Abstract
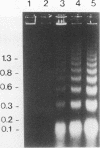
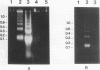
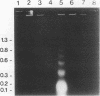
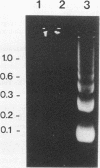
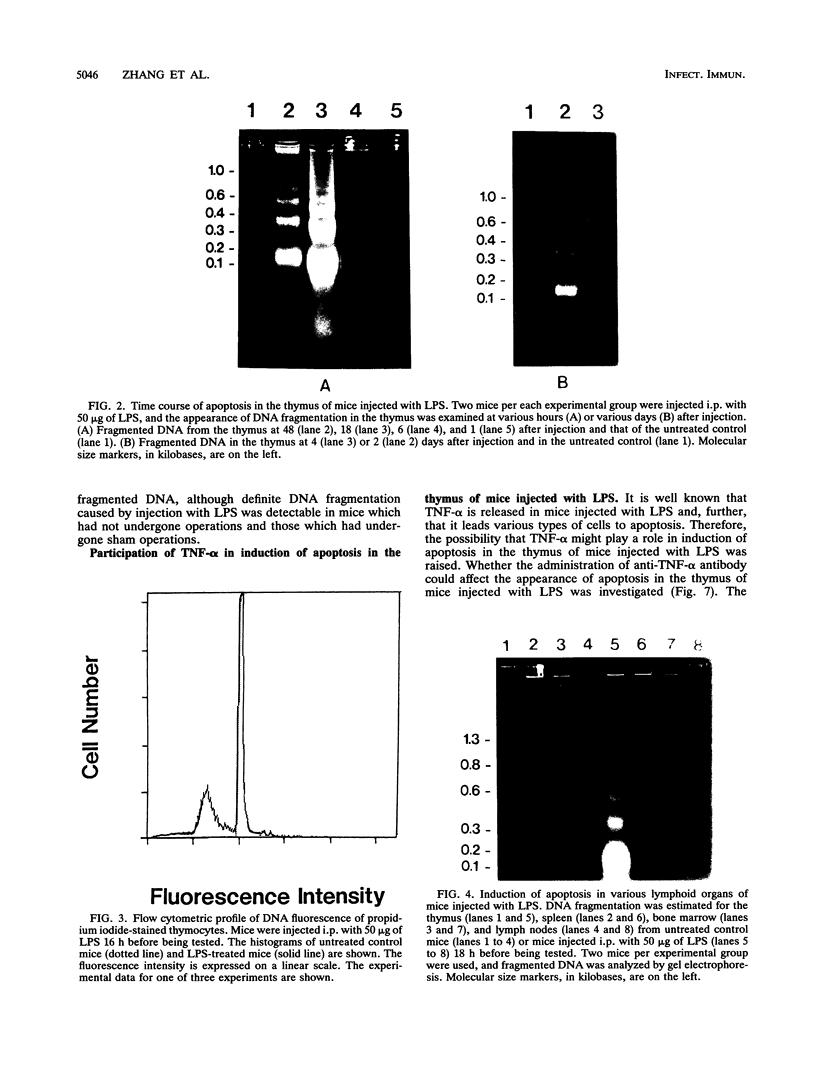
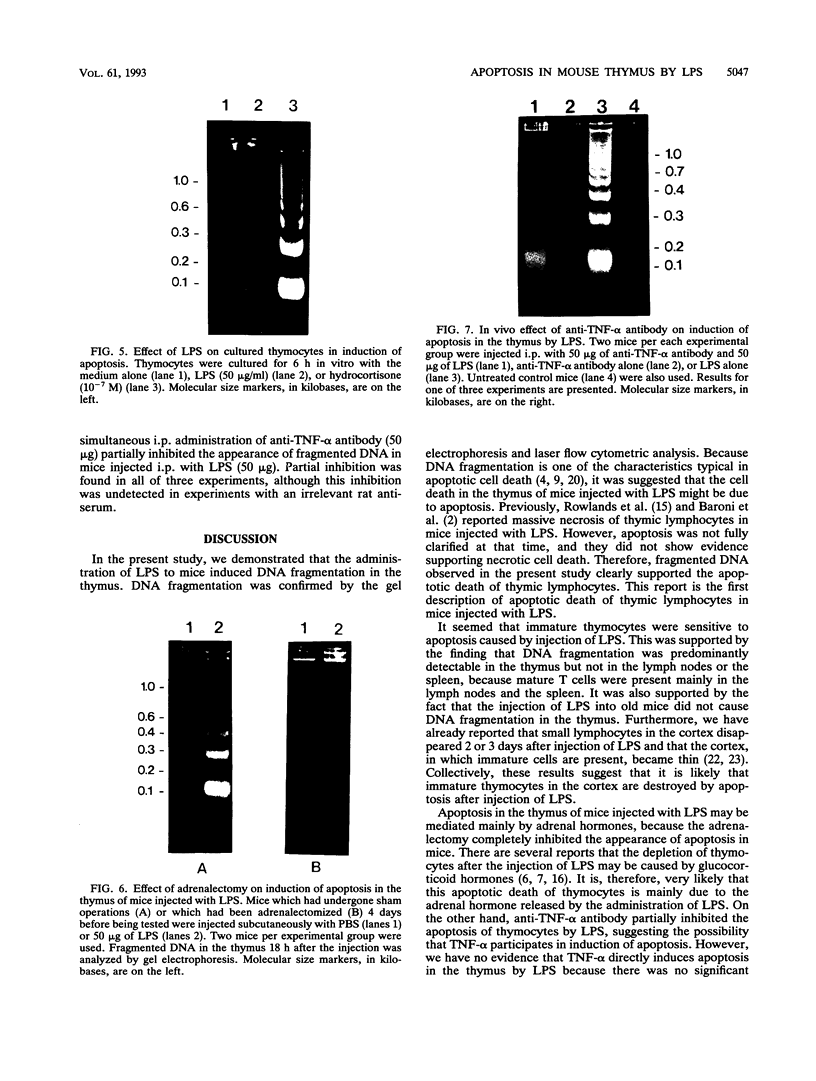
In vivo administration of bacterial lipopolysaccharide to mice induced DNA fragmentation in the thymus. Fragmented DNA was confirmed by agarose gel electrophoresis and laser flow cytometry. DNA fragmentation was predominantly detected in the thymus of young mice, while it was undetectable in the spleen, bone marrow, and lymph nodes. DNA fragmentation in the thymus was roughly dependent on the dose of lipopolysaccharide injected and reached the peak about 18 h after the injection. The addition of lipopolysaccharide to in vitro cultures of thymocytes did not cause DNA fragmentation, suggesting that lipopolysaccharide was unable to induce apoptosis of thymocytes directly. The injection of lipopolysaccharide induced no significant DNA fragmentation in adrenalectomized mice. The injection of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody together with lipopolysaccharide partially inhibited the appearance of DNA fragmentation in the thymus. On the basis of the fact that DNA fragmentation is one of the characteristics typical in apoptotic cell death, it was suggested that lipopolysaccharide could induce apoptosis in the mouse thymus in vivo. This apoptosis in the thymus might be mediated mainly by the adrenal hormones, but it is likely that tumor necrosis factor alpha might also participate in it.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adorini L., Ruco L., Uccini S., De Franceschi G. S., Baroni C. D., Doria G. Biological effects of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in vivo. II. Selection in the mouse thymus of PHA- and con A-responsive cells. Immunology. 1976 Aug;31(2):225–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baroni C. D., De Franceschi G. S., Uccini S., Adorini L., Cnen G. D., Ruco L. Biological effects of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in vivo. I. Selection in the mouse thymus of killer and helper cells. Immunology. 1976 Aug;31(2):217–224. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouckaert P., Everaerdt B., Fiers W. The glucocorticoid antagonist RU38486 mimics interleukin-1 in its sensitization to the lethal and interleukin-6-inducing properties of tumor necrosis factor. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Apr;22(4):981–986. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J., Duke R. C. Glucocorticoid activation of a calcium-dependent endonuclease in thymocyte nuclei leads to cell death. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):38–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J. Programmed cell death in the immune system. Adv Immunol. 1991;50:55–85. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60822-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGHERTY T. F. Effect of hormones on lympatic tissue. Physiol Rev. 1952 Oct;32(4):379–401. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1952.32.4.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EGDAHL R. H. The differential response of the adrenal cortex and medulla to bacterial endotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jul;38(7):1120–1125. doi: 10.1172/JCI103888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facchinetti A., Tessarollo L., Mazzocchi M., Kingston R., Collavo D., Biasi G. An improved method for the detection of DNA fragmentation. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Jan 24;136(1):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90258-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golstein P., Ojcius D. M., Young J. D. Cell death mechanisms and the immune system. Immunol Rev. 1991 Jun;121:29–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lázár G., Jr, Duda E., Lázár G. Effect of RU 38486 on TNF production and toxicity. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 17;308(2):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81261-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinet N., Vaillant P., Charles T., Lambert J., Martinet Y. Dexamethasone modulation of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (cachectin) release by activated normal human alveolar macrophages. Eur Respir J. 1992 Jan;5(1):67–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ryan J. L. Bacterial endotoxins and host immune responses. Adv Immunol. 1979;28:293–450. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60802-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ulevitch R. J. The effects of bacterial endotoxins on host mediation systems. A review. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):526–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletti I., Migliorati G., Pagliacci M. C., Grignani F., Riccardi C. A rapid and simple method for measuring thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Jun 3;139(2):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90198-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLANDS D. T., Jr, CLAMAN H. N., KIND P. D. THE EFFECT OF ENDOTOXIN ON THE THYMUS OF YOUNG MICE. Am J Pathol. 1965 Feb;46:165–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLESINGER M., MARK R. WASTING DISEASE INDUCED IN YOUNG MICE BY ADMINISTRATION OF CORTISOL ACETATE. Science. 1964 Feb 28;143(3609):965–966. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3609.965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellins K. S., Cohen J. J. Gene induction by gamma-irradiation leads to DNA fragmentation in lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3199–3206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark J. M., Neale M. L. The influence of oestrone on the production of tumour necrosis factor by human peripheral blood adherent cells. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1991 Nov;3(6):337–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1991.tb04258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Kerr J. F., Currie A. R. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokochi T., Inoue Y., Yokoo J., Kimura Y., Kato N. Retention of bacterial lipopolysaccharide at the site of subcutaneous injection. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1786–1791. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1786-1791.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokochi T., Nakashima I., Kato N. Adjuvant action of capsular polysaccharide of Klebsiella pneumoniae on antibody response. VIII. Its effect on the size and the number of cells of regional lymph node and other lymphoid organs. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(2):141–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb00572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokochi T., Nakashima I., Kato N., Asai J., Iijima S. Adjuvant action of capsular polysaccharide of Klebsiella pneumoniae on antibody response. IX. Its effect on the histology of the regional lymph node and other lymphoid organs. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(10):933–944. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]