Abstract
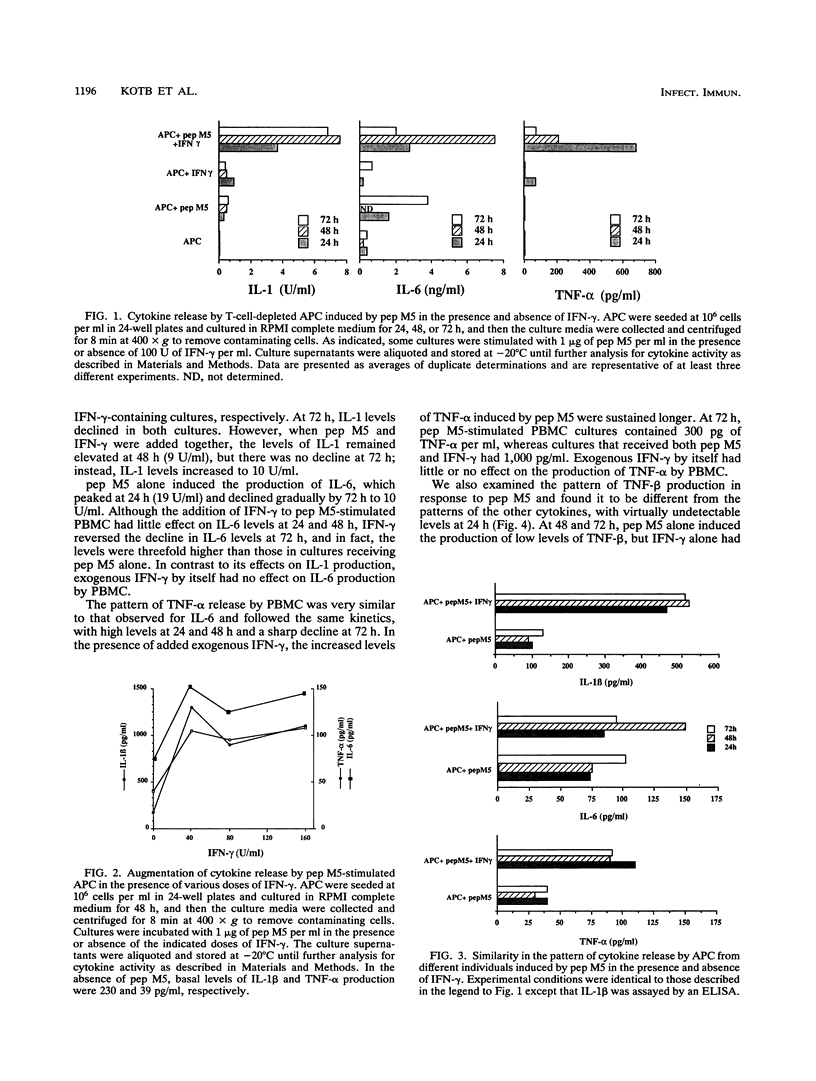
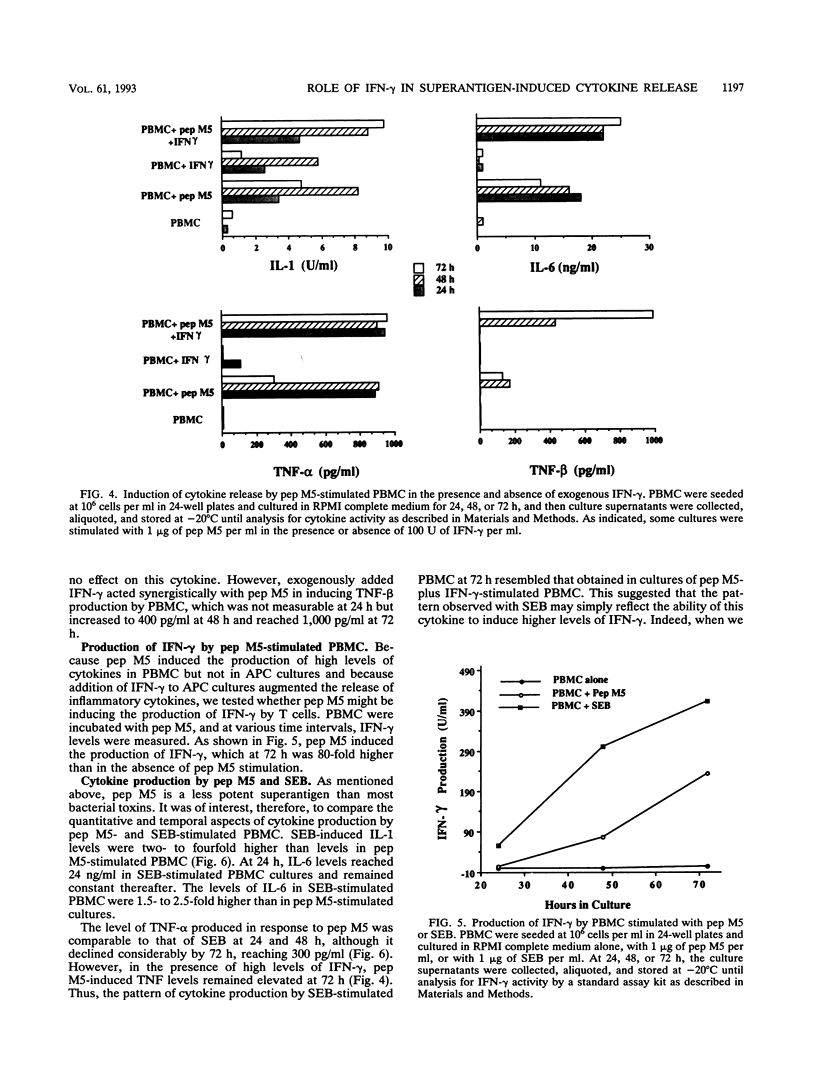
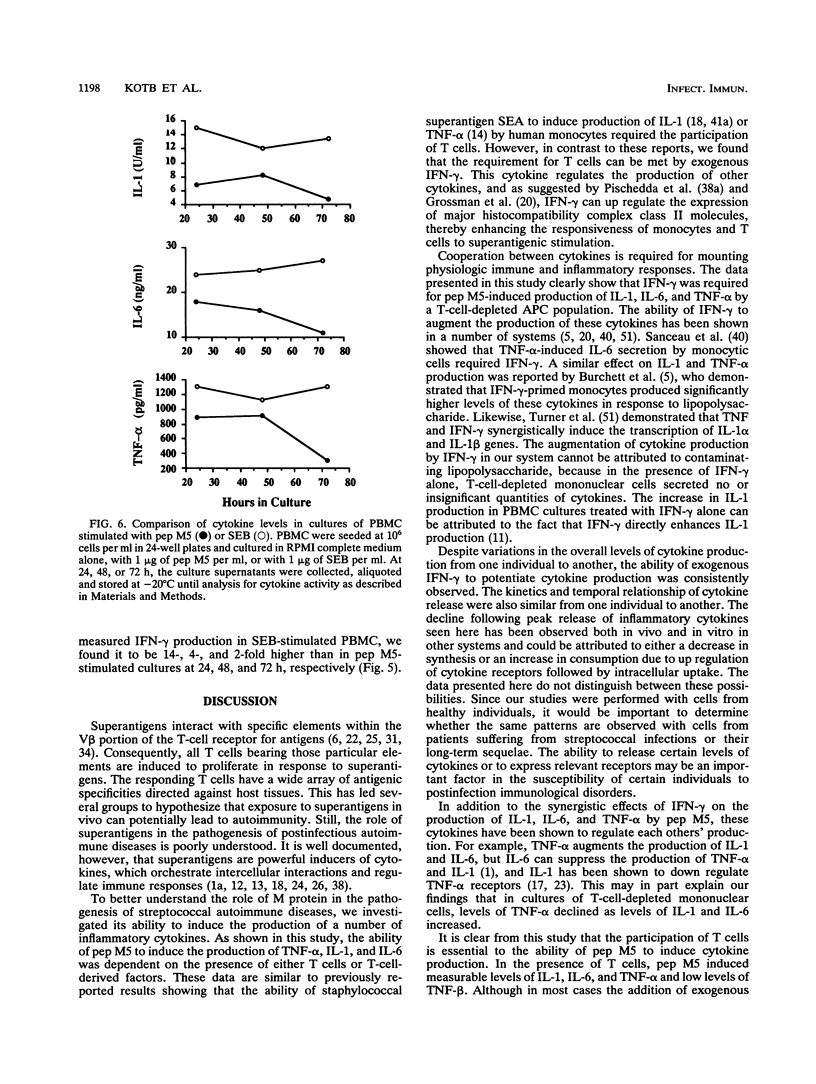
We undertook this study to determine the quality, quantity, and temporal relationship of pep M5-induced cytokine release. The ability of pep M5 to stimulate interleukin-1 (IL-1) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) production by a T-cell-depleted, monocyte- and B-cell-enriched cell population was dependent on the presence of T cells. The requirement for T cells could be met by addition of exogenous gamma interferon (IFN-gamma). In the presence of IFN-gamma, pep M5 induced the release of TNF-alpha, IL-1, and IL-6, TNF-alpha levels peaked at 24 h, while IL-1 and IL-6 levels peaked at 48 h. pep M5 induced T cells to produce IFN-gamma, which may have accounted for the ability of the super antigen to induce the production of IL-1, IL-6, TNF-alpha, and TNF-beta by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). The addition of excess IFN-gamma to cultures of pep M5 and PBMC did not further increase the release of these cytokines at 24 and 48 h but resulted in sustained higher levels at 72 h. Interestingly, TNF-beta production occurred only in the presence of pep M5 and exogenous IFN-gamma. The ability of pep M5 to induce cytokine production was compared with that of a potent super antigen, staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB). SEB was a 2- to 14-fold-more-potent inducer of IFN-gamma production. Furthermore, the profile of cytokine released by PBMC in response to this super antigen mimicked that seen with pep M5 in the presence of exogenous IFN-gamma. In conclusion, pep M5 induces the production of cytokines that are involved in immune regulation and inflammation. These cytokines also play a major role in human T-cell responses to this super antigen.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aderka D., Le J. M., Vilcek J. IL-6 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor production in cultured human monocytes, U937 cells, and in mice. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3517–3523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson J., Nagy S., Björk L., Abrams J., Holm S., Andersson U. Bacterial toxin-induced cytokine production studied at the single-cell level. Immunol Rev. 1992 Jun;127:69–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb01409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H., Stollerman G. H., Johnson R. H., Ofek I., Bisno A. L. Human immune response to immunization with a structurally defined polypeptide fragment of streptococcal M protein. J Exp Med. 1979 Oct 1;150(4):862–877. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.4.862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisno A. L. Group A streptococcal infections and acute rheumatic fever. N Engl J Med. 1991 Sep 12;325(11):783–793. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199109123251106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchett S. K., Weaver W. M., Westall J. A., Larsen A., Kronheim S., Wilson C. B. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin and IL-1 secretion in human mononuclear phagocytes. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3473–3481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Atkin C. L. The Mycoplasma arthritidis T-cell mitogen, MAM: a model superantigen. Immunol Today. 1991 Aug;12(8):271–276. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90125-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone L. A., Woodard D. R., Schlievert P. M., Tomory G. S. Clinical and bacteriologic observations of a toxic shock-like syndrome due to Streptococcus pyogenes. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 16;317(3):146–149. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707163170305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale J. B., Simpson W. A., Ofek I., Beachey E. H. Blastogenic responses of human lymphocytes to structurally defined polypeptide fragments of streptococcal M protein. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1499–1505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danis V. A., Kulesz A. J., Nelson D. S., Brooks P. M. Cytokine regulation of human monocyte interleukin-1 (IL-1) production in vitro. Enhancement of IL-1 production by interferon (IFN) gamma, tumour necrosis factor-alpha, IL-2 and IL-1, and inhibition by IFN-alpha. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Jun;80(3):435–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly R. P., Levine J., Hartwell D. Q., Frendl G., Fenton M. J., Beller D. I. Aberrant regulation of IL-1 expression in macrophages from young autoimmune-prone mice. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3231–3239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastgate J. A., Symons J. A., Wood N. C., Grinlinton F. M., di Giovine F. S., Duff G. W. Correlation of plasma interleukin 1 levels with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1988 Sep 24;2(8613):706–709. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast D. J., Schlievert P. M., Nelson R. D. Toxic shock syndrome-associated staphylococcal and streptococcal pyrogenic toxins are potent inducers of tumor necrosis factor production. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):291–294. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.291-294.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast D. J., Shannon B. J., Herriott M. J., Kennedy M. J., Rummage J. A., Leu R. W. Staphylococcal exotoxins stimulate nitric oxide-dependent murine macrophage tumoricidal activity. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2987–2993. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2987-2993.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H., Dohlsten M., Andersson U., Hedlund G., Ericsson P., Hansson J., Sjögren H. O. Production of TNF-alpha and TNF-beta by staphylococcal enterotoxin A activated human T cells. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4663–4669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischetti V. A. Streptococcal M protein. Sci Am. 1991 Jun;264(6):58–65. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0691-58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B., Schmidt K. H., Gerlach D., Köhler W. Separation of T-cell-stimulating activity from streptococcal M protein. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1767–1770. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1767-1770.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. M., Posnett D. N., Tumang J. R., Cole B. C., Crow M. K. A potential role for microbial superantigens in the pathogenesis of systemic autoimmune disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Apr;34(4):468–480. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessani S., McCandless S., Baglioni C. Downregulation of tumor necrosis factor receptors of macrophages by interferons and interleukin-1. Role of protein kinase C activation. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 1988 Oct-Dec;2(4):166–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gjörloff A., Fischer H., Hedlund G., Hansson J., Kenney J. S., Allison A. C., Sjögren H. O., Dohlsten M. Induction of interleukin-1 in human monocytes by the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin A requires the participation of T cells. Cell Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;137(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90056-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomi T., Shiohara T., Munakata T., Imanishi K., Nagashima M. Interleukin 1 alpha, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and interferon gamma in psoriasis. Arch Dermatol. 1991 Jun;127(6):827–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman D., Cook R. G., Sparrow J. T., Mollick J. A., Rich R. R. Dissociation of the stimulatory activities of staphylococcal enterotoxins for T cells and monocytes. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1831–1841. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haq A. U. Failure of hydrocortisone to suppress the interferon-gamma-induced augmentation of interleukin 1 secretion of aged human monocytes. Immunobiology. 1988 Jul;177(3):245–253. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(88)80044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman A., Kappler J. W., Marrack P., Pullen A. M. Superantigens: mechanism of T-cell stimulation and role in immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:745–772. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtmann H., Wallach D. Down regulation of the receptors for tumor necrosis factor by interleukin 1 and 4 beta-phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1161–1167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikejima T., Dinarello C. A., Gill D. M., Wolff S. M. Induction of human interleukin-1 by a product of Staphylococcus aureus associated with toxic shock syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1984 May;73(5):1312–1320. doi: 10.1172/JCI111334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Russell J. K., Pontzer C. H. Staphylococcal enterotoxin microbial superantigens. FASEB J. 1991 Sep;5(12):2706–2712. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.12.1916093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jupin C., Anderson S., Damais C., Alouf J. E., Parant M. Toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 as an inducer of human tumor necrosis factors and gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):752–761. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. E., Clark C. An improved rosetting assay for detection of human T lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Jul;5(2):131–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe Y., Ochi A. Programmed cell death and extrathymic reduction of Vbeta8+ CD4+ T cells in mice tolerant to Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):245–248. doi: 10.1038/349245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Gillis S., Mizel S. B., Shevach E. M., Malek T. R., Dinarello C. A., Lachman L. B., Janeway C. A., Jr Growth of a cloned helper T cell line induced by a monoclonal antibody specific for the antigen receptor: interleukin 1 is required for the expression of receptors for interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1339–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourn R. G., Belloni P. Endothelial cell production of nitrogen oxides in response to interferon gamma in combination with tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1, or endotoxin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 May 2;82(9):772–776. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.9.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeuwenberg J. F., von Asmuth E. J., Jeunhomme T. M., Buurman W. A. IFN-gamma regulates the expression of the adhesion molecule ELAM-1 and IL-6 production by human endothelial cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 1;145(7):2110–2114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackensen A., Galanos C., Engelhardt R. Modulating activity of interferon-gamma on endotoxin-induced cytokine production in cancer patients. Blood. 1991 Dec 15;78(12):3254–3258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Kappler J. The staphylococcal enterotoxins and their relatives. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):705–711. doi: 10.1126/science.2185544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micusan V. V., Desrosiers M., Gosselin J., Mercier G., Oth D., Bhatti A. R., Heremans H., Billiau A. Stimulation of T cells and induction of interferon by toxic shock syndrome toxin 1. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jan-Feb;11 (Suppl 1):S305–S312. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_1.s305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. C., Gray E. D., Mansour M., Abdin Z. H., Kamel R., Zaher S., Regelmann W. E. Cytokines and immunoglobulin in rheumatic heart disease: production by blood and tonsillar mononuclear cells. J Rheumatol. 1989 Nov;16(11):1436–1442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. The glomerular permeability determined by dextran clearance using Sephadex gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):77–82. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hehir R. E., Lamb J. R. Induction of specific clonal anergy in human T lymphocytes by Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8884–8888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsonnet J., Gillis Z. A. Production of tumor necrosis factor by human monocytes in response to toxic-shock-syndrome toxin-1. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):1026–1033. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pischedda F., Bottaro G., Dickson J., Ward R., Cappa A. P., Kirchner H. Defective T-cell activation by Mycoplasma arthritidis mitogen is restored by interferon-gamma. Cell Immunol. 1989 Apr 15;120(1):188–194. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90186-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rellahan B. L., Jones L. A., Kruisbeek A. M., Fry A. M., Matis L. A. In vivo induction of anergy in peripheral V beta 8+ T cells by staphylococcal enterotoxin B. J Exp Med. 1990 Oct 1;172(4):1091–1100. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.4.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. H., Kehoe M. A. Group A streptococcal M proteins: virulence factors and protective antigens. Immunol Today. 1992 Sep;13(9):362–367. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90173-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanceau J., Wijdenes J., Revel M., Wietzerbin J. IL-6 and IL-6 receptor modulation by IFN-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human monocytic cell line (THP-1). Priming effect of IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;147(8):2630–2637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlievert P. M. Role of toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 in toxic shock syndrome: overview. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jan-Feb;11 (Suppl 1):S107–S109. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_1.s107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- See R. H., Kum W. W., Chang A. H., Goh S. H., Chow A. W. Induction of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 by purified staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 requires the presence of both monocytes and T lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2612–2618. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2612-2618.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L. Invasive group A streptococcus infections. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;14(1):2–11. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. L., Tanner M. H., Winship J., Swarts R., Ries K. M., Schlievert P. M., Kaplan E. Severe group A streptococcal infections associated with a toxic shock-like syndrome and scarlet fever toxin A. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 6;321(1):1–7. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907063210101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollerman G. H. Changing group A streptococci. The reappearance of streptococcal 'toxic shock'. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Jun;148(6):1268–1270. doi: 10.1001/archinte.148.6.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollerman G. H. Rheumatogenic group A streptococci and the return of rheumatic fever. Adv Intern Med. 1990;35:1–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomai M. A., Aelion J. A., Dockter M. E., Majumdar G., Spinella D. G., Kotb M. T cell receptor V gene usage by human T cells stimulated with the superantigen streptococcal M protein. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):285–288. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomai M. A., Schlievert P. M., Kotb M. Distinct T-cell receptor V beta gene usage by human T lymphocytes stimulated with the streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins and pep M5 protein. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):701–705. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.701-705.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomai M., Kotb M., Majumdar G., Beachey E. H. Superantigenicity of streptococcal M protein. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):359–362. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M., Chantry D., Buchan G., Barrett K., Feldmann M. Regulation of expression of human IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta genes. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3556–3561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veasy L. G., Wiedmeier S. E., Orsmond G. S., Ruttenberg H. D., Boucek M. M., Roth S. J., Tait V. F., Thompson J. A., Daly J. A., Kaplan E. L. Resurgence of acute rheumatic fever in the intermountain area of the United States. N Engl J Med. 1987 Feb 19;316(8):421–427. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198702193160801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitnack E., Beachey E. H. Antiopsonic activity of fibrinogen bound to M protein on the surface of group A streptococci. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):1042–1045. doi: 10.1172/JCI110508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



