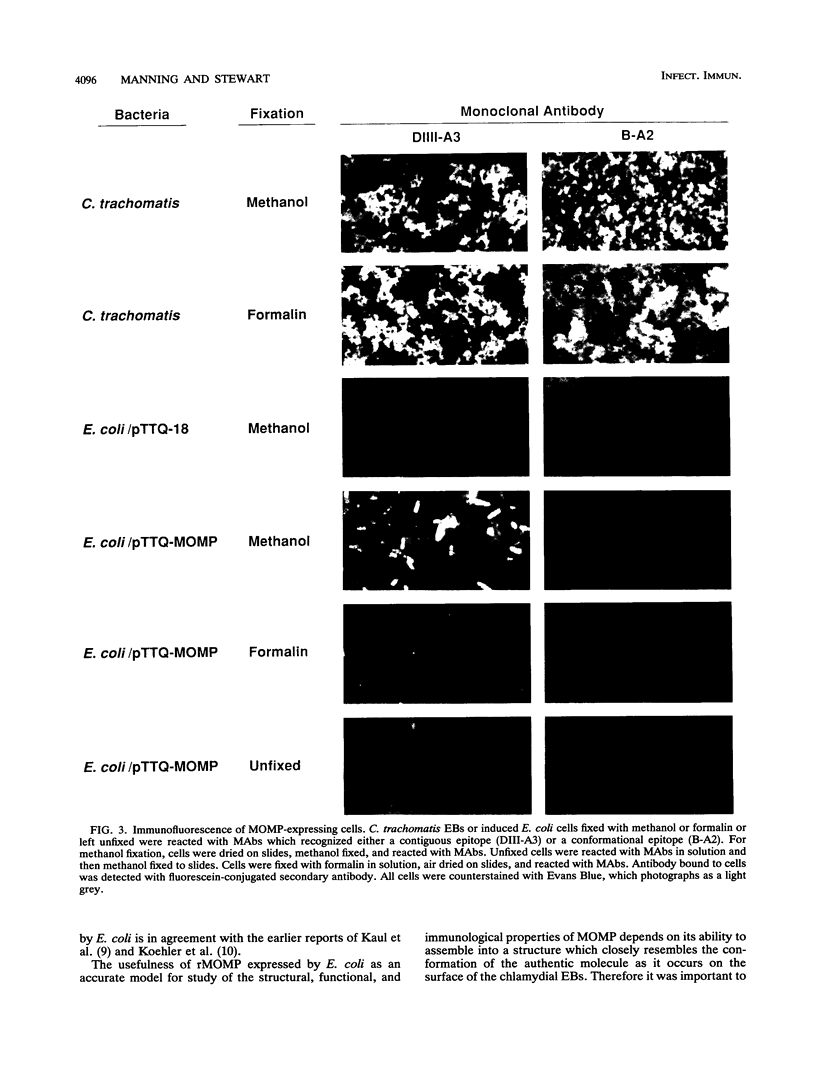


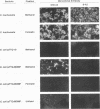
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehr W., Zhang Y. X., Joseph T., Su H., Nano F. E., Everett K. D., Caldwell H. D. Mapping antigenic domains expressed by Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4000–4004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Amano K., Hackstadt T., Perry L., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydia trachomatis has penicillin-binding proteins but not detectable muramic acid. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):420–428. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.420-428.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Hitchcock P. J. Monoclonal antibody against a genus-specific antigen of Chlamydia species: location of the epitope on chlamydial lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):306–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.306-314.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Kromhout J., Schachter J. Purification and partial characterization of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1161–1176. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1161-1176.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett A. J., Harrison M. J., Manire G. P. A search for the bacterial mucopeptide component, muramic acid, in Chlamydia. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jan;80(1):315–318. doi: 10.1099/00221287-80-1-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaul R., Duncan M. J., Guest J., Wenman W. M. Expression of the Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein-encoding gene in Escherichia coli: role of the 3' end in mRNA stability. Gene. 1990 Mar 1;87(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90499-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler J. E., Birkelund S., Stephens R. S. Overexpression and surface localization of the Chlamydia trachomatis major outer membrane protein in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(9):1087–1094. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark M. J. Multicopy expression vectors carrying the lac repressor gene for regulated high-level expression of genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;51(2-3):255–267. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su H., Watkins N. G., Zhang Y. X., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydia trachomatis-host cell interactions: role of the chlamydial major outer membrane protein as an adhesin. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):1017–1025. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.1017-1025.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su H., Zhang Y. X., Barrera O., Watkins N. G., Caldwell H. D. Differential effect of trypsin on infectivity of Chlamydia trachomatis: loss of infectivity requires cleavage of major outer membrane protein variable domains II and IV. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2094–2100. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2094-2100.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washington A. E., Gove S., Schachter J., Sweet R. L. Oral contraceptives, Chlamydia trachomatis infection, and pelvic inflammatory disease. A word of caution about protection. JAMA. 1985 Apr 19;253(15):2246–2250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Hatch T. P., Woese C. R. Eubacterial origin of chlamydiae. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):570–574. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.570-574.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter L., Goldy A. S., Baer C. Prevalence and epidemiologic correlates of Chlamydia trachomatis in rural and urban populations. Sex Transm Dis. 1990 Jan-Mar;17(1):30–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. X., Stewart S., Joseph T., Taylor H. R., Caldwell H. D. Protective monoclonal antibodies recognize epitopes located on the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):575–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]