Abstract
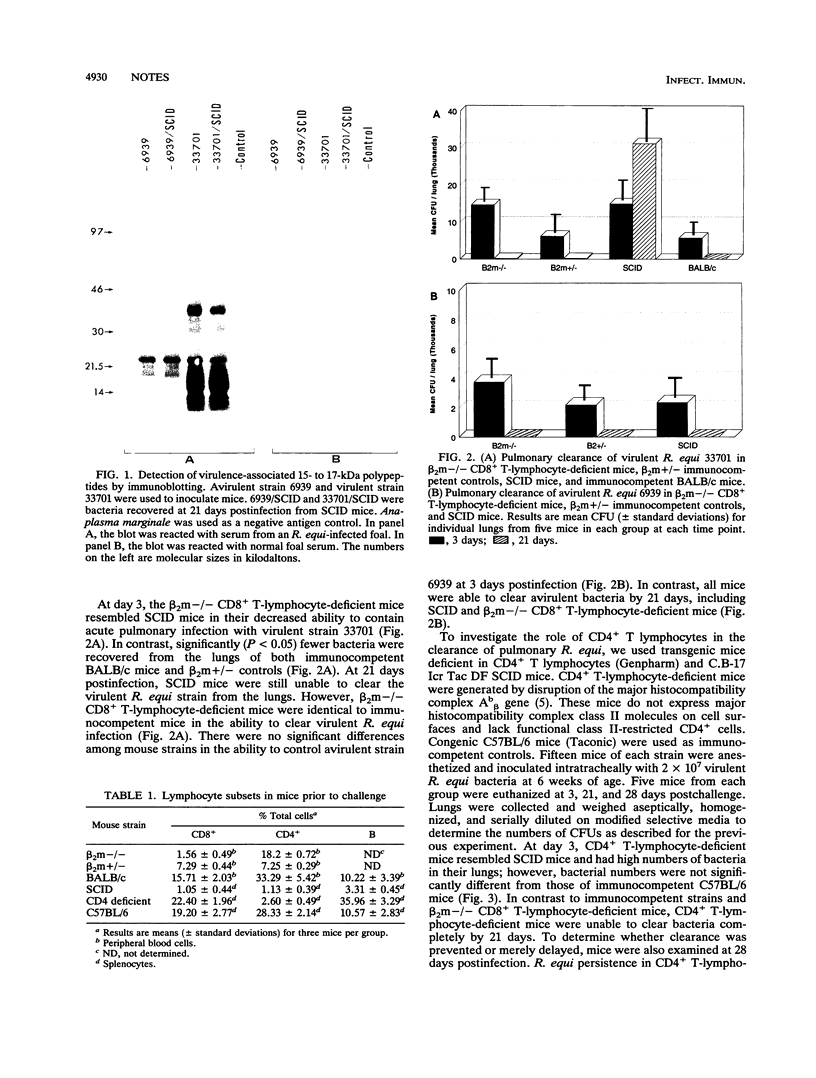
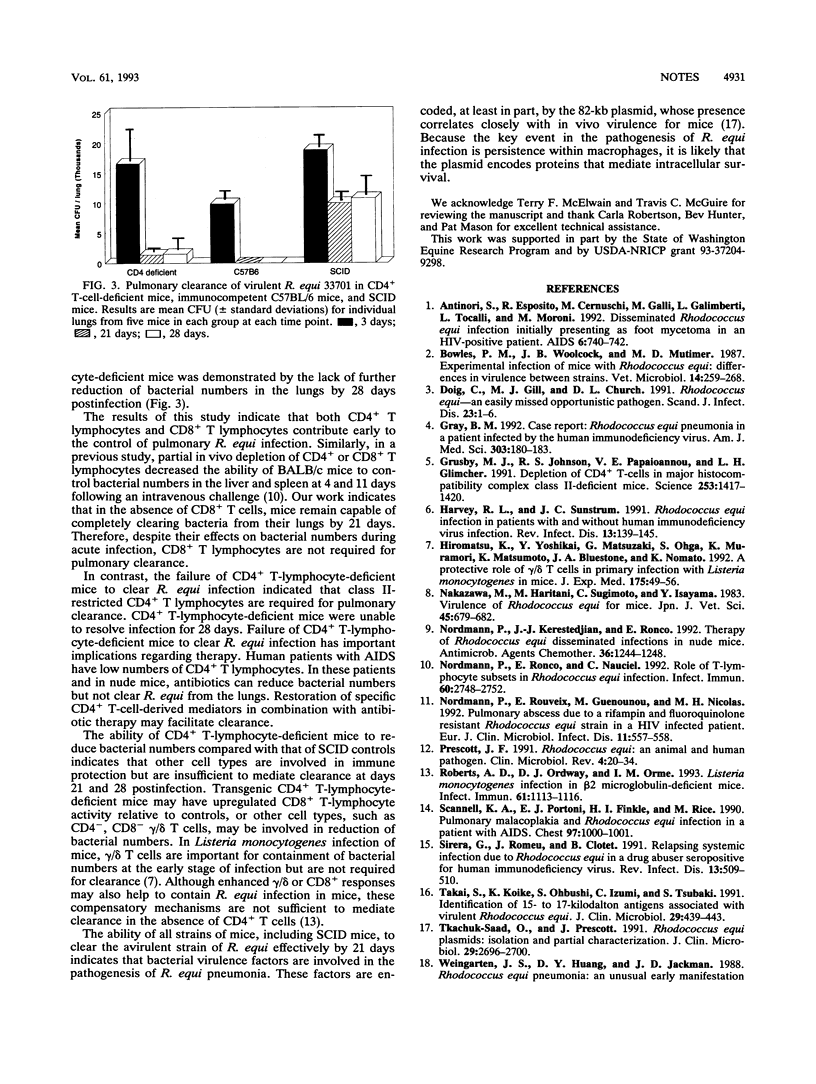
Pulmonary clearance of Rhodococcus equi requires functional T lymphocytes. In this study, CD8+ T-lymphocyte-deficient transgenic mice cleared virulent R. equi from the lungs while infection in CD4+ T-lymphocyte-deficient transgenic mice persisted. Although both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells function early in pulmonary defense against R. equi, clearance is dependent on CD4+ T lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antinori S., Esposito R., Cernuschi M., Galli M., Galimberti L., Tocalli L., Moroni M. Disseminated Rhodococcus equi infection initially presenting as foot mycetoma in an HIV-positive patient. AIDS. 1992 Jul;6(7):740–742. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199207000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowles P. M., Woolcock J. B., Mutimer M. D. Experimental infection of mice with Rhodococcus equi: differences in virulence between strains. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Aug;14(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig C., Gill M. J., Church D. L. Rhodococcus equi--an easily missed opportunistic pathogen. Scand J Infect Dis. 1991;23(1):1–6. doi: 10.3109/00365549109023367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray B. M. Case report: Rhodococcus equi pneumonia in a patient infected by the human immunodeficiency virus. Am J Med Sci. 1992 Mar;303(3):180–183. doi: 10.1097/00000441-199203000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grusby M. J., Johnson R. S., Papaioannou V. E., Glimcher L. H. Depletion of CD4+ T cells in major histocompatibility complex class II-deficient mice. Science. 1991 Sep 20;253(5026):1417–1420. doi: 10.1126/science.1910207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. L., Sunstrum J. C. Rhodococcus equi infection in patients with and without human immunodeficiency virus infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jan-Feb;13(1):139–145. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.1.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromatsu K., Yoshikai Y., Matsuzaki G., Ohga S., Muramori K., Matsumoto K., Bluestone J. A., Nomoto K. A protective role of gamma/delta T cells in primary infection with Listeria monocytogenes in mice. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):49–56. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa M., Haritani M., Sugimoto C., Isayama Y. Virulence of Rhodococcus equi for mice. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1983 Oct;45(5):679–682. doi: 10.1292/jvms1939.45.679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann P., Kerestedjian J. J., Ronco E. Therapy of Rhodococcus equi disseminated infections in nude mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jun;36(6):1244–1248. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.6.1244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann P., Ronco E., Nauciel C. Role of T-lymphocyte subsets in Rhodococcus equi infection. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2748–2752. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2748-2752.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordmann P., Rouveix E., Guenounou M., Nicolas M. H. Pulmonary abscess due to a rifampin and fluoroquinolone resistant Rhodococcus equi strain in a HIV infected patient. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;11(6):557–558. doi: 10.1007/BF01960815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F. Rhodococcus equi: an animal and human pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jan;4(1):20–34. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. D., Ordway D. J., Orme I. M. Listeria monocytogenes infection in beta 2 microglobulin-deficient mice. Infect Immun. 1993 Mar;61(3):1113–1116. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.3.1113-1116.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scannell K. A., Portoni E. J., Finkle H. I., Rice M. Pulmonary malacoplakia and Rhodococcus equi infection in a patient with AIDS. Chest. 1990 Apr;97(4):1000–1001. doi: 10.1378/chest.97.4.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirera G., Romeu J., Clotet B., Velasco P., Arnal J., Rius F., Foz M. Relapsing systemic infection due to Rhodococcus equi in a drug abuser seropositive for human immunodeficiency virus. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 May-Jun;13(3):509–510. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.3.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
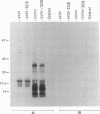
- Takai S., Koike K., Ohbushi S., Izumi C., Tsubaki S. Identification of 15- to 17-kilodalton antigens associated with virulent Rhodococcus equi. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Mar;29(3):439–443. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.3.439-443.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkachuk-Saad O., Prescott J. Rhodococcus equi plasmids: isolation and partial characterization. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Dec;29(12):2696–2700. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.12.2696-2700.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolcock J. B., Farmer A. M., Mutimer M. D. Selective medium for Corynebacterium equi isolation. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 May;9(5):640–642. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.5.640-642.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yager J. A., Prescott C. A., Kramar D. P., Hannah H., Balson G. A., Croy B. A. The effect of experimental infection with Rhodococcus equi on immunodeficient mice. Vet Microbiol. 1991 Aug 30;28(4):363–376. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(91)90071-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zijlstra M., Bix M., Simister N. E., Loring J. M., Raulet D. H., Jaenisch R. Beta 2-microglobulin deficient mice lack CD4-8+ cytolytic T cells. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):742–746. doi: 10.1038/344742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zijlstra M., Li E., Sajjadi F., Subramani S., Jaenisch R. Germ-line transmission of a disrupted beta 2-microglobulin gene produced by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):435–438. doi: 10.1038/342435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink M. C., Yager J. A., Prescott J. F., Fernando M. A. Electron microscopic investigation of intracellular events after ingestion of Rhodococcus equi by foal alveolar macrophages. Vet Microbiol. 1987 Aug;14(3):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(87)90117-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]