Abstract
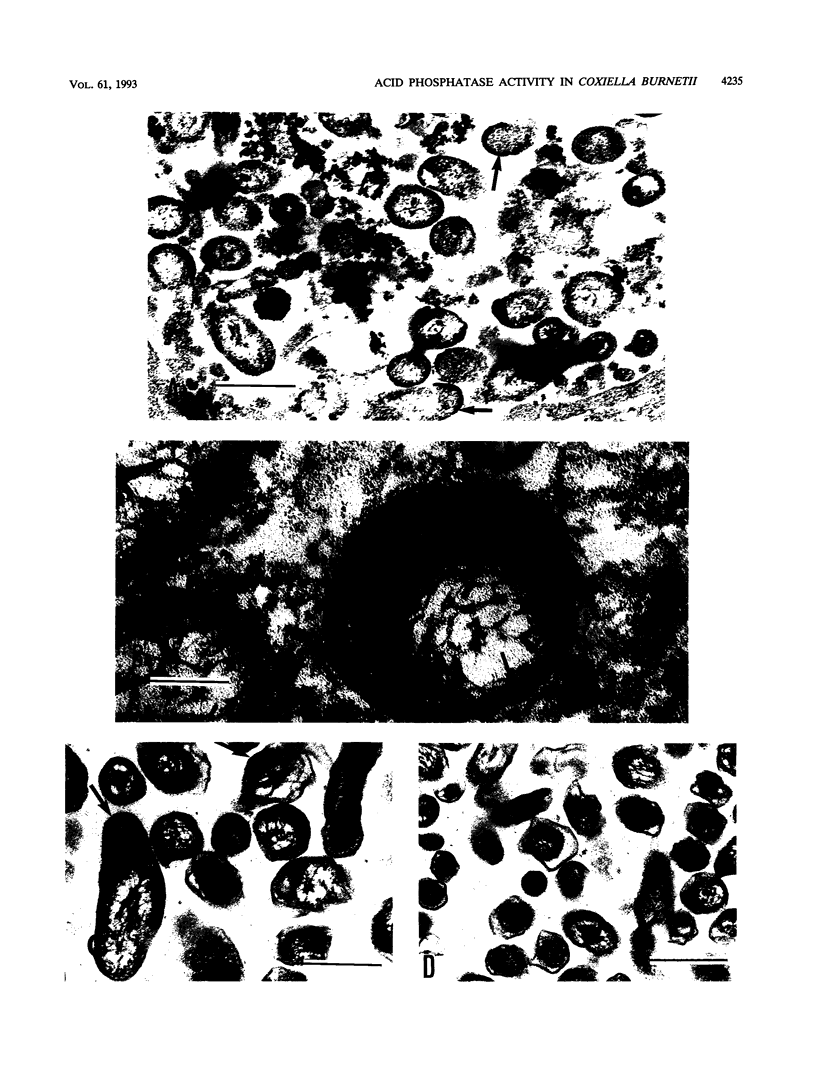
High-speed supernatant fluids derived from sonicated Coxiella burnetii contained considerable acid phosphatase activity when assayed by using 4-methylumbelliferylphosphate; they also contained a factor that blocked superoxide anion production by human neutrophils stimulated with formyl-Met-Leu-Phe. The pH optimum of the enzyme was approximately 5.0. The level of phosphatase activity detected in several isolates of C. burnetii implicated in acute (Nine Mile) and chronic (S Q217, PRS Q177, K Q154) Q fever was 25 to 60 times greater than that reported in other microorganisms, including Leishmania and Legionella spp. The enzyme was found in rickettsiae grown in different hosts (L929 cells and embryonated eggs) and, in the case of L929 cells, for both short periods (less than a month) and the long term (years). Cytochemical techniques coupled with electron microscopy localized the phosphatase activity to the periplasmic gap in the parasite. Ion-exchange chromatography revealed a major species of the enzyme and showed that the enzyme of the parasite was distinct from that of the host cell (L929 fibroblasts); its apparent molecular weight was 74,000. Phosphatase inhibitors (i.e., molybdate heteropolyanions) had differential effects on the phosphatases of the parasite and host cell. C. burnetii supernatant fluid inhibited superoxide anion production by formyl-Met-Leu-Phe-stimulated human neutrophils; molybdate inhibitors reversed the inhibition. Treatment of C. burnetii-infected L929 cells with one of the molybdate compounds (complex B') significantly reduced the level of infection and did not affect the viability or growth of the host cell. These data suggest that the acid phosphatase of the parasite may be a major virulence determinant, allowing the agent to avoid being killed during uptake by phagocytes and subsequently in the phagolysosome.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akporiaye E. T., Baca O. G. Superoxide anion production and superoxide dismutase and catalase activities in Coxiella burnetii. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):520–523. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.520-523.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akporiaye E. T., Rowatt J. D., Aragon A. A., Baca O. G. Lysosomal response of a murine macrophage-like cell line persistently infected with Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1155–1162. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1155-1162.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akporiaye E. T., Stefanovich D., Tsosie V., Baca G. Coxiella burnetii fails to stimulate human neutrophil superoxide anion production. Acta Virol. 1990 Feb;34(1):64–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. C. Evaluation of serum opsonic capacity by quantitating the initial chemiluminescent response from phagocytizing polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):828–833. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.828-833.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M., Kipnes R. S., Curnutte J. T. Biological defense mechanisms. The production by leukocytes of superoxide, a potential bactericidal agent. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):741–744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca O. G., Akporiaye E. T., Aragon A. S., Martinez I. L., Robles M. V., Warner N. L. Fate of phase I and phase II Coxiella burnetii in several macrophage-like tumor cell lines. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):258–266. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.258-266.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca O. G., Scott T. O., Akporiaye E. T., DeBlassie R., Crissman H. A. Cell cycle distribution patterns and generation times of L929 fibroblast cells persistently infected with Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):366–369. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.366-369.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmüller Y., Mauel J. Studies on the mechanisms of macrophage activation: possible involvement of oxygen metabolites in killing of Leishmania enrietti by activated mouse macrophages. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Mar;29(3):181–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton P. R., Kordová N., Paretsky D. Electron microscopic studies of the rickettsia Coxiella burneti: entry, lysosomal response, and fate of rickettsial DNA in L-cells. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Feb;17(2):143–150. doi: 10.1139/m71-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton P. R., Stueckemann J., Welsh R. M., Paretsky D. Some ultrastructural effects of persistent infections by the rickettsia Coxiella burnetii in mouse L cells and green monkey kidney (Vero) cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):556–566. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.556-566.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das S., Saha A. K., Remaley A. T., Glew R. H., Dowling J. N., Kajiyoshi M., Gottlieb M. Hydrolysis of phosphoproteins and inositol phosphates by cell surface phosphatase of Leishmania donovani. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Aug;20(2):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J. N., Saha A. K., Glew R. H. Virulence factors of the family Legionellaceae. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):32–60. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.32-60.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Czuczman M. S., Diven W. F., Berens R. L., Pope M. T., Katsoulis D. E. Partial purification and characterization of particulate acid phosphatase of Leishmania donovani promastigotes. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1982;72(4):581–590. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(82)90510-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidaris C. G., Bonventre P. F. A role for oxygen-dependent mechanisms in killing of Leishmania donovani tissue forms by activated macrophages. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):850–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer T. J., Nelson K. E., Crispen R. G., Andersen B. R. Mycobacterium leprae fails to stimulate phagocytic cell superoxide anion generation. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):514–520. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.514-520.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Interaction of the legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) with human phagocytes. II. Antibody promotes binding of L. pneumophila to monocytes but does not inhibit intracellular multiplication. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):398–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Cohn Z. A. Macrophage oxygen-dependent antimicrobial activity. I. Susceptibility of Toxoplasma gondii to oxygen intermediates. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):938–949. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newburger P. E., Chovaniec M. E., Cohen H. J. Activity and activation of the granulocyte superoxide-generating system. Blood. 1980 Jan;55(1):85–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaley A. T., Kuhns D. B., Basford R. E., Glew R. H., Kaplan S. S. Leishmanial phosphatase blocks neutrophil O-2 production. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11173–11175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman M. J., Coriz P. D., Baca O. G. A proposed model to explain persistent infection of host cells with Coxiella burnetii. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 May;132(5):1415–1422. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-5-1415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha A. K., Crans D. C., Pope M. T., Simone C. M., Glew R. H. Inhibition of human seminal fluid and Leishmania donovani phosphatases by molybdate heteropolyanions. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3511–3517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha A. K., Dowling J. N., LaMarco K. L., Das S., Remaley A. T., Olomu N., Pope M. T., Glew R. H. Properties of an acid phosphatase from Legionella micdadei which blocks superoxide anion production by human neutrophils. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Nov 15;243(1):150–160. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90783-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha A. K., Dowling J. N., Pasculle A. W., Glew R. H. Legionella micdadei phosphatase catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in human neutrophils. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Aug 15;265(1):94–104. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90375-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel J. E., Frazier M. E., Mallavia L. P. Correlation of plasmid type and disease caused by Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):775–779. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.775-779.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasada M., Johnston R. B., Jr Macrophage microbicidal activity. Correlation between phagocytosis-associated oxidative metabolism and the killing of Candida by macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):85–98. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberman R., Fiset P. Method for counting Rickettsiae and Chlamydiae in purified suspensions. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):259–261. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.259-261.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzianabos T., Moss C. W., McDade J. E. Fatty acid composition of rickettsiae. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Mar;13(3):603–605. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.3.603-605.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinbaum D. L., Benner R. R., Dowling J. N., Alpern A., Pasculle A. W., Donowitz G. R. Interaction of Legionella micdadei with human monocytes. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):68–73. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.68-73.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Dobson M. E., Samuel J. E., Dasch G. A., Mallavia L. P., Baca O., Mandelco L., Sechrest J. E., Weiss E., Woese C. R. Phylogenetic diversity of the Rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4202–4206. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4202-4206.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Peacock M. G., McCaul T. F. Immunological and biological characterization of Coxiella burnetii, phases I and II, separated from host components. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):840–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.840-851.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Tsai V., Remington J. S. Failure to trigger the oxidative metabolic burst by normal macrophages: possible mechanism for survival of intracellular pathogens. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):328–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeaman M. R., Roman M. J., Baca O. G. Antibiotic susceptibilities of two Coxiella burnetii isolates implicated in distinct clinical syndromes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jul;33(7):1052–1057. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.7.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]