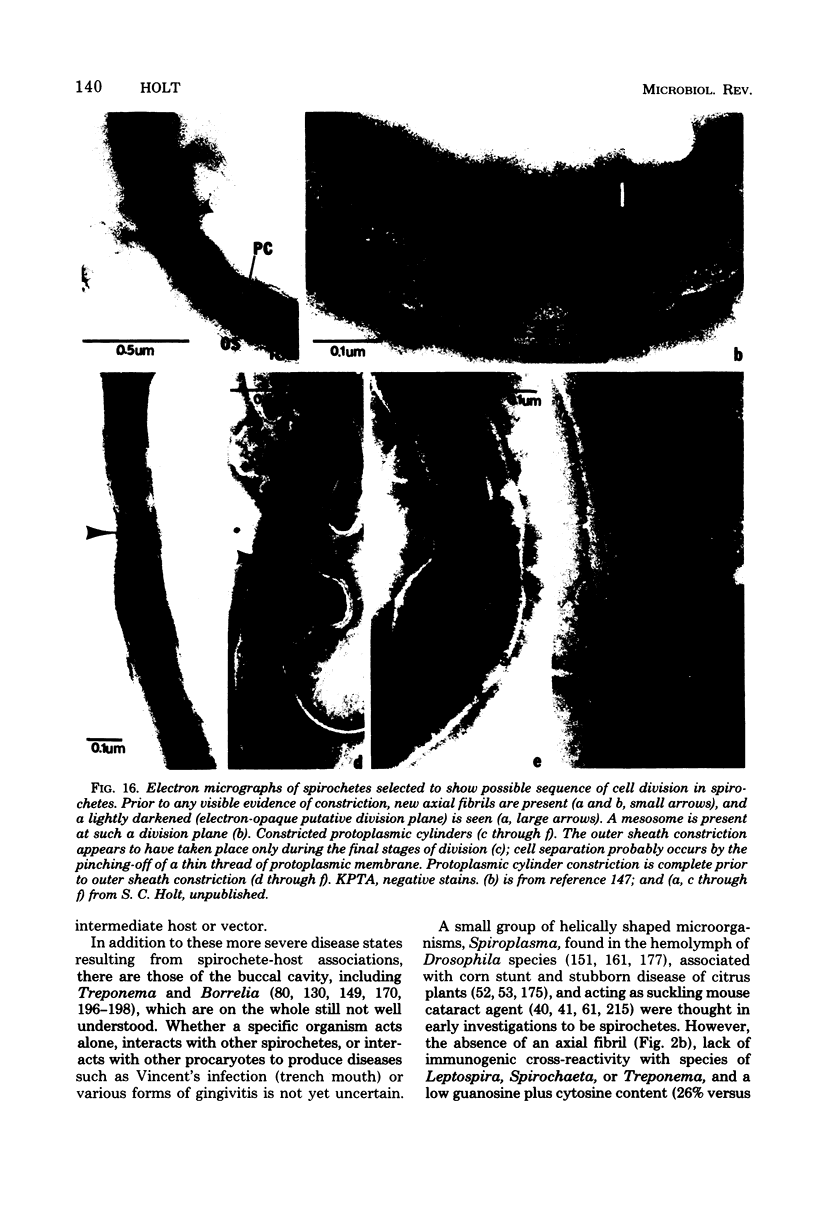
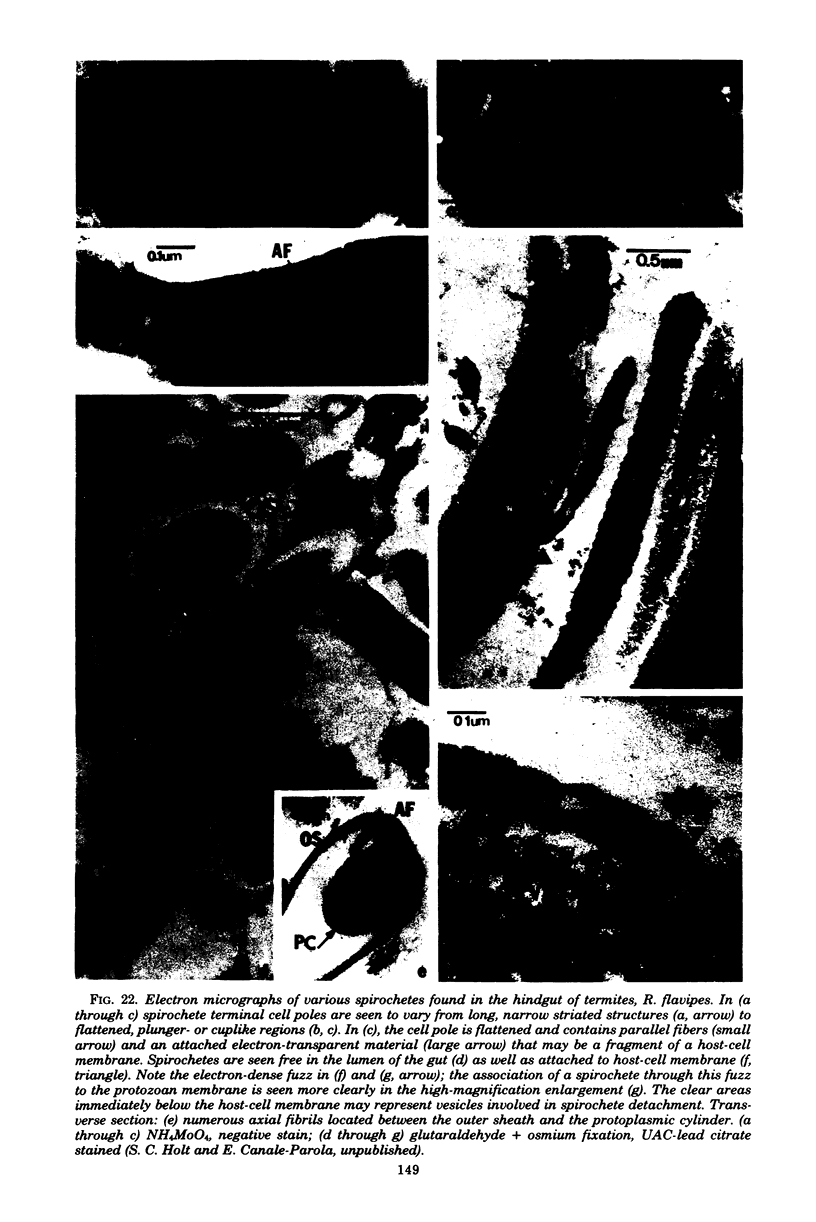
Full text
PDF












































Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAM D., KOFFLER H. IN VITRO FORMATION OF FLAGELLA-LIKE FILAMENTS AND OTHER STRUCTURES FROM FLAGELLIN. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jul;9:168–185. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abram D., Mitchen J. R., Koffler H., Vatter A. E. Differentiation within the bacterial flagellum and isolation of the proximal hook. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):250–261. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.250-261.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abram D., Vatter A. E., Koffler H. Attachment and structural features of flagella of certain bacilli. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2045–2068. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2045-2068.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams G. A., Tornabene T. G., Yaguchi M. Cell wall lipopolysaccharides from Neisseria catarrhalis. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Apr;15(4):365–374. doi: 10.1139/m69-067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aeschlimann A., Geigy R., Hecker H. Observations of the Ultrastructure of Various Borrelia species (blood and tissue forms). Acta Trop. 1968;25(2):176–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. L., Johnson R. C. Electron microscopy of immune disruption of leptospires: action of complement and lysozyme. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2293–2309. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2293-2309.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auran N. E., Johnson R. C., Ritzi D. M. Isolation of the outer sheath of Leptospira and its immunogenic properties in hamsters. Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):968–975. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.968-975.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azuma I., Taniyama T., Yamamura Y., Yanagihara Y., Hattori Y. Chemical studies on the cell walls of Leptorspira biflexa strain Urawa and Treponema pallidum strain Reiter. Jpn J Microbiol. 1975 Feb;19(1):45–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1975.tb00846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BABUDIERI B. Die Feinstruktur der Leptospiren und anderer Spirochäten. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1958 Dec;173(5-6):386–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BABUDIERI B. [The cell structure and serology of Leptospira]. Ergeb Mikrobiol Immunitatsforsch Exp Ther. 1960;33:259–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P. The isolation and characteristics of a spirochete from the bovine rumen. J Bacteriol. 1952 Sep;64(3):325–335. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.3.325-335.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. F., Loosli C. G. The ultrastructure of encapsulated Diplococcus pneumoniae type 1 before and after exposure to type specific antibody. Lab Invest. 1966 Apr;15(4):716–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C. How spirochetes may swim. J Theor Biol. 1976 Feb;56(2):269–273. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(76)80074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bharier M. A., Eiserling F. A., Rittenberg S. C. Eletron microscopic observations on the structure of Treponema zuelzerae and its axial filaments. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):413–421. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.413-421.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bharier M. A., Rittenberg S. C. Chemistry of axial filaments of Treponema zuezerae. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):422–429. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.422-429.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bharier M. A., Rittenberg S. C. Immobilization effects of anticell and antiaxial filament sera on Treponema zuelzerae. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):430–437. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.430-437.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bharier M., Allis D. Purification and characterization of axial filaments from Treponema phagedenis biotype reiterii (the Reiter treponeme). J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1434–1442. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1434-1442.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch-Andersen A., Hovind Hougen K., Borg-Petersen C. Electron microscopy of Leptospira. 1. Leptospira strain Pomona. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Dec;81(6):665–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bladen H. A., Hampp E. G. Ultrastructure of Treponema microdentium and Borrelia vincentii. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1180–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1180-1191.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore R. P., Canale-Parola E. Morphological and ecological characteristics of Spirochaeta plicatilis. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973;89(4):273–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00408895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore W. F., Taylor D. J. An agent possibly associated with swine dysentery. Vet Rec. 1970 Jul 11;87(2):59–60. doi: 10.1136/vr.87.2.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanquet P. R. Ultrahistochemical study on the ruthenium red surface staining. I. Processes which give rise to electron-dense marker. Histochemistry. 1976 May 28;47(2):63–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00492555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanquet P. R. Ultrahistochemical study on the ruthenium red surface staining. II. Nature and affinity of the electron dense marker. Histochemistry. 1976 Jun 28;47(3):175–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00489961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloodgood R. A., Fitzharris T. P. Specific associations of prokaryotes with symbiotic flagellate protozoa from the hindgut of the termite Reticulitermes and the wood-eating roack Cryptocercus. Cytobios. 1976;17(66):103–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Shortening of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pili after RNA-phage adsorption. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Sep;72(2):303–319. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-2-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breznak J. A., Brill W. J., Mertins J. W., Coppel H. C. Nitrogen fixation in termites. Nature. 1973 Aug 31;244(5418):577–580. doi: 10.1038/244577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breznak J. A. Symbiotic relationships between termites and their intestinal microbiota. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1975;(29):559–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIANSEN A. H. Studies on the antigenic structure of Treponema pallidum. 2. Isolation and purification of polysaccharides from Reiter's apathogenic strain. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1962;56:166–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK H. F. SUCKLING MOUSE CATARACT AGENT. J Infect Dis. 1964 Dec;114:476–487. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.5.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CZEKALOWSKI J. W., EAVES G. The structure of leptospirae as revealed by electron microscopy. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Jan-Apr;69(1-2):129–132. doi: 10.1002/path.1700690118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CZEKALOWSKI J. W. Electron microscope study of Leptospira. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1963;29:29–34. doi: 10.1007/BF02046036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canale-Parola E., Udris Z., Mandel M. The classification of free-living spirochetes. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968;63(4):385–397. doi: 10.1007/BF00412124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A., Faine S. Electron-microscopic evidence for reactions of axial filaments of Leptospira with IgM and IgG antibodies. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(4):571–577. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. Y., Brown D. M., Glazer A. N. Characterization of the subunits of the flagella of Proteus vulgaris. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5196–5200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Costerton J. W. Localization of alkaline phosphatase in three gram-negative rumen bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):424–440. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.424-440.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Ingram J. M., Costerton J. W. Alkaline phosphatase localization and spheroplast formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Dec;16(12):1319–1324. doi: 10.1139/m70-218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark H. F., Karzon D. T. Growth curve studies of the suckling mouse cataract agent in individual compartments of the eye. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jul;131(3):693–696. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Bazire G., London J. Basal organelles of bacterial flagella. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):458–465. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.458-465.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Ingram J. M., Cheng K. J. Structure and function of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):87–110. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.87-110.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D. Shape of Treponema pallidum. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):943–944. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.943-944.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'ALESSANDRO G., DEL CARPIO C. A lipopolysaccharide antigen of the Treponema. Nature. 1958 Apr 5;181(4614):991–992. doi: 10.1038/181991b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. P., Mulcahy D., Takeuchi A., Savage D. C. Location and description of spiral-shaped microorganisms in the normal rat cecum. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):184–192. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.184-192.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. E., Worley J. F., Whitcomb R. F., Ishijima T., Steere R. L. Helical filaments produced by a Mycoplasma-like organism associated with corn stunt disease. Science. 1972 May 5;176(4034):521–523. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4034.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Adler J. Fine structure and isolation of the hook-basal body complex of flagella from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):384–395. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.384-395.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drusin L. M., Rouiller G. C., Chapman G. B. Electron microscopy of Treponema pallidum occurring in a human primary lesion. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):951–955. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.951-955.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elizan T. S., Fabiyi A., Clark H. F. Suckling mouse cataract agent (SMCA)-induced hydrocephalus and chronic brain infection in newborn rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Jan;139(1):51–55. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Morowitz H. J. Characterization of the plasma membrane of Mycoplasma laidlawii. IV. Structure and composition of membrane and aggregated components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 29;150(3):385–396. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandsen S. L., Chase D. G. Paneth cell function: phagocytosis and intracellular digestion of intestinal microorganisms. I. Hexamita muris. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Nov;41(3):296–318. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90071-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandsen S. L., Chase D. G. Paneth cell function: phagocytosis and intracellular digestion of intestinal microorganisms. II. Spiral microorganism. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Nov;41(3):319–333. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finco D. R., Low D. G. Endotoxin properties of Leptospira canicola. Am J Vet Res. 1967 Nov;28(127):1863–1872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox E. N. M proteins of group A streptococci. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):57–86. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.57-86.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINGER C. D. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF MURAMIC ACID FROM TWO SPIROCHAETES: BORRELIA DUTTONI AND LEPTOSPIRA BIFLEXA. Nature. 1963 Jul 13;199:159–159. doi: 10.1038/199159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gear E. V., Jr Dobbins WO 3d,+DOBBINS WO III: Rectal biopsy. A review of its diagnostic usefulness. Gastroenterology. 1968 Oct;55(4):522–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Houte J. V. Bacterial adherence in oral microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:19–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glauert A. M., Lucy J. A. Electron microscopy of lipids: effects of pH and fixatives on the appearance of a macromolecular assembly of lipid micelles in negatively stained preparations. J Microsc. 1969;89(1):1–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1969.tb00645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glock R. D., Harris D. L., Kluge J. P. Localization of spirochetes with the structural characteristics of Treponema hyodysenteriae in the lesions of swine dysentery. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):167–178. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.167-178.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glock R. D., Harris D. L. Swine dysentery. II. Characterization of lesions in pigs inoculated with Treponema hyodysenteriae in pure and mixed culture. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1972 Jan;67(1):65–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDY P. H., Jr, LEE Y. C., NELL E. E. USE OF A BACTERIAL CULTURE FILTRATE AS AN AID TO THE ISOLATION AND GROWTH OF ANEROBIC SPIROCHETES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1521–1525. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1521-1525.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDY P. H., Jr, NELL E. E. Study of the antigenic structure of Treponema pallidum by specific agglutination. Am J Hyg. 1957 Sep;66(2):160–172. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habeeb A. J., Hiramoto R. Reaction of proteins with glutaraldehyde. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):16–26. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90554-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamdy A. H., Glenn M. W. Transmission of swine dysentery with Treponema hyodysenteriae and Vibrio coli. Am J Vet Res. 1974 Jun;35(6):791–797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy P. H., Jr, Fredericks W. R., Nell E. E. Isolation and antigenic characteristics of axial filaments from the Reiter Treponeme. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):380–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.380-386.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland W. A., Lee F. D. Intestinal spirochaetosis. Br Med J. 1967 Sep 16;3(5567):718–719. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5567.718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. L., Glock R. D., Christensen C. R., Kinyon J. M. Inoculation of pigs with Treponema hyodysenteriae (new species) and reproduction f the disease. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1972 Jan;67(1):61–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. L., Kinyon J. M., Mullin M. T., Glock R. D. Isolation and propagation of spirochetes from the colon of swine dysentery affected pigs. Can J Comp Med. 1972 Jan;36(1):74–76. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppel L. A. Selective release of enzymes from bacteria. Science. 1967 Jun 16;156(3781):1451–1455. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3781.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollande A., Gharagozlou I., Grassé P. P. Morphologie infrastructurale de Pillotina calotermitidis nov. gen., nov. sp., Spirochaetale de l'intestin de Calotermes praecox. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1967 Oct 30;265(18):1309–1312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C., Canale-Parola E. Fine structure of Spirochaeta stenostrepta, a free-living, anaerobic spirochete. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):822–835. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.822-835.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougen K. H., Birch-Andersen A. Electron microscopy of endoflagella and microtubules in Treponema reiter. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(1):37–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougen K. H. Electron microscopy of Borrelia merionesi and Borrelia recurrentis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Dec;82(6):799–809. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougen K. H. Further observations on the ultrastructure of Treponema pallidum nichols. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(2):297–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougen K. H. The ultrastructure of cultivable treponemes. 1. Treponema phagedenis, Treponema vincentii and Treponema refringens. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Jun;82(3):329–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougen K. H. The ultrastructure of cultivable treponemes. 2. Treponema calligyrum, Treponema minutum and Treponema microdentium. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Aug;82(4):495–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougen K. H. The ultrastructure of cultivable treponemes. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Apr;83(2):91–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovind-Hougen K., Birch-Andersen A., Jensen H. J. Ultrastructure of cells of Treponema pertenue obtained from experimentally infected hamsters. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1976 Apr;84(2):101–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1976.tb01909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovind-Hougen K. Determination by means of electron microscopy of morphological criteria of value for classification of some spirochetes, in particular treponemes. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1976;(255):1–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R., Olander H. J., Williams C. B. Swine dysentery: pathogenicity of Treponema hyodysenteriae. Am J Vet Res. 1975 Jul;36(7):971–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino T. Genetics and chemistry of bacterial flagella. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Dec;33(4):454–475. doi: 10.1128/br.33.4.454-475.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. W., Zey P. N. Ultrastructure of lipopolysaccharide isolated from Treponema pallidum. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):838–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.838-844.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S., Black S. H. Ultrastructure of Treponema pallidum Nichols following lysis by physical and chemical methods. I. Envelope, wall, membrane and fibrils. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;76(4):308–324. doi: 10.1007/BF00408528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S., Black S. H. Ultrastructure of Treponema pallidum Nichols following lysis by physical and chemical methods. II. Axial filaments. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;76(4):325–340. doi: 10.1007/BF00408529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jepsen O. B., Hougen K. H., Birch-Andersen A. Electron microscopy of treponema pallidum Nichols. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;74(2):241–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb03477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Ritzi D. M., Livermore B. P. Outer envelope of virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):291–295. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.291-295.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Wachter M. S., Ritzi D. M. Treponeme outer cell envelope: solubilization and reaggregation. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):249–258. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.249-258.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. M., Zeigler J. A., Jones R. H. Experimental syphilis vaccines in rabbits. I. Differential protection with an adjuvant spectrum. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Feb;52(1):9–17. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. H., Nevin T. A., Guest W. J., Logan L. C. Lytic effect of trypsin, lysozyme, and complement on Treponema pallidum. Br J Vener Dis. 1968 Sep;44(3):193–200. doi: 10.1136/sti.44.3.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph R., Canale-Parola E. Axial fibrils of anaerobic spirochetes: ultrastructure and chemical characteristics. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;81(2):146–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00412325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph R., Holt S. C., Canale-Parola E. Peptidoglycan of free-living anaerobic spirochetes. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):426–435. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.426-435.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A., SECHAUD J. Electron microscope study of DNA-containing plasms. II. Vegetative and mature phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Nov 25;4(6):671–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.6.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kats L. N., Konstantinova N. D., Anan'in V. V. Nekotorye osobennosti submikroskopicheskoi struktury tsitoplazmaticheskogo tsilindra u leptospir. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1968 Mar;45(3):64–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingmüller G., Ishibashi Y., Radke K. Der elektronenmikroskopische Aufbau des Treponema pallidum. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol. 1968;233(2):197–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Ensign J. C. Isolation and chemical structure of the peptidoglycan of Spirillum serpens cell walls. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jan;95(1):201–210. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.1.201-210.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo E., Ueta N. Composition of fatty acids and carbohydrates in Leptospira. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):459–467. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.459-467.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LISTGARTEN M. A., SOCRANSKY S. S. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY AS AN AID IN THE TAXONOMIC DIFFERENTIATION OF ORAL SPIROCHETES. Arch Oral Biol. 1965 Jan-Feb;10:127–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(65)90064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LISTGARTEN M. A., SOCRANSKY S. S. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF AXIAL FIBRILS, OUTER ENVELOPE, AND CELL DIVISION OF CERTAIN ORAL SPIROCHETES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1087–1103. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1087-1103.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauderdale V., Goldman J. N. Serial ultrathin sectioning demonstrating the intracellularity of T. Pallidum. An electron microscopic study. Br J Vener Dis. 1972 Apr;48(2):87–96. doi: 10.1136/sti.48.2.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach W. D., Lee A., Stubbs R. P. Localization of bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract: a possible explanation of intestinal spirochaetosis. Infect Immun. 1973 Jun;7(6):961–972. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.6.961-972.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F. D., Kraszewski A., Gordon J., Howie J. G., McSeveney D., Harland W. A. Intestinal spirochaetosis. Gut. 1971 Feb;12(2):126–133. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.2.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz P. J., Schaechter M. The attachment of the bacterial chromosome to the cell membrane. Int Rev Cytol. 1975;41:1–28. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60964-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Importance of nutrition in gingival crevice microbial ecology. Periodontics. 1968 Dec;6(6):245–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J., Inniss W. E. Electron microscopic study of lipopolysaccharide from an avian strain of Escherichia coli O18. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):238–243. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.238-243.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):347–368. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELSTAM J. Preparation and properties of the mucopeptides of cell walls of gram-negative bacteria. Biochem J. 1962 Aug;84:294–299. doi: 10.1042/bj0840294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTINEZ R. J., ROSENBERG E. THERMAL TRANSITION OF SPIRILLUM SERPENS FLAGELLA. J Mol Biol. 1964 May;8:702–707. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLBERT E. Elektronenmikroskopischer Beitrag zur Morphologie des Bewegungsapparates von Borrelien. Z Hyg Infektionskr. 1956;142(3):203–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin H. H., Heilmann H. D., Preusser H. J. State of the rigid-layer in celll walls of some gram-negative Bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;83(4):332–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00425246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R. J., Brown D. M., Glazer A. N. The formation of bacterial flagella. 3. Characterization of the subunits of the flagella of Bacillus subtilis and Spirillum serpens. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 28;28(1):45–51. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80076-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller N. G., Wilson R. B. IN VIVO AND IN VITRO OBSERVATIONS OF LEPTOSPIRA POMONA BY ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Bacteriol. 1962 Sep;84(3):569–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.3.569-576.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudd S., Polevitzky K., Anderson T. F. Bacterial Morphology as shown by the Electron Microscope: V. Treponema pallidum, T. macrodentium and T. microdentium. J Bacteriol. 1943 Jul;46(1):15–24. doi: 10.1128/jb.46.1.15-24.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEVIN T. A., HAMPP E. G., DUEY B. V. Interaction between Borrelia vincetii and an oral diphtheroid. J Bacteriol. 1960 Dec;80:783–786. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.6.783-786.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauman R. K., Holt S. C., Cox C. D. Purification, ultrastructure, and composition of axial filaments from Leptospira. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):264–280. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.264-280.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oishi K., Poulson D. F. A virus associated with SR-spirochetes of Drosophila nebulosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1565–1572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovcinnikov N. M., Delectorskij V. V. Further study of ultrathin sections of Treponema pallidum under the electron microscope. Br J Vener Dis. 1968 Mar;44(1):1–34. doi: 10.1136/sti.44.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovcinnikov N. M., Delektorskij V. V. Further studies of the morphology of Treponema pallidum under the electron microscope. Br J Vener Dis. 1969 Jun;45(2):87–116. doi: 10.1136/sti.45.2.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovcinnikov N. M., Delektorskij V. V. Morphology of Treponema pallidum. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;35(2):223–229. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovcinnikov N. M., Delektorskij V. V. Treponema pallidum in nerve fibres. Br J Vener Dis. 1975 Feb;51(1):10–18. doi: 10.1136/sti.51.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovcinnikov N. M., Delektorskij V. V. Treponema pertenue under the electron microscope. Br J Vener Dis. 1970 Oct;46(5):349–379. doi: 10.1136/sti.46.5.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PILLOT J., DUPOUEY P. COMPOSITION ANTIG'ENIQUE DES TR'EPON'EMES. IV. SOLUBILISATION ET PURIFICATION DES ANTIG'ENES POLYOSIDIQUES DU TR'EPON'EME REITER. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Mar;106:456–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POULSON D. F., SAKAGUCHI B. Nature of "sex-ratio" agent in Drosophila. Science. 1961 May 12;133(3463):1489–1490. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3463.1489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROKOPCHUK A. IA, PROKOPCHUK V. A., BONDAROVICH A. G. Vozbuditeli kozhnykh i venericheskikh boleznèi v izobrazhenii elektronnogo mikroskopa. Vestn Venerol Dermatol. 1951 May-Jun;3:20–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palit A., Hamilton R. C., Gulasekharam J. Further studies on leptospiral genus-specific antigen: its ultrastructure and immunochemistry. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jun;82(2):223–236. doi: 10.1099/00221287-82-2-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate J. L., Ordal E. J. The fine structure of Chondrococcus columnaris. 3. The surface layers of Chondrococcus columnaris. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):37–51. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillot J., Ryter A. Structure des spirochètes. 1. Etude des generes Treponema, Borrelia et Leptospira au microscope electronique. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Jun;108(6):791–804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITCHIE A. E., ELLINGHAUSEN H. C. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF LEPTOSPIRES. I. ANATOMICAL FEATURES OF LEPTOSPIRA POMONA. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:223–233. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.223-233.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. D. The ultrastructure of cell membranes and their derivatives. Biochem Soc Symp. 1959;16:3–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichle R. E., Lewin R. A. Purification and structure of rhapidosomes. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Mar;14(3):211–213. doi: 10.1139/m68-036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. M., Simmons J. R. An agent possibly associated with swine dysentery. Vet Rec. 1970 Jan 3;86(1):22–22. doi: 10.1136/vr.86.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfelder G., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Composition of lipopolysaccharides from Myxococcus fulvus and other fruiting and non-fruiting myxobacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1974 May 15;44(2):411–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAKAGUCHI B., OISHI K., KOBAYASHI S. INTERFERENCE BETWEEN "SEX-RATIO" AGENTS OF DROSOPHILA WILLISTONI AND DROSOPHILA NEBULOSA. Science. 1965 Jan 8;147(3654):160–162. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3654.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNEIDER M. D. Isolation and chemical composition of complement-fixing antigens from leptospires. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Jan;85(1):32–37. doi: 10.3181/00379727-85-20776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHRICKER R. L., HANSON L. E. Precipitating antigens of leptospires. I. Chemical properties and serologic activity of soluble fractions of Leptospira pomona. Am J Vet Res. 1963 Jul;24:854–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMPSON C. F., WHITE F. H. Electron microscope studies and staining reactions of leptospires. J Infect Dis. 1961 Nov-Dec;109:243–250. doi: 10.1093/infdis/109.3.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOCRANSKY S. S., GIBBONS R. J., DALE A. C., BORTNICK L., ROSENTHAL E., MACDONALD J. B. The microbiota of the gingival crevice area of man. I. Total microscopic and viable counts and counts of specific organisms. Arch Oral Biol. 1963 May-Jun;8:275–280. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(63)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saheb S. A., Berthiaume L. Etude au microscope electronique d'un spirochète isolé du porc. Rev Can Biol. 1973 Mar;32(1):3–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salton M. R. Structure and function of bacterial cell membranes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:417–442. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.002221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Associations of indigenous microorganisms with gastrointestinal mucosal epithelia. Am J Clin Nutr. 1970 Nov;23(11):1495–1501. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/23.11.1495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., Blumershine R. V. Surface-surface associations in microbial communities populating epithelial habitats in the murine gastrointestinal ecosystem: scanning electron microscopy. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):240–250. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.240-250.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., Dubos R., Schaedler R. W. The gastrointestinal epithelium and its autochthonous bacterial flora. J Exp Med. 1968 Jan 1;127(1):67–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Localization of certain indigenous microorganisms on the ileal villi of rats. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1505–1506. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1505-1506.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., McAllister J. S., Davis C. P. Anaerobic bacteria on the mucosal epithelium of the murine large bowel. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):492–502. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.492-502.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Joseph R. A directly cross-linked L-ornithine-containing peptidoglycan in cell walls of Spirochaeta stenostrepta. FEBS Lett. 1973 Oct 1;36(1):83–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80342-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinagawa M., Yanagawa R. Isolation and characterization of a leptospiral type-specific antigen. Infect Immun. 1972 Jan;5(1):12–19. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.1.12-19.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. E., Arnott H. J. EPI- and endobiotic bacteria associated with Pyrsonympha vertens, a symbiotic protozoon of the termite Reticulitermes flavipes. Trans Am Microsc Soc. 1974 Apr;93(2):180–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. E., Buhse H. E., Jr, Stamler S. J. Possible formation and development of spirochaete attachment sites found on the surface of symbiotic polymastigote flagellates of the termite Reticulitermes flavipes. Biosystems. 1975 Nov;7(3-4):374–379. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(75)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S. Relationship of bacteria to the etiology of periodontal disease. J Dent Res. 1970 Mar-Apr;49(2):203–222. doi: 10.1177/00220345700490020401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer E. L., Roth I. L. The ultrastructure of the capsules of Diplococcus pneumoniae and Klebsiella pneumoniae stained with ruthenium red. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):21–31. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stead A., Main J. S., Ward M. E., Watt P. J. Studies on lipopolysaccharides isolated from strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):123–131. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Studies on gonococcus infection. I. Pili and zones of adhesion: their relation to gonococcal growth patterns. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):886–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes J. A., Kalan J. Intracellular Treponema pallidum in cells of a syphilitic lesion of the uterine cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1975 Jun 1;122(3):361–367. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(75)90185-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes J. A., Miller J. N. Intracellular location of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) in the rabbit testis. Infect Immun. 1971 Sep;4(3):307–314. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.3.307-314.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes J. A., Miller J. N. Ultrastructural studies of treponemes: location of axial filaments and some dimensions of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain), Treponema denticola, and Treponema reiteri. Infect Immun. 1973 Jan;7(1):100–110. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.1.100-110.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEYA K., MORI R., TODA T. Studies on the structure of Leptospira as revealed by the electron microscope. Jpn J Microbiol. 1957 Apr;1(2):99–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1957.tb00014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER T. B., HOLLANDER D. H. Cortisone in experimental syphilis; a preliminary note. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1950 Nov;87(5):505–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER T. B., HOLLANDER D. H. Studies on the mechanism of action of cortisone in experimental syphilis. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1954 Sep;38(5):371–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Zeller J. A. Scanning electron microscopic observations on the surface of the normal and spirochete-infested colonic mucosa of the rhesus monkey. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Aug;40(3):313–324. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi A., Zeller J. A. Ultrastructural identification of spirochetes and flagellated microbes at the brush border of the large intestinal epithelium of the rhesus monkey. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):1008–1018. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.1008-1018.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. J., Blakemore W. F. Spirochaetal invasion of the colonic epithelium in swine dysentery. Res Vet Sci. 1971 Mar;12(2):177–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. N., Hunter D., Clark A. An agent possibly associated with swine dysentery. Vet Rec. 1970 Feb 21;86(8):228–228. doi: 10.1136/vr.86.8.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Whitcomb R. F., Williamson D. L., Clark H. F. Suckling mouse cataract agent is a helical wall-free prokaryote (spiroplasma) pathogenic for vertebrates. Nature. 1976 Jan 15;259(5539):117–120. doi: 10.1038/259117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyson G. E. Distinctive renal lesion of spirochete-infected brine shrimp. J Bacteriol. 1974 Aug;119(2):629–631. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.2.629-631.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyson G. E. Phagocytosis and digestion of spirochetes by amebocytes of infected brine shrimp. J Invertebr Pathol. 1975 Jul;26(1):105–111. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(75)90175-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyson G. E. Tubular structures associated with intracytoplasmic spirochetes. Cell Tissue Res. 1975;158(3):333–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00223830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyson G. E. Ultrastructure of a spirochete found in tissues of the brine shrimp, Artemia salina. Arch Microbiol. 1974;99(4):281–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00696243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushijima T. Morphology and chemistry of the bacterial cell wall. 1. The location of mucopeptide in the cell wall of Bacteroides convexus and its chemical composition. Jpn J Microbiol. 1970 Jan;14(1):15–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1970.tb00487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENTINE R. C. Contrast enhancement in the electron microscopy of viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1961;8:287–318. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60688-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallejo M. T. Spirochaetales micro-organisms: an agent possibly associated with swine dysentery. Vet Rec. 1969 Nov 15;85(20):562–563. doi: 10.1136/vr.85.20.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk W. A. Cell wall lipopolysaccharides from xanthomonas species. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):39–42. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.39-42.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachter M. S., Johnson R. C. Treponeme outer envelope: chemical analysis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1976 Jan;151(1):97–100. doi: 10.3181/00379727-151-39151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wecke J., Bartunek J., Stüttgen G. Treponema pallidum in early syphilitic lesions in humans during high-dosage penicillin therapy. An electron microscopical study. Arch Dermatol Res. 1976 Nov 26;257(1):1–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00569109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand S. E., Strobel P. L., Glassman L. H. Electron microscopic anatomy of pathogenic Treponema pallidum. J Invest Dermatol. 1972 Apr;58(4):186–204. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12539907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagawa R., Faine S. Morphological and serological analysis of leptospiral structure. Nature. 1966 Aug 20;211(5051):823–826. doi: 10.1038/211823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara Y., Mifuchi I. Microfibers present in surface structure of Leptospira. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2403–2406. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2403-2406.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeigler J. A., Jones A. M., Jones R. H., Kubica K. M. Demonstration of extracellular material at the surface of pathogenic T. pallidum cells. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Feb;52(1):1–8. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeigler J. A., VanEseltine W. P. Isolation and chemical characterization of outer envelope of Leptospira pomona. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jul;21(7):1102–1112. doi: 10.1139/m75-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]