Abstract
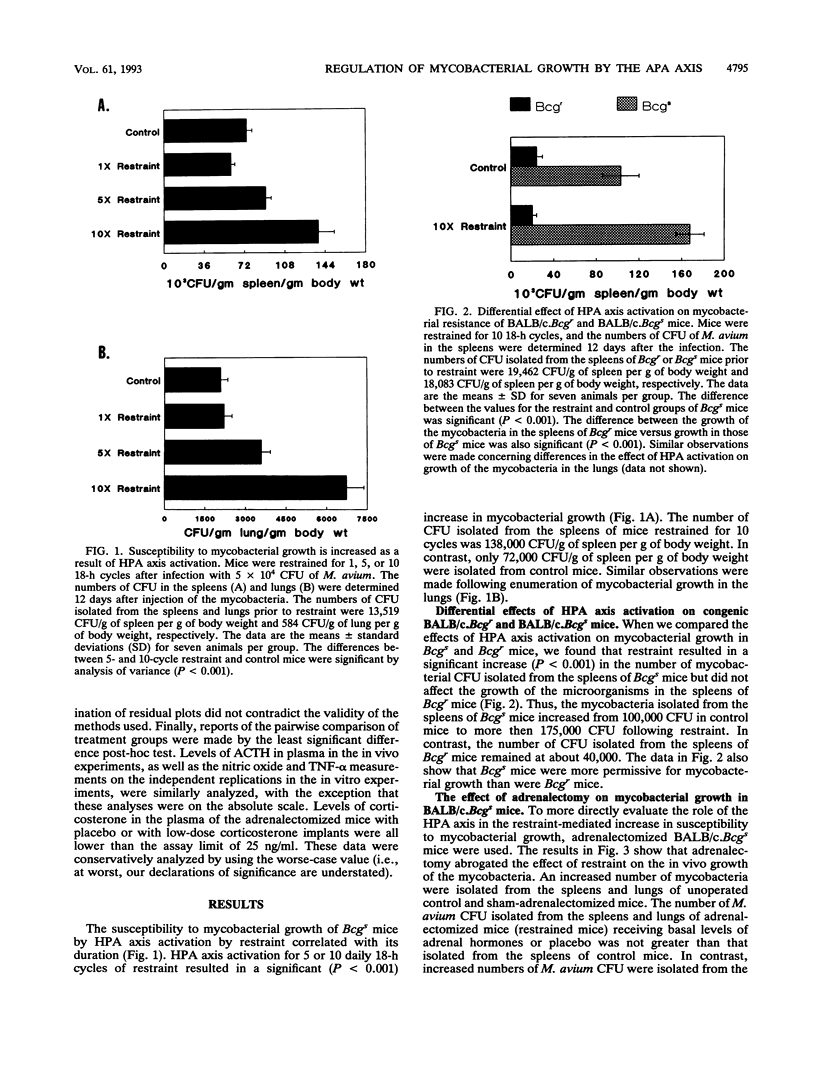
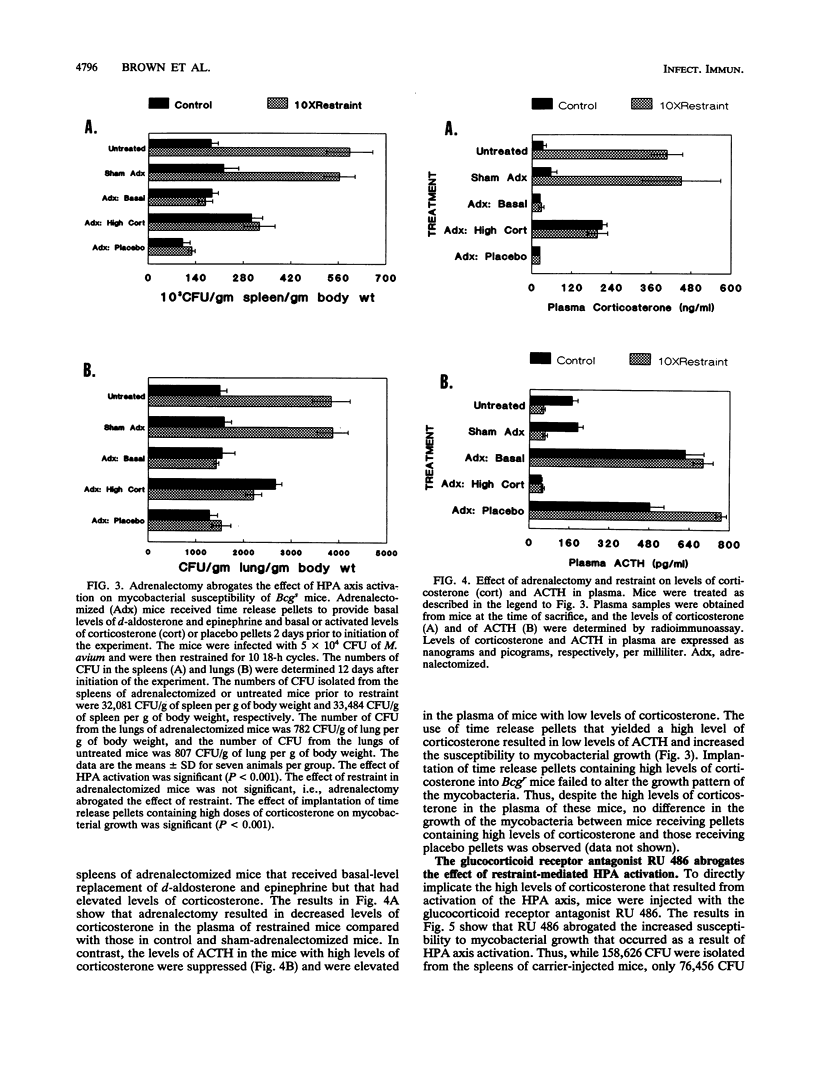
The role of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis in regulating the growth of Mycobacterium avium in Mycobacterium bovis BCG-resistant and -susceptible congenic mice was evaluated. Restraint was used to activate the HPA axis, which resulted in an increase in the level of corticosterone in the plasma. Activation of the HPA axis increased the susceptibility of BALB/c.Bcgs mice to the growth of M. avium. In contrast, the growth of M. avium was not altered in BALB/c.Bcgr mice as a result of HPA activation. Adrenalectomy abolished the effect of HPA activation on mycobacterial growth, as did treatment of the mice with a glucocorticoid receptor antagonist, RU 486. Activation of the HPA axis also resulted in the increased susceptibility of splenic macrophages from Bcgs mice but not from Bcgr mice to M. avium growth in vitro. The production of tumor necrosis factor alpha and of reactive nitrogen intermediates by splenic macrophages from both strains of mice was suppressed as a result of HPA activation. The implications of these findings for resistance controlled by Bcg and for susceptibility to mycobacterial growth are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelberg R., Sarmento A. M. The role of macrophage activation and of Bcg-encoded macrophage function(s) in the control of Mycobacterium avium infection in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jun;80(3):324–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Krochin N., Milsark I. W., Luedke C., Cerami A. Control of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor) synthesis: mechanisms of endotoxin resistance. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3754653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell J. M., Roach T. I., Kiderlen A., Kaye P. M. Role of Lsh in regulating macrophage priming/activation. Res Immunol. 1989 Oct;140(8):798–805. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(89)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blalock J. E. A molecular basis for bidirectional communication between the immune and neuroendocrine systems. Physiol Rev. 1989 Jan;69(1):1–32. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1989.69.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch A. B., Rieder H. L., Kelly G. D., Cauthen G. M., Hayden C. H., Snider D. E. The epidemiology of tuberculosis in the United States. Semin Respir Infect. 1989 Sep;4(3):157–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R. Tuberculosis. Back to a frightening future. Nature. 1992 Aug 13;358(6387):538–539. doi: 10.1038/358538b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breder C. D., Dinarello C. A., Saper C. B. Interleukin-1 immunoreactive innervation of the human hypothalamus. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):321–324. doi: 10.1126/science.3258444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan J., Xing Y., Magliozzo R. S., Bloom B. R. Killing of virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis by reactive nitrogen intermediates produced by activated murine macrophages. J Exp Med. 1992 Apr 1;175(4):1111–1122. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee D., Roberts A. D., Lowell K., Brennan P. J., Orme I. M. Structural basis of capacity of lipoarabinomannan to induce secretion of tumor necrosis factor. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1249–1253. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1249-1253.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Mycobacterial disease, immunosuppression, and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989 Oct;2(4):360–377. doi: 10.1128/cmr.2.4.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. H., Knight B. C., Ivanyi J. Mechanisms of recrudescence of Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1719–1724. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1719-1724.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., Elkins N. Relative permissiveness of macrophages from black and white people for virulent tubercle bacilli. Infect Immun. 1990 Mar;58(3):632–638. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.3.632-638.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham E. T., Jr, De Souza E. B. Interleukin 1 receptors in the brain and endocrine tissues. Immunol Today. 1993 Apr;14(4):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90281-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Rosa M., Radomski M., Carnuccio R., Moncada S. Glucocorticoids inhibit the induction of nitric oxide synthase in macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1246–1252. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91583-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold A. O. Association of tuberculosis with alcoholism. South Med J. 1976 Oct;69(10):1336–1337. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197610000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesch I. E., Kaufmann S. H. Mechanisms involved in mycobacterial growth inhibition by gamma interferon-activated bone marrow macrophages: role of reactive nitrogen intermediates. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3213–3218. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3213-3218.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. C., Wagner D. A., Glogowski J., Skipper P. L., Wishnok J. S., Tannenbaum S. R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha D. K., Gardner I. D., Lawton J. W. Characterization of macrophage function in Mycobacterium lepraemurium-infected mice: sensitivity of mice to endotoxin and release of mediators and lysosomal enzymes after endotoxin treatment. Parasite Immunol. 1983 Sep;5(5):513–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1983.tb00765.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan M. M., Vogel S. N. Inhibition of macrophage tumoricidal activity by glucocorticoids. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):513–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudolin V. Tuberculosis and alcoholism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Apr 25;252:353–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb19179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONES H. W., Jr, ROBERTS J., BRANTNER J. Incidence of tuberculosis among homeless men. J Am Med Assoc. 1954 Jul 31;155(14):1222–1223. doi: 10.1001/jama.1954.03690320026008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. C., Zwilling B. S. Continuous expression of I-A antigen by peritoneal macrophages from mice resistant to Mycobacterium bovis (strain BCG). J Leukoc Biol. 1985 Nov;38(5):635–647. doi: 10.1002/jlb.38.5.635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiecolt-Glaser J. K., Dura J. R., Speicher C. E., Trask O. J., Glaser R. Spousal caregivers of dementia victims: longitudinal changes in immunity and health. Psychosom Med. 1991 Jul-Aug;53(4):345–362. doi: 10.1097/00006842-199107000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochi A. The global tuberculosis situation and the new control strategy of the World Health Organization. Tubercle. 1991 Mar;72(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(91)90017-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. W., Tsou A. P., Chan H., Thomas J., Petrie K., Eugui E. M., Allison A. C. Glucocorticoids selectively inhibit the transcription of the interleukin 1 beta gene and decrease the stability of interleukin 1 beta mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liew F. Y., Li Y., Moss D., Parkinson C., Rogers M. V., Moncada S. Resistance to Leishmania major infection correlates with the induction of nitric oxide synthase in murine macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Dec;21(12):3009–3014. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur H., Murray H. W., Jones T. C. Effect of hydrocortisone on macrophage response to lymphokine. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):709–714. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.709-714.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey P. J., Charrier K. GM-CSF administration augments the survival of ity-resistant A/J mice, but not ity-susceptible C57BL/6 mice, to a lethal challenge with Salmonella typhimurium. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):557–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagami P. H., Yoshikawa T. T. Tuberculosis in the geriatric patient. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1983 Jun;31(6):356–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1983.tb05747.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J., Izzo A. A. Mycobacterial virulence. Virulent strains of Mycobacteria tuberculosis have faster in vivo doubling times and are better equipped to resist growth-inhibiting functions of macrophages in the presence and absence of specific immunity. J Exp Med. 1993 Jun 1;177(6):1723–1733. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.6.1723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M. A mouse model of the recrudescence of latent tuberculosis in the elderly. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Mar;137(3):716–718. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.3.716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINCOCK T. A. ALCOHOLISM IN TUBERCULOUS PATIENTS. Can Med Assoc J. 1964 Oct 17;91:851–854. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., O'Brien A. D., Skamene E., Gros P., Forget A., Kongshavn P. A., Wax J. S. A BALB/c congenic strain of mice that carries a genetic locus (Ityr) controlling resistance to intracellular parasites. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1234–1235. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1234-1235.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. E., Farer L. S. The rising age of the tuberculosis patient: a sign of success and failure. J Infect Dis. 1980 Dec;142(6):946–948. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.6.946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramarathinam L., Niesel D. W., Klimpel G. R. Ity influences the production of IFN-gamma by murine splenocytes stimulated in vitro with Salmonella typhimurium. J Immunol. 1993 May 1;150(9):3965–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramarathinam L., Niesel D. W., Klimpel G. R. Salmonella typhimurium induces IFN-gamma production in murine splenocytes. Role of natural killer cells and macrophages. J Immunol. 1993 May 1;150(9):3973–3981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach T. I., Kiderlen A. F., Blackwell J. M. Role of inorganic nitrogen oxides and tumor necrosis factor alpha in killing Leishmania donovani amastigotes in gamma interferon-lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages from Lshs and Lshr congenic mouse strains. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3935–3944. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3935-3944.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rook G. A., Steele J., Ainsworth M., Leveton C. A direct effect of glucocorticoid hormones on the ability of human and murine macrophages to control the growth of M. tuberculosis. Eur J Respir Dis. 1987 Oct;71(4):286–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salkowski C. A., Vogel S. N. IFN-gamma mediates increased glucocorticoid receptor expression in murine macrophages. J Immunol. 1992 May 1;148(9):2770–2777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salkowski C. A., Vogel S. N. Lipopolysaccharide increases glucocorticoid receptor expression in murine macrophages. A possible mechanism for glucocorticoid-mediated suppression of endotoxicity. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 15;149(12):4041–4047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner A. Therapeutic concentrations of glucocorticoids suppress the antimicrobial activity of human macrophages without impairing their responsiveness to gamma interferon. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1755–1764. doi: 10.1172/JCI112166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurr E., Buschman E., Malo D., Gros P., Skamene E. Immunogenetics of mycobacterial infections: mouse-human homologies. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):634–639. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurr E., Skamene E., Forget A., Gros P. Linkage analysis of the Bcg gene on mouse chromosome 1. Identification of a tightly linked marker. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4507–4513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh J. H., Peterson R. H., Moore M. A. IL-1 modulation of cytokine receptors on bone marrow cells. In vitro and in vivo studies. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1273–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder D. S., Unanue E. R. Corticosteroids inhibit murine macrophage Ia expression and interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):1803–1805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead W. W. Genetics and resistance to tuberculosis. Could resistance be enhanced by genetic engineering? Ann Intern Med. 1992 Jun 1;116(11):937–941. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-11-937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead W. W., Senner J. W., Reddick W. T., Lofgren J. P. Racial differences in susceptibility to infection by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. N Engl J Med. 1990 Feb 15;322(7):422–427. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199002153220702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokvis H., Langermans J. A., de Backer-Vledder E., van der Hulst M. E., van Furth R. Hydrocortisone treatment of BCG-infected mice impairs the activation and enhancement of antimicrobial activity of peritoneal macrophages. Scand J Immunol. 1992 Aug;36(2):299–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1992.tb03103.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland R. W., Wahl L. M., Finbloom D. S. Corticosteroids enhance the binding of recombinant interferon-gamma to cultured human monocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1577–1580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodos C. M., Povinelli L., Molina R., Sherry B., Titus R. G. Role of tumor necrosis factor in macrophage leishmanicidal activity in vitro and resistance to cutaneous leishmaniasis in vivo. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2839–2842. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2839-2842.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan W., Vriend C. Y., Wetmore L., Gartner J. G., Greenberg A. H., Nance D. M. The effects of stress on splenic immune function are mediated by the splenic nerve. Brain Res Bull. 1993;30(1-2):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(93)90044-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren M. K., Vogel S. N. Opposing effects of glucocorticoids on interferon-gamma-induced murine macrophage Fc receptor and Ia antigen expression. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2462–2469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegeshaus E., Balasubramanian V., Smith D. W. Immunity to tuberculosis from the perspective of pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3671–3676. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3671-3676.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman S. H., Shellhaas J., Butler L. D. Differential regulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor synthesis: effects of endogenous and exogenous glucocorticoids and the role of the pituitary-adrenal axis. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Feb;19(2):301–305. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwilling B. S., Brown D., Christner R., Faris M., Hilburger M., McPeek M., Van Epps C., Hartlaub B. A. Differential effect of restraint stress on MHC class II expression by murine peritoneal macrophages. Brain Behav Immun. 1990 Dec;4(4):330–338. doi: 10.1016/0889-1591(90)90036-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwilling B. S., Brown D., Pearl D. Induction of major histocompatibility complex class II glycoproteins by interferon-gamma: attenuation of the effects of restraint stress. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Mar;37(1-2):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90162-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwilling B. S., Salkowitz J., Laufman H., Pearl D. Differences in the expression of histocompatibility antigen-DR and in anti-mycobacterial activity of monocytes from HIV-infected individuals. AIDS. 1991 Nov;5(11):1327–1332. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199111000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwilling B. S., Vespa L., Massie M. Regulation of I-A expression by murine peritoneal macrophages: differences linked to the Bcg gene. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1372–1376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



