Abstract
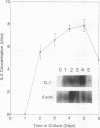
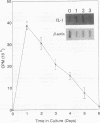
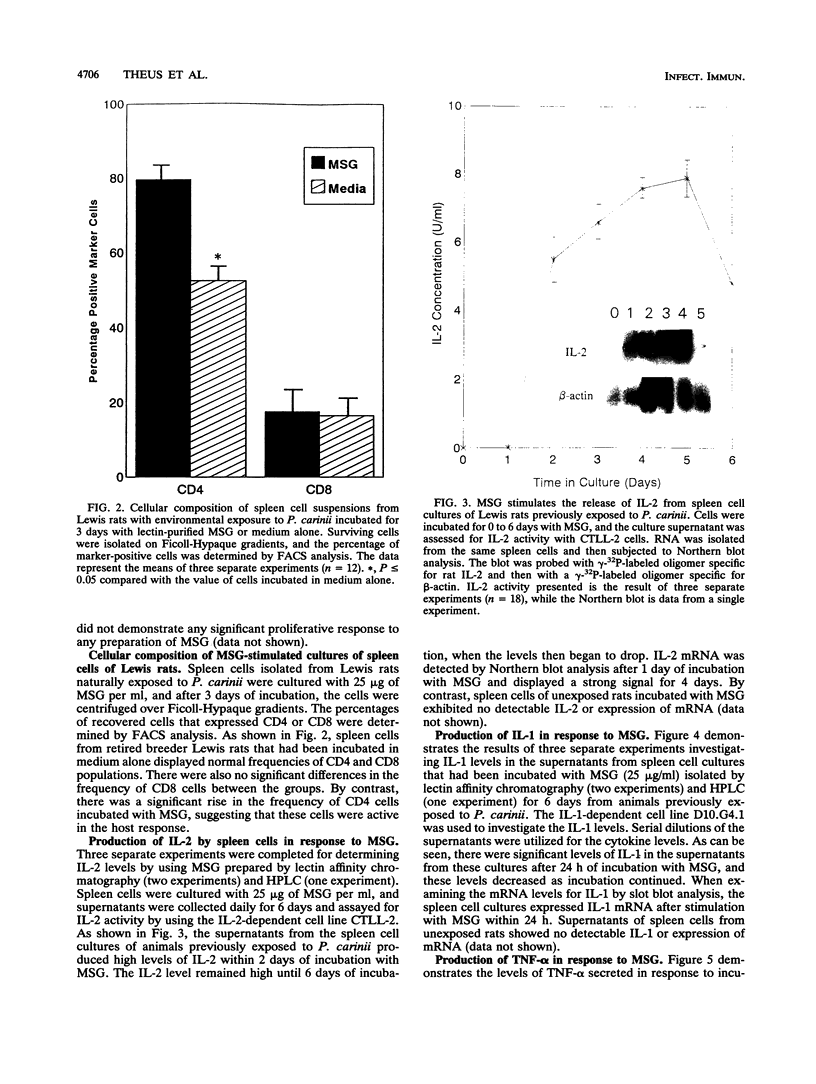
Naturally derived T-cell responses by rats to a 120-kDa major surface glycoprotein (MSG) of rat-derived Pneumocystis carinii were analyzed in vitro. Specific cytokines elicited by the T-cell response to the MSG were also identified. MSG was purified from rat-derived P. carinii by three different techniques: lectin affinity chromatography, sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis followed by electroelution, and size-exclusion high-performance liquid chromatography. The cell-mediated immunity of spleen cells isolated from Lewis rats with and without natural exposure to P. carinii to the purified MSG was studied. Exposure to P. carinii was monitored by the presence or absence of serum antibodies to P. carinii antigens by Western blotting (immunoblotting). A T-cell proliferative response to the MSG was identified only with spleen cells isolated from rats exposed to P. carinii and peaked at 4 days. Flow cytometric analysis revealed that the percentage of CD4 cells was significantly increased during the proliferative response to MSG. MSG also elicited secretion of tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-1, and interleukin-2, with peak activity of these cytokines occurring after 12, 24, and 48 h, respectively, of culture. These findings suggest that MSG is important in host T-cell recognition of and immune response to P. carinii by recruitment of inflammatory cells and cytokine production.
Full text
PDF

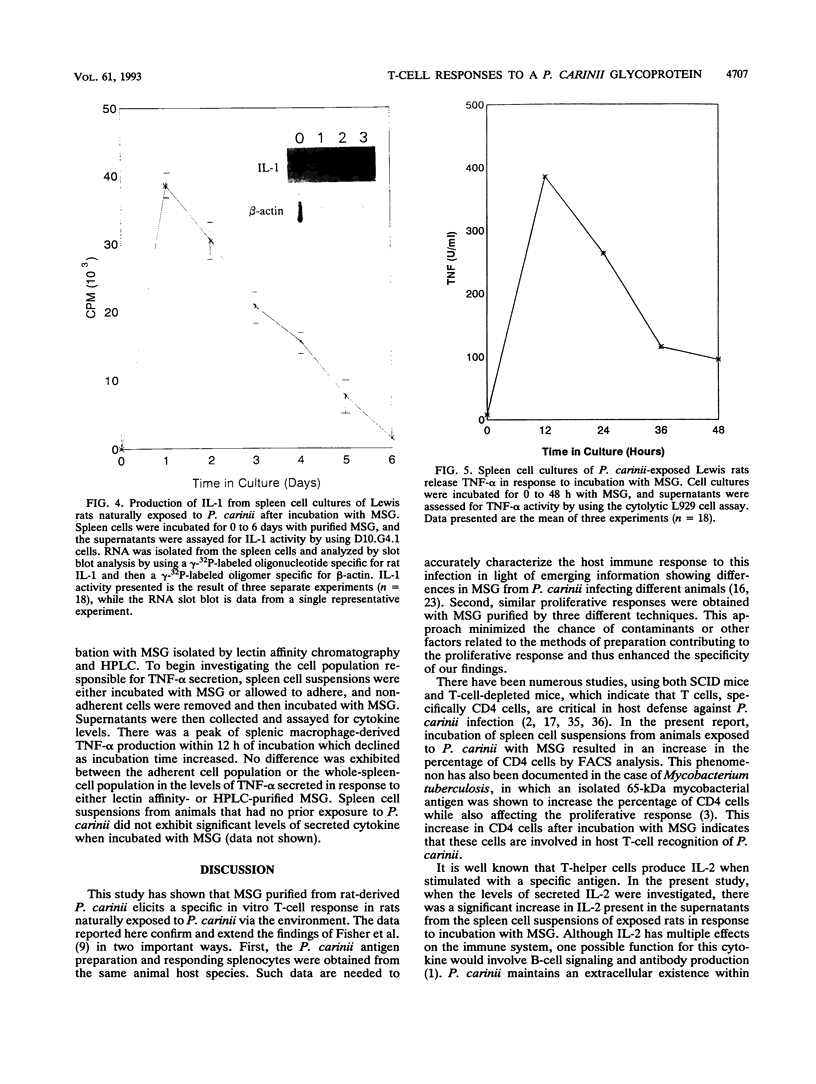


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai K. I., Lee F., Miyajima A., Miyatake S., Arai N., Yokota T. Cytokines: coordinators of immune and inflammatory responses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:783–836. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck J. M., Warnock M. L., Curtis J. L., Sniezek M. J., Arraj-Peffer S. M., Kaltreider H. B., Shellito J. E. Inflammatory responses to Pneumocystis carinii in mice selectively depleted of helper T lymphocytes. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Aug;5(2):186–197. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.2.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boom W. H., Wallis R. S., Chervenak K. A. Human Mycobacterium tuberculosis-reactive CD4+ T-cell clones: heterogeneity in antigen recognition, cytokine production, and cytotoxicity for mononuclear phagocytes. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2737–2743. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2737-2743.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Havell E. A., Gigliotti F., Harmsen A. G. Interleukin-6 production in a murine model of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: relation to resistance and inflammatory response. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):97–102. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.97-102.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Havell E. A., Harmsen A. G. Importance of endogenous tumor necrosis factor alpha and gamma interferon in host resistance against Pneumocystis carinii infection. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1279–1284. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1279-1284.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Havell E. A., Moldawer L. L., McIntyre K. W., Chizzonite R. A., Harmsen A. G. Interleukin 1: an important mediator of host resistance against Pneumocystis carinii. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):713–718. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Stefano J. A., Cushion M. T., Sleight R. G., Walzer P. D. Analysis of Pneumocystis carinii cyst wall. I. Evidence for an outer surface membrane. J Protozool. 1990 Sep-Oct;37(5):428–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1990.tb01167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast L. D., Beatty P., Hansen J. A., Newman W. T cell nature and heterogeneity of recognition structures of human natural killer (NK) cells. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2404–2410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. J., Gigliotti F., Zauderer M., Harmsen A. G. Specific T-cell response to a Pneumocystis carinii surface glycoprotein (gp120) after immunization and natural infection. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3372–3376. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3372-3376.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Ballou L. R., Hughes W. T., Mosley B. D. Purification and initial characterization of a ferret Pneumocystis carinii surface antigen. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):848–854. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F. Host species-specific antigenic variation of a mannosylated surface glycoprotein of Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1992 Feb;165(2):329–336. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigliotti F., Hughes W. T. Passive immunoprophylaxis with specific monoclonal antibody confers partial protection against Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis in animal models. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1666–1668. doi: 10.1172/JCI113503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves D. C., Li X. H., Paiva W. D. Delayed-type hypersensitivity response in mice to Pneumocystis carinii. J Protozool. 1991 Nov-Dec;38(6):49S–52S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves D. C., McNabb S. J., Worley M. A., Downs T. D., Ivey M. H. Analyses of rat Pneumocystis carinii antigens recognized by human and rat antibodies by using western immunoblotting. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):96–103. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.96-103.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagler D. N., Deepe G. S., Pogue C. L., Walzer P. D. Blastogenic responses to Pneumocystis carinii among patients with human immunodeficiency (HIV) infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Oct;74(1):7–13. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidaris P. J., Wright T. W., Gigliotti F., Haidaris C. G. Expression and characterization of a cDNA clone encoding an immunodominant surface glycoprotein of Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis. 1992 Nov;166(5):1113–1123. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.5.1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmsen A. G., Chen W. Resolution of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in CD4+ lymphocyte-depleted mice given aerosols of heat-treated Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):881–886. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmsen A. G., Stankiewicz M. T cells are not sufficient for resistance to Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in mice. J Protozool. 1991 Nov-Dec;38(6):44S–45S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan M. M., Vogel S. N. Production of tumor necrosis factor by rIFN-gamma-primed C3H/HeJ (Lpsd) macrophages requires the presence of lipid A-associated proteins. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4196–4202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Gillis S., Mizel S. B., Shevach E. M., Malek T. R., Dinarello C. A., Lachman L. B., Janeway C. A., Jr Growth of a cloned helper T cell line induced by a monoclonal antibody specific for the antigen receptor: interleukin 1 is required for the expression of receptors for interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1339–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolls J. K., Beck J. M., Nelson S., Summer W. R., Shellito J. Alveolar macrophage release of tumor necrosis factor during murine Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1993 Apr;8(4):370–376. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/8.4.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Halpern J. L., Swan J. C., Moss J., Parrillo J. E., Masur H. Identification of antigens and antibodies specific for Pneumocystis carinii. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 15;140(6):2023–2031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs J. A., Powell F., Edman J. C., Lundgren B., Martinez A., Drew B., Angus C. W. Multiple genes encode the major surface glycoprotein of Pneumocystis carinii. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):6034–6040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal R., Parsons R. G. Stabilization of proteins immobilized on Sepharose from leakage by glutaraldehyde crosslinking. Anal Biochem. 1980 Feb;102(1):72–76. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90319-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linke M. J., Cushion M. T., Walzer P. D. Properties of the major antigens of rat and human Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1547–1555. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1547-1555.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linke M. J., Walzer P. D. Identification and purification of a soluble species of gp120 released by zymolyase treatment of Pneumocystis carinii. J Protozool. 1991 Nov-Dec;38(6):176S–178S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren B., Lipschik G. Y., Kovacs J. A. Purification and characterization of a major human Pneumocystis carinii surface antigen. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):163–170. doi: 10.1172/JCI114966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manger B., Weiss A., Weyand C., Goronzy J., Stobo J. D. T cell activation: differences in the signals required for IL 2 production by nonactivated and activated T cells. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):3669–3673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight A. J., Classon B. J. Biochemical and immunological properties of rat recombinant interleukin-2 and interleukin-4. Immunology. 1992 Feb;75(2):286–292. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peglow S. L., Smulian A. G., Linke M. J., Pogue C. L., Nurre S., Crisler J., Phair J., Gold J. W., Armstrong D., Walzer P. D. Serologic responses to Pneumocystis carinii antigens in health and disease. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):296–306. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesanti E. L. Interaction of cytokines and alveolar cells with Pneumocystis carinii in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1991 Mar;163(3):611–616. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.3.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pottratz S. T., Paulsrud J., Smith J. S., Martin W. J., 2nd Pneumocystis carinii attachment to cultured lung cells by pneumocystis gp 120, a fibronectin binding protein. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):403–407. doi: 10.1172/JCI115318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding J. A., Armstrong M. Y., Ullu E., Richards F. F. Identification and isolation of a major cell surface glycoprotein of Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2149–2157. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2149-2157.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roths J. B., Sidman C. L. Both immunity and hyperresponsiveness to Pneumocystis carinii result from transfer of CD4+ but not CD8+ T cells into severe combined immunodeficiency mice. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):673–678. doi: 10.1172/JCI115910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shellito J., Suzara V. V., Blumenfeld W., Beck J. M., Steger H. J., Ermak T. H. A new model of Pneumocystis carinii infection in mice selectively depleted of helper T lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1686–1693. doi: 10.1172/JCI114621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smulian A. G., Stringer J. R., Linke M. J., Walzer P. D. Isolation and characterization of a recombinant antigen of Pneumocystis carinii. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):907–915. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.907-915.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smulian A. G., Theus S. A., Denko N., Walzer P. D., Stringer J. R. A 55 kDa antigen of Pneumocystis carinii: analysis of the cellular immune response and characterization of the gene. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(5):745–753. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamburrini E., De Luca A., Ventura G., Maiuro G., Siracusano A., Ortona E., Antinori A. Pneumocystis carinii stimulates in vitro production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by human macrophages. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1991;180(1):15–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00191696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theus S. A., Tabor D. R., Gandy J., Barnett J. B. Alteration of macrophage cytotoxicity through endogenous interferon and tumor necrosis factor alpha induction by propanil. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;118(1):46–52. doi: 10.1006/taap.1993.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., LaBine M., Redington T. J., Cushion M. T. Lymphocyte changes during chronic administration of and withdrawal from corticosteroids: relation to Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2502–2508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Linke M. J. A comparison of the antigenic characteristics of rat and human Pneumocystis carinii by immunoblotting. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2257–2265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walzer P. D., Stanforth D., Linke M. J., Cushion M. T. Pneumocystis carinii: immunoblotting and immunofluorescent analyses of serum antibodies during experimental rat infection and recovery. Exp Parasitol. 1987 Jun;63(3):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(87)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]