Abstract
Purified nucleocapsid protein (N protein) from transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) enhanced hammerhead ribozyme self-cleavage and favored nucleic acid annealing, properties that define RNA chaperones, as previously reported. Several TGEV N-protein deletion mutants were expressed in Escherichia coli and purified, and their RNA binding ability and RNA chaperone activity were evaluated. The smallest N-protein domain analyzed with RNA chaperone activity, facilitating DNA and RNA annealing, contained the central unstructured region (amino acids 117 to 268). Interestingly, N protein and its deletion mutants with RNA chaperone activity enhanced template switching in a retrovirus-derived heterologous system, reinforcing the concept that TGEV N protein is an RNA chaperone that could be involved in template switching. This result is in agreement with the observation that in vivo, N protein is not necessary for TGEV replication, but it is required for efficient transcription.
RNA chaperones are proteins that allow the proper folding of nucleic acids (4, 12). Several characteristics distinguish RNA chaperones from other RNA binding proteins: a lack of specificity; they are transiently needed; and there is no energy requirement for their function (19). RNA chaperone activity cannot be predicted based on the protein domain structure or the existence of discrete motifs. In the case of virus-encoded RNA chaperones, even RNA chaperone proteins of the same viral genus have little sequence similarity. Nevertheless, RNA chaperones have the highest frequency of disordered regions, and it has been proposed that they act according to an entropy transfer model, allowing correct RNA folding by successive cycles of protein-substrate order-disorder (5, 32). In fact, protein disorder has been the selected criterion for investigating the chaperone activity of candidate viral RNA chaperone proteins (14, 36). The list of virus-encoded RNA chaperones has been quickly growing. Nevertheless, their role in the viral life cycle as RNA chaperones is still unclear, mainly due to the difficulty of analyzing in vivo the chaperone activity of these proteins in viral infection.
Coronaviruses are enveloped viruses of the Coronaviridae family, included in the Nidovirales order (7, 10). Their genomes are positive-sense, single-stranded RNAs (ssRNAs) of around 30 kb, the largest known viral RNA genomes. The 5′ two-thirds of the genomic RNA encodes the replicase proteins. The 3′ third of the genome encodes structural and nonstructural proteins. Coronavirus transcription leads to a nested set of subgenomic (sg) mRNAs that are generated by a discontinuous mechanism. This process implies base pairing of nascent RNAs of negative polarity, synthesized under the control of transcription-regulating sequences (TRSs) preceding each gene, with sequences located at the 3′ end of the leader within the genomic RNA (21, 23, 35).
Coronavirus nucleocapsid protein (N protein) has a structural role and is involved in RNA synthesis (1, 6). The N proteins from different coronaviruses vary in length and primary sequence. Nevertheless, some motifs with functional relevance are conserved, and N proteins share a three-domain organization according to sequence similarity (18). Recently, based on disorder predictions, a modular organization including two structured domains separated by a long disordered region was proposed for coronavirus N protein (2, 36). Using transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) as a model, RNA chaperone activity has been demonstrated for N protein (36). RNA chaperone activity was also reported for severe and acute respiratory syndrome virus (SARS-CoV) N protein, and it was postulated as a general activity of all coronavirus nucleocapsid proteins (36).
The template switch during discontinuous RNA synthesis in coronavirus transcription is a complex process that includes several steps: the slowing down and stopping of nucleic acid synthesis, the template switch itself, reassociation of the nascent nucleic acid strand with the acceptor sequence, and elongation of the nascent strand using the acceptor nucleic acid as a template (8). To accomplish some of these steps, we have proposed that RNA chaperones, such as TGEV N protein, could decrease the energy barrier needed to dissociate the nascent minus RNA chain from the genomic RNA template (36). This decrease in the energy threshold would facilitate the nascent RNA chain template switch to hybridize with the TRS of the leader sequence during discontinuous transcription.
The role of coronavirus N protein in RNA synthesis has been controversial. On one hand, it has been reported that viral replicase gene products suffice for coronavirus replication (30). On the other, the same authors and others have reported that addition of N protein enhances RNA synthesis (1, 22, 31). Whether this enhancement is due to an increase in replication, transcription, or both has not been clearly established.
In this article, we report the generation of a set of TGEV N-protein deletion mutants and the analysis of their RNA chaperone activity, using annealing assays. The role of wild-type (wt) N protein and deletion mutants in template switching was evaluated in vitro using a retrovirus-derived strand transfer system. Our data indicated that the central disordered domain of the TGEV N protein has RNA chaperone activity and facilitates template switching in vitro. Moreover, the role of N protein in vivo in TGEV replication and transcription was evaluated. Interestingly, the results reported in this paper indicate that N protein is not essential for TGEV RNA replication. In contrast, it is required for efficient transcription. These data reinforce the hypothesis of N protein having a role in template switching.
Nucleic acid binding of N protein deletion mutants.
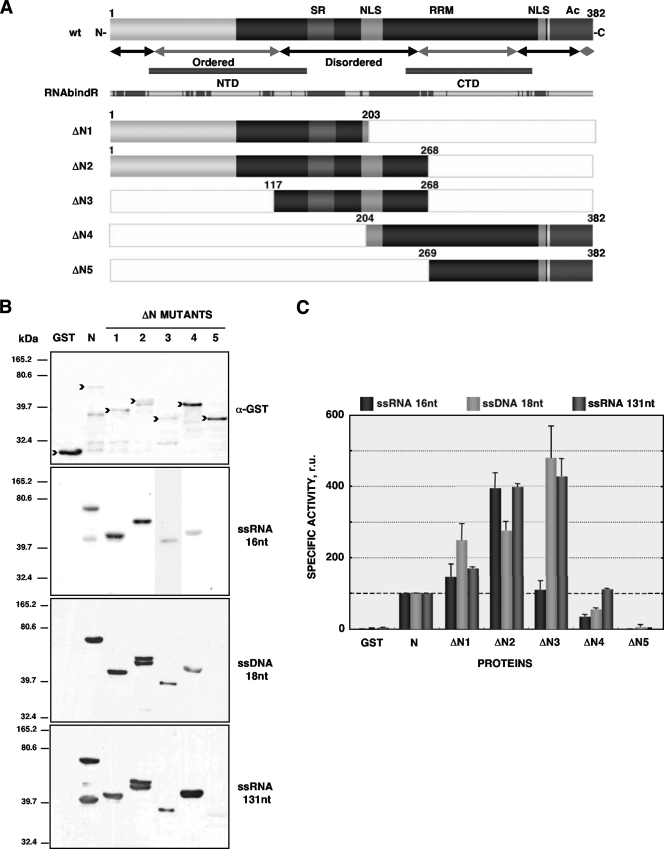
To locate a TGEV N protein domain with nucleic acid chaperone activity, a set of deletion mutants was designed according to several criteria: predicted domain distribution, order-disorder pattern, predicted location of crystallized N-terminal (NTD) and C-terminal (CTD) domains from other coronavirus N proteins, and predicted RNA-binding residues (Fig. 1A). The corresponding fragments of TGEV N-protein coding sequence were amplified by PCR and cloned into the plasmid pGEX-4T-2. The N-protein mutants ΔN1, ΔN2, ΔN3, ΔN4, and ΔN5 (Fig. 1A) were successfully expressed and purified from Escherichia coli as previously described (36).
FIG. 1.
Nucleic acid binding of N protein mutants. (A) Scheme of TGEV full-length N protein (wt, upper bar) and deletion mutants (ΔN, lower bars). Disorder-order pattern, residues corresponding to crystallized amino- and carboxy-terminal domains (NTD and CTD, respectively), and prediction of RNA binding residues according to the RNAbindR server (28, 29) are indicated. Labels on the left indicate the protein name. SR, Ser-rich domain; RRM, RNA recognition motif; NLS, nuclear localization signal; Ac, acidic domain. The numbers indicate the corresponding amino acids in N protein. (B) Western blot of protein fractions (upper panel) and Northwestern blot using different biotin-labeled probes (lower panels). Proteins were detected with an antibody specific for the GST tag (α-GST). Nondegraded protein species are indicated by black arrowheads. The nature of the nucleic acid probe is indicated at the right of the figure. The numbers on the left indicate molecular masses in kDa. (C) The intensity of the bands binding the probe was estimated by densitometry and corrected by the amount of intact protein in each case. Binding of N protein was considered to be 100 relative units (r.u.) of activity in each case; this threshold is indicated by the black dashed line. Error bars represent the standard deviations from four independent experiments.
RNA chaperone activity requires nucleic acid binding, and the ability of the constructed N protein deletion mutants to bind different nucleic acid species was evaluated by Northwestern blotting. Purified protein fractions were separated in 10% SDS-PAGE gels and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. Blocking and incubation with biotin-labeled probes was performed as previously described (26). Three types of probes were used: 16-nucleotide (nt) single-stranded RNAs of both viral (leader TRS) and cellular (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase) origins, 18-nt single-stranded DNAs (ssDNAs), and longer ssRNAs of around 130 nt (acceptor and donor RNAs from the retrovirus-derived template switch system). Probe sequences are available from the authors upon request. Biotinylated RNAs were detected using the BrightStar BioDetect kit (Ambion) (Fig. 1B). The intensity of the binding was estimated by band densitometry. Since full-length TGEV N protein and its deletion mutants were prone to degradation, a property related to the disordered nature of the protein (16, 27, 34), binding values were calculated with reference to the amount of each intact protein fragment (Fig. 1B, top panel). As expected, the glutathione S-transferase (GST) control protein did not bind to any nucleic acid probe, while N protein bound to all nucleic acid species (Fig. 1C). N-protein mutants lacking the C-terminal domain (ΔN1 and ΔN2) and mutant ΔN3, containing just the central disorder domain of N protein, bound to all nucleic acid probes as well as or even better than N protein. The mutant ΔN4 hardly bound short nucleic acids, but it bound long ssRNAs as well as N protein. Finally, the mutant ΔN5, containing just the C-terminal domain of N protein, did not bind any nucleic acid (Fig. 1C). These results are in agreement with previously reported RNA binding domains for other coronavirus N proteins (2, 3, 9, 13, 17, 20, 24-27).
RNA chaperone activity of N-protein deletion mutants determined by nucleic acid annealing assays.
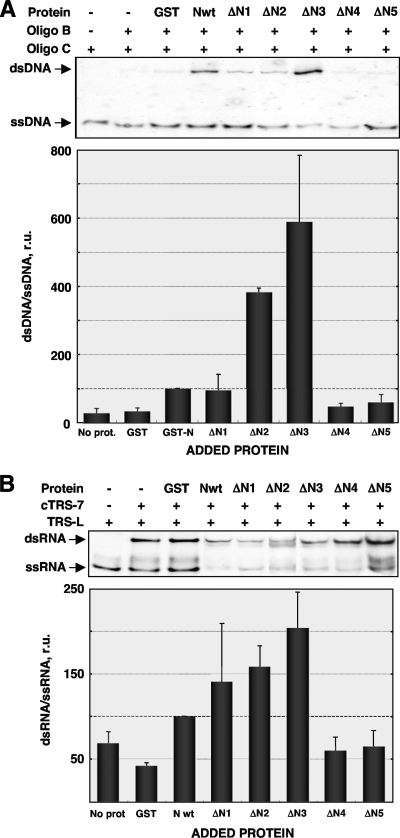
Facilitation of rapid and accurate nucleic acid annealing is one of the properties of RNA chaperones in general and coronavirus N protein in particular (36). Both DNA and RNA annealing assays, followed by proteinase K treatment to rule out nucleic acid aggregation mediated by protein binding, were performed as previously described (36). In the absence of protein or in the presence of GST, background levels of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) were obtained (Fig. 2A). The amount of dsDNA was increased in the presence of full-length N protein, as expected. The mutants ΔN1 and ΔN2 also increased the formation of dsDNA. Incubation with the mutant ΔN3, containing the central disordered domain of N protein, showed the largest increase in dsDNA levels. In contrast, incubation with the mutants ΔN4 and ΔN5 provided background levels of dsDNA (Fig. 2A). Similar results were obtained when the base pairing of viral TRS RNAs was analyzed (Fig. 2B). Altogether, these data suggested that the mutants ΔN1, ΔN2, and ΔN3 may have RNA chaperone activity.
FIG. 2.
Nucleic acid annealing assays. (A) DNA annealing assays were performed using an 18-mer biotin-labeled DNA oligonucleotide (Oligo C) and a 56-mer unlabeled DNA oligonucleotide (Oligo B) that under reaction conditions forms a stable secondary structure that must be unwound to allow double-stranded DNA formation. The ratio of dsDNA to ssDNA was estimated by densitometry (graph) and referenced to that obtained in the presence of wt N protein, considered 100 relative units (r.u.) (indicated by the black dashed line). (B) RNA annealing assays were performed using a biotin-labeled 16-mer RNA oligonucleotide representing the transcription regulating sequence of the leader (TRS-L) and an unlabeled 16-mer RNA oligonucleotide with the complementary sequence to the gene 7 TRS (cTRS-7). The ratio of dsRNA to ssRNA was estimated as for panel A. Error bars in panels A and B represent the standard deviations for results from four independent experiments.
Role of N protein in in vitro template switching.
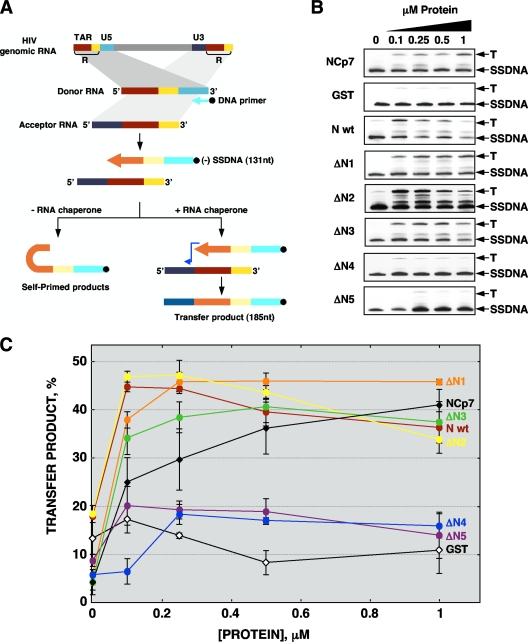
An in vitro template switch system based on human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) was used to evaluate the involvement of N protein in template switching (11). Using a labeled DNA primer, HIV reverse transcriptase (RT) synthesizes a cDNA copy of a donor RNA of 131 nt (strong-stop DNA [SSDNA]). In the presence of an RNA chaperone, template switching occurs, and a labeled transfer product of 185 nt was obtained (Fig. 3A). This system has strong RNA chaperone activity requirements in different steps, such as the unwinding of stable nucleic acid secondary structures, inhibition of self-priming, enhancement of template switching, an increase in RNase H activity, and improvement in RT processivity (15). Template switch reactions were performed as previously described (11), except for the use of a biotin-labeled DNA primer and detection of biotinylated reaction products with the BrightStar BioDetect kit.
FIG. 3.
In vitro template switching assay. (A) HIV-derived template switching system. Using a biotin-labeled DNA primer, HIV RT synthesizes a cDNA copy of a donor RNA of 131 nt (strong-stop DNA [SSDNA]). In the presence of an RNA chaperone, template switching occurs and a labeled transfer product (T) of 185 nt was obtained. R, repeated sequences, including transactivation response (TAR) element sequence. (B) Template switch assay in the presence of control NCp7 and GST proteins or TGEV N protein deletion mutants. (C) Template switch efficiency was estimated by densitometry of labeled T and SSDNA bands, and the transfer product amount was calculated as a percentage of the ratio T/(T + SSDNA) in each case. Error bars represent the standard deviations from four independent experiments.
In the presence of increasing amounts of HIV nucleocapsid protein (NCp7), a well-known RNA chaperone, an increase in the formation of transfer product was observed (Fig. 3B). In contrast, the levels of transfer product remained constant in the presence of the GST negative control protein (Fig. 3B). The generation of transfer product as the result of template switching was monitored in the presence of full-length N protein and its deletion mutants (Fig. 3B). Template switch efficiency was estimated by densitometry as previously described (11) (Fig. 3C). An increase in the TGEV N protein concentration led to an increase in the amounts of transfer product (Fig. 3C). This result indicated that TGEV N protein acts as an RNA chaperone in the HIV-derived system, facilitating template switching in vitro. Incubation with N-protein mutants lacking the C terminus (ΔN1 and ΔN2) and the mutant ΔN3, containing the central disorder domain of N protein, also produced an increase in the levels of transfer product (Fig. 3C). In contrast, the mutants ΔN4 and ΔN5 did not produce an increase in the amounts of transfer product (Fig. 3C). It is worth noting that at the higher concentrations analyzed, wt N protein and mutants ΔN2 and ΔN3 led to a decrease in the amount of transfer product (Fig. 3C). This effect is probably a consequence of the RNA chaperone activity of the proteins, enhancing the RNA degradation due to nucleases present in the protein fractions (15, 36).
The purification of in vitro active coronavirus replication-transcription complexes was recently described (33). Unfortunately, these systems cannot be used to analyze the role of chaperones in template switching, since their chemical components are not fully defined. Most importantly, it is likely that these systems will already include the N protein with the RNA chaperone activity that we would like to evaluate, in addition to other cellular proteins that also have RNA chaperone activity.
Role of N protein in in vivo coronavirus RNA synthesis.
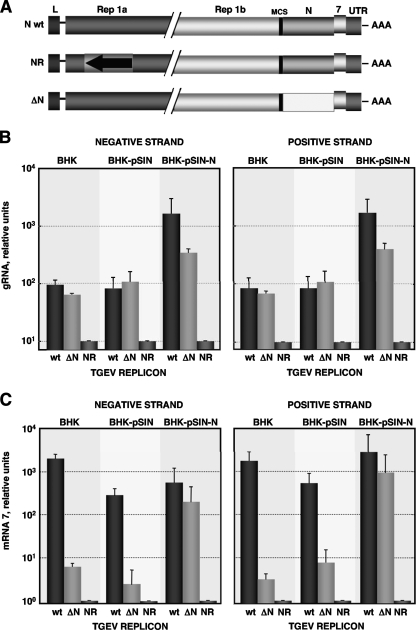
Using TGEV-derived replicons, our group has previously reported the requirement of N protein for efficient RNA synthesis (1). To dissect the role of N protein in coronavirus replication and transcription, TGEV replicons containing full-length N protein (N wt) or lacking N protein (ΔN) were used (Fig. 4A). Their replication and transcription levels were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR using specific TaqMan assays for negative and positive strands, respectively. RNA levels were compared in all cases with the levels obtained from a nonreplicative replicon (NR) (Fig. 4A), leading to background reference levels of replication (Fig. 4B) and transcription (Fig. 4C). In the absence of N protein, genomic RNA levels of the replicons including or lacking N protein were similar when both negative and positive RNA strands were analyzed. Furthermore, addition of N protein in trans led to an up to 10-fold increase of replication levels for both replicons (Fig. 4B). These data indicate that N protein is not essential for coronavirus replication, and they are in agreement with previous observations (30). The TGEV replicon containing full-length N protein transcribed very efficiently (Fig. 4C). In contrast, replicon ΔN, lacking N protein, led to basal levels of transcription that were increased up to 100-fold by adding N protein in trans (Fig. 4C). These data indicate that although not absolutely essential, N protein is required for efficient coronavirus transcription. The obtained results confirm previous data on the enhancement of RNA synthesis by N protein (1, 31), indicating that the increase in RNA synthesis from the presence of N protein is due mainly to an increase in transcription levels.
FIG. 4.
In vivo coronavirus RNA synthesis. (A) Scheme of TGEV-derived replicons, containing full-length N protein (N wt) or lacking N protein (ΔN). A nonreplicative replicon (NR) containing full-length N protein, but unable to replicate due to a mutation affecting several replicase genes, was also used. All replicons contain gene 7 to allow measurement of transcription (1). (B) Quantification of negative and positive strands of genomic RNA (gRNA) using specific TaqMan assays. Experiments were performed as previously described (1), including a DNase I treatment to eliminate DNA from transfection. BHK-pSIN, BHK cells transfected with Sindbis virus replicon; BHK-pSIN-N, BHK cells expressing N protein from Sindbis virus replicon. (C) Transcription levels measured by quantification of subgenomic mRNA of gene 7, both negative and positive strand, using specific TaqMan assays. Error bars represent the standard deviations from five independent experiments.
Overall, the results shown indicate that the RNA chaperone activity of TGEV N protein is located in its central disordered domain (aa 117 to 268) and that this activity requires the ability to bind RNA and additional characteristics present in the ΔN3 N-protein fragment. To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of a nonretroviral RNA chaperone acting in an in vitro template switching system. The results obtained confirm the RNA chaperone activity of TGEV N protein and its potential role in template switching. In agreement with this, in vivo results indicated that N protein is required for efficient transcription. Nevertheless, additional experimental evidence will be required to definitively establish the implication of N protein in coronavirus template switching.
Acknowledgments
We thank F. Almazan for critically reading the manuscript and helpful discussions. We are also grateful to J. G. Levin and R. J. Gorelick for kindly providing plasmids for the HIV-derived template switch assay and purified NCp7, respectively.
This work was supported by grants from Comisión Interministerial de Ciencia y Tecnología (CICYT) (no. BIO2007-60978), the Conserjeria de Educación y Cultura de la Comunidad de Madrid (S-SAL-0185/06), the European Communities (PoRRSCon, EU-245141), and the National Pork Board (NPB#08-197). S.Z., I.S., and J.L.G.C. received contracts from the Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) and Comunidad Autónoma de Madrid.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 2 December 2009.
REFERENCES
- 1.Almazan, F., C. Galan, and L. Enjuanes. 2004. The nucleoprotein is required for efficient coronavirus genome replication. J. Virol. 78:12683-12688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chang, C. K., S. C. Sue, T. H. Yu, C. M. Hsieh, C. K. Tsai, Y. C. Chiang, S. J. Lee, H. H. Hsiao, W. J. Wu, W. L. Chang, C. H. Lin, and T. H. Huang. 2006. Modular organization of SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid protein. J. Biomed. Sci. 13:59-72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chen, C. Y., C. Chang, Y. W. Chang, S. C. Sue, H. Bai, L. Riang, C. D. Hsiao, and T. Huang. 2007. Structure of the SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid protein RNA-binding dimerization domain suggests a mechanism for helical packaging of viral RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 368:1075-1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cristofari, G., and J. L. Darlix. 2002. The ubiquitous nature of RNA chaperone proteins. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 72:223-268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dyson, H. J., and P. E. Wright. 2005. Intrinsically unstructured proteins and their functions. Nat. Rev. 6:197-208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Enjuanes, L., F. Almazan, I. Sola, and S. Zuñiga. 2006. Biochemical aspects of coronavirus replication and virus-host interaction. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 60:211-230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Enjuanes, L., A. E. Gorbalenya, R. J. de Groot, J. A. Cowley, J. Ziebuhr, and E. J. Snijder. 2008. The Nidovirales, p. 419-430. In B. W. J. Mahy, M. Van Regenmortel, P. Walker, and D. Majumder-Russell (ed.), Encyclopedia of virology, 3rd ed. Elsevier Ltd., Oxford, United Kingdom.
- 8.Enjuanes, L., I. Sola, S. Zuñiga, and J. L. Moreno. 2007. Coronavirus RNA synthesis: transcription, p. 81-107. In V. Thiel (ed.), Coronaviruses: molecular and cellular biology. Caister Academic Press, Norfolk, United Kingdom.
- 9.Fan, H., A. Ooi, Y. W. Tan, S. Wang, S. Fang, D. X. Liu, and J. Lescar. 2005. The nucleocapsid protein of coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus: crystal structure of its N-terminal domain and multimerization properties. Structure 13:1859-1868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gorbalenya, A. E., L. Enjuanes, J. Ziebuhr, and E. J. Snijder. 2006. Nidovirales: evolving the largest RNA virus genome. Virus Res. 117:17-37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Guo, J., L. E. Henderson, J. Bess, B. Kane, and J. G. Levin. 1997. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 nucleocapsid protein promotes efficient strand transfer and specific viral DNA synthesis by inhibiting TAR-dependent self-priming from minus-strand strong-stop DNA. J. Virol. 71:5178-5188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Herschlag, D. 1995. RNA chaperones and the RNA folding problem. J. Biol. Chem. 270:20871-20874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Huang, Q., L. Yu, A. M. Petros, A. Gunasekera, Z. Liu, N. Xu, P. Hajduk, J. Mack, S. W. Fesik, and E. T. Olejniczak. 2004. Structure of the N-terminal RNA-binding domain of the SARS CoV nucleocapsid protein. Biochemistry 43:6059-6063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ivanyi-Nagy, R., J. Lavergne, C. Gabus, D. Ficheux, and J. Darlix. 2008. RNA chaperoning and intrinsic disorder in the core proteins of Flaviviridae. Nucleic Acids Res. 36:2618-2633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Levin, J. G., J. Guo, I. Rouzina, and K. Musier-Forsyth. 2005. Nucleic acid chaperone activity of HIV-1 nucleocapsid protein: critical role in reverse transcription and molecular mechanism. Prog. Nucleic. Acids Res. Mol. Biol. 80:217-286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mark, J., X. Li, T. Cyr, S. Fournier, B. Jaentschke, and M. A. Hefford. 2008. SARS coronavirus: unusual lability of the nucleocapsid protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 377:429-433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nelson, G. W., S. A. Stohlman, and S. M. Tahara. 2000. High affinity interaction between nucleocapsid protein and leader/intergenic sequence of mouse hepatitis virus RNA. J. Gen. Virol. 81:181-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Parker, M. M., and P. S. Masters. 1990. Sequence comparison of the N genes of five strains of the coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus suggests a three domain structure for the nucleocapsid protein. Virology 179:463-468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rajkowitsch, L., D. Chen, S. Stampfl, K. Semrad, C. Waldsich, O. Mayer, M. F. Jantsch, R. Konrat, U. Bläsi, and R. Schroeder. 2007. RNA chaperones, RNA annealers and RNA helicases. RNA Biol. 4:118-130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Saikatendu, K. S., J. S. Joseph, V. Subramanian, B. W. Neuman, M. J. Buchmeier, R. C. Stevens, and P. Kuhn. 2007. Ribonucleocapsid formation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus through molecular action of the N-terminal domain of N protein. J. Virol. 81:3913-3921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sawicki, S. G., D. L. Sawicki, and S. G. Siddell. 2007. A contemporary view of coronavirus transcription. J. Virol. 81:20-29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schelle, B., N. Karl, B. Ludewig, S. G. Siddell, and V. Thiel. 2005. Selective replication of coronavirus genomes that express nucleocapsid protein. J. Virol. 79:6620-6630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sola, I., J. L. Moreno, S. Zuñiga, S. Alonso, and L. Enjuanes. 2005. Role of nucleotides immediately flanking the transcription-regulating sequence core in coronavirus subgenomic mRNA synthesis. J. Virol. 79:2506-2516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Spencer, K., and J. A. Hiscox. 2006. Characterisation of the RNA binding properties of the coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus nucleocapsid protein amino-terminal region. FEBS Lett. 580:5993-5998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Takeda, M., C. Chang, T. Ikeya, P. Güntert, Y. Chang, Y. I. Hsu, T. Huang, and M. Kainosho. 2008. Solution structure of the C-terminal dimerization domain of SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid protein solved by the SAIL-NMR method. J. Mol. Biol. 380:608-622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tan, Y. W., S. Fang, H. Fan, J. Lescar, and D. X. Liu. 2006. Amino acid residues critical for RNA-binding in the N-terminal domain of the nucleocapsid protein are essential determinants for the infectivity of coronavirus in cultured cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:4816-4825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tang, T. K., M. P. Wu, S. T. Chen, M. H. Hou, M. H. Hong, F. M. Pan, H. M. Yu, J. H. Chen, C. W. Yao, and A. H. Wang. 2005. Biochemical and immunological studies of nucleocapsid proteins of severe acute respiratory syndrome and 229E human coronaviruses. Proteomics 5:925-937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Terribilini, M., J. H. Lee, C. Yan, R. L. Jernigan, V. Honavar, and D. Dobbs. 2006. Prediction of RNA binding sites in proteins from amino acid sequence. RNA 12:1450-1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Terribilini, M., J. D. Sander, J. H. Lee, P. Zaback, R. L. Jernigan, V. Honavar, and D. Dobbs. 2007. RNABindR: a server for analyzing and predicting RNA-binding sites in proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 35:W578-W584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Thiel, V., J. Herold, B. Schelle, and S. G. Siddell. 2001. Viral replicase gene products suffice for coronavirus discontinuous transcription. J. Virol. 75:6676-6681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Thiel, V., N. Karl, B. Schelle, P. Disterer, I. Klagge, and S. G. Siddell. 2003. Multigene RNA vector based on coronavirus transcription. J. Virol. 77:9790-9798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tompa, P., and P. Csermely. 2004. The role of structural disorder in the function of RNA and protein chaperones. FASEB J. 18:1169-1175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.van Hemert, M. J., S. H. van den Worm, K. Knoops, A. M. Mommaas, A. E. Gorbalenya, and E. J. Snijder. 2008. SARS-coronavirus replication/transcription complexes are membrane-protected and need a host factor for activity in vitro. PLoS Pathog. 4:e1000054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wang, Y., X. Wu, Y. Wang, B. Li, H. Zhou, G. Yuan, Y. Fu, and Y. Luo. 2004. Low stability of nucleocapsid protein in SARS virus. Biochemistry 43:11103-11108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zuñiga, S., I. Sola, S. Alonso, and L. Enjuanes. 2004. Sequence motifs involved in the regulation of discontinuous coronavirus subgenomic RNA synthesis. J. Virol. 78:980-994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zuñiga, S., I. Sola, J. L. Moreno, P. Sabella, J. Plana-Duran, and L. Enjuanes. 2007. Coronavirus nucleocapsid protein is an RNA chaperone. Virology 357:215-227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]