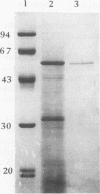
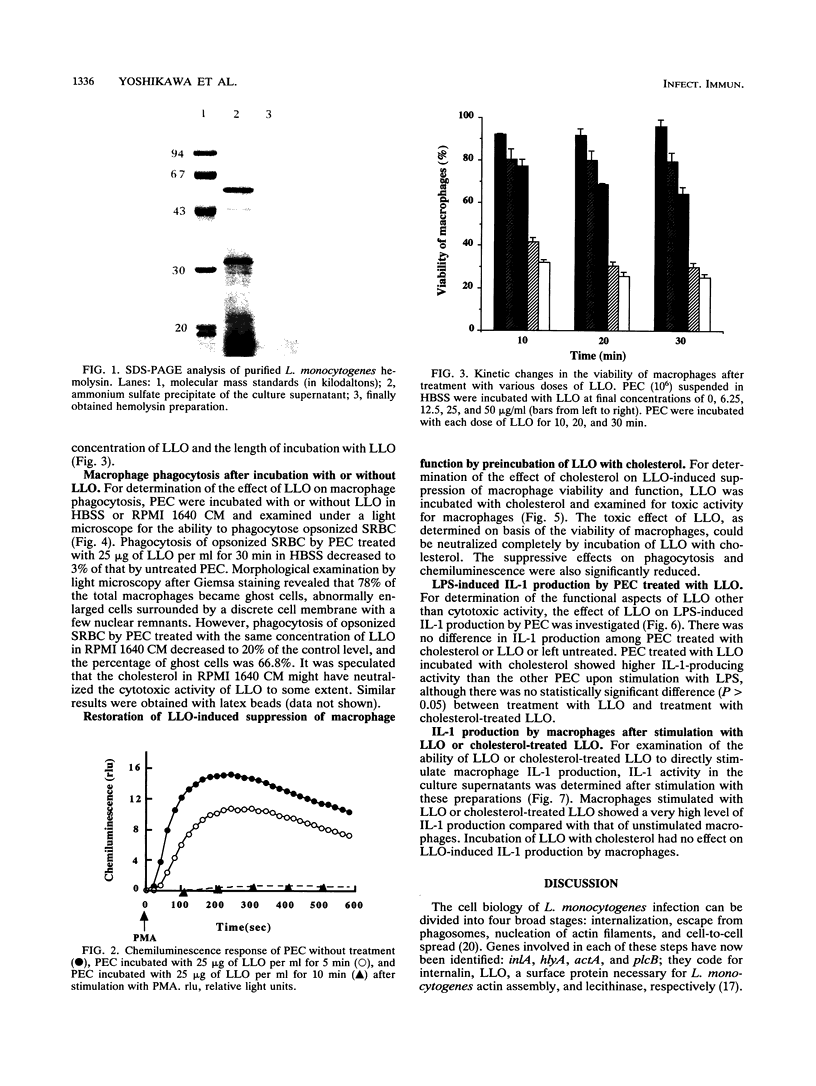
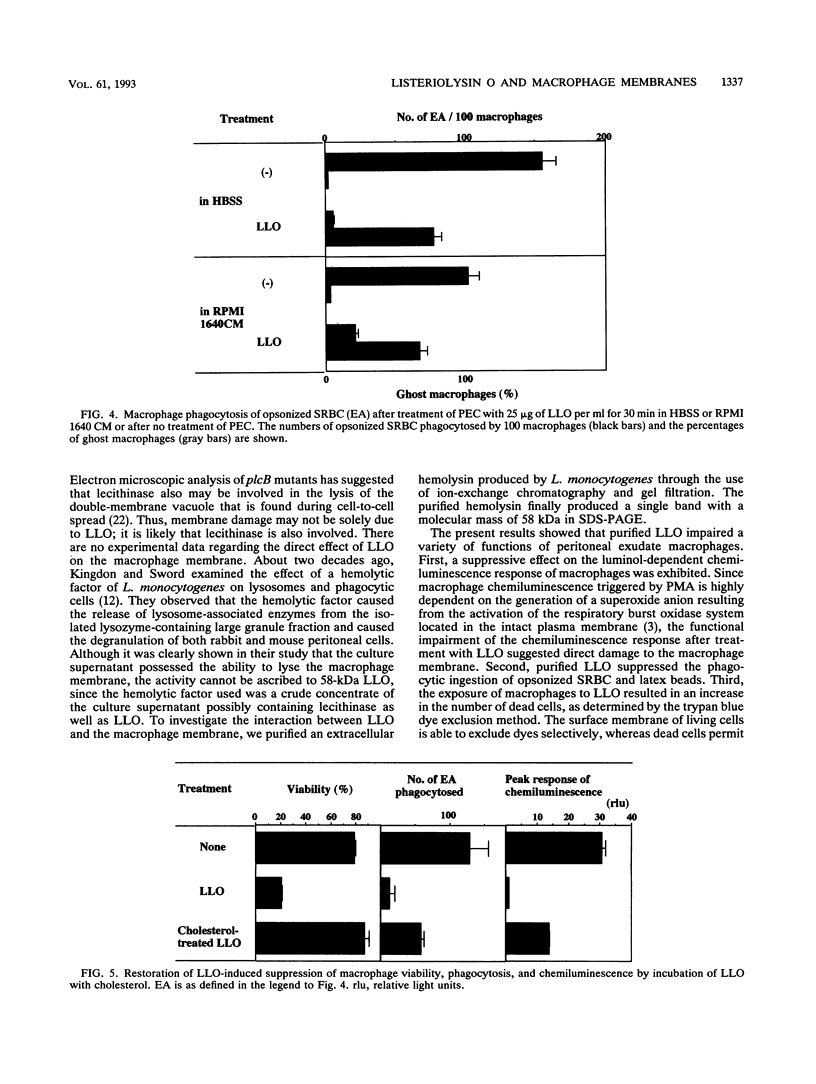
Abstract
To obtain some insight into the interaction between listeriolysin O (LLO) and the macrophage membrane, we examined the effect of purified Listeria monocytogenes hemolysin on the viability and functions of mouse peritoneal exudate macrophages. The study showed that purified LLO impaired a variety of functions of the macrophages. First, it suppressed the luminol-dependent chemiluminescence response of macrophages. Second, it suppressed the phagocytic ingestion of opsonized sheep erythrocytes and latex beads. Third, exposure of macrophages to LLO resulted in an increase in dead cells, as determined by the trypan blue dye exclusion method. An interesting observation of this study is that the LLO-induced production of interleukin-1 from macrophages could not be blocked by preincubation with cholesterol, while the membrane-damaging ability could be blocked by cholesterol. The dissociation of the blocking effects of cholesterol suggests that the interleukin-1-inducing ability of LLO may be distinct from its membrane-damaging ability.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alouf J. E., Geoffroy C. Production, purification, and assay of streptolysin O. Methods Enzymol. 1988;165:52–59. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(88)65011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielecki J., Youngman P., Connelly P., Portnoy D. A. Bacillus subtilis expressing a haemolysin gene from Listeria monocytogenes can grow in mammalian cells. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):175–176. doi: 10.1038/345175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A. The human neutrophil respiratory burst oxidase. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jun;161(6):1140–1147. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.6.1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura T., Suzuki T., Mitsuyama M., Saito H., Nomoto K. Antibody-independent protection against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in mice after treatment with a homologous strain vaccine. J Med Microbiol. 1989 Feb;28(2):101–108. doi: 10.1099/00222615-28-2-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Sansonetti P. Transposon mutagenesis as a tool to study the role of hemolysin in the virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):50–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.50-55.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy C., Gaillard J. L., Alouf J. E., Berche P. Purification, characterization, and toxicity of the sulfhydryl-activated hemolysin listeriolysin O from Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1987 Jul;55(7):1641–1646. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.7.1641-1646.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. L., Killinger A. H. Listeria monocytogenes and listeric infections. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Jun;30(2):309–382. doi: 10.1128/br.30.2.309-382.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of microorganisms. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Jan-Feb;4(1):104–123. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.1.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Mitsuyama M., Muramori K., Tsukada H., Nomoto K. Interleukin-1-induced promotion of T-cell differentiation in mice immunized with killed Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3973–3979. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3973-3979.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINS E. M., NJOKU-OBI A. N., ADAMS E. W. PURIFICATION OF THE SOLUBLE HEMOLYSINS OF LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Aug;88:418–424. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.2.418-424.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingdon G. C., Sword C. P. Biochemical and Immunological Effects of Listeria monocytogenes Hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1970 Apr;1(4):363–372. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.4.363-372.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingdon G. C., Sword C. P. Effects of Listeria monocytogenes Hemolysin on Phagocytic Cells and Lysosomes. Infect Immun. 1970 Apr;1(4):356–362. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.4.356-362.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengaud J., Vicente M. F., Chenevert J., Pereira J. M., Geoffroy C., Gicquel-Sanzey B., Baquero F., Perez-Diaz J. C., Cossart P. Expression in Escherichia coli and sequence analysis of the listeriolysin O determinant of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1988 Apr;56(4):766–772. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.4.766-772.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuyama M., Igarashi K., Kawamura I., Ohmori T., Nomoto K. Difference in the induction of macrophage interleukin-1 production between viable and killed cells of Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1990 May;58(5):1254–1260. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.5.1254-1260.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NJOKU-OBI A. N., JENKINS E. M., NJOKU-OBI J. C., ADAMS J., COVINGTON V. PRODUCTION AND NATURE OF LISTERIA MONOCYTOGENES HEMOLYSINS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:1–8. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.1-8.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Chakraborty T., Goebel W., Cossart P. Molecular determinants of Listeria monocytogenes pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1263–1267. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1263-1267.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Jacks P. S., Hinrichs D. J. Role of hemolysin for the intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuchat A., Swaminathan B., Broome C. V. Epidemiology of human listeriosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Apr;4(2):169–183. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Portnoy D. A. Actin filaments and the growth, movement, and spread of the intracellular bacterial parasite, Listeria monocytogenes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;109(4 Pt 1):1597–1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.4.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada H., Kawamura I., Fujimura T., Igarashi K., Arakawa M., Mitsuyama M. Induction of macrophage interleukin-1 production by Listeria monocytogenes hemolysin. Cell Immunol. 1992 Mar;140(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90173-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Boland J. A., Kocks C., Dramsi S., Ohayon H., Geoffroy C., Mengaud J., Cossart P. Nucleotide sequence of the lecithinase operon of Listeria monocytogenes and possible role of lecithinase in cell-to-cell spread. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):219–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.219-230.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]