Abstract
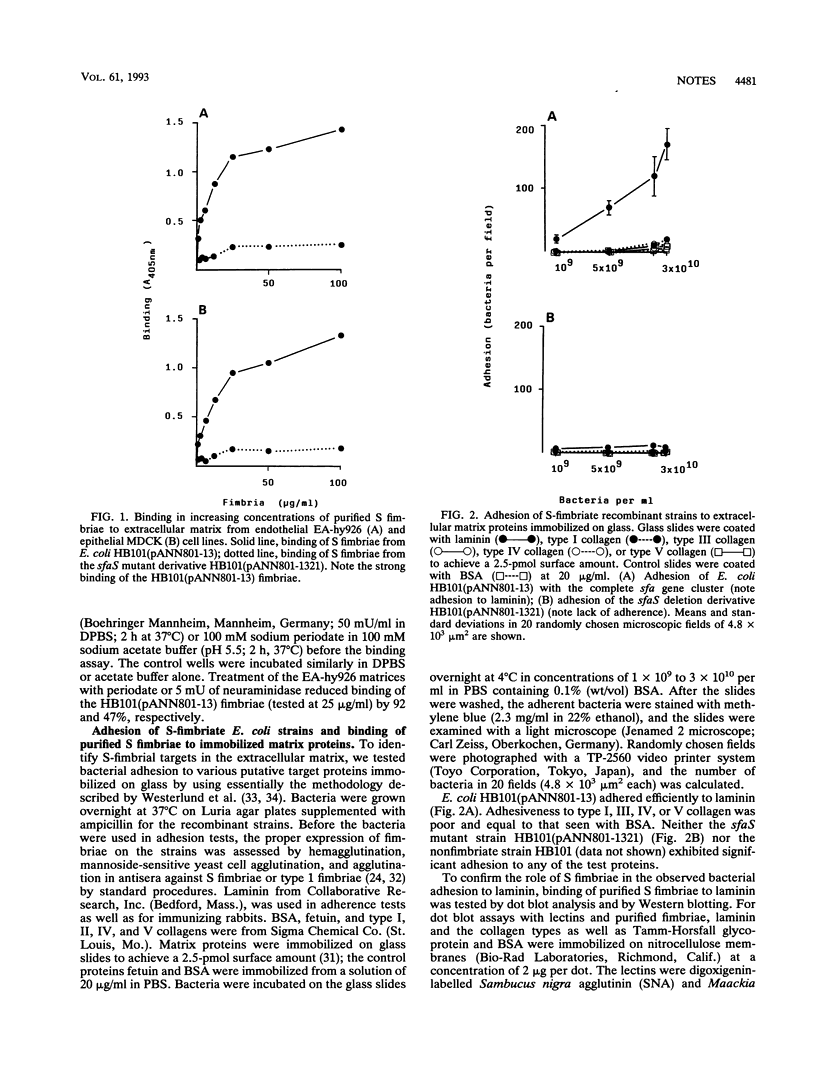
S fimbriae purified from recombinant Escherichia coli HB101(pANN801-13) bound strongly to extracellular matrices of cultured endothelial and epithelial cells; only poor binding was seen with the fimbriae purified from the sfaS mutant strain HB101(pANN801-1321). E. coli HB101(pANN801-13) adhered strongly to laminin immobilized on glass; no adhesion was seen to type I, III, IV, or V collagen. Strain HB101(pANN801-1321) failed to adhere to any of the target proteins. Adhesion to laminin of strain HB101(pANN801-13) was inhibited by sialyl-alpha-2,3-lactose as well as by periodate oxidation and neuraminidase treatment of laminin. In Western blotting, the purified S fimbriae recognized more strongly the A chain than the B chains of laminin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arumugham R. G., Hsieh T. C., Tanzer M. L., Laine R. A. Structures of the asparagine-linked sugar chains of laminin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Aug 6;883(1):112–126. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90142-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck K., Hunter I., Engel J. Structure and function of laminin: anatomy of a multidomain glycoprotein. FASEB J. 1990 Feb 1;4(2):148–160. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.2.2404817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean J. W., 3rd, Chandrasekaran S., Tanzer M. L. A biological role of the carbohydrate moieties of laminin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12553–12562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgell C. J., McDonald C. C., Graham J. B. Permanent cell line expressing human factor VIII-related antigen established by hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3734–3737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara S., Shinkai H., Deutzmann R., Paulsson M., Timpl R. Structure and distribution of N-linked oligosaccharide chains on various domains of mouse tumour laminin. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 1;252(2):453–461. doi: 10.1042/bj2520453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker J., Kestler H., Hoschützky H., Jann K., Lottspeich F., Korhonen T. K. Cloning and characterization of the S fimbrial adhesin II complex of an Escherichia coli O18:K1 meningitis isolate. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):544–550. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.544-550.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker J., Schmidt G., Hughes C., Knapp S., Marget M., Goebel W. Cloning and characterization of genes involved in production of mannose-resistant, neuraminidase-susceptible (X) fimbriae from a uropathogenic O6:K15:H31 Escherichia coli strain. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):434–440. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.434-440.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedman K., Johansson S., Vartio T., Kjellén L., Vaheri A., Hök M. Structure of the pericellular matrix: association of heparan and chondroitin sulfates with fibronectin-procollagen fibers. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):663–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90221-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C. C. Functional role of laminin carbohydrate. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen T. K., Nurmiaho E. L., Ranta H., Edén C. S. New Method for isolation of immunologically pure pili from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):569–575. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.569-575.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen T. K., Valtonen M. V., Parkkinen J., Väisänen-Rhen V., Finne J., Orskov F., Orskov I., Svenson S. B., Mäkelä P. H. Serotypes, hemolysin production, and receptor recognition of Escherichia coli strains associated with neonatal sepsis and meningitis. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):486–491. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.486-491.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen T. K., Virkola R., Lähteenmäki K., Björkman Y., Kukkonen M., Raunio T., Tarkkanen A. M., Westerlund B. Penetration of fimbriate enteric bacteria through basement membranes: a hypothesis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Dec 15;100(1-3):307–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb14057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen T. K., Väisänen-Rhen V., Rhen M., Pere A., Parkkinen J., Finne J. Escherichia coli fimbriae recognizing sialyl galactosides. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):762–766. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.762-766.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukkonen M., Raunio T., Virkola R., Lähteenmäki K., Mäkelä P. H., Klemm P., Clegg S., Korhonen T. K. Basement membrane carbohydrate as a target for bacterial adhesion: binding of type I fimbriae of Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli to laminin. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jan;7(2):229–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S. Choroid plexus: target for systemic disease and pathway to the brain. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):231–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Rao C. N., Wewer U. M. Biochemical interactions of tumor cells with the basement membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1037–1057. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Timpl R. Laminin and other basement membrane components. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:57–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh J. R., McDonald K. L. The mitotic spindle. Sci Am. 1989 Oct;261(4):48–56. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican1089-48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio A. M. Laminin: multiple forms, multiple receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;2(5):845–849. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90082-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowicki B., Vuopio-Varkila J., Viljanen P., Korhonen T. K., Mäkelä P. H. Fimbrial phase variation and systemic E. coli infection studied in the mouse peritonitis model. Microb Pathog. 1986 Aug;1(4):335–347. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsén A., Jonsson A., Normark S. Fibronectin binding mediated by a novel class of surface organelles on Escherichia coli. Nature. 1989 Apr 20;338(6217):652–655. doi: 10.1038/338652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkkinen J., Hacker J., Korhonen T. K. Enhancement of tissue plasminogen activator-catalyzed plasminogen activation by Escherichia coli S fimbriae associated with neonatal septicaemia and meningitis. Thromb Haemost. 1991 May 6;65(5):483–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkkinen J., Korhonen T. K., Pere A., Hacker J., Soinila S. Binding sites in the rat brain for Escherichia coli S fimbriae associated with neonatal meningitis. J Clin Invest. 1988 Mar;81(3):860–865. doi: 10.1172/JCI113395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkkinen J., Ristimäki A., Westerlund B. Binding of Escherichia coli S fimbriae to cultured human endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2256–2259. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2256-2259.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkkinen J., Virkola R., Korhonen T. K. Identification of factors in human urine that inhibit the binding of Escherichia coli adhesins. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2623–2630. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2623-2630.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saukkonen K. M., Nowicki B., Leinonen M. Role of type 1 and S fimbriae in the pathogenesis of Escherichia coli O18:K1 bacteremia and meningitis in the infant rat. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):892–897. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.892-897.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmoll T., Hoschützky H., Morschhäuser J., Lottspeich F., Jann K., Hacker J. Analysis of genes coding for the sialic acid-binding adhesin and two other minor fimbrial subunits of the S-fimbrial adhesin determinant of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1735–1744. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokurenko E. V., Courtney H. S., Abraham S. N., Klemm P., Hasty D. L. Functional heterogeneity of type 1 fimbriae of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4709–4719. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4709-4719.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkkanen A. M., Allen B. L., Westerlund B., Holthöfer H., Kuusela P., Risteli L., Clegg S., Korhonen T. K. Type V collagen as the target for type-3 fimbriae, enterobacterial adherence organelles. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1353–1361. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valkonen K. H., Veijola J., Dagberg B., Uhlin B. E. Binding of basement-membrane laminin by Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2133–2141. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virkola R., Westerlund B., Holthöfer H., Parkkinen J., Kekomäki M., Korhonen T. K. Binding characteristics of Escherichia coli adhesins in human urinary bladder. Infect Immun. 1988 Oct;56(10):2615–2622. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.10.2615-2622.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerlund B., Kuusela P., Risteli J., Risteli L., Vartio T., Rauvala H., Virkola R., Korhonen T. K. The O75X adhesin of uropathogenic Escherichia coli is a type IV collagen-binding protein. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Mar;3(3):329–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerlund B., van Die I., Kramer C., Kuusela P., Holthöfer H., Tarkkanen A. M., Virkola R., Riegman N., Bergmans H., Hoekstra W. Multifunctional nature of P fimbriae of uropathogenic Escherichia coli: mutations in fsoE and fsoF influence fimbrial binding to renal tubuli and immobilized fibronectin. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Dec;5(12):2965–2975. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01856.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M. Adhesive recognition sequences. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):12809–12812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




