Abstract
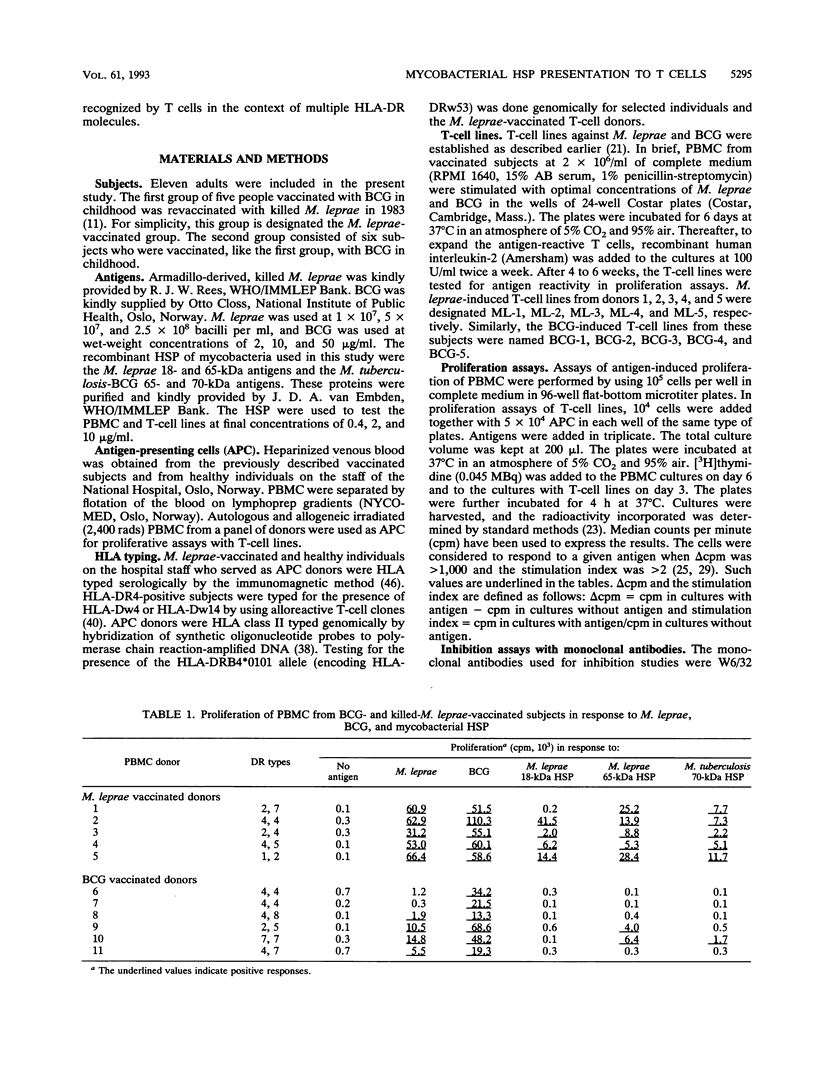
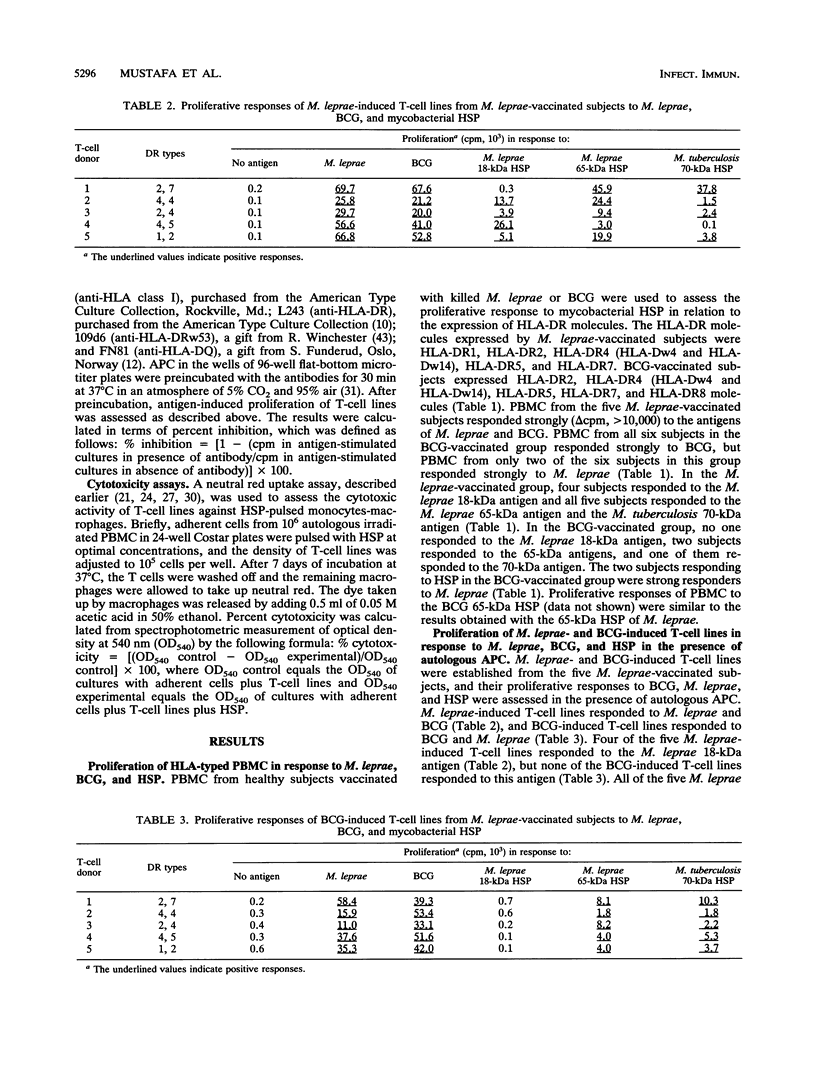
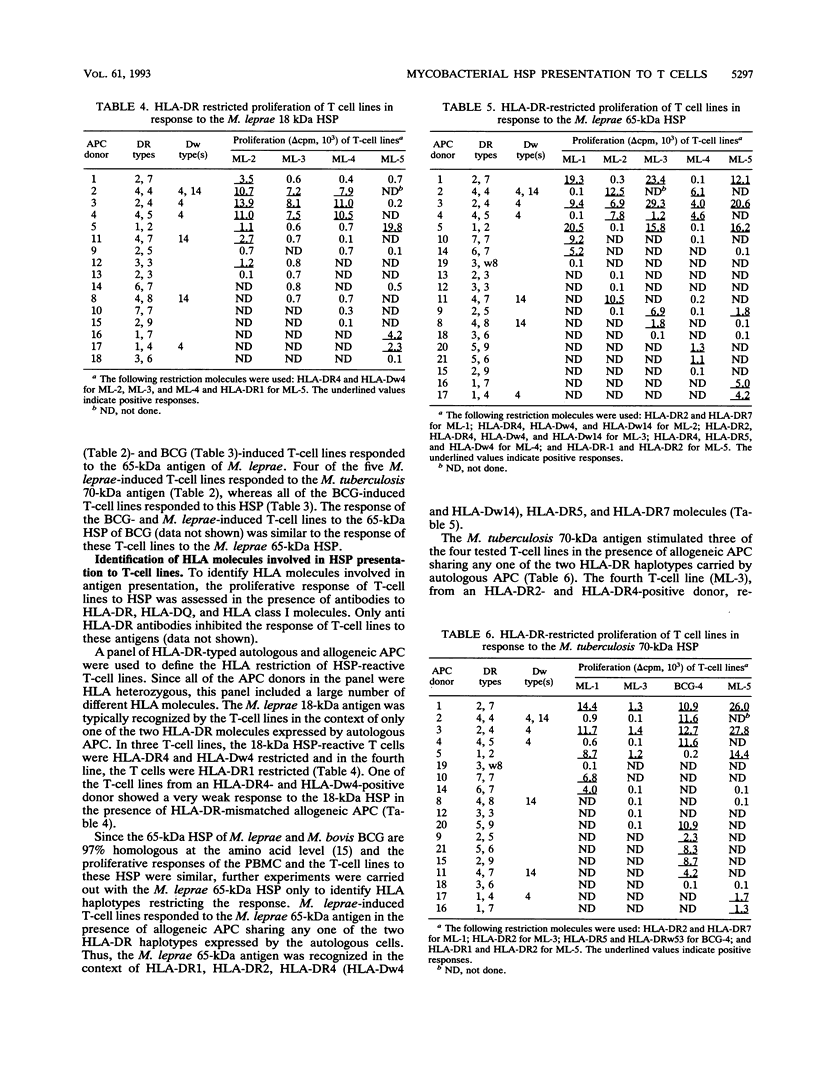
Heat shock proteins (HSP) are considered to be important targets of the immune response to mycobacteria and, as such, relevant to subunit vaccine design. If HSP are major antigens in cell-mediated immunity, they should be recognized in the context of most of the HLA-DR molecules required for presentation of mycobacterial antigens to T cells. We tested peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and T-cell lines from Mycobacterium leprae- and M. bovis BCG-vaccinated subjects for proliferation in response to the 18- and 65-kDa HSP of M. leprae, the 65-kDa HSP of M. bovis BCG, and the 70-kDa HSP of M. tuberculosis. Irrespective of HLA types, PBMC showing a strong response to M. leprae proliferated in response to mycobacterial HSP. HLA restriction analysis with T-cell lines showed that the M. leprae 18-kDa HSP was recognized in the context of HLA-DR4, HLA-Dw4, and HLA-DR1 molecules. The T-cell lines recognized the M. leprae 65-kDa HSP in the context of all of the HLA-DR molecules expressed by autologous antigen-presenting cells, i.e., HLA-DR1, HLA-DR2, HLA-DR5, HLA-DR7, and importantly HLA-DR4 (HLA-Dw4 and HLA-Dw14), which is relevant to autoimmunity. The M. tuberculosis 70-kDa antigen was also presented to the T-cell lines by HLA-DR1, HLA-DR2, HLA-DR5, and HLA-DR7 molecules. In addition, this HSP was recognized in the context of the HLA-DRw53 molecule, which is frequently expressed in many regions where leprosy is endemic. The T-cell lines proliferating in response to a given HSP lysed autologous monocytes-macrophages pulsed with that HSP. The results demonstrate that PBMC from individuals immunized with M. leprae respond to mycobacterial HSP and that these HSP are presented to T cells by multiple HLA-DR molecules, a prerequisite for their application in the next generation of subunit vaccines.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ab B. K., Kiessling R., Van Embden J. D., Thole J. E., Kumararatne D. S., Pisa P., Wondimu A., Ottenhoff T. H. Induction of antigen-specific CD4+ HLA-DR-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes as well as nonspecific nonrestricted killer cells by the recombinant mycobacterial 65-kDa heat-shock protein. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Feb;20(2):369–377. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams E., Garsia R. J., Hellqvist L., Holt P., Basten A. T cell reactivity to the purified mycobacterial antigens p65 and p70 in leprosy patients and their household contacts. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 May;80(2):206–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05235.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergholtz B. O., Thorsby E. Macrophage-dependent response of immune human T lymphocytes to PPD in vitro. Influence of HLA-D histocompatibility. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(8):779–786. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb02151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billingham M. E., Carney S., Butler R., Colston M. J. A mycobacterial 65-kD heat shock protein induces antigen-specific suppression of adjuvant arthritis, but is not itself arthritogenic. J Exp Med. 1990 Jan 1;171(1):339–344. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.1.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer J. G., Marsh S. G., Albert E. D., Bodmer W. F., Dupont B., Erlich H. A., Mach B., Mayr W. R., Parham P., Sasazuki T. Nomenclature for factors of the HLA system, 1991. WHO Nomenclature Committee for factors of the HLA system. Tissue Antigens. 1992 Apr;39(4):161–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1992.tb01932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton W. J., Hellqvist L., Basten A., Inglis A. S. Immunoreactivity of a 70 kD protein purified from Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guerin by monoclonal antibody affinity chromatography. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):695–708. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier N. A., Heffron F. Induction of Salmonella stress proteins upon infection of macrophages. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):730–732. doi: 10.1126/science.1970672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockrell H. M., Stoker N. G., Lee S. P., Jackson M., Grant K. A., Jouy N. F., Lucas S. B., Hasan R., Hussain R., McAdam K. P. T-cell recognition of the 18-kilodalton antigen of Mycobacterium leprae. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1979–1983. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1979-1983.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill H. K., Mustafa A. S., Godal T. Induction of delayed-type hypersensitivity in human volunteers immunized with a candidate leprosy vaccine consisting of killed Mycobacterium leprae. Bull World Health Organ. 1986;64(1):121–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holte H., Blomhoff H. K., Beiske K., Funderud S., Torjesen P., Gaudernack G., Stokke T., Smeland E. B. Intracellular events associated with inhibition of B cell activation by monoclonal antibodies to HLA class II antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jul;19(7):1221–1225. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husson R. N., Young R. A. Genes for the major protein antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: the etiologic agents of tuberculosis and leprosy share an immunodominant antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1679–1683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janson A. A., Klatser P. R., van der Zee R., Cornelisse Y. E., de Vries R. R., Thole J. E., Ottenhoff T. H. A systematic molecular analysis of the T cell-stimulating antigens from Mycobacterium leprae with T cell clones of leprosy patients. Identification of a novel M. leprae HSP 70 fragment by M. leprae-specific T cells. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 15;147(10):3530–3537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jindal S., Dudani A. K., Singh B., Harley C. B., Gupta R. S. Primary structure of a human mitochondrial protein homologous to the bacterial and plant chaperonins and to the 65-kilodalton mycobacterial antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2279–2283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H. CD8+ T lymphocytes in intracellular microbial infections. Immunol Today. 1988 Jun;9(6):168–174. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie K. R., Adams E., Britton W. J., Garsia R. J., Basten A. Sequence and immunogenicity of the 70-kDa heat shock protein of Mycobacterium leprae. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 1;147(1):312–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehlert A., Young D. B. Biochemical and antigenic characterization of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis 71kD antigen, a member of the 70kD heat-shock protein family. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Feb;3(2):125–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb01801.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Bloom B. R., Bajardi A. C., Grisso C. L., Sieling P. A., Alland D., Convit J., Fan X. D., Hunter S. W., Brennan P. J. A major T cell antigen of Mycobacterium leprae is a 10-kD heat-shock cognate protein. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):275–284. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munk M. E., Schoel B., Kaufmann S. H. T cell responses of normal individuals towards recombinant protein antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Nov;18(11):1835–1838. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa A. S., Gill H. K., Nerland A., Britton W. J., Mehra V., Bloom B. R., Young R. A., Godal T. Human T-cell clones recognize a major M. leprae protein antigen expressed in E. coli. Nature. 1986 Jan 2;319(6048):63–66. doi: 10.1038/319063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa A. S., Godal T. BCG induced CD4+ cytotoxic T cells from BCG vaccinated healthy subjects: relation between cytotoxicity and suppression in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Aug;69(2):255–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa A. S., Godal T. In vitro induction of human suppressor T cells by mycobacterial antigens. BCG activated OKT4+ cells mediate suppression of antigen induced T cell proliferation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Apr;52(1):29–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa A. S. Identification of T-cell-activating recombinant antigens shared among three candidate antileprosy vaccines, killed M. leprae, M. bovis BCG, and mycobacterium w. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1988 Jun;56(2):265–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa A. S., Kvalheim G., Degre M., Godal T. Mycobacterium bovis BCG-induced human T-cell clones from BCG-vaccinated healthy subjects: antigen specificity and lymphokine production. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):491–497. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.491-497.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa A. S., Oftung F., Gill H. K., Natvig I. Characteristics of human T-cell clones from BCG and killed M. leprae vaccinated subjects and tuberculosis patients. Recognition of recombinant mycobacterial antigens. Lepr Rev. 1986 Dec;57 (Suppl 2):123–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa A. S., Qvigstad E. HLA-DR-restricted antigen-induced proliferation and cytotoxicity mediated by CD4+ T-cell clones from subjects vaccinated with killed M. leprae. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1989 Mar;57(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerland A. H., Mustafa A. S., Sweetser D., Godal T., Young R. A. A protein antigen of Mycobacterium leprae is related to a family of small heat shock proteins. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5919–5921. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5919-5921.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oftung F., Mustafa A. S., Husson R., Young R. A., Godal T. Human T cell clones recognize two abundant Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein antigens expressed in Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):927–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oftung F., Mustafa A. S., Shinnick T. M., Houghten R. A., Kvalheim G., Degre M., Lundin K. E., Godal T. Epitopes of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis 65-kilodalton protein antigen as recognized by human T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2749–2754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oftung F., Shinnick T. M., Mustafa A. S., Lundin K. E., Godal T., Nerland A. H. Heterogeneity among human T cell clones recognizing an HLA-DR4,Dw4-restricted epitope from the 18-kDa antigen of Mycobacterium leprae defined by synthetic peptides. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1478–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Miller E. S., Roberts A. D., Furney S. K., Griffin J. P., Dobos K. M., Chi D., Rivoire B., Brennan P. J. T lymphocytes mediating protection and cellular cytolysis during the course of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Evidence for different kinetics and recognition of a wide spectrum of protein antigens. J Immunol. 1992 Jan 1;148(1):189–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottenhoff T. H., Ab B. K., Van Embden J. D., Thole J. E., Kiessling R. The recombinant 65-kD heat shock protein of Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guerin/M. tuberculosis is a target molecule for CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes that lyse human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1947–1952. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottenhoff T. H., Haanen J. B., Geluk A., Mutis T., Ab B. K., Thole J. E., van Schooten W. C., van den Elsen P. J., de Vries R. R. Regulation of mycobacterial heat-shock protein-reactive T cells by HLA class II molecules: lessons from leprosy. Immunol Rev. 1991 Jun;121:171–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00828.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottenhoff T. H., Neuteboom S., Elferink D. G., de Vries R. R. Molecular localization and polymorphism of HLA class II restriction determinants defined by Mycobacterium leprae-reactive helper T cell clones from leprosy patients. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):1923–1939. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parronchi P., De Carli M., Manetti R., Simonelli C., Sampognaro S., Piccinni M. P., Macchia D., Maggi E., Del Prete G., Romagnani S. IL-4 and IFN (alpha and gamma) exert opposite regulatory effects on the development of cytolytic potential by Th1 or Th2 human T cell clones. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 1;149(9):2977–2983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Res P. C., Orsini D. L., Van Laar J. M., Janson A. A., Abou-Zeid C., De Vries R. R. Diversity in antigen recognition by Mycobacterium tuberculosis-reactive T cell clones from the synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1297–1302. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard J. Synthetic peptides as vaccines. Nature. 1987 Nov 12;330(6144):106–107. doi: 10.1038/330106b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rønningen K. S., Spurkland A., Markussen G., Iwe T., Vartdal F., Thorsby E. Distribution of HLA class II alleles among Norwegian Caucasians. Hum Immunol. 1990 Dec;29(4):275–281. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(90)90041-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Vodkin M. H., Williams J. C. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis 65-kilodalton antigen is a heat shock protein which corresponds to common antigen and to the Escherichia coli GroEL protein. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):446–451. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.446-451.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toguchi T., Burmester G., Nunez-Roldan A., Gregersen P., Seremetis S., Lee S., Szer I., Winchester R. Evidence for the separate molecular expression of four distinct polymorphic Ia epitopes on cells of DR4 homozygous individuals. Hum Immunol. 1984 Jun;10(2):69–81. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(84)90074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartdal F., Gaudernack G., Funderud S., Bratlie A., Lea T., Ugelstad J., Thorsby E. HLA class I and II typing using cells positively selected from blood by immunomagnetic isolation--a fast and reliable technique. Tissue Antigens. 1986 Nov;28(5):301–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1986.tb00500.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Tokunaga K., Matsuki K., Takeuchi F., Matsuta K., Maeda H., Omoto K., Juji T. Putative amino acid sequence of HLA-DRB chain contributing to rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2263–2268. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B. Stress proteins, arthritis, and autoimmunity. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Dec;32(12):1497–1504. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780321202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wordsworth B. P., Lanchbury J. S., Sakkas L. I., Welsh K. I., Panayi G. S., Bell J. I. HLA-DR4 subtype frequencies in rheumatoid arthritis indicate that DRB1 is the major susceptibility locus within the HLA class II region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10049–10053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Bloom B. R., Grosskinsky C. M., Ivanyi J., Thomas D., Davis R. W. Dissection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens using recombinant DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2583–2587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Elliott T. J. Stress proteins, infection, and immune surveillance. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90861-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Mehra V., Sweetser D., Buchanan T., Clark-Curtiss J., Davis R. W., Bloom B. R. Genes for the major protein antigens of the leprosy parasite Mycobacterium leprae. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):450–452. doi: 10.1038/316450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A. Stress proteins and immunology. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:401–420. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eden W., Thole J. E., van der Zee R., Noordzij A., van Embden J. D., Hensen E. J., Cohen I. R. Cloning of the mycobacterial epitope recognized by T lymphocytes in adjuvant arthritis. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):171–173. doi: 10.1038/331171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Broek M. F., Hogervorst E. J., Van Bruggen M. C., Van Eden W., van der Zee R., van den Berg W. B. Protection against streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis by pretreatment with the 65-kD mycobacterial heat shock protein. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):449–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


