Abstract
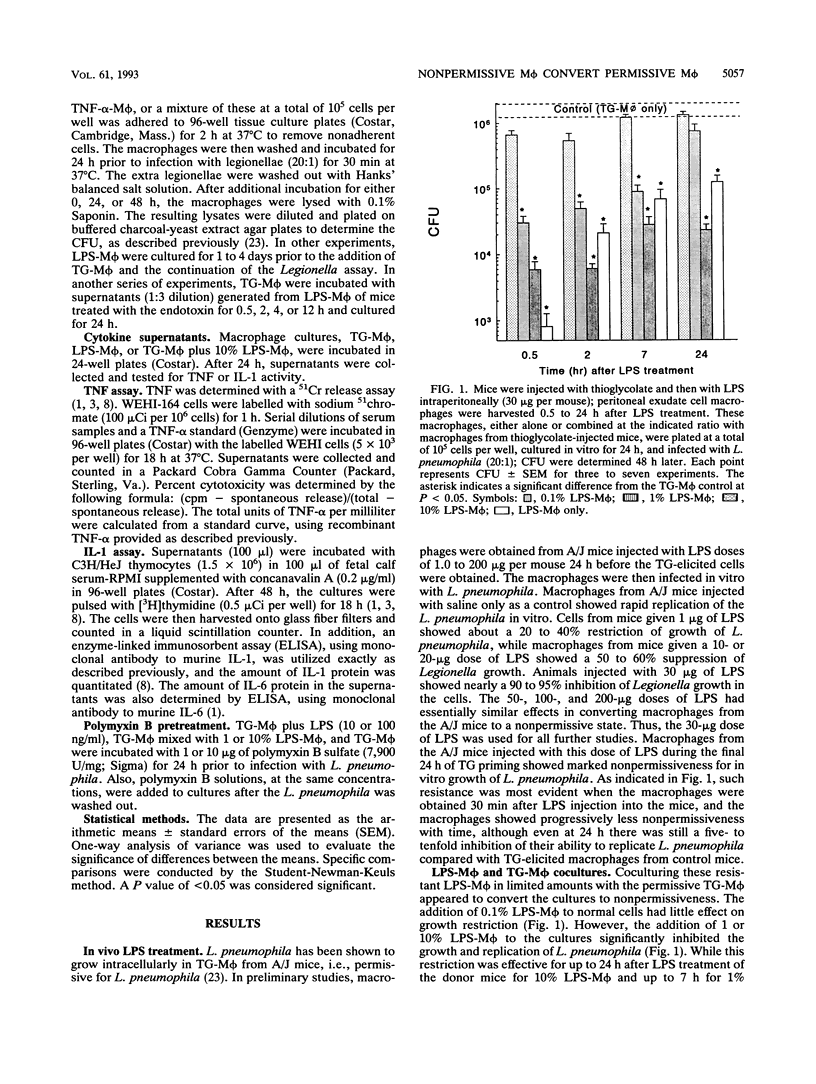
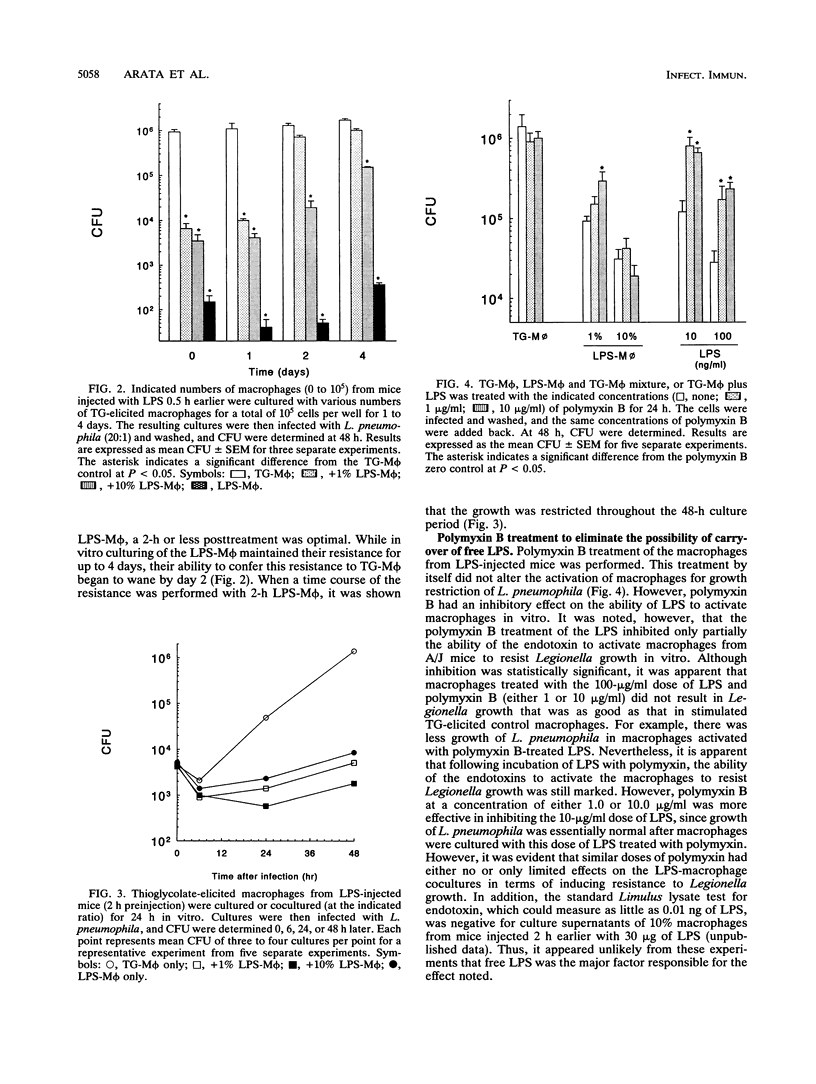
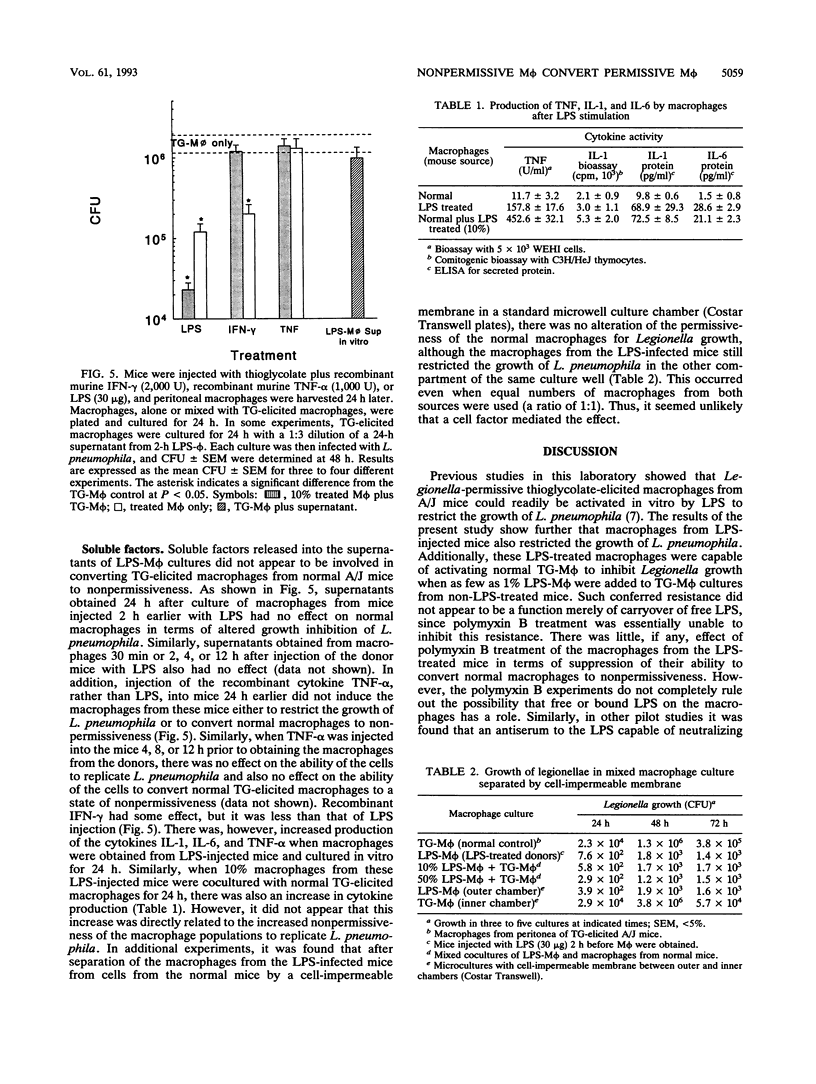
Macrophages can be activated by lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from gram-negative bacteria to evince a number of biological activities, including increased resistance to intracellular infection by opportunistic bacteria. In the present study, intraperitoneal injection of LPS into A/J mice activated peritoneal macrophages so that they resisted subsequent in vitro infection with Legionella pneumophila. Coculture of these macrophages with those from nontreated A/J mice converted the entire population of cells from permissive to nonpermissive. This effect did not appear to be mediated by soluble factors released from the LPS-treated macrophages, since the levels of interleukins-1 and -6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha produced by the macrophages were not found to be markedly elevated at the time when the macrophages from the LPS-treated mice were most effective in converting normal macrophages to nonpermissiveness. Furthermore, macrophages from mice injected intraperitoneally with either interferon or tumor necrosis factor alpha did not evince nonpermissiveness and also did not have the ability to convert normal spleen cells to nonpermissiveness. Polymyxin B, a known inactivator of LPS activity, did not inhibit the macrophages from the LPS-treated mice from inducing this resistance. It seemed unlikely that free LPS released from the macrophages mediated this effect. The results of this study thus showed that macrophages activated by LPS in vivo can evince nonpermissiveness for Legionella growth in vitro and also can induce macrophages from normal, permissive mice to become nonpermissive for Legionella growth in vitro.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arata S., Newton C., Klein T. W., Yamamoto Y., Friedman H. Legionella pneumophila induced tumor necrosis factor production in permissive versus nonpermissive macrophages. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1993 May;203(1):26–29. doi: 10.3181/00379727-203-43568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj N., Nash T. W., Horwitz M. A. Interferon-gamma-activated human monocytes inhibit the intracellular multiplication of Legionella pneumophila. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2662–2669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard D. K., Friedman H., Klein T. W., Djeu J. Y. Induction of interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor by Legionella pneumophila: augmentation of human neutrophil bactericidal activity. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Jun;45(6):538–545. doi: 10.1002/jlb.45.6.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C. The pathogenesis of sepsis. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Sep 15;115(6):457–469. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-6-457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M. Involvement of cytokines in determining resistance and acquired immunity in murine tuberculosis. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Nov;50(5):495–501. doi: 10.1002/jlb.50.5.495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Role of interleukin-1 in infectious diseases. Immunol Rev. 1992 Jun;127:119–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb01411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egawa K., Klein T. W., Yamamoto Y., Newton C. A., Friedman H. Enhanced growth restriction of Legionella pneumophila in endotoxin-treated macrophages. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1992 Jul;200(3):338–342. doi: 10.3181/00379727-200-43439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H., Newton C., Widen R., Klein T. W., Spitzer J. A. Continuous endotoxin infusion suppresses rat spleen cell production of cytokines. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1992 Mar;199(3):360–364. doi: 10.3181/00379727-199-43369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Moldawer L. L., Helfgott D., Kilian P. L., Sehgal P. B. Type I IL-1 receptor blockade exacerbates murine listeriosis. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 1;148(5):1486–1492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirillo E., Decandia P., Ribaud M. R., Cannuscio B., De Simone C., Antonaci S. Enhancement of polymorphonuclear cell phagocytosis by lipid A-activated monocytes via cell-to-cell contact. A possible role for membrane-associated cytokines. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 1992;14(3):343–354. doi: 10.3109/08923979209005398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai N., Arata S., Mashimo J., Okuda K., Aihara Y., Kotani S., Takada H., Shiba T., Kusumoto S., Imoto M. Synthetic Salmonella-type lipid A antigen with high serological specificity. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):43–48. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.43-48.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein T. W., Yamamoto Y., Brown H. K., Friedman H. Interferon-gamma induced resistance to Legionella pneumophila in susceptible A/J mouse macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Jan;49(1):98–103. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.1.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei M. G., Stimpson S. A., Morrison D. C. Specific endotoxic lipopolysaccharide-binding receptors on murine splenocytes. III. Binding specificity and characterization. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1925–1932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z., Simpson R. J., Cheers C. Recombinant interleukin-6 protects mice against experimental bacterial infection. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):4402–4406. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.4402-4406.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn W. A., Golenbock D. T. Lipopolysaccharide antagonists. Immunol Today. 1992 Jul;13(7):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90009-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. W., Libby D. M., Horwitz M. A. IFN-gamma-activated human alveolar macrophages inhibit the intracellular multiplication of Legionella pneumophila. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3978–3981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman G. W., Gan H. X., McCarthy P. L., Jr, Remold H. G. Survival of human macrophages infected with Mycobacterium avium intracellulare correlates with increased production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and IL-6. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3942–3948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumann R. R., Leong S. R., Flaggs G. W., Gray P. W., Wright S. D., Mathison J. C., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J. Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1429–1431. doi: 10.1126/science.2402637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerrett S. J., Martin T. R. Recombinant murine interferon-gamma reversibly activates rat alveolar macrophages to kill Legionella pneumophila. J Infect Dis. 1992 Dec;166(6):1354–1361. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.6.1354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias P. S., Soldau K., Ulevitch R. J. Identification of a lipid A binding site in the acute phase reactant lipopolysaccharide binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10867–10871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Levin S. M., Jong M. T., Chad Z., Kabbash L. G. CR3 (CD11b/CD18) expresses one binding site for Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptides and a second site for bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):175–183. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Mathison J. C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1698311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y., Klein T. W., Newton C. A., Widen R., Friedman H. Growth of Legionella pneumophila in thioglycolate-elicited peritoneal macrophages from A/J mice. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):370–375. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.370-375.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


