Abstract
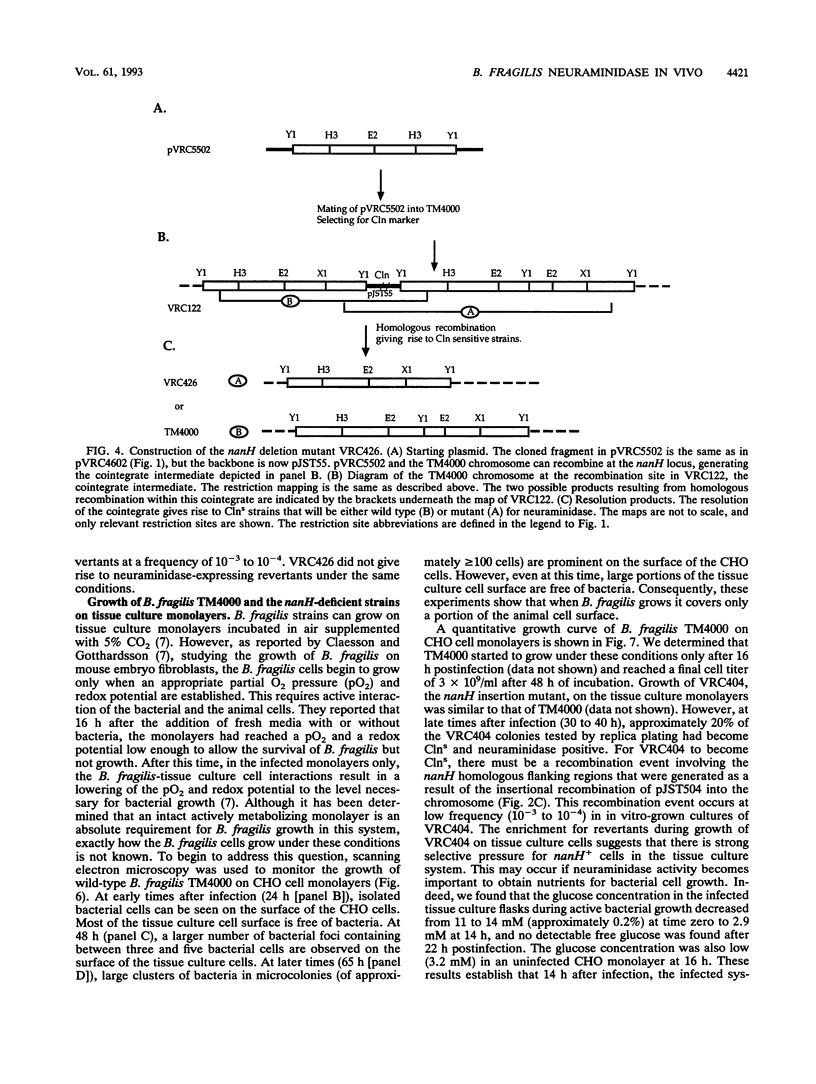
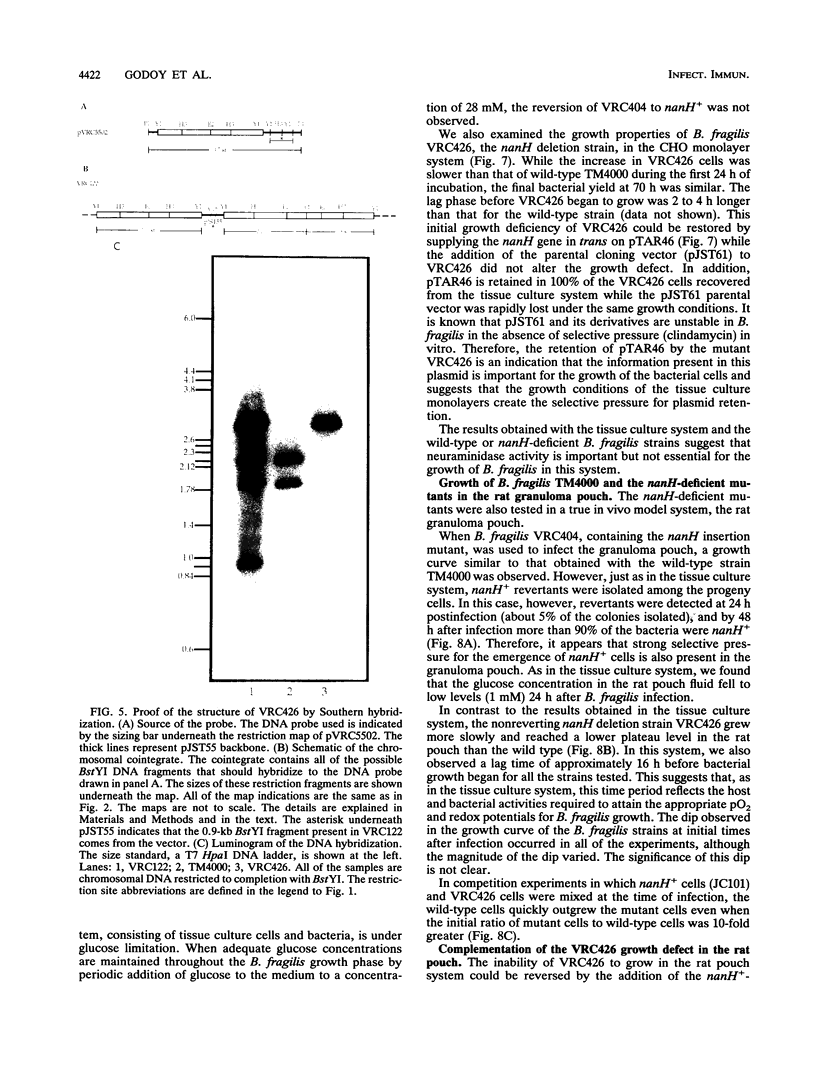
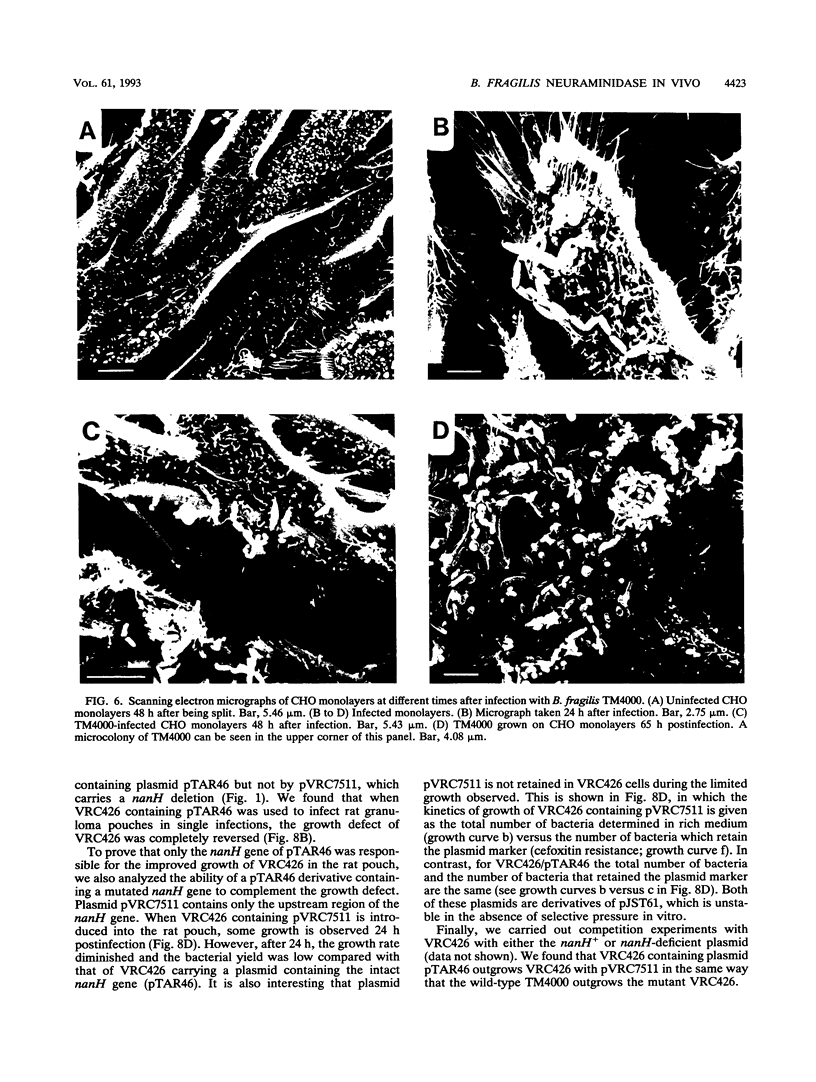
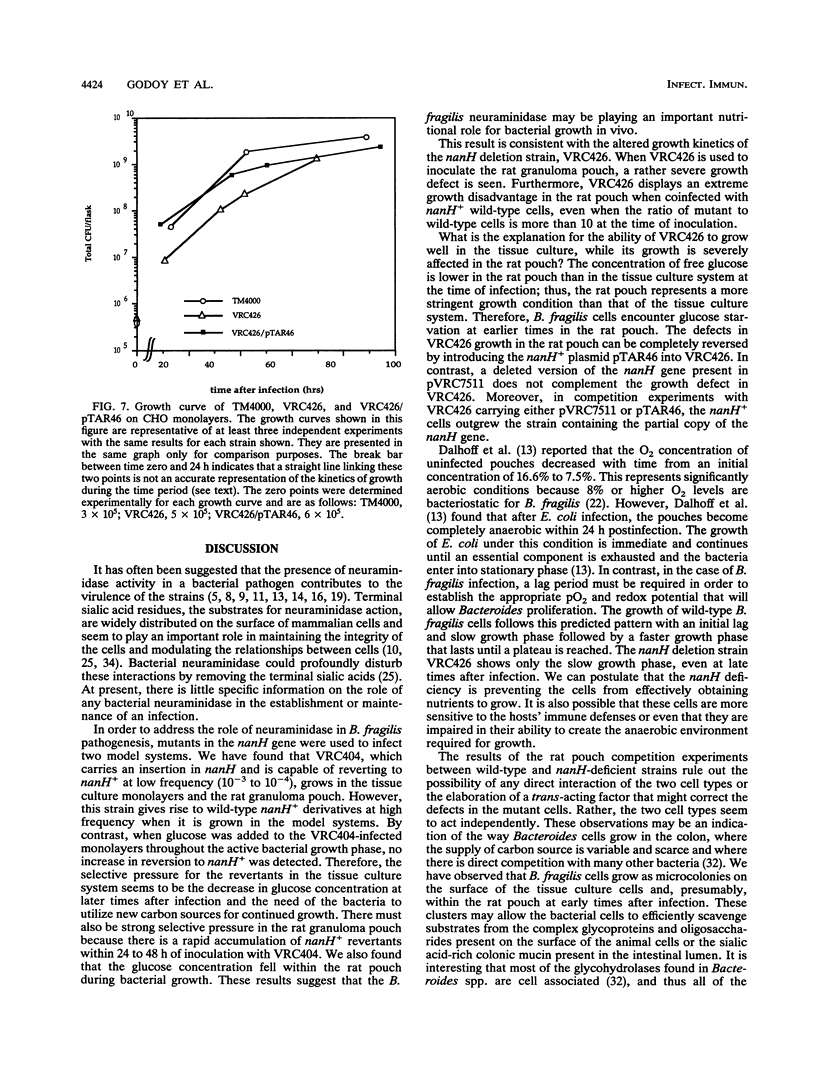
Two Bacteroides fragilis neuraminidase-deficient mutants were used to study the role of neuraminidase activity in growth of B. fragilis in tissue culture monolayers (CHO cells) and in the in vivo rat granuloma pouch. The nanH structural gene for neuraminidase was cloned from B. fragilis TM4000 and was used to create two isogenic strains with chromosomal disruptions at the nanH gene. B. fragilis VRC404 contains an insertion flanked by disrupted copies of the nanH gene, and B. fragilis VRC426 contains a deletion of a significant portion of nanH coding sequences. The insertion mutant VRC404 is capable of reverting to nanH+. It grew as well as the wild type in CHO monolayers. However, between 48 and 72 h after infection, the bacterial population was enriched with nanH+ bacterial cells (10 to 20%). In the rat pouch 48 h after infection, more than 90% of the population sampled had become nanH+. The deletion mutant VRC426 showed a severe growth defect in the rat pouch model. In addition, VRC426 was efficiently outgrown by the wild type in competition experiments, even when the mutant was present at 10 times the number of wild-type cells at the time of infection. A common characteristic of both model systems is a drastic decrease in the free glucose concentration 16 to 24 h postinfection. We suggest that neuraminidase activity may be required for B. fragilis to grow to maximal levels in the tissue culture and rat pouch systems by making other carbon sources available after glucose levels are reduced.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ada G. L., Jones P. D. The immune response to influenza infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;128:1–54. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71272-2_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arora D. J., Houde M. Purified glycoproteins of influenza virus stimulate cell-mediated cytotoxicity in vivo. Nat Immun Cell Growth Regul. 1988;7(5-6):287–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. O., Lindqvist L., Nord C. E. Purification of glycoside hydrolases from Bacteroides fragilis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):40–47. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.40-47.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. O., Nord C. E., Wadström T. Formation of glycosidases in batch and continuous culture of Bacteroides fragilis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):269–273. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.269-273.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry A. M., Paton J. C., Glare E. M., Hansman D., Catcheside D. E. Cloning and expression of the pneumococcal neuraminidase gene in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1988 Nov 30;71(2):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. G., Straus D. C. Characterization of neuraminidases produced by various serotypes of group B streptococci. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.1-6.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson B. E., Gotthardsson I. H. A tissue culture model for study of growth promotion and antimicrobial susceptibility in Bacteroides fragilis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Jan;21(1):17–26. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman P. M. Structural basis of antigenic variation: studies of influenza virus neuraminidase. Immunol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;70(Pt 3):209–214. doi: 10.1038/icb.1992.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Wright D. G. Mobilization of sialidase from intracellular stores to the surface of human neutrophils and its role in stimulated adhesion responses of these cells. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):2067–2076. doi: 10.1172/JCI115536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csete M., Lev B. I., Pereira M. E. An influenza virus model for Trypanosoma cruzi infection: interactive roles for neuraminidase and lectin. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;117:153–165. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70538-0_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalhoff A., Frank G., Luckhaus G. The granuloma pouch: an in vivo model for pharmacokinetic and chemotherapeutic investigations. I. Biochemical and histological characterization. Infection. 1982 Nov-Dec;10(6):354–360. doi: 10.1007/BF01642299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Regulation by membrane sialic acid of beta1H-dependent decay-dissociation of amplification C3 convertase of the alternative complement pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1971–1975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galen J. E., Ketley J. M., Fasano A., Richardson S. H., Wasserman S. S., Kaper J. B. Role of Vibrio cholerae neuraminidase in the function of cholera toxin. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):406–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.406-415.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán C. A., Platé M., Pruzzo C. Role of neuraminidase-dependent adherence in Bacteroides fragilis attachment to human epithelial cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Sep 1;59(1-2):187–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1989.tb03107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht D. W., Malamy M. H. Tn4399, a conjugal mobilizing transposon of Bacteroides fragilis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3603–3608. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3603-3608.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. T., Farmer S., Greiff D. Neuraminidase activities of clinical isolates of Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):272–273. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.272-273.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama T., Barksdale L. Neuraminidase of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1565–1581. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1565-1581.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. W., Lee R. T., Lee Y. C., Thomas G. H., Reynolds L. W., Uchida Y. The synthesis of 4-methylumbelliferyl alpha-ketoside of N-acetylneuraminic acid and its use in a fluorometric assay for neuraminidase. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jan 1;101(1):166–174. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A. B., Johnston J., Mayhew J. W., Gorbach S. L. Effect of dissolved oxygen and Eh and Bacteroides fragilis during continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):168–172. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.168-172.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palese P., Tobita K., Ueda M., Compans R. W. Characterization of temperature sensitive influenza virus mutants defective in neuraminidase. Virology. 1974 Oct;61(2):397–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilatte Y., Bignon J., Lambré C. R. Sialic acids as important molecules in the regulation of the immune system: pathophysiological implications of sialidases in immunity. Glycobiology. 1993 Jun;3(3):201–218. doi: 10.1093/glycob/3.3.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard N. J., Tally F. P., Malamy M. H. Tn4400, a compound transposon isolated from Bacteroides fragilis, functions in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1248–1255. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1248-1255.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen S. D., Chi S. I., True D. D., Singer M. S., Yednock T. A. Intravenously injected sialidase inactivates attachment sites for lymphocytes on high endothelial venules. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):1895–1902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe B., Rothe B., Roggentin P., Schauer R. The sialidase gene from Clostridium septicum: cloning, sequencing, expression in Escherichia coli and identification of conserved sequences in sialidases and other proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Apr;226(1-2):190–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00273603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo T. A., Thompson J. S., Godoy V. G., Malamy M. H. Cloning and expression of the Bacteroides fragilis TAL2480 neuraminidase gene, nanH, in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2594–2600. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2594-2600.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A. Energy sources of major intestinal fermentative anaerobes. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jan;32(1):158–163. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.1.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Webster R. G., Ennis F. A. Antibodies to HA and NA augment uptake of influenza A viruses into cells via Fc receptor entry. Virology. 1991 May;182(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90664-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka H., Ito F., Iwasaki T. Purification and characterization of a sialidase from Bacteroides fragilis SBT3182. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Nov 30;189(1):524–529. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91589-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. S., Malamy M. H. Sequencing the gene for an imipenem-cefoxitin-hydrolyzing enzyme (CfiA) from Bacteroides fragilis TAL2480 reveals strong similarity between CfiA and Bacillus cereus beta-lactamase II. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2584–2593. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2584-2593.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vimr E. R., Lawrisuk L., Galen J., Kaper J. B. Cloning and expression of the Vibrio cholerae neuraminidase gene nanH in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1495–1504. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1495-1504.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]