Abstract
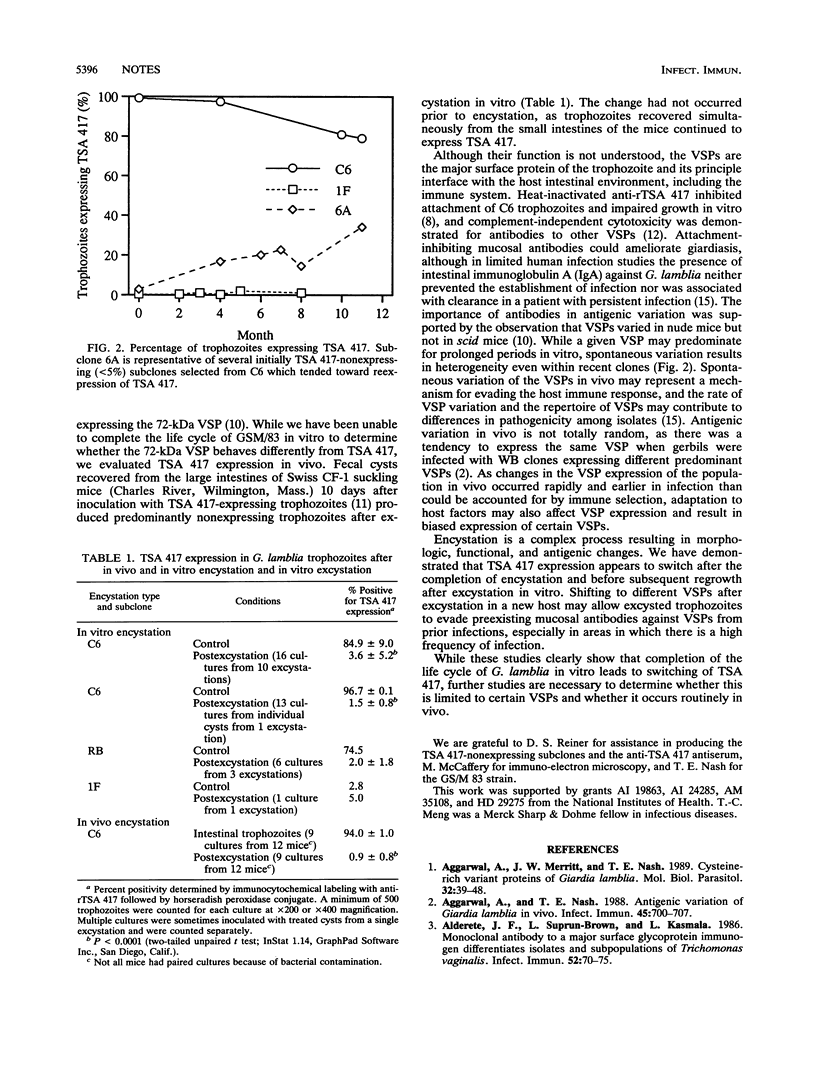
Expression of TSA 417, the predominant cysteine-rich variable surface protein of Giardia lamblia WB clone C6 trophozoites, did not change during encystation in vitro. However, in vitro excystation of cysts derived in vitro or in vivo consistently produced TSA 417 nonexpressing trophozoite populations, suggesting that completion of the life cycle leads to antigenic switching.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal A., Merritt J. W., Jr, Nash T. E. Cysteine-rich variant surface proteins of Giardia lamblia. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Jan 1;32(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Suprun-Brown L., Kasmala L. Monoclonal antibody to a major surface glycoprotein immunogen differentiates isolates and subpopulations of Trichomonas vaginalis. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):70–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.70-75.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum K. F., Berens R. L., Jones R. H., Marr J. J. A new method for cloning Giardia lamblia, with a discussion of the statistical considerations of limiting dilution. J Parasitol. 1988 Apr;74(2):267–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher S. E., Gillin F. D. Excystation of in vitro-derived Giardia lamblia cysts. Infect Immun. 1990 Nov;58(11):3516–3522. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.11.3516-3522.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Boucher S. E., Rossi S. S., Reiner D. S. Giardia lamblia: the roles of bile, lactic acid, and pH in the completion of the life cycle in vitro. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Aug;69(2):164–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Hagblom P., Harwood J., Aley S. B., Reiner D. S., McCaffery M., So M., Guiney D. G. Isolation and expression of the gene for a major surface protein of Giardia lamblia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4463–4467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B., Harriman G. R., Conrad J. T., Nash T. E. Antigenic variation in Giardia lamblia: cellular and humoral immune response in a mouse model. Parasite Immunol. 1990 Nov;12(6):659–673. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1990.tb00995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottstein B., Nash T. E. Antigenic variation in Giardia lamblia: infection of congenitally athymic nude and scid mice. Parasite Immunol. 1991 Nov;13(6):649–659. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1991.tb00560.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. R., Guerrant R. L., Pearson R. D., Hewlett E. L. Giardia lamblia infection of suckling mice. J Infect Dis. 1983 Feb;147(2):217–221. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.2.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Aggarwal A. Cytotoxicity of monoclonal antibodies to a subset of Giardia isolates. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2628–2632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Conrad J. T., Merritt J. W., Jr Variant specific epitopes of Giardia lamblia. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1990 Aug;42(1):125–132. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(90)90120-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Herrington D. A., Levine M. M., Conrad J. T., Merritt J. W., Jr Antigenic variation of Giardia lamblia in experimental human infections. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4362–4369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Herrington D. A., Losonsky G. A., Levine M. M. Experimental human infections with Giardia lamblia. J Infect Dis. 1987 Dec;156(6):974–984. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.6.974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Merritt J. W., Jr, Conrad J. T. Isolate and epitope variability in susceptibility of Giardia lamblia to intestinal proteases. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1334–1340. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1334-1340.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner D. S., Douglas H., Gillin F. D. Identification and localization of cyst-specific antigens of Giardia lamblia. Infect Immun. 1989 Mar;57(3):963–968. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.3.963-968.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice E. W., Schaefer F. W., 3rd Improved in vitro excystation procedure for Giardia lamblia cysts. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Dec;14(6):709–710. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.6.709-710.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickerman K. Trypanosome sociology and antigenic variation. Parasitology. 1989;99 (Suppl):S37–S47. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000083402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegelbauer K., Overath P. Surface antigen change during differentiation of Trypanosoma brucei. Biochem Soc Trans. 1990 Oct;18(5):731–733. doi: 10.1042/bst0180731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]