Abstract
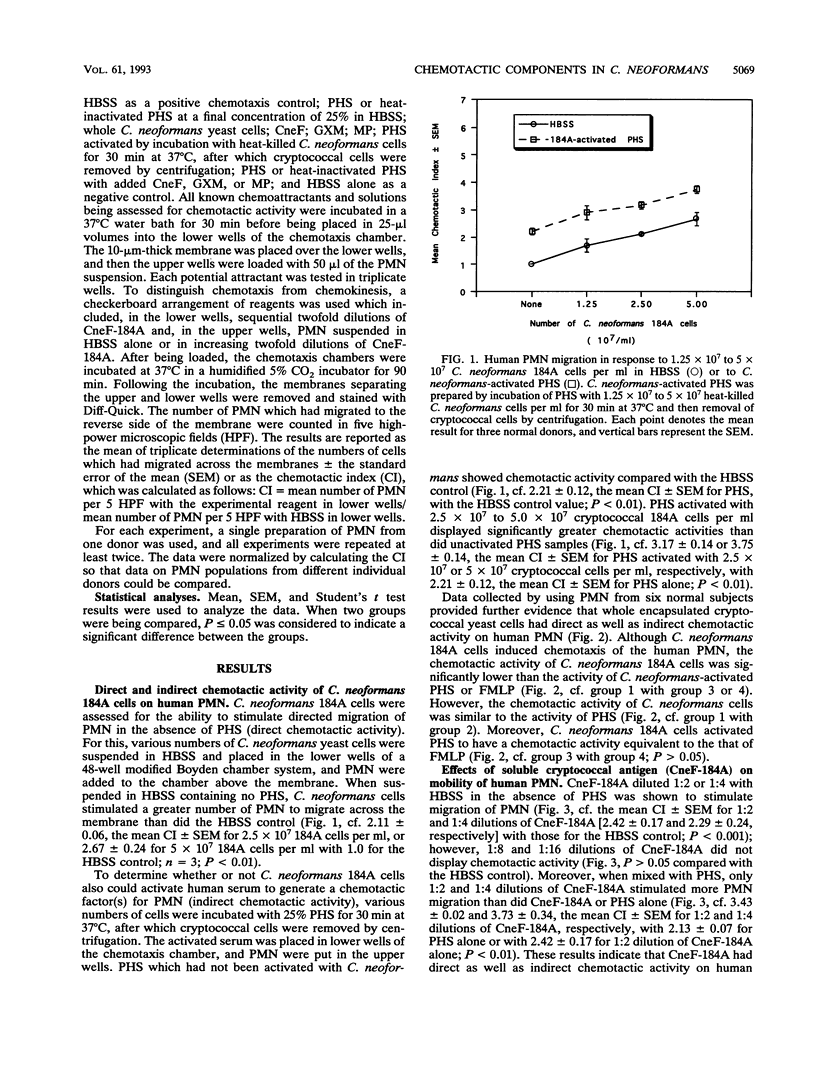
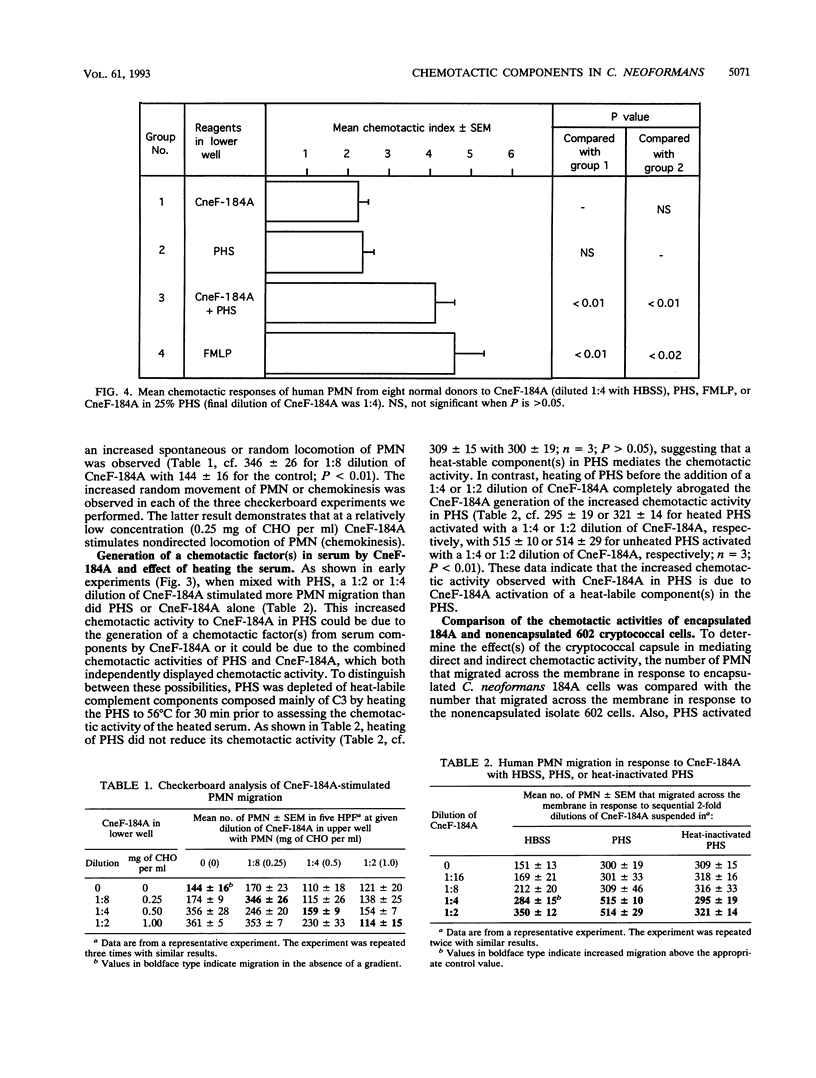
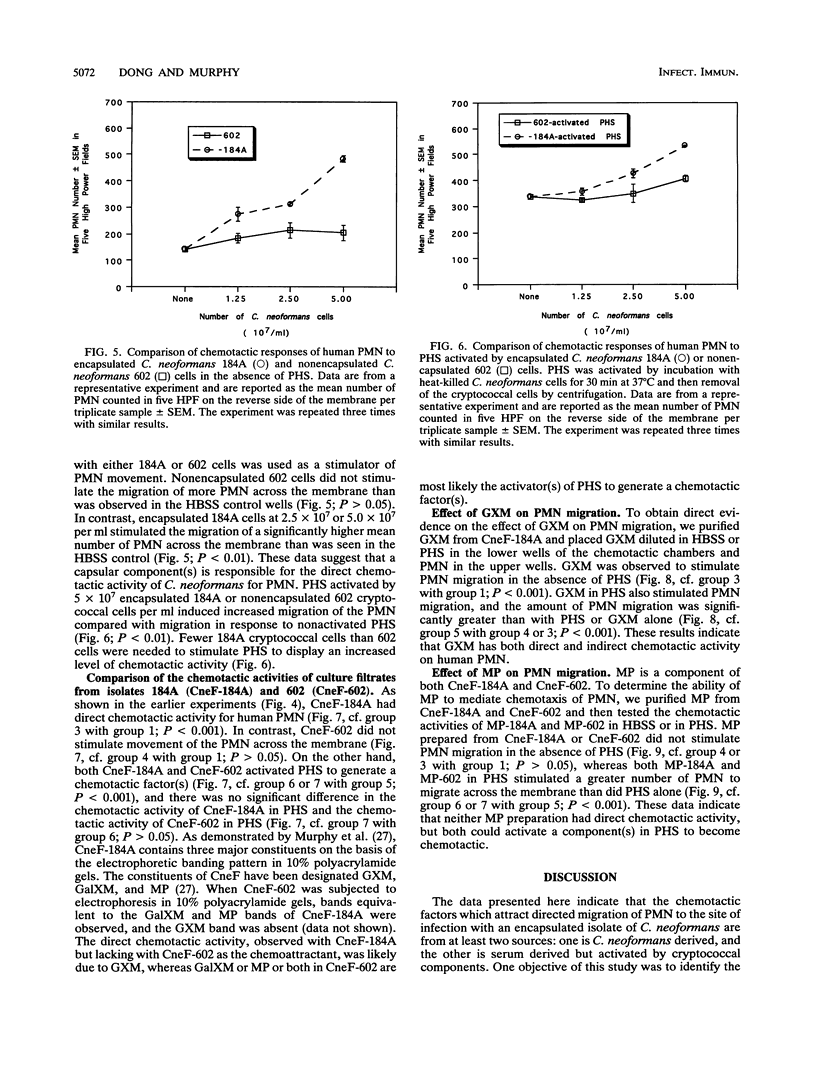
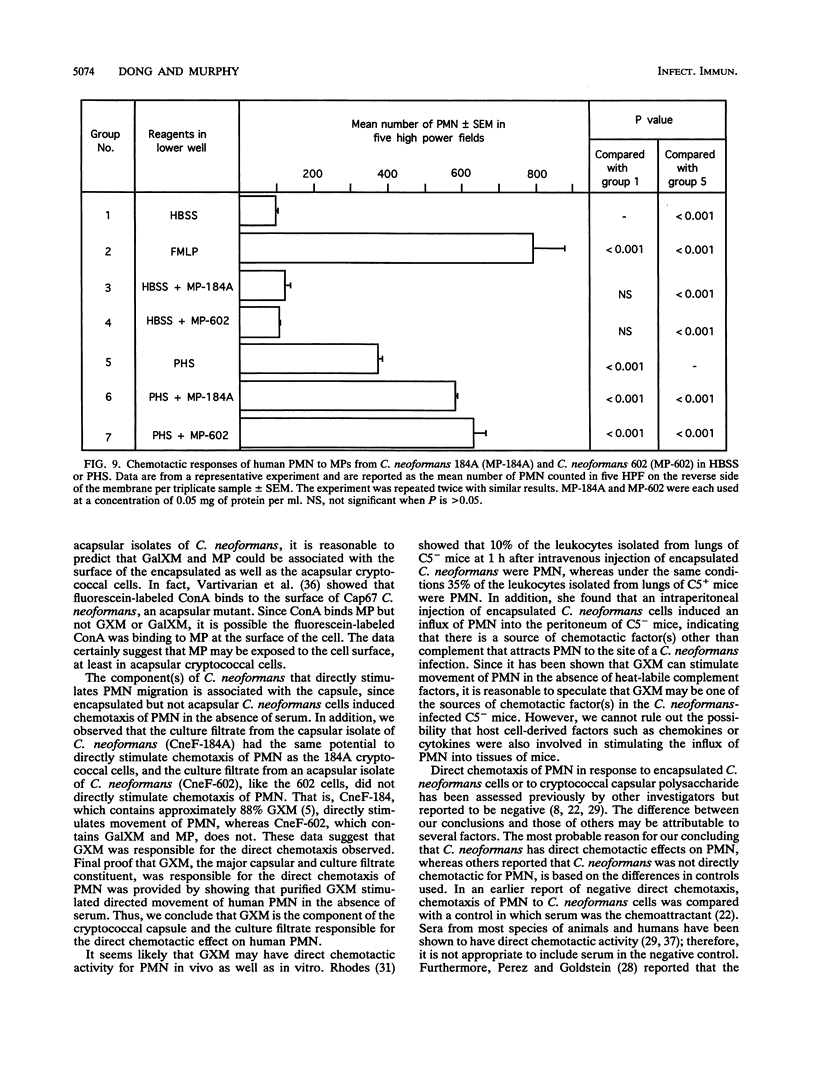
The mobility of human neutrophils (PMN) in response to encapsulated or nonencapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans cells or cryptococcal culture filtrate (CneF) and its components was studied by using a 48-well modified Boyden chamber. Encapsulated C. neoformans (isolate 184A) cells and CneF-184A stimulated directed migration of human PMN in the absence of serum (direct chemotactic activity) and activated a heat-labile component(s) in fresh human serum to become a chemoattractant(s) for human PMN (indirect chemotactic activity). At a 1:8 dilution (0.25 mg of carbohydrate per ml), CneF-184A displayed chemokinetic activity when assessed with a checkerboard assay. Nonencapsulated C. neoformans isolate 602 cells did not have direct chemotactic activity but did have indirect chemotactic activity. The capsule of C. neoformans is composed predominantly of glucuronoxylomannan (GXM). Purified GXM displayed both direct and indirect chemotactic activity. CneF-184A contains, in addition to GXM, a concanavalin A-binding mannoprotein (MP), whereas CneF-602 contains no GXM but does contain MP. CneF-184A showed direct chemotactic activity and CneF-602 did not. Both CneF-184A and CneF-602 displayed indirect chemotactic activity for human PMN. In addition, purified MP from CneF-184A, like CneF-602, showed only indirect chemotactic activity. These results indicate that GXM contributes to the direct chemotactic activity of PMN observed with the whole encapsulated yeast cells and the unfractionated CneF derived from the encapsulated cells. Both MP and GXM from encapsulated C. neoformans cells mediate indirect chemotactic activity on human PMN.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker E. L. The short and happy life of neutrophil activation. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Apr;47(4):378–389. doi: 10.1002/jlb.47.4.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee A. K., Bennett J. E., Glaudemans C. P. Capsular polysaccharides of Cryptococcus neoformans. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Sep-Oct;6(5):619–624. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.5.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan K. L., Murphy J. W. Characterization of cellular infiltrates and cytokine production during the expression phase of the anticryptococcal delayed-type hypersensitivity response. Infect Immun. 1993 Jul;61(7):2854–2865. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.7.2854-2865.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer G. S., Sans M. D. Cryptococcus neoformans. II. Phagocytosis by human leukocytes. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1480–1483. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1480-1483.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E. Chemotactic factor produced by Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):568–573. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.568-573.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Bennett J. E. Prognostic factors in cryptococcal meningitis. A study in 111 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Feb;80(2):176–181. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-2-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Erickson N. F., 3rd Chemotaxis of human neutrophils and monocytes induced by Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):380–382. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.380-382.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Root R. K., Bennett J. E. Factors influencing killing of Cryptococcus neoformans by human leukocytes in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):367–376. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng R. H., Bishburg E., Smith S. M., Kapila R. Cryptococcal infections in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Med. 1986 Jul;81(1):19–23. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(86)90176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Komorowski R. A. Histologic response to capsule-deficient Cryptococcus neoformans. Arch Pathol. 1973 Dec;96(6):383–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. N., Henson P. M., Otani A., Hugli T. E. Chemotactic response to human C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins. I. Evaluation of C3a and C5a leukotaxis in vitro and under stimulated in vivo conditions. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):109–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadebusch H. H., Johnson A. G. Natural host resistance to infection with Cryptococcus neoformans. V. The influence of cationic tissue proteins upon phagocytosis and on circulating antibody synthesis. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):566–572. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvath L., Falk W., Leonard E. J. Rapid quantitation of neutrophil chemotaxis: use of a polyvinylpyrrolidone-free polycarbonate membrane in a multiwell assembly. J Immunol Methods. 1980;37(1):39–45. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidore M. R., Murphy J. W. Natural cellular resistance of beige mice against Cryptococcus neoformans. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3624–3631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P. G., Cherniak R., Jones R. G., Stortz C. A., Reiss E. Cell-wall glucans of Cryptococcus neoformans Cap 67. Carbohydr Res. 1990 Apr 2;198(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(90)84273-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalina M., Kletter Y., Aronson M. The interaction of phagocytes and the large-sized parasite Cryptococcus neoformans: cytochemical and ultrastructural study. Cell Tissue Res. 1974;152(2):165–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00224692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Gotschlich E. C. The capsule of cryptococcus neoformans passively inhibits phagocytosis of the yeast by macrophages. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1675–1680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R. Non-encapsulated variant of Cryptococcus neoformans. II. Surface receptors for cryptococcal polysaccharide and their role in inhibition of phagocytosis by polysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):99–106. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.99-106.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Wilson M. A., Murphy J. W. Early events in initiation of alternative complement pathway activation by the capsule of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3101–3110. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3101-3110.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laxalt K. A., Kozel T. R. Chemotaxigenesis and activation of the alternative complement pathway by encapsulated and non-encapsulated Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):435–440. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.435-440.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mei W., Dong Z. M., Liao B. L., Xu H. B. Study of immune function of cancer patients influenced by supplemental zinc or selenium-zinc combination. Biol Trace Elem Res. 1991 Jan;28(1):11–19. doi: 10.1007/BF02990458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mello S. B., Farsky S. H., Sannomiya P., Garcia-Leme J. Inhibition of neutrophil chemotaxis and chemokinesis associated with a plasma protein in aging rats: selective depression of cell responses mediated by complement-derived chemoattractants. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Jan;51(1):46–52. doi: 10.1002/jlb.51.1.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. F., Mitchell T. G. Killing of Cryptococcus neoformans strains by human neutrophils and monocytes. Infect Immun. 1991 Jan;59(1):24–28. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.1.24-28.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., Cozad G. C. Immunological unresponsiveness induced by cryptococcal capsular polysaccharide assayed by the hemolytic plaque technique. Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):896–901. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.896-901.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., Mosley R. L., Cherniak R., Reyes G. H., Kozel T. R., Reiss E. Serological, electrophoretic, and biological properties of Cryptococcus neoformans antigens. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):424–431. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.424-431.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perfect J. R., Durack D. T. Chemotactic activity of cerebrospinal fluid in experimental cryptococcal meningitis. Sabouraudia. 1985 Feb;23(1):37–45. doi: 10.1080/00362178585380071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss E., Cherniak R., Eby R., Kaufman L. Enzyme immunoassay detection of IgM to galactoxylomannan of Cryptococcus neoformans. Diagn Immunol. 1984;2(2):109–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. C. Contribution of complement component C5 to the pathogenesis of experimental murine cryptococcosis. Sabouraudia. 1985 Jun;23(3):225–234. doi: 10.1080/00362178585380331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth M. J., Zachariae C. O., Norihisa Y., Ortaldo J. R., Hishinuma A., Matsushima K. IL-8 gene expression and production in human peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 1;146(11):3815–3823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurmond L. M., Mitchell T. G. Blastomyces dermatitidis chemotactic factor: kinetics of production and biological characterization evaluated by a modified neutrophil chemotaxis assay. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):87–93. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.87-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartivarian S. E., Reyes G. H., Jacobson E. S., James P. G., Cherniak R., Mumaw V. R., Tingler M. J. Localization of mannoprotein in Cryptococcus neoformans. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6850–6852. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6850-6852.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H. B., Mei W. D., Dong Z. M., Liao B. L. Study of the oxidative metabolic function and chemotaxis of neutrophils from patients with cancer influenced by selenium yeast. Biol Trace Elem Res. 1990 Jun;25(3):201–209. doi: 10.1007/BF02990415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



