Abstract
Recombinant Salmonella typhimurium aroA aroD mutants which expressed ovalbumin were constructed. The two expression constructs used were based on either pUC18 or pBR322. The pBR322-based construct was more stable in vitro and in vivo than the pUC-based construct. Salmonellae containing the stable pBR322-based plasmid induced major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL), in contrast to salmonellae containing the pUC18-based expression construct. The priming of MHC class I-restricted CTL was increased by multiple immunizations. The study described in this report suggest that S. typhimurium delta aro mutants have the capacity to induce MHC class I-restricted CTL against carried antigens and that MHC class I-restricted CTL responses require stable in vivo expression of the target antigen. Further, the results indicate that the Salmonella typhi delta aro mutants currently undergoing evaluation in studies with humans may be good carriers of viral antigens with CTL determinants.
Full text
PDF

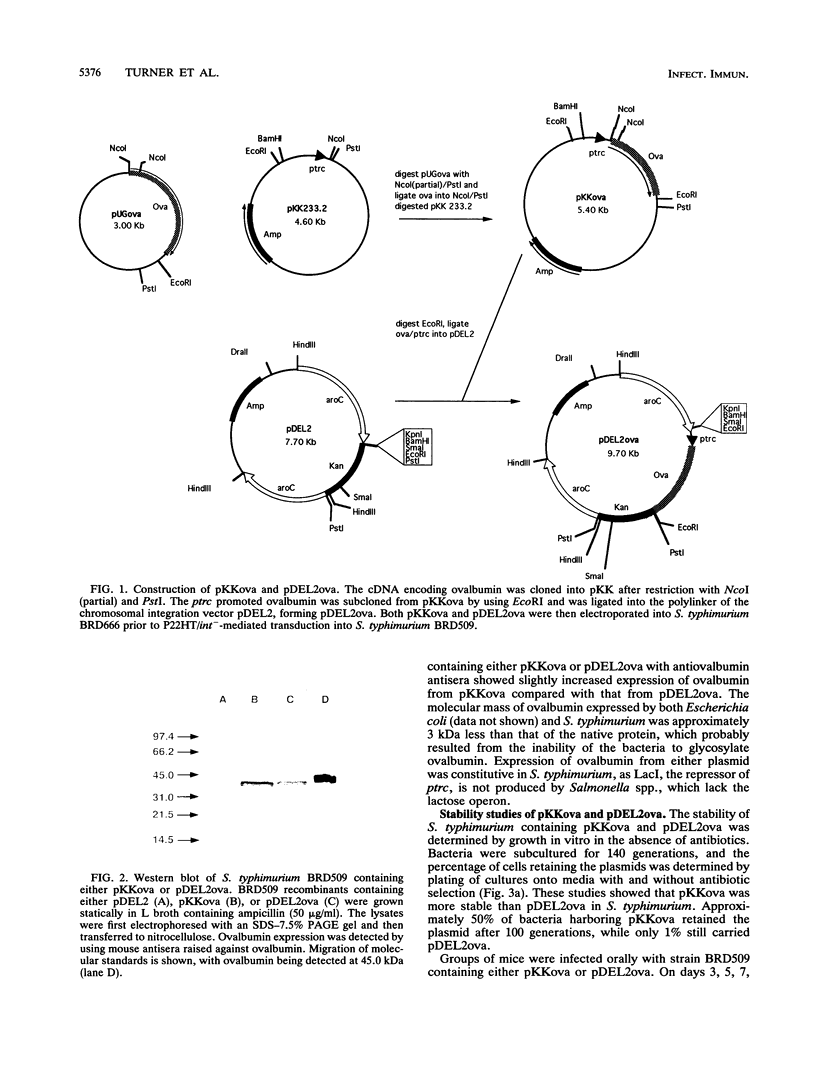
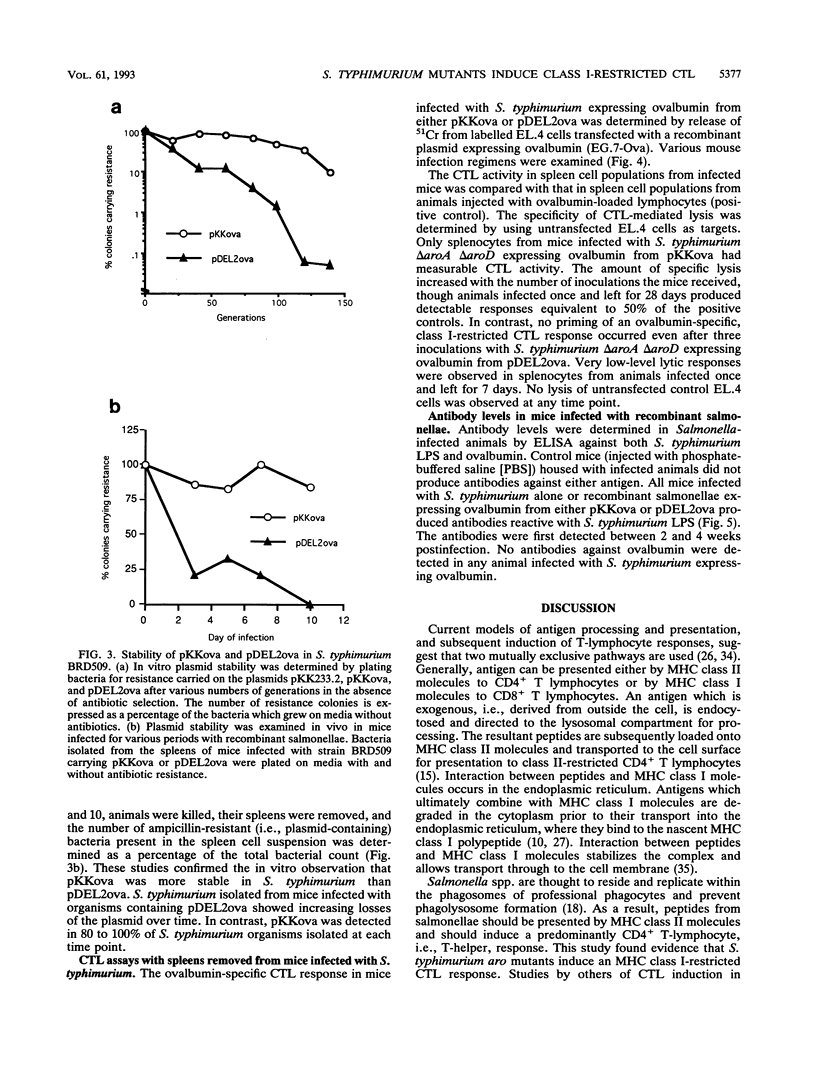
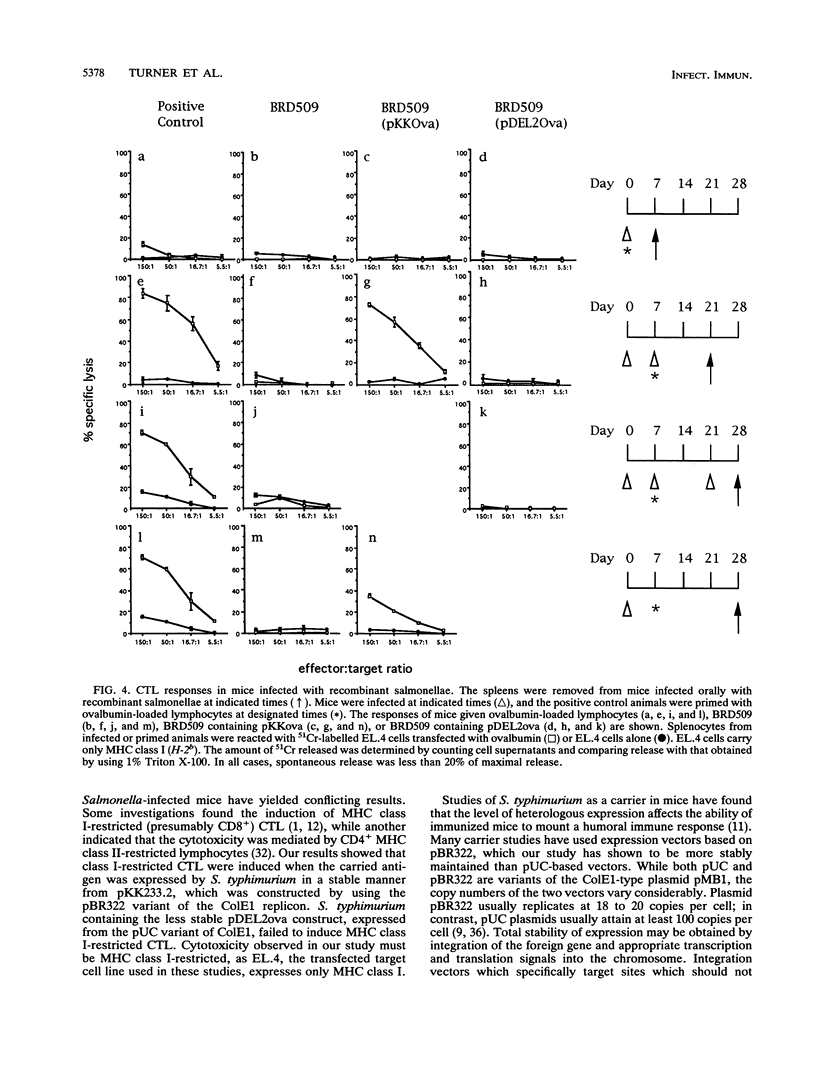


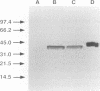
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal A., Kumar S., Jaffe R., Hone D., Gross M., Sadoff J. Oral Salmonella: malaria circumsporozoite recombinants induce specific CD8+ cytotoxic T cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1083–1090. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binotto J., MacLachlan P. R., Sanderson K. E. Electrotransformation in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. Can J Microbiol. 1991 Jun;37(6):474–477. doi: 10.1139/m91-078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., Hormaeche C. E., Demarco de Hormaeche R., Winther M., Dougan G., Maskell D. J., Stocker B. A. An attenuated aroA Salmonella typhimurium vaccine elicits humoral and cellular immunity to cloned beta-galactosidase in mice. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):86–92. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone F. R., Bevan M. J. Class I-restricted processing and presentation of exogenous cell-associated antigen in vivo. J Exp Med. 1990 Feb 1;171(2):377–387. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.2.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield S. N., Fairweather N., Charles I., Pickard D., Levine M., Hone D., Posada M., Strugnell R. A., Dougan G. Construction of a genetically defined Salmonella typhi Ty2 aroA, aroC mutant for the engineering of a candidate oral typhoid-tetanus vaccine. Vaccine. 1992;10(1):53–60. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(92)90420-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. L., Venables L. M., Nicholas R. A., Cullen G. A., Hormaeche C. E. Vaccination of chickens with chicken-derived Salmonella enteritidis phage type 4 aroA live oral Salmonella vaccines. Vaccine. 1992;10(4):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(92)90160-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias L., Cervantes L., Covarrubias A., Soberón X., Vichido I., Blanco A., Kupersztoch-Portnoy Y. M., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. V. Mobilization and coding properties of pBR322 and several deletion derivatives including pBR327 and pBR328. Gene. 1981 Jan-Feb;13(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. H., Yewdell J. W., Eisenlohr L. C., Johnson P. R., Bennink J. R. Antigen presentation requires transport of MHC class I molecules from the endoplasmic reticulum. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):715–718. doi: 10.1126/science.2137259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairweather N. F., Chatfield S. N., Makoff A. J., Strugnell R. A., Bester J., Maskell D. J., Dougan G. Oral vaccination of mice against tetanus by use of a live attenuated Salmonella carrier. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1323–1326. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1323-1326.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn J. L., Weiss W. R., Norris K. A., Seifert H. S., Kumar S., So M. Generation of a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response using a Salmonella antigen-delivery system. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2111–2118. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germanier R. Immunity in experimental salmonellosis. 3. Comparative immunization with viable and heat-inactivated cells of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):792–797. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.792-797.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin H. G., Barrow P. A. Construction of an aroA mutant of Salmonella serotype Gallinarum: its effectiveness in immunization against experimental fowl typhoid. Vaccine. 1993;11(4):457–462. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(93)90288-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding C. V., Collins D. S., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Unanue E. R. Liposome-encapsulated antigens are processed in lysosomes, recycled, and presented to T cells. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90647-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):238–239. doi: 10.1038/291238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H. S. Pathogenesis and immunity in murine salmonellosis. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):390–409. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.390-409.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishibashi Y., Arai T. Specific inhibition of phagosome-lysosome fusion in murine macrophages mediated by Salmonella typhimurium infection. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1990 May;2(1):35–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb03476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Hug E., De Libero G. Listeria monocytogenes-reactive T lymphocyte clones with cytolytic activity against infected target cells. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):363–368. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovacsovics-Bankowski M., Clark K., Benacerraf B., Rock K. L. Efficient major histocompatibility complex class I presentation of exogenous antigen upon phagocytosis by macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):4942–4946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.4942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V., Collins F. M. Host-parasite relations in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):573–583. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McReynolds L., O'Malley B. W., Nisbet A. D., Fothergill J. E., Givol D., Fields S., Robertson M., Brownlee G. G. Sequence of chicken ovalbumin mRNA. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):723–728. doi: 10.1038/273723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller I. A., Chatfield S., Dougan G., Desilva L., Joysey H. S., Hormaeche C. Bacteriophage P22 as a vehicle for transducing cosmid gene banks between smooth strains of Salmonella typhimurium: use in identifying a role for aroD in attenuating virulent Salmonella strains. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jan;215(2):312–316. doi: 10.1007/BF00339734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. W., Carbone F. R., Bevan M. J. Introduction of soluble protein into the class I pathway of antigen processing and presentation. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):777–785. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison L. A., Lukacher A. E., Braciale V. L., Fan D. P., Braciale T. J. Differences in antigen presentation to MHC class I-and class II-restricted influenza virus-specific cytolytic T lymphocyte clones. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):903–921. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuchtern J. G., Bonifacino J. S., Biddison W. E., Klausner R. D. Brefeldin A implicates egress from endoplasmic reticulum in class I restricted antigen presentation. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):223–226. doi: 10.1038/339223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer J. D., Wick M. J., Roberts R. L., Findlay K., Normark S. J., Harding C. V. Phagocytic processing of bacterial antigens for class I MHC presentation to T cells. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):359–362. doi: 10.1038/361359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker B. A., Hoiseth S. K., Smith B. P. Aromatic-dependent "Salmonella sp." as live vaccine in mice and calves. Dev Biol Stand. 1983;53:47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strugnell R., Dougan G., Chatfield S., Charles I., Fairweather N., Tite J., Li J. L., Beesley J., Roberts M. Characterization of a Salmonella typhimurium aro vaccine strain expressing the P.69 antigen of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1992 Oct;60(10):3994–4002. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.10.3994-4002.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacket C. O., Hone D. M., Curtiss R., 3rd, Kelly S. M., Losonsky G., Guers L., Harris A. M., Edelman R., Levine M. M. Comparison of the safety and immunogenicity of delta aroC delta aroD and delta cya delta crp Salmonella typhi strains in adult volunteers. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):536–541. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.536-541.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tite J. P., Gao X. M., Hughes-Jenkins C. M., Lipscombe M., O'Callaghan D., Dougan G., Liew F. Y. Anti-viral immunity induced by recombinant nucleoprotein of influenza A virus. III. Delivery of recombinant nucleoprotein to the immune system using attenuated Salmonella typhimurium as a live carrier. Immunology. 1990 Aug;70(4):540–546. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A., Bodmer H. Antigen recognition by class I-restricted T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:601–624. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A., Elliott T., Cerundolo V., Foster L., Barber B., Tse A. Assembly of MHC class I molecules analyzed in vitro. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):285–295. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90366-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. A rapid and sensitive method for plasmid copy number comparisons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 25;17(14):5866–5866. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.14.5866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. Immunological surveillance against altered self components by sensitised T lymphocytes in lymphocytic choriomeningitis. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):547–548. doi: 10.1038/251547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]