Volume 133, No. 3, March 2, 2009. Pages 327–343.
Please note that in the original Fig. 2, “103” was missing from the y axes. The correct figure appears below.
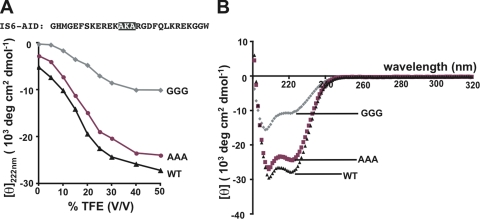
Figure 2.
Glycine substitution in IS6-AID linker disrupts helical structure. (A) Mean residue ellipticity at 222 nm for IS6-AID linker peptide, and AAA and GGG mutant peptides as a function of TFE concentration. Peptide sequence is shown. Black highlights the site of the GGG and AAA mutations. (B) IS6-AID linker peptide CD spectra at a peptide concentration of 50 μM in 50% TFE.