Abstract
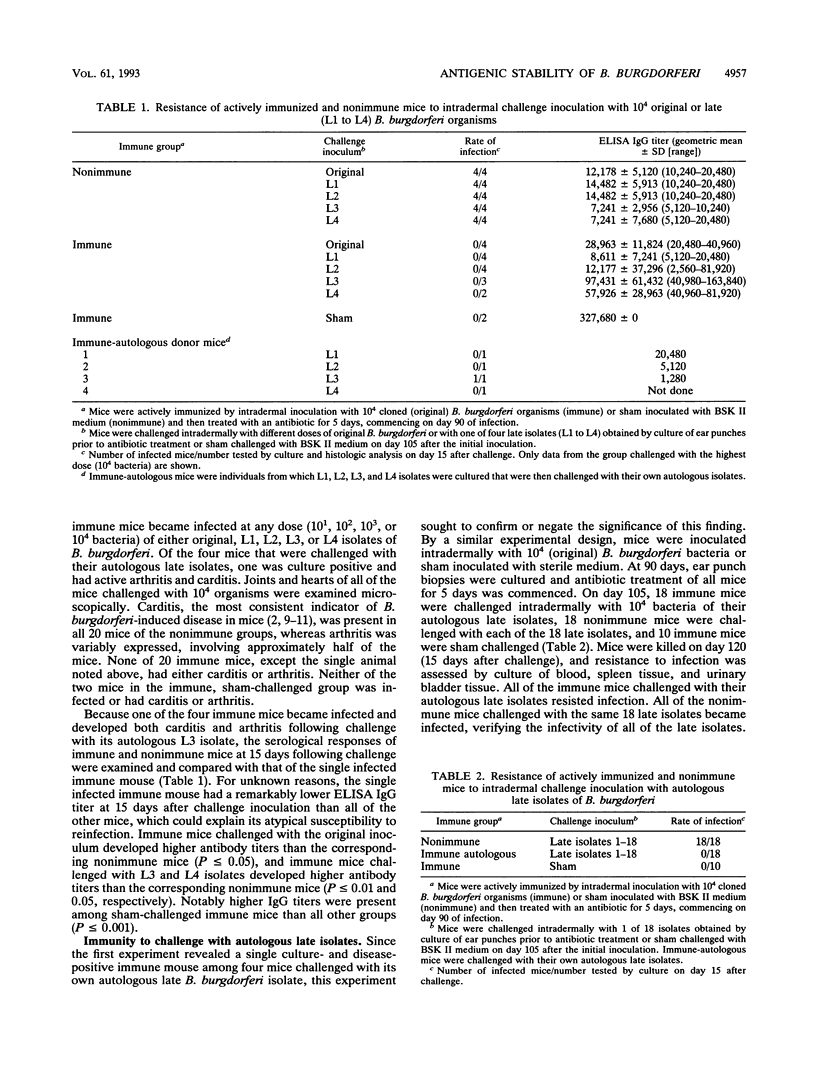
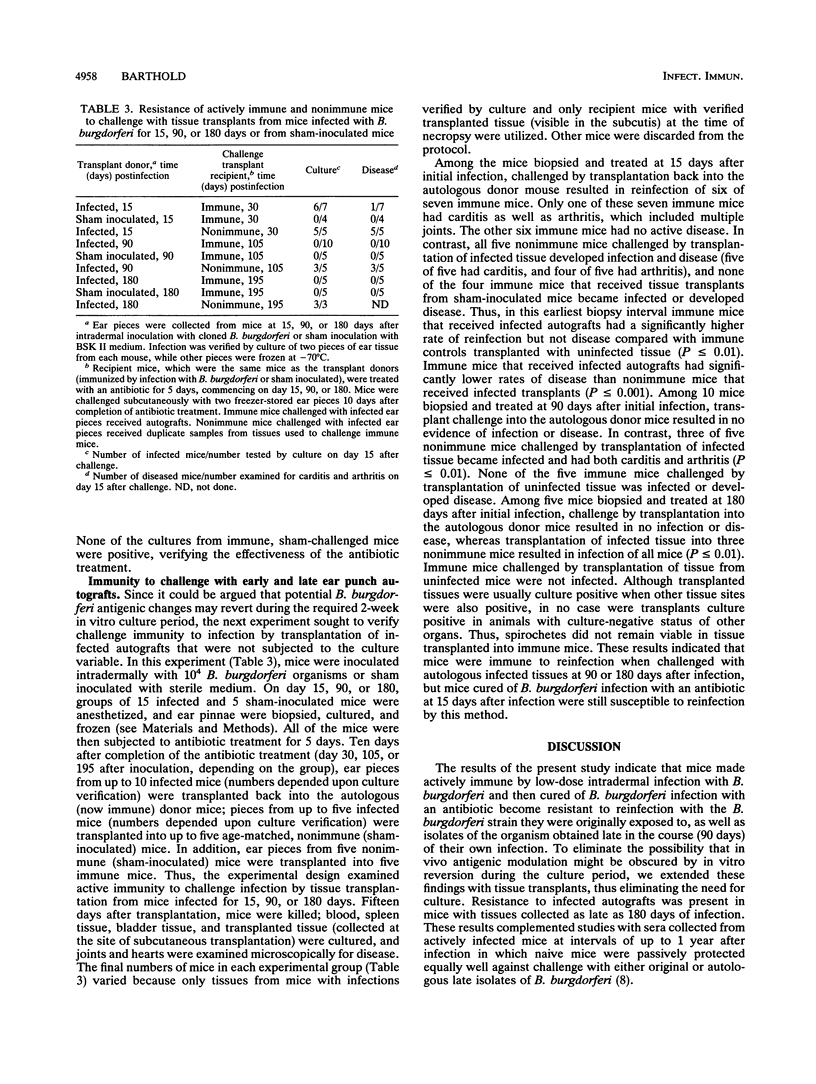
Mice were actively immunized by intradermal inoculation with 10(4) cloned Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria and then cured of the B. burgdorferi infection with an antibiotic after 90 days. They were resistant to intradermal 10(2)- or 10(4)-bacterium challenge infection with either the original cloned B. burgdorferi or B. burgdorferi isolated from each punch biopsies at 90 days of infection (prior to antibiotic treatment), including autologous B. burgdorferi isolates. In contrast, sham-infected (nonimmune) mice were susceptible to challenge infection with both early and late B. burgdorferi isolates. Since there was a potential for in vitro modification of the spirochetes during the 2-week culture period which would obscure results, an alternate means of challenge infection, using tissue transplants, was implemented. By using the same approach, mice were immunized by infection, treated with antibiotics, but challenged by subcutaneous transplantation of ear skin pieces biopsied and frozen prior to antibiotic treatment. Mice were infected for 15, 90, or 180 days before biopsy and antibiotic treatment and then transplant challenged with autologous infected tissue. Sham-immunized mice received infected tissue, and immune mice received uninfected tissue as controls. Mice infected for only 15 days, but not mice infected for 90 or 180 days, could be reinfected by autografts, whereas nonimmune mice became infected with tissues collected at each of these intervals and immune mice transplanted with normal skin were uninfected. These results indicate that immunity to B. burgdorferi is effective against the original inoculum, late isolates of the spirochete, or infected tissues collected at intervals of up to 180 days, suggesting that there is no significant antigenic change in B. burgdorferi during chronic infection.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel M. J., Allan S., Jacobson R. H., Lauderdale T. L., Chang Y. F., Shin S. J., Thomford J. W., Todhunter R. J., Summers B. A. Experimental Lyme disease in dogs produces arthritis and persistent infection. J Infect Dis. 1993 Mar;167(3):651–664. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.3.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong A. L., Barthold S. W., Persing D. H., Beck D. S. Carditis in Lyme disease susceptible and resistant strains of laboratory mice infected with Borrelia burgdorferi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Aug;47(2):249–258. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1992.47.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Hovmark A., Hederstedt B. The spirochetal etiology of acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans Herxheimer. Acta Derm Venereol. 1984;64(6):506–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbrink E., Hovmark A. Successful cultivation of spirochetes from skin lesions of patients with erythema chronicum migrans Afzelius and acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1985 Apr;93(2):161–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1985.tb02870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Carter C. J., Burman N., Freitag C. S., Garon C. F., Bergström S. Tandem insertion sequence-like elements define the expression site for variable antigen genes of Borrelia hermsii. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):390–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.390-397.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Molecular biology of antigenic variation in Lyme borreliosis and relapsing fever: a comparative analysis. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1991;77:88–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Bockenstedt L. K. Passive immunizing activity of sera from mice infected with Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1993 Nov;61(11):4696–4702. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.11.4696-4702.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Persing D. H., Armstrong A. L., Peeples R. A. Kinetics of Borrelia burgdorferi dissemination and evolution of disease after intradermal inoculation of mice. Am J Pathol. 1991 Aug;139(2):263–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., Sidman C. L., Smith A. L. Lyme borreliosis in genetically resistant and susceptible mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Nov;47(5):605–613. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1992.47.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthold S. W., de Souza M. S., Janotka J. L., Smith A. L., Persing D. H. Chronic Lyme borreliosis in the laboratory mouse. Am J Pathol. 1993 Sep;143(3):959–971. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerlin P., Peter O., Bretz A. G., Postic D., Baranton G., Piffaretti J. C. Population genetic analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi isolates by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1677–1683. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1677-1683.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callister S. M., Schell R. F., Case K. L., Lovrich S. D., Day S. P. Characterization of the borreliacidal antibody response to Borrelia burgdorferi in humans: a serodiagnostic test. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jan;167(1):158–164. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.1.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defosse D. L., Duray P. H., Johnson R. C. The NIH-3 immunodeficient mouse is a model for Lyme borreliosis myositis and carditis. Am J Pathol. 1992 Jul;141(1):3–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duray P. H., Johnson R. C. The histopathology of experimentally infected hamsters with the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1986 Feb;181(2):263–269. doi: 10.3181/00379727-181-42251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duray P. H., Steere A. C. Clinical pathologic correlations of Lyme disease by stage. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:65–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikrig E., Tao H., Kantor F. S., Barthold S. W., Flavell R. A. Evasion of protective immunity by Borrelia burgdorferi by truncation of outer surface protein B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4092–4096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgilis K., Peacocke M., Klempner M. S. Fibroblasts protect the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, from ceftriaxone in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1992 Aug;166(2):440–444. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.2.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovmark A., Asbrink E., Olsson I. The spirochetal etiology of lymphadenosis benigna cutis solitaria. Acta Derm Venereol. 1986;66(6):479–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Russell M., Duray P. H. Experimental infection of the hamster with Borrelia burgdorferi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:258–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Russell M. Passive immunization of hamsters against experimental infection with the Lyme disease spirochete. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):713–714. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.713-714.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochi S. K., Johnson R. C., Dalmasso A. P. Complement-mediated killing of the Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi. Role of antibody in formation of an effective membrane attack complex. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 1;146(11):3964–3970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochi S. K., Johnson R. C. Role of immunoglobulin G in killing of Borrelia burgdorferi by the classical complement pathway. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):314–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.314-321.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Y., Sturrock A., Weis J. J. Intracellular localization of Borrelia burgdorferi within human endothelial cells. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):671–678. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.671-678.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi R. T., Garon C. F. Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Borrelia: a comparison of North American and European isolates of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):241–244. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.241-244.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery R. R., Nathanson M. H., Malawista S. E. The fate of Borrelia burgdorferi, the agent for Lyme disease, in mouse macrophages. Destruction, survival, recovery. J Immunol. 1993 Feb 1;150(3):909–915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody K. D., Barthold S. W., Terwilliger G. A., Beck D. S., Hansen G. M., Jacoby R. O. Experimental chronic Lyme borreliosis in Lewis rats. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Feb;42(2):165–174. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1990.42.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadelman R. B., Pavia C. S., Magnarelli L. A., Wormser G. P. Isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi from the blood of seven patients with Lyme disease. Am J Med. 1990 Jan;88(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90122-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Carter C. J., Howell J. K., Barbour A. G. Low-passage-associated proteins of Borrelia burgdorferi B31: characterization and molecular cloning of OspD, a surface-exposed, plasmid-encoded lipoprotein. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4662–4672. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4662-4672.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preac Mursic V., Patsouris E., Wilske B., Reinhardt S., Gross B., Mehraein P. Persistence of Borrelia burgdorferi and histopathological alterations in experimentally infected animals. A comparison with histopathological findings in human Lyme disease. Infection. 1990 Nov-Dec;18(6):332–341. doi: 10.1007/BF01646399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preac-Mursic V., Weber K., Pfister H. W., Wilske B., Gross B., Baumann A., Prokop J. Survival of Borrelia burgdorferi in antibiotically treated patients with Lyme borreliosis. Infection. 1989 Nov-Dec;17(6):355–359. doi: 10.1007/BF01645543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehrig J. T., Piesman J., Hunt A. R., Keen M. G., Happ C. M., Johnson B. J. The hamster immune response to tick-transmitted Borrelia burgdorferi differs from the response to needle-inoculated, cultured organisms. J Immunol. 1992 Dec 1;149(11):3648–3653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P. A., Schwan T., Hogan D. Recombination between genes encoding major outer surface proteins A and B of Borrelia burgdorferi. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Oct;6(20):3031–3040. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01761.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadziene A., Thompson P. A., Barbour A. G. In vitro inhibition of Borrelia burgdorferi growth by antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jan;167(1):165–172. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Gern L., Wallich R., Kramer M. D., Prester M., Simon M. M. Distinct patterns of protective antibodies are generated against Borrelia burgdorferi in mice experimentally inoculated with high and low doses of antigen. Immunol Lett. 1993 May;36(2):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(93)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Justus C. W., Museteanu C., Simon M. M. Demonstration of antigen-specific T cells and histopathological alterations in mice experimentally inoculated with Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):41–47. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.41-47.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidli J., Hunziker T., Moesli P., Schaad U. B. Cultivation of Borrelia burgdorferi from joint fluid three months after treatment of facial palsy due to Lyme borreliosis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):905–906. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. L., Schell R. F., Hejka A. G., England D. M. Passive immunization prevents induction of Lyme arthritis in LSH hamsters. Infect Immun. 1990 Jan;58(1):144–148. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.1.144-148.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. L., Schell R. F., Lovrich S. D., Callister S. M., Coe J. E. Characterization of the protective antibody response to Borrelia burgdorferi in experimentally infected LSH hamsters. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):1916–1921. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.1916-1921.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Garon C. F. Changes in infectivity and plasmid profile of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, as a result of in vitro cultivation. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1831–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1831-1836.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Karstens R. H., Schrumpf M. E., Simpson W. J. Changes in antigenic reactivity of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease spirochete, during persistent infection in mice. Can J Microbiol. 1991 Jun;37(6):450–454. doi: 10.1139/m91-074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Kime K. K., Schrumpf M. E., Coe J. E., Simpson W. J. Antibody response in white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus) experimentally infected with the Lyme disease spirochete (Borrelia burgdorferi). Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3445–3451. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3445-3451.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Simpson W. J. Factors influencing the antigenic reactivity of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease spirochete. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1991;77:94–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snydman D. R., Schenkein D. P., Berardi V. P., Lastavica C. C., Pariser K. M. Borrelia burgdorferi in joint fluid in chronic Lyme arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Jun;104(6):798–800. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-104-6-798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanek G., Klein J., Bittner R., Glogar D. Isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi from the myocardium of a patient with longstanding cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jan 25;322(4):249–252. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199001253220407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczepanski A., Benach J. L. Lyme borreliosis: host responses to Borrelia burgdorferi. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):21–34. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.21-34.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sădziene A., Rosa P. A., Thompson P. A., Hogan D. M., Barbour A. G. Antibody-resistant mutants of Borrelia burgdorferi: in vitro selection and characterization. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):799–809. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Souza M. S., Smith A. L., Beck D. S., Terwilliger G. A., Fikrig E., Barthold S. W. Long-term study of cell-mediated responses to Borrelia burgdorferi in the laboratory mouse. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):1814–1822. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.1814-1822.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


