Abstract
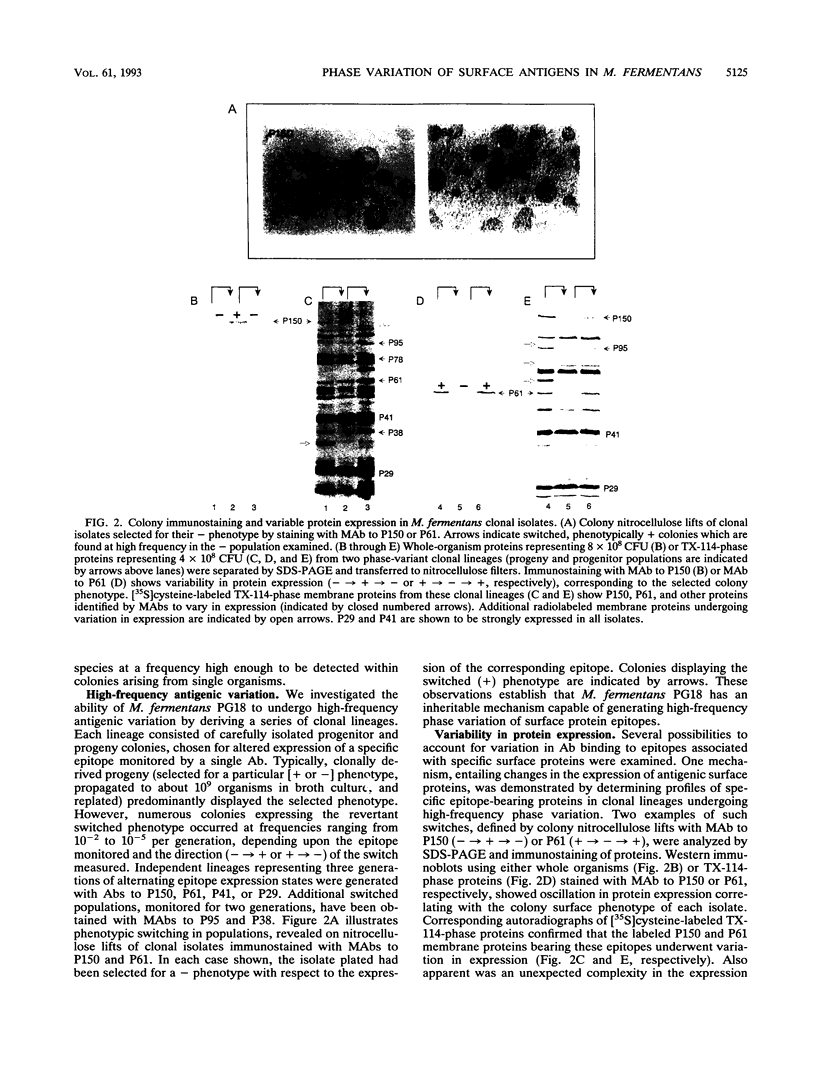
Mycoplasma fermentans, a wall-less prokaryote, is currently under investigation as a potential human pathogen. Recently, several surface lipoproteins have been shown to vary in expression between M. fermentans strains. Using specific antibodies to these lipoproteins, we investigated the extent and nature of antigenic variation within this species. Immunoscreening of type strain PG18 agar-grown colonies revealed marked heterogeneity in expression of distinct surface lipoproteins. Subsequent isolation and propagation of clonal isolates established isogenic lineages which displayed high-frequency (10(-2) to 10(-5) per generation) antigenic phase variation. [35S]cysteine-labeled protein profiles and Western immunoblots of phase-variant clones showed that several distinct integral membrane proteins undergo noncoordinate variation in expression. In addition to differential expression of epitope-bearing lipoproteins, differential accessibility of epitopes to antibodies was also documented as a mechanism generating surface phenotypic variation. Examination of one strain-variant antigen showed high-frequency phase variation to underlie previously observed antigenic differences between strains of this species. Thus, M. fermentans has a complex system capable of creating rapid changes in surface mosaics. This may profoundly affect mycoplasma-host interactions and may limit the methods by which populations of M. fermentans may be studied in vivo.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer F. A., Wear D. J., Angritt P., Lo S. C. Mycoplasma fermentans (incognitus strain) infection in the kidneys of patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and associated nephropathy: a light microscopic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural study. Hum Pathol. 1991 Jan;22(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(91)90063-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bricker T. M., Boyer M. J., Keith J., Watson-McKown R., Wise K. S. Association of lipids with integral membrane surface proteins of Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):295–301. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.295-301.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson M. S., Hayes M. M., Wang R. Y., Armstrong D., Kundsin R. B., Lo S. C. Detection and isolation of Mycoplasma fermentans from urine of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected patients. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1993 May;117(5):511–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARD D. G., FREUNDT E. A. The classification and nomenclature of organisms of the pleuropneumonia group. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Feb;14(1):197–207. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-1-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakkarainen K., Jansson E., Ranki A., Valle S. L., Krohn K. J. Serological responses to mycoplasmas in HIV-infected and non-infected individuals. AIDS. 1992 Nov;6(11):1287–1292. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199211000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Wu H. C. Lipoproteins in bacteria. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Jun;22(3):451–471. doi: 10.1007/BF00763177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaître M., Guétard D., Hénin Y., Montagnier L., Zerial A. Protective activity of tetracycline analogs against the cytopathic effect of the human immunodeficiency viruses in CEM cells. Res Virol. 1990 Jan-Feb;141(1):5–16. doi: 10.1016/0923-2516(90)90052-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. C., Dawson M. S., Newton P. B., 3rd, Sonoda M. A., Shih J. W., Engler W. F., Wang R. Y., Wear D. J. Association of the virus-like infectious agent originally reported in patients with AIDS with acute fatal disease in previously healthy non-AIDS patients. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Sep;41(3):364–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. C., Shih J. W., Newton P. B., 3rd, Wong D. M., Hayes M. M., Benish J. R., Wear D. J., Wang R. Y. Virus-like infectious agent (VLIA) is a novel pathogenic mycoplasma: Mycoplasma incognitus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Nov;41(5):586–600. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.41.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. C., Tsai S., Benish J. R., Shih J. W., Wear D. J., Wong D. M. Enhancement of HIV-1 cytocidal effects in CD4+ lymphocytes by the AIDS-associated mycoplasma. Science. 1991 Mar 1;251(4997):1074–1076. doi: 10.1126/science.1705362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo S. C., Wang R. Y., Newton P. B., 3rd, Yang N. Y., Sonoda M. A., Shih J. W. Fatal infection of silvered leaf monkeys with a virus-like infectious agent (VLIA) derived from a patient with AIDS. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Apr;40(4):399–409. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.40.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICOL C. S., EDWARD D. G. Role of organisms of the pleuropneumonia group in human genital infections. Br J Vener Dis. 1953 Sep;29(3):141–150. doi: 10.1136/sti.29.3.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson L. D., Renshaw C. A., Shane S. W., Barile M. F. Successive synovial Mycoplasma hominis isolates exhibit apparent antigenic variation. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3327–3329. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3327-3329.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUITER M., WENTHOLT H. M. Isolation of a pleuropneumonia-like organism from a skin lesion associated with a fusospirochetal flora. J Invest Dermatol. 1955 Jan;24(1):31–34. doi: 10.1038/jid.1955.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosengarten R., Wise K. S. Phenotypic switching in mycoplasmas: phase variation of diverse surface lipoproteins. Science. 1990 Jan 19;247(4940):315–318. doi: 10.1126/science.1688663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosengarten R., Wise K. S. The Vlp system of Mycoplasma hyorhinis: combinatorial expression of distinct size variant lipoproteins generating high-frequency surface antigenic variation. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4782–4793. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4782-4793.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saillard C., Carle P., Bové J. M., Bébéar C., Lo S. C., Shih J. W., Wang R. Y., Rose D. L., Tully J. G. Genetic and serologic relatedness between Mycoplasma fermentans strains and a mycoplasma recently identified in tissues of AIDS and non-AIDS patients. Res Virol. 1990 May-Jun;141(3):385–395. doi: 10.1016/0923-2516(90)90010-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Städtlander C. T., Zuhua C., Watson H. L., Cassell G. H. Protein and antigen heterogeneity among strains of Mycoplasma fermentans. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3319–3322. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3319-3322.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R. Y., Shih J. W., Grandinetti T., Pierce P. F., Hayes M. M., Wear D. J., Alter H. J., Lo S. C. High frequency of antibodies to Mycoplasma penetrans in HIV-infected patients. Lancet. 1992 Nov 28;340(8831):1312–1316. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92493-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise K. S. Adaptive surface variation in mycoplasmas. Trends Microbiol. 1993 May;1(2):59–63. doi: 10.1016/0966-842X(93)90034-O. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise K. S., Kim M. F., Theiss P. M., Lo S. C. A family of strain-variant surface lipoproteins of Mycoplasma fermentans. Infect Immun. 1993 Aug;61(8):3327–3333. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.8.3327-3333.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogev D., Rosengarten R., Watson-McKown R., Wise K. S. Molecular basis of Mycoplasma surface antigenic variation: a novel set of divergent genes undergo spontaneous mutation of periodic coding regions and 5' regulatory sequences. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4069–4079. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04983.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]