Abstract
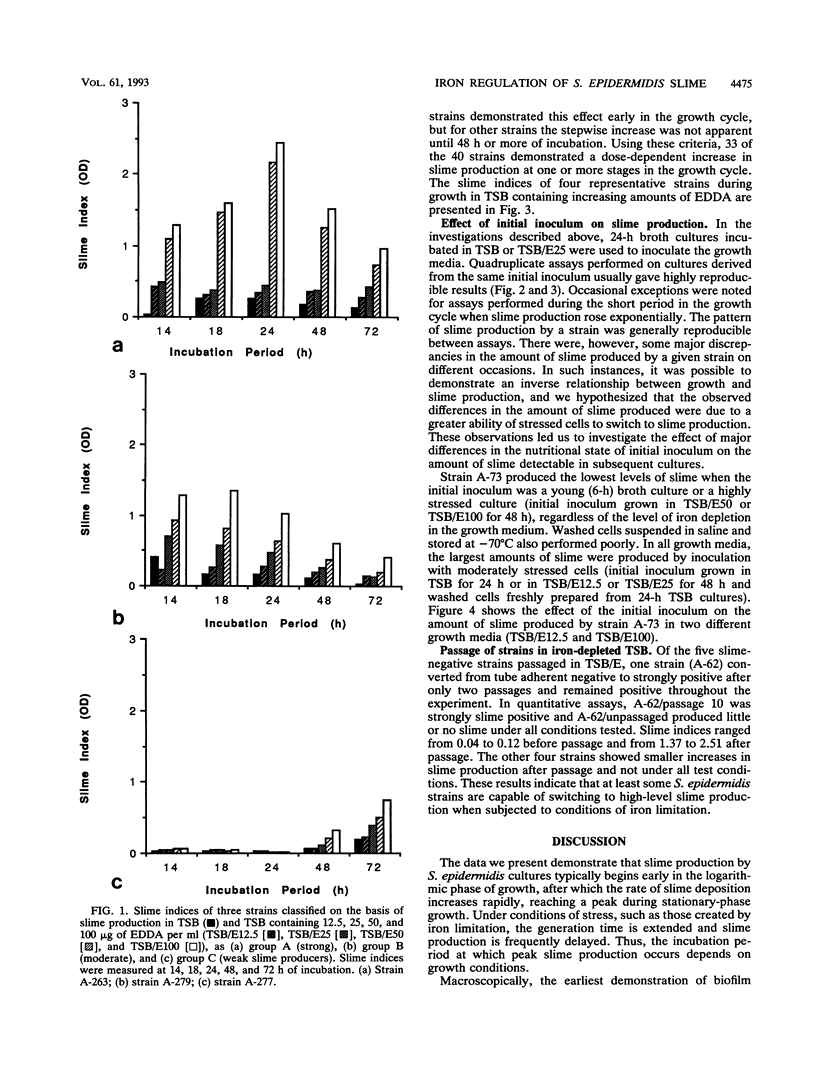
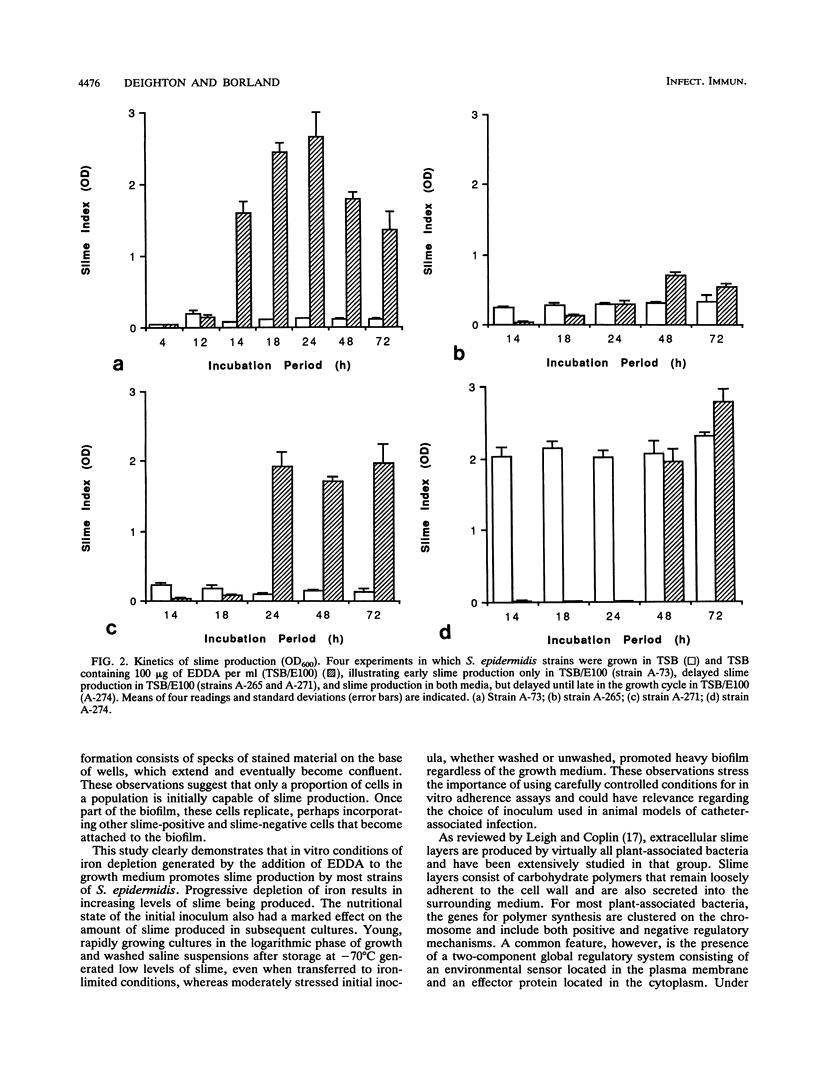
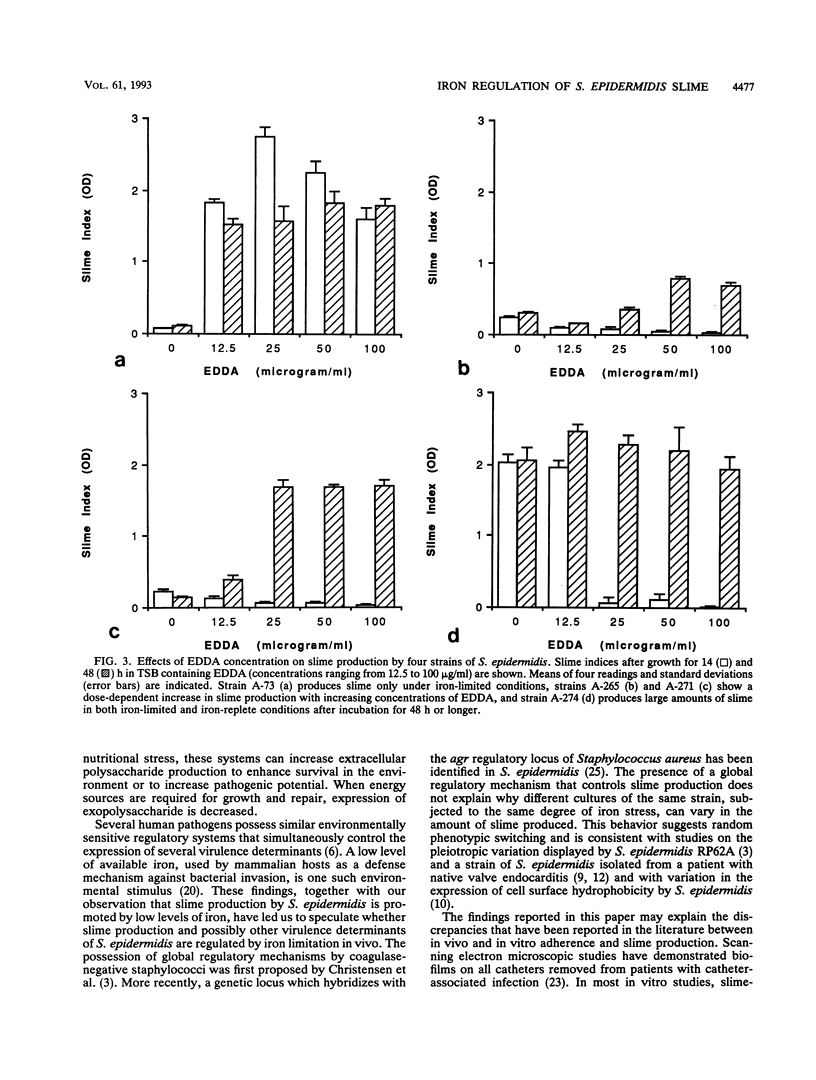
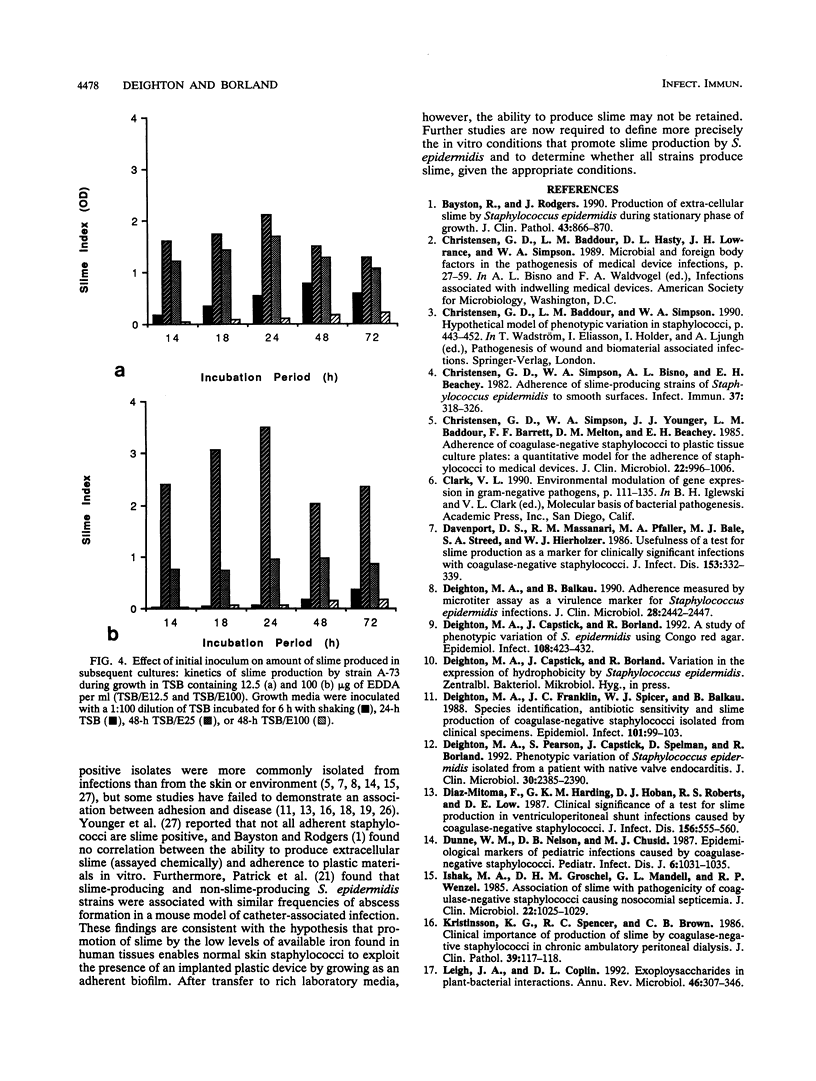
Slime production by most strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis was enhanced by conditions of iron limitation produced by the addition of ethylenediamine-di-o-hydroxyphenol acetic acid to the growth medium. The density of the biofilm which formed on the base of microtiter plates was dependent on the degree of iron limitation, the stage of the growth cycle, and the nutritional state of the initial inoculum. One repeatedly slime-negative S. epidermidis strain, passaged in tryptic soya broth containing ethylenediamine-di-o-hydroxyphenol acetic acid, expressed high levels of slime after two passages. These observations suggest that iron limitation is one factor that regulates slime production by S. epidermidis. These findings could explain inconsistencies between the in vivo observation that biofilms invariably form on implanted catheters and the in vitro finding that some isolates from catheter-associated infection fail to produce slime.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayston R., Rodgers J. Production of extra-cellular slime by Staphylococcus epidermidis during stationary phase of growth: its association with adherence to implantable devices. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Oct;43(10):866–870. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.10.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Adherence of slime-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):318–326. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.318-326.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Younger J. J., Baddour L. M., Barrett F. F., Melton D. M., Beachey E. H. Adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates: a quantitative model for the adherence of staphylococci to medical devices. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):996–1006. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.996-1006.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport D. S., Massanari R. M., Pfaller M. A., Bale M. J., Streed S. A., Hierholzer W. J., Jr Usefulness of a test for slime production as a marker for clinically significant infections with coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):332–339. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deighton M. A., Balkau B. Adherence measured by microtiter assay as a virulence marker for Staphylococcus epidermidis infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Nov;28(11):2442–2447. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.11.2442-2447.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deighton M. A., Capstick J., Borland R. A study of phenotypic variation of Staphylococcus epidermidis using Congo red agar. Epidemiol Infect. 1992 Dec;109(3):423–432. doi: 10.1017/s095026880005041x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deighton M., Pearson S., Capstick J., Spelman D., Borland R. Phenotypic variation of Staphylococcus epidermidis isolated from a patient with native valve endocarditis. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Sep;30(9):2385–2390. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.9.2385-2390.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Mitoma F., Harding G. K., Hoban D. J., Roberts R. S., Low D. E. Clinical significance of a test for slime production in ventriculoperitoneal shunt infections caused by coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):555–560. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne W. M., Jr, Nelson D. B., Chusid M. J. Epidemiologic markers of pediatric infections caused by coagulase-negative staphylococci. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Nov;6(11):1031–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishak M. A., Gröschel D. H., Mandell G. L., Wenzel R. P. Association of slime with pathogenicity of coagulase-negative staphylococci causing nosocomial septicemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):1025–1029. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.1025-1029.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristinsson K. G., Spencer R. C., Brown C. B. Clinical importance of production of slime by coagulase negative staphylococci in chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Jan;39(1):117–118. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. A., Coplin D. L. Exopolysaccharides in plant-bacterial interactions. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1992;46:307–346. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.46.100192.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlam H. A., Noble W. C., Marples R. R., Bayston R., Phillips I. The epidemiology of peritonitis caused by coagulase-negative staphylococci in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Nov;30(3):167–174. doi: 10.1099/00222615-30-3-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needham C. A., Stempsey W. Incidence, adherence, and antibiotic resistance of coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species causing human disease. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1984 Sep;2(4):293–299. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(84)90060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick C. C., Plaunt M. R., Hetherington S. V., May S. M. Role of the Staphylococcus epidermidis slime layer in experimental tunnel tract infections. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1363–1367. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1363-1367.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Locci R., Pulverer G. Adherence and growth of coagulase-negative staphylococci on surfaces of intravenous catheters. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):479–482. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J. Iron-Binding Catechols and Virulence in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):445–456. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.445-456.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West T. E., Walshe J. J., Krol C. P., Amsterdam D. Staphylococcal peritonitis in patients on continuous peritoneal dialysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):809–812. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.809-812.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younger J. J., Christensen G. D., Bartley D. L., Simmons J. C., Barrett F. F. Coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from cerebrospinal fluid shunts: importance of slime production, species identification, and shunt removal to clinical outcome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):548–554. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



