Abstract
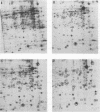
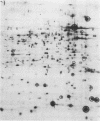
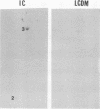
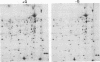
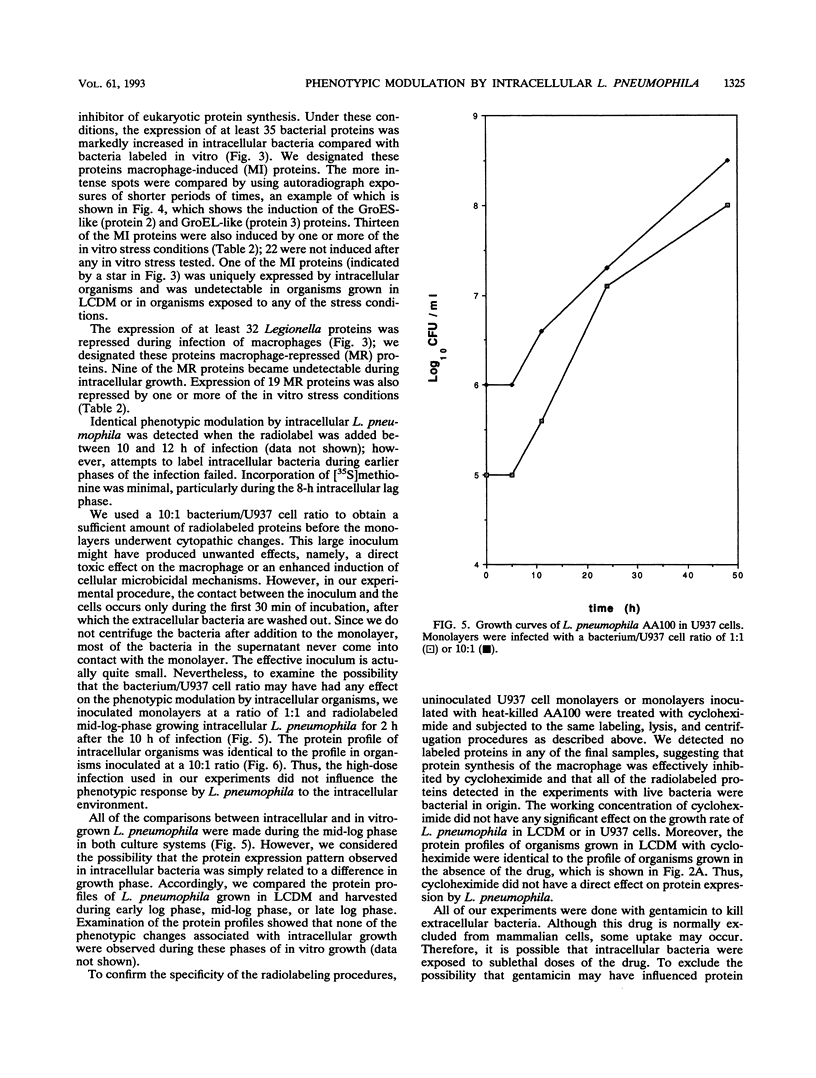
Since many pathogenic bacteria manifest a coordinate regulation of gene expression in response to different environmental stimuli, we examined the phenotypic response of Legionella pneumophila to infection of macrophage-like U937 cells. Intracellular L. pneumophila was radiolabeled, and cell extracts were subjected to two-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. At least 35 Legionella proteins were selectively induced during infection of macrophages, and one of these proteins was not detected in organisms grown in vitro. Expression of at least 32 proteins was selectively repressed during infection of macrophages, and 9 of these proteins were undetectable in intracellularly grown organisms. Thirteen of the macrophage-induced proteins were also induced by one or more of several stress conditions in vitro, and two of these proteins were the heat shock GroEL- and GroES-like proteins. Nineteen of the macrophage-repressed proteins were also repressed by one or more of the stress conditions in vitro. Our data showed that intracellular L. pneumophila manifested a phenotypic modulation and a global stress response to the intracellular environment of the macrophage. The data suggested that multiple regulons are involved in this modulation, which may contribute to the survival of L. pneumophila within alveolar macrophages.
Full text
PDF
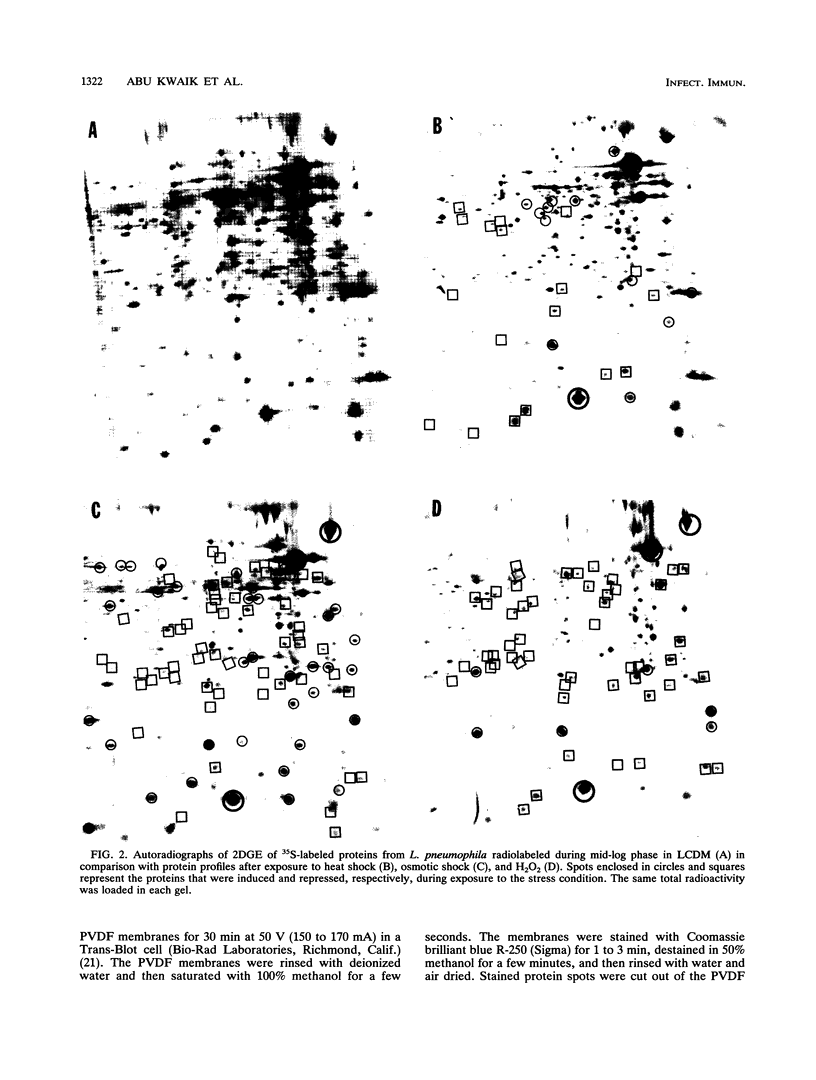






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blander S. J., Horwitz M. A. Vaccination with the major secretory protein of Legionella pneumophila induces cell-mediated and protective immunity in a guinea pig model of Legionnaires' disease. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):691–705. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier N. A., Heffron F. Induction of Salmonella stress proteins upon infection of macrophages. Science. 1990 May 11;248(4956):730–732. doi: 10.1126/science.1970672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciotto N., Eisenstein B. I., Engleberg N. C., Shuman H. Genetics and molecular pathogenesis of Legionella pneumophila, an intracellular parasite of macrophages. Mol Biol Med. 1989 Oct;6(5):409–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A., Iglewski B. H. Purification and characterization of an extracellular protease of Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):736–743. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.736-743.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H., Brenner D. J., Moss C. W., Steigerwalt A. G., Francis E. M., George W. L. Legionella wadsworthii species nova: a cause of human pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Dec;97(6):809–813. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-6-809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein P. H. Comparative study of selective media for isolation of Legionella pneumophila from potable water. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):697–699. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.697-699.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Gorman G. W., Langford N. C., Rasheed J. K., Mackel D. C., Baine W. B. Charcoal-yeast extract agar: primary isolation medium for Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Oct;10(4):437–441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.4.437-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. S., Shotts E. B., Jr, Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Martin W. T. Proliferation of Legionella pneumophila as an intracellular parasite of the ciliated protozoan Tetrahymena pyriformis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Mar;47(3):467–471. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.3.467-471.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields P. I., Groisman E. A., Heffron F. A Salmonella locus that controls resistance to microbicidal proteins from phagocytic cells. Science. 1989 Feb 24;243(4894 Pt 1):1059–1062. doi: 10.1126/science.2646710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Cherry W. B., Orrison L. H., Thacker L. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila from nonepidemic-related aquatic habitats. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1239–1242. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1239-1242.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman E. A., Chiao E., Lipps C. J., Heffron F. Salmonella typhimurium phoP virulence gene is a transcriptional regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7077–7081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen K., Bangsborg J. M., Fjordvang H., Pedersen N. S., Hindersson P. Immunochemical characterization of and isolation of the gene for a Borrelia burgdorferi immunodominant 60-kilodalton antigen common to a wide range of bacteria. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2047–2053. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2047-2053.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Butler C. A., Quinn F. D. Cloning and temperature-dependent expression in Escherichia coli of a Legionella pneumophila gene coding for a genus-common 60-kilodalton antigen. Infect Immun. 1989 Jun;57(6):1731–1739. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.6.1731-1739.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. S., Houston L., Butler C. A. Legionella pneumophila htpAB heat shock operon: nucleotide sequence and expression of the 60-kilodalton antigen in L. pneumophila-infected HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3380–3387. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3380-3387.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Characterization of avirulent mutant Legionella pneumophila that survive but do not multiply within human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1310–1328. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Formation of a novel phagosome by the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1319–1331. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Maxfield F. R. Legionella pneumophila inhibits acidification of its phagosome in human monocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):1936–1943. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. The Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) inhibits phagosome-lysosome fusion in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2108–2126. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lema M. W., Brown A., Butler C. A., Hoffman P. S. Heat-shock response in Legionella pneumophila. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Oct;34(10):1148–1153. doi: 10.1139/m88-202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Mekalanos J. J., Falkow S. Coordinate regulation and sensory transduction in the control of bacterial virulence. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):916–922. doi: 10.1126/science.2537530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. I. PhoP/PhoQ: macrophage-specific modulators of Salmonella virulence? Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2073–2078. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz C. S., Chen J. X., Shuman H. A. Isolation and characterization of auxotrophic mutants of Legionella pneumophila that fail to multiply in human monocytes. Infect Immun. 1988 Jun;56(6):1449–1455. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.6.1449-1455.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. P., Belland R. J., Lyng K., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydial disease pathogenesis. The 57-kD chlamydial hypersensitivity antigen is a stress response protein. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1271–1283. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyström T., Neidhardt F. C. Cloning, mapping and nucleotide sequencing of a gene encoding a universal stress protein in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(21):3187–3198. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne N. R., Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of Legionella pneumophila is mediated by human monocyte complement receptors. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1377–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman E., Jiwa A. H., Engleberg N. C., Eisenstein B. I. Growth of Legionella pneumophila in a human macrophage-like (U937) cell line. Microb Pathog. 1988 Aug;5(2):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinnan G. V., Schooley R., Dolin R., Ennis F. A., Gross P., Gwaltney J. M. Serologic responses and systemic reactions in adults after vaccination with monovalent A/USSR/77 and trivalent A/USSR/77, A/Texas/77, B/Hong Kong/72 influenza vaccines. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):748–757. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowbotham T. J. Current views on the relationships between amoebae, legionellae and man. Isr J Med Sci. 1986 Sep;22(9):678–689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanBogelen R. A., Neidhardt F. C. Ribosomes as sensors of heat and cold shock in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5589–5593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodkin M. H., Williams J. C. A heat shock operon in Coxiella burnetti produces a major antigen homologous to a protein in both mycobacteria and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1227–1234. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1227-1234.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren W. J., Miller R. D. Growth of Legionnaires disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) in chemically defined medium. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.50-55.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr Legionnaires disease: historical perspective. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jan;1(1):60–81. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.1.60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D., Lathigra R., Hendrix R., Sweetser D., Young R. A. Stress proteins are immune targets in leprosy and tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4267–4270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]