Abstract
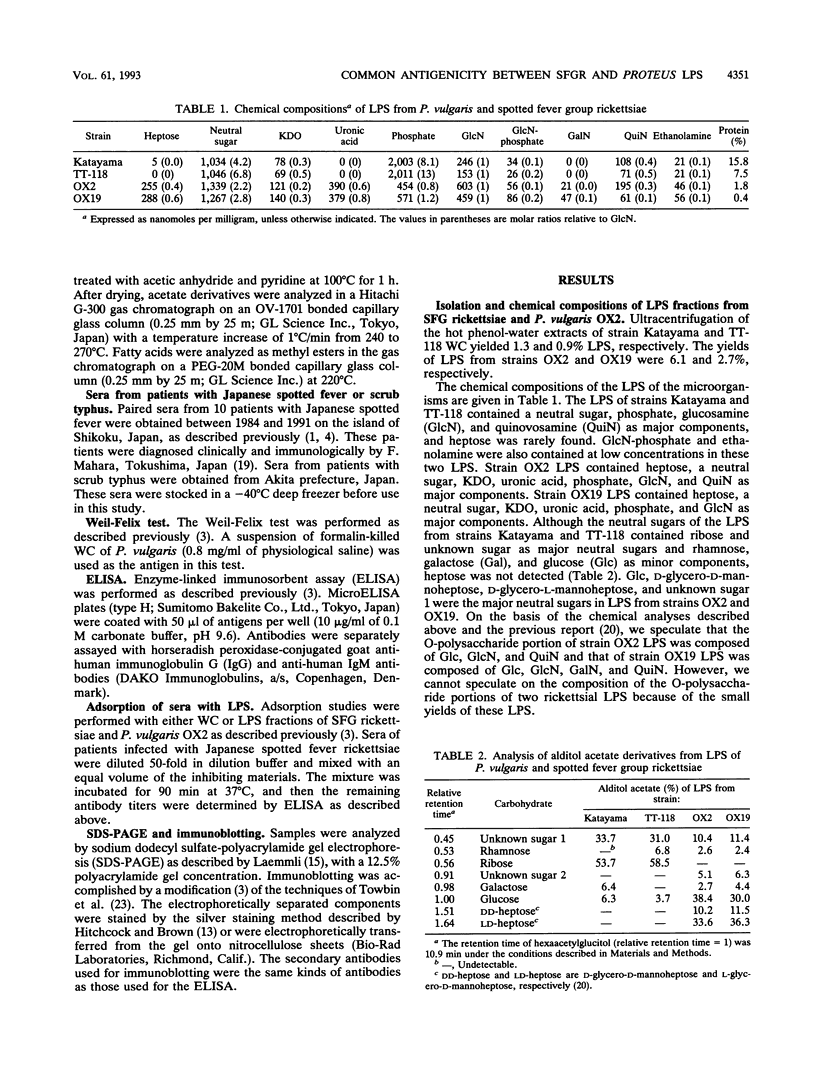
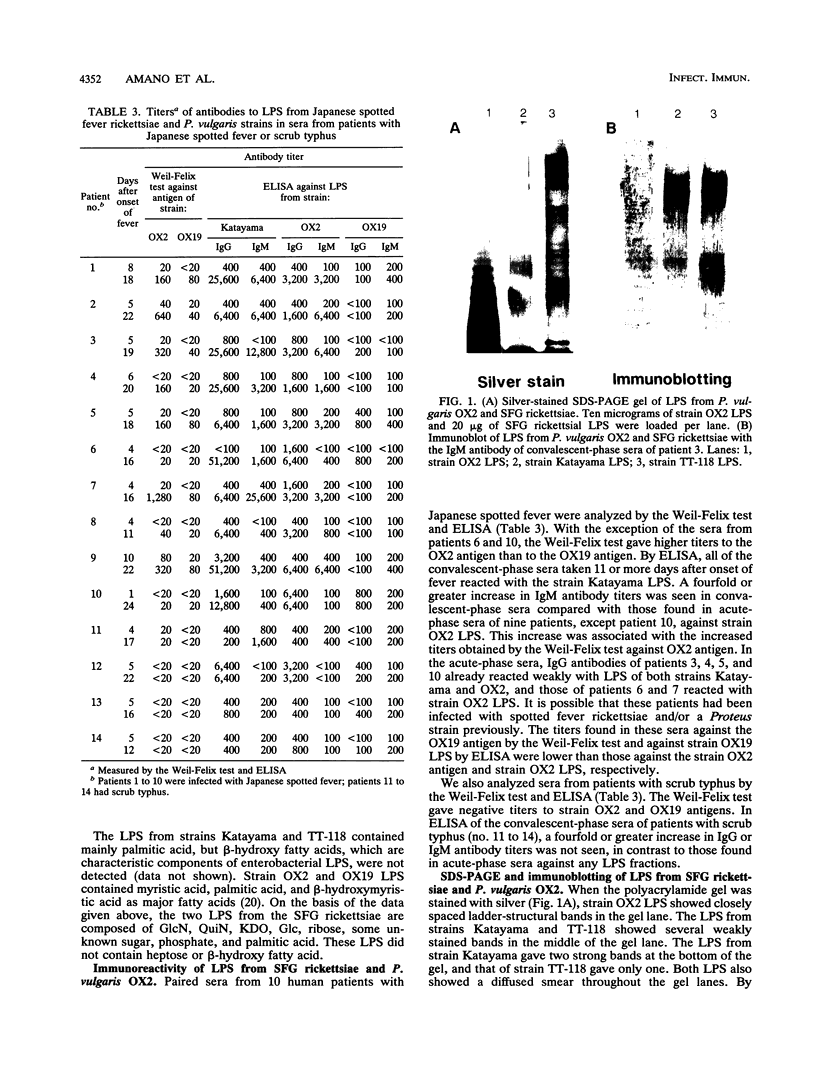
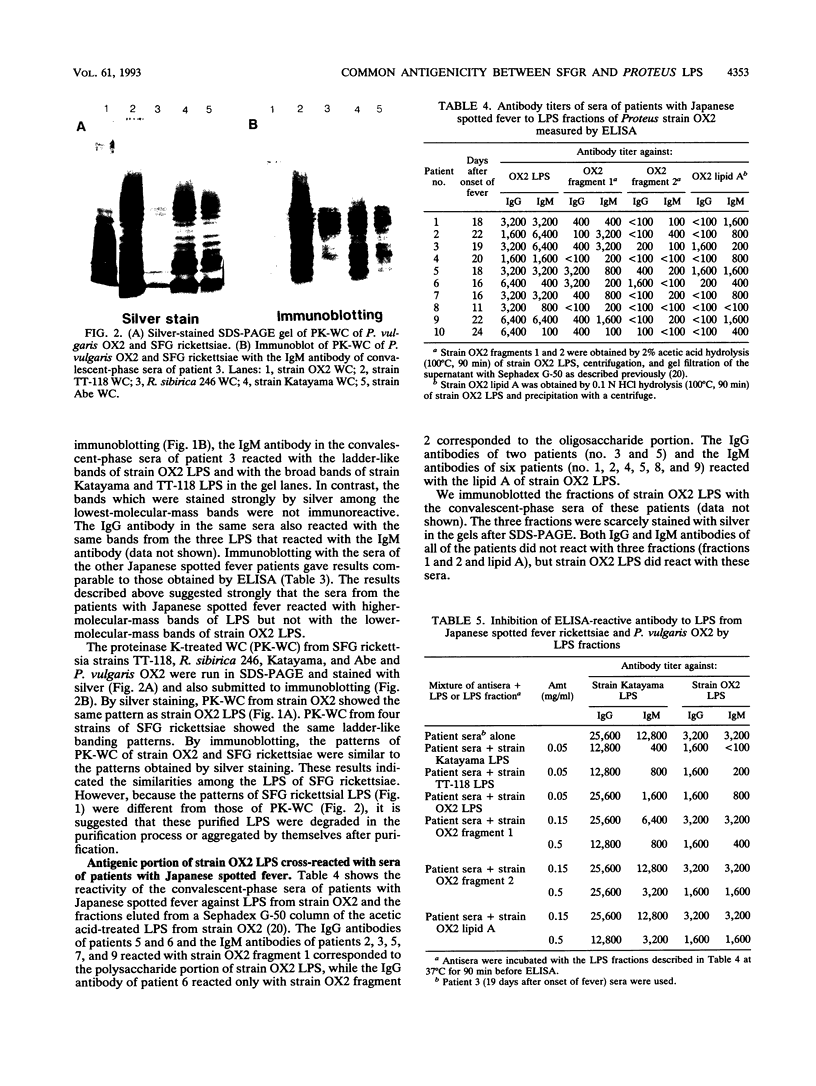
The lipopolysaccharides (LPS) isolated from spotted fever group (SFG) rickettsia strains Thai tick typhus TT-118 and Katayama were characterized by chemical analyses, sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and immunoblotting. These LPS did not contain heptose, but they contained 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (KDO), glucosamine, quinovosamine, phosphate, ribose, an unknown neutral sugar, and palmitic acid. Resolution of the apparent molecular masses of these LPS by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and staining with silver showed ladder-like bands. In an ELISA, convalescent-phase sera from 10 patients with Japanese spotted fever reacted with LPS from the Katayama strain, and 90% (9 of 10) of these sera also reacted with LPS isolated from Proteus vulgaris OX2. Immunoblotting revealed that the sera reacted with the high-molecular-mass bands of LPS from SFG rickettsiae, in addition to those of OX2 LPS. In an ELISA, immunoglobulin M antibodies from these sera reacted with the O-polysaccharide and lipid A portions of LPS from P. vulgaris OX2. The epitopes common to LPS of SFG rickettsiae and P. vulgaris OX2 may be in the O-polysaccharide and lipid A portions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano K., Hatakeyama H., Okuta M., Suto T., Mahara F. Serological studies of antigenic similarity between Japanese spotted fever rickettsiae and Weil-Felix test antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Sep;30(9):2441–2446. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.9.2441-2446.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano K., Hatakeyama H., Sasaki Y., Ito R., Tamura A., Suto T. Electron microscopic studies on the in vitro proliferation of spotted fever group rickettsia isolated in Japan. Microbiol Immunol. 1991;35(8):623–629. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1991.tb01594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano K., Mizushiri S., Fujii S., Fukushi K., Suto T. Immunological characterization of lipopolysaccharides from Proteus strains used in Weil-Felix test and reactivity with patient sera of tsutsugamushi diseases. Microbiol Immunol. 1990;34(2):135–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1990.tb00998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano K., Suzuki N., Hatakeyama H., Kasahara Y., Fujii S., Fukushi K., Suto T., Mahara F. The reactivity between rickettsiae and Weil-Felix test antigens against sera of rickettsial disease patients. Acta Virol. 1992 Jan;36(1):67–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano K., Tamura A., Ohashi N., Urakami H., Kaya S., Fukushi K. Deficiency of peptidoglycan and lipopolysaccharide components in Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2290–2292. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2290-2292.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano K., Williams J. C. Chemical and immunological characterization of lipopolysaccharides from phase I and phase II Coxiella burnetii. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):994–1002. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.994-1002.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano K., Williams J. C., Missler S. R., Reinhold V. N. Structure and biological relationships of Coxiella burnetii lipopolysaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4740–4747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano K., Williams J. C. Peptidoglycan of Legionella pneumophila: apparent resistance to lysozyme hydrolysis correlates with a high degree of peptide cross-linking. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):520–526. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.520-526.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anacker R. L., Philip R. N., Williams J. C., List R. H., Mann R. E. Biochemical and immunochemical analysis of Rickettsia rickettsii strains of various degrees of virulence. Infect Immun. 1984 Jun;44(3):559–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.3.559-564.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenkrantz N., Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkhanis Y. D., Zeltner J. Y., Jackson J. J., Carlo D. J. A new and improved microassay to determine 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate in lipopolysaccharide of Gram-negative bacteria. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):595–601. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., LEINER K. Y., WU M. L., FARR A. L. The quantitative histochemistry of brain. I. Chemical methods. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahara F., Koga K., Sawada S., Taniguchi T., Shigemi F., Suto T., Tsuboi Y., Ooya A., Koyama H., Uchiyama T. [The first report of the rickettsial infections of spotted fever group in Japan: three clinical cases]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1985 Nov;59(11):1165–1171. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.59.1165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushiri S., Amano K., Fuji S., Fukushi K., Watanabe M. Chemical characterization of lipopolysaccharides from Proteus strains used in Weil-Felix test. Microbiol Immunol. 1990;34(2):121–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1990.tb00997.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teysseire N., Raoult D. Comparison of Western immunoblotting and microimmunofluorescence for diagnosis of Mediterranean spotted fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Feb;30(2):455–460. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.2.455-460.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Tashiro F., Funato T., Kitamura Y. Isolation of a spotted fever group Rickettsia from a patient with febrile exanthematous illness in Shikoku, Japan. Microbiol Immunol. 1986;30(12):1323–1326. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1986.tb03053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov E. V., Kaca W., Rózalski A., Shashkov A. S., Cedzynski M., Knirel Y. A., Kochetkov N. K. Structural and immunochemical studies of O-specific polysaccharide of Proteus vulgaris 5/43 belonging to OX19 group (O-variants). Eur J Biochem. 1991 Aug 15;200(1):195–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb21067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]