Abstract
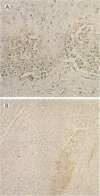
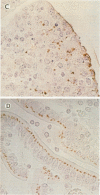
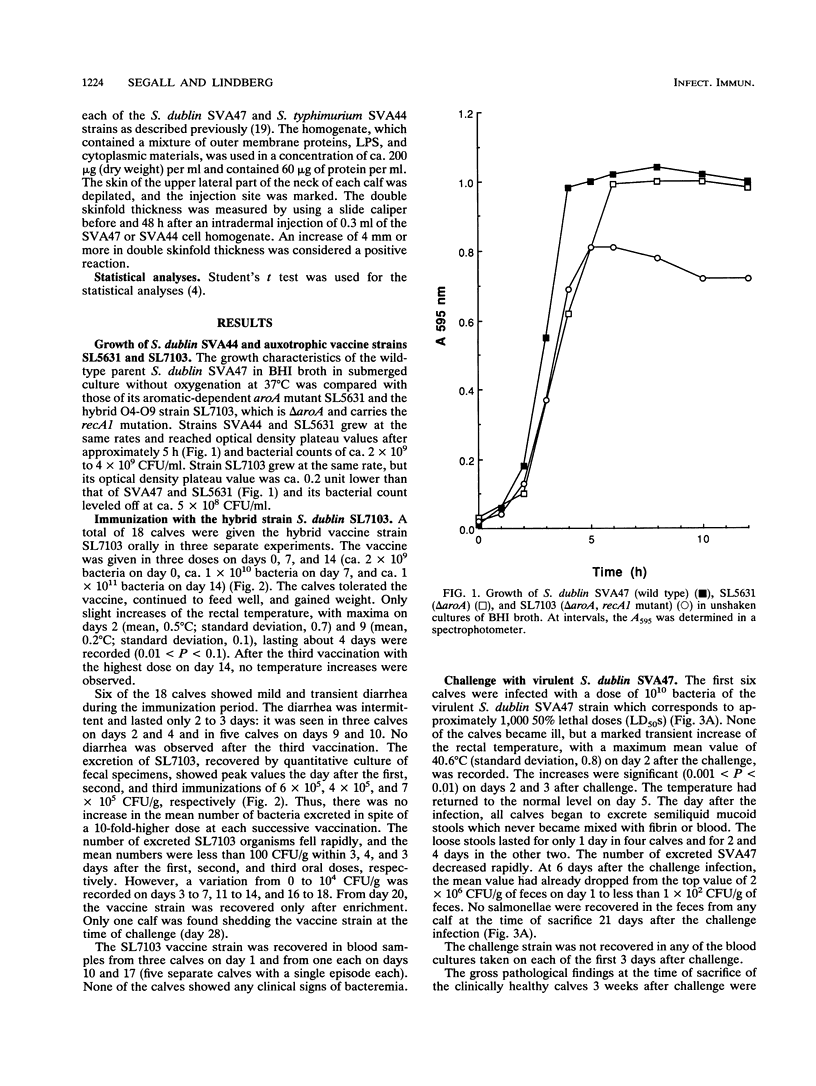
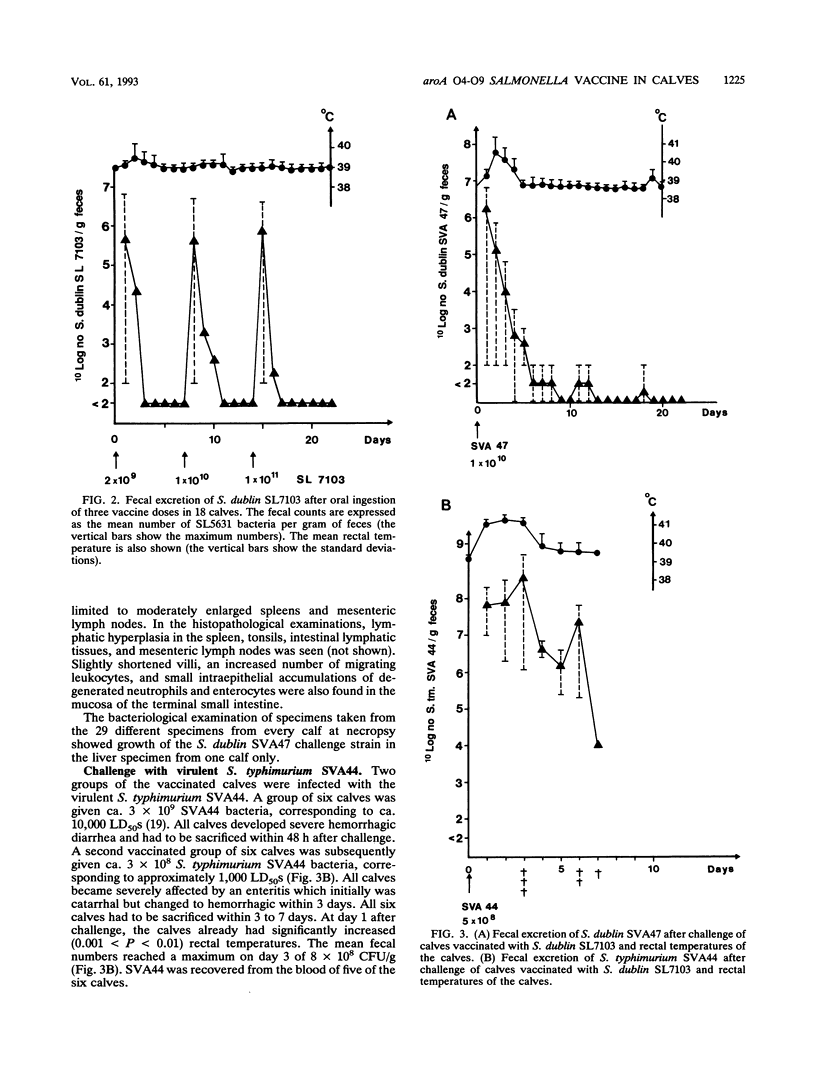
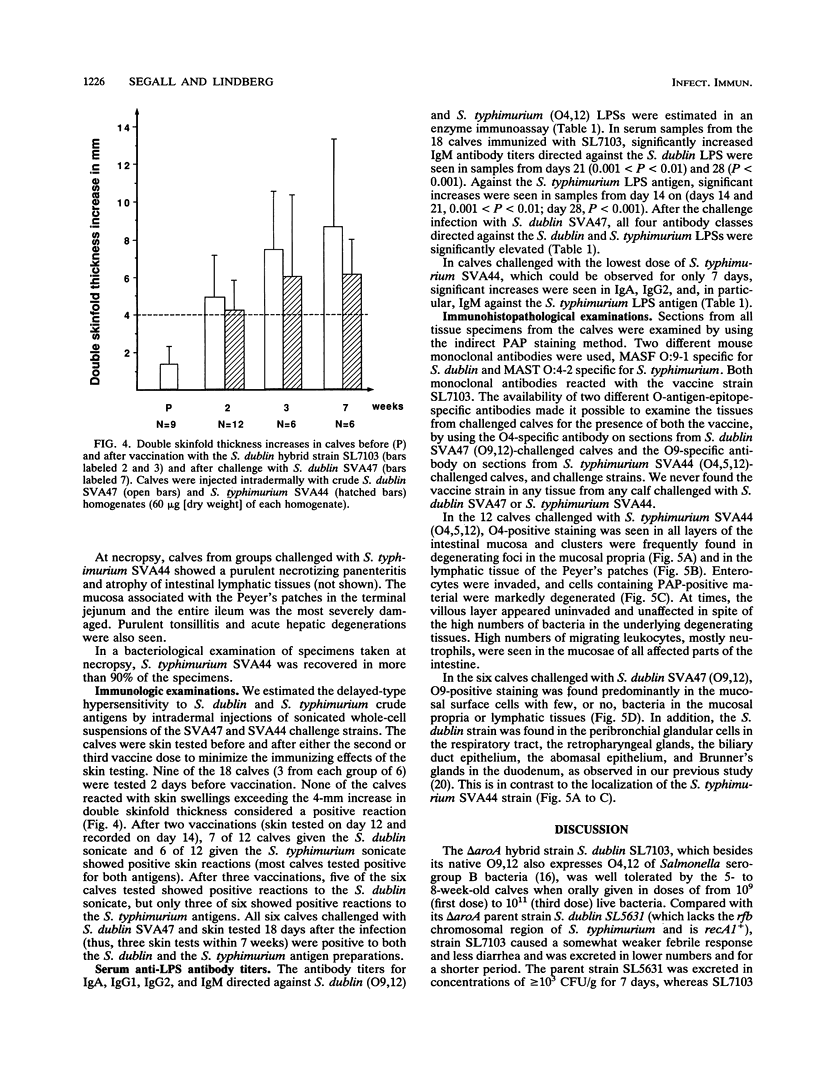
Three groups of six calves each, 5 to 7 weeks old, were orally vaccinated with the live aromatic-dependent delta aroA Salmonella dublin (O9,12) hybrid strain SL7103 with the O4,12-specifying rfb gene cluster from Salmonella typhimurium. SL7103 was given in three weekly doses, increasing from 2 x 10(9) to 1 x 10(11) bacteria per ml, was well tolerated, and caused mild, short-term temperature increases which diminished with each immunization. The strain was shed for up to 1 week. Strain SL7103 elicited significant (P < 0.001) and equal anti-S. dublin and -S. typhimurium lipopolysaccharide serum antibody responses and skin delayed-type hypersensitivity immune responses. Six vaccinated calves orally challenged with 10(10) CFU (equivalent to 1,000 50% lethal doses) of the virulent parent strain S. dublin SVA47 were protected and experienced only transient fever and mild mucoid diarrhea. However, six vaccinated calves orally challenged with 3 x 10(9) CFU and another six challenged with 3 x 10(8) CFU (equivalent to 1,000 50% lethal doses) of the virulent S. typhimurium SVA44 became bacteremic with a profuse hemorrhagic diarrhea and had to be sacrificed within 2 to 7 days. The results suggest that the S. typhimurium antilipopolysaccharide immunity was insufficient to provide a solid protective efficacy against oral S. typhimurium infection. The immunohistopathological examination revealed that S. typhimurium SVA44 could be found in all layers of the intestinal mucosa and the lymphatic tissues of the Peyer's patches. In contrast, S. dublin SVA47 was found predominantly in the columnar enterocytes of the jejunum and ileum and the follicle-associated epithelium over the Peyer's patches. In addition, SVA47 was found in the glandular tissues of the duodenal and tonsillar areas and in the lungs. This suggests that the S. typhimurium and S. dublin strains have different virulence traits determining their tissue localization and dissemination.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clarke R. C., Gyles C. L. Galactose epimeraseless mutants of Salmonella typhimurium as live vaccines for calves. Can J Vet Res. 1986 Apr;50(2):165–173. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke R. C., Gyles C. L. Vaccination of calves with a diaminopimelic acid mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. Can J Vet Res. 1987 Jan;51(1):32–38. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd, Kelly S. M. Salmonella typhimurium deletion mutants lacking adenylate cyclase and cyclic AMP receptor protein are avirulent and immunogenic. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3035–3043. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3035-3043.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):238–239. doi: 10.1038/291238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isibasi A., Ortiz V., Vargas M., Paniagua J., González C., Moreno J., Kumate J. Protection against Salmonella typhi infection in mice after immunization with outer membrane proteins isolated from Salmonella typhi 9,12,d, Vi. Infect Immun. 1988 Nov;56(11):2953–2959. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.11.2953-2959.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. N., Weintraub A., Lindberg A. A., Stocker B. A. Construction of Salmonella strains with both antigen O4 (of group B) and antigen O9 (of group D). J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1911–1915. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1911-1915.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusi N., Nurminen M., Saxén H., Mäkelä P. H. Immunization with major outer membrane protein (porin) preparations in experimental murine salmonellosis: effect of lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):328–332. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.328-332.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Segall T., Weintraub A., Stocker B. A. Antibody response and protection against challenge in mice vaccinated intraperitoneally with a live aroA O4-O9 hybrid Salmonella dublin strain. Infect Immun. 1993 Apr;61(4):1211–1221. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.4.1211-1221.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt F. F., Smith B. P., Reina-Guerra M., Habasha F., Johnson E. Relationship of cutaneous delayed hypersensitivity to protection from challenge exposure with Salmonella typhimurium in calves. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Jun;45(6):1081–1085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertsson J. A., Lindberg A. A., Hoiseth S., Stocker B. A. Salmonella typhimurium infection in calves: protection and survival of virulent challenge bacteria after immunization with live or inactivated vaccines. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):742–750. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.742-750.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall T., Lindberg A. A. Experimental oral Salmonella dublin infection in calves. A bacteriological and pathological study. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1991 May;38(3):169–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1991.tb00859.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall T., Lindberg A. A. Salmonella dublin experimental infection in calves: protection after oral immunization with an auxotrophic aroA live vaccine. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1991 Mar;38(2):142–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1991.tb00857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. P., Reina-Guerra M., Hoiseth S. K., Stocker B. A., Habasha F., Johnson E., Merritt F. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium as modified live vaccines for calves. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Jan;45(1):59–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. P., Reina-Guerra M., Stocker B. A., Hoiseth S. K., Johnson E. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella dublin as a parenteral modified live vaccine for calves. Am J Vet Res. 1984 Nov;45(11):2231–2235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocker B. A., Hoiseth S. K., Smith B. P. Aromatic-dependent "Salmonella sp." as live vaccine in mice and calves. Dev Biol Stand. 1983;53:47–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub A., Johnson B. N., Stocker B. A., Lindberg A. A. Structural and immunochemical studies of the lipopolysaccharides of Salmonella strains with both antigen O4 and antigen O9. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1916–1922. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1916-1922.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]