Abstract
Streptococcus mutans, a bioflim-forming gram-positive bacterium that resides in the human oral cavity, is considered to be the primary etiological agent of human dental caries. A cell-envelope stress sensing histidine kinase, LiaS, is considered to be important for expression of virulence factors such as glucan-binding protein C and mutacin production. In this communication, a liaS mutant was subjected to phenotypic microarray (PM) analysis of about 2000 phenotypes that includes utilization of various carbon, nitrogen, phosphate, and sulfur sources; osmolytes; metabolic inhibitors; and susceptibility to toxic compounds, including several types of antibiotics. Compared to the parental strain UA159, the liaS mutant strain (IBS148) was more tolerant to various inhibitors that target protein synthesis, DNA synthesis, and cell-wall biosynthesis. Some of the key findings of the PM analysis were confirmed in independent growth studies and by using antibiotic discs and E-test strips for susceptibility testing.
INTRODUCTION
The human pathogen Streptococcus mutans is a gram-positive bacterium with low G+C content that resides in the oral cavity, and is considered to be the primary etiological agent in the formation of dental caries (Loesche, 1986). This pathogen has evolved a biofilm lifestyle for survival in the dental plaque formed on the tooth surface (Hamada & Slade, 1980). S. mutans is also an inducer of infective endocarditis, with more than 14% of viridians streptococcus-induced endocarditis caused by S. mutans (Hamada & Slade, 1980; Loesche, 1986; Ullman et al., 1988). S. mutans uses sucrose, which is often present in the dietary carbohydrates, and converts it to sticky polysaccharides known as glucans (Banas & Vickerman, 2003; Kuramitsu, 1993). With the help of surface associated proteins that bind to glucan, S. mutans colonizes in the oral cavity through the formation of diverse, multispecies biofilms on the tooth surface, commonly known as dental plaque. This organism has developed several mechanisms to maintain its presence in the oral cavity (Carlsson & Hamilton, 1994) and to withstand drastic environmental changes (Ahn et al., 2006; Lemos et al., 2005).
Adaptive responses of bacteria to environmental changes, such as nutrient limitation, oxygen deprivation, antibiotic stress, and osmotic shock, are regulated by the so-called “two-component” signal transduction system (TCS) pathways (Dalton & Scott, 2004; El-Sharoud, 2005; Mascher et al., 2006; Verneuil et al., 2004). TCS typically consists of a membrane-bound sensor histidine kinase and a cytoplasmic response regulator, with a common biochemical mechanism involving phosphoryl group transfer between two distinct protein components. The sensor histidine kinase is composed of two components: an amino-terminal sensor/input domain that detects specific stimuli from the extracellular environment, and a cytoplasmic transmitter/histidine phosphotransferase domain that autophosphorylates at a specific histidine residue in response to stimulation of the sensor domain (Fabret et al., 1999; Mascher, 2006). The genome of S. mutans UA159 encodes a total of 14 TCS (Biswas et al., 2008), in addition to an orphan response regulator, CovR (Ajdic et al., 2002; Biswas & Biswas, 2006). These TCS are critical for survival under adverse conditions, as well as for regulation of virulence-associated factors of this pathogen (Biswas et al., 2007; Biswas et al., 2008; Biswas & Biswas, 2006; Idone et al., 2003).
LiaSR is a TCS that believed to be a part of a complex regulatory networks that monitors and responds to cell-envelope stress in Bacillus subtilis (Gardete et al., 2006; Jordan et al., 2006). Homologous systems such as VraSR in Staphylococcus aureus (Gardete et al., 2006; Jordan et al., 2006) and CesSR in Lactococcus lactis (Martinez et al., 2007) have been shown to function in a similar manner. LiaS and VraS both belong to a subclass of intramembrane-sensing histidine kinases (IM-HK) that are found exclusively in Gram-positive bacteria with a low G+C content (Firmicutes) (Mascher, 2006). Most IM-HKs sense various stresses to the cell envelope, and the gene targets of these TCSs are those that are involved in the maintenance of cell envelope integrity, mediation of antibiotic resistance, or detoxification processes (Mascher, 2006). In Streptococcus pneumoniae, a LiaSR homolog, TCS03 (SP0386 and SP0387), was expressed as a part of the vancomycin stress response of this microorganism (Haas et al., 2005).
LiaSR and VraSR are induced by various inhibitors of cell wall synthesis, but only VraSR has been shown to have a direct effect on the expression of genes related to peptidoglycan synthesis and antibiotic resistance (Butcher et al., 2007; Gardete et al., 2006). LiaSR is activated in the presence of sublethal concentrations of lipid II-interacting antibiotics, including bacitracin, vancomycin, ramoplanin, and nicin, and strongly induces expression of its own locus (Mascher et al., 2003; Mascher et al., 2004). LiaSR is also activated in the presence of cationic antimicrobial peptides, and, to a lesser extent, alkaline shock, detergents, ethanol, exposure to organic solvents, and secretion stress (Mascher, 2006). Additionally, it has also been reported that LiaSR regulates the expression of the lia operon during the transition from exponential growth phase to stationary phase, in the absence of exogenous cell-wall inhibitors and in the presence of an as yet unidentified stimulus (Jordan et al., 2007). VraSR of S. aureus is also activated in the presence of cell-wall inhibiting antibiotics, such as β-lactams (i.e. methicillin, oxacillin, etc) or glycopeptides (i.e. vancomycin); however, in contrast to LiaSR, activation of VraSR leads to the overexpression of a number of genes, including those associated with cell-wall biosynthesis and β-lactam antibiotic resistance (Gardete et al., 2006; Kuroda et al., 2003; Yin et al., 2006).
In S. mutans, SMU.486/SMU.487 locus, which was formerly known as RR11/HK11 (Li et al., 2002), encodes a TCS that is homologous to LiaSR (Biswas et al., 2008). A recent study in our laboratory with the sensor kinase LiaS of S. mutans UA159 revealed several novel findings. It was found that LiaS negatively regulates expression of gbpC gene, which encodes a glucan binding protein essential for biofilm-formation and cariogenecity (Biswas et al., 2008; Chong et al., 2008). LiaS was also shown to regulate expression and secretion of mutacin, a bacteriocin produced by S. mutans to suppress the growth of other competitor bacteria present in the dental plaque (Chong et al., 2008). In another study, Li et. al. (Li et al., 2002) showed that mutations in LiaS in S. mutans NG8, resulted in the formation of aberrant biofilms and an acid-sensitive phenotype. Therefore, LiaS appears to be very important for the pathogenesis of S. mutans.
To gain a complete understanding of the role of LiaS in S. mutans biology, physiological and phenotypical changes of a liaS mutant was compared to its isogenic parental strain using phenotypic microarray (PM) technology (Biswas & Biswas, 2005; Bochner et al., 2001; Zhou et al., 2003). PM is an integrated system of cellular assays for the simultaneous, high-throughput screening of a large number of phenotypes. Here we report the results of PM analysis performed with a liaS mutant in which we examined nearly 2000 cellular phenotypes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains and growth conditions
S. mutans strains, UA159 and IBS148 (Chong et al., 2008), were routinely grown in Todd-Hewitt medium (BBL; Becton Dickinson) supplemented with 0.2% yeast extract (THY) at 37°C. When necessary, spectinomycin (Sp, 300 μg·ml−1) was included in the growth medium. For some confirmatory growth experiments, S. mutans cultures were grown in THY containing 1% NaCl, 3% Na2SO4 or other chemicals as indicated.
PM analysis
PM analysis was performed using Biolog’s PM service facility. A total of 20 96-well PM plates constituting eight metabolic panels (PM1 to PM8); and 12 sensitivity panels (PM9 to PM20) were used in this study. To assess the altered phenotypes of the liaS mutant (IBS148), the growth was compared to its parent S. mutans UA159 strain. The basic growth media and the conditions for PM analysis were published previously (Biswas & Biswas, 2005; Bochner et al., 2001; Zhou et al., 2003). The inoculating cell densities used in this study were 1:13 dilution of 81% transmittance for both metabolic and sensitivity panels. PM analysis was conducted in duplicate after incubation of the strains at 37°C for 72 hours. An average height difference threshold of 50 for metabolic panels and a difference threshold of 60 for sensitivity panels were used to consider the difference between the two growths significant. The data were further confirmed by Student’s t test. The growth kinetics for UA159 was displayed as a red tracing, while IBS148 was displayed as a green tracing. The phenotypic changes listed in Table 1 were the changes detected in both PM runs (for a complete analysis, see Table S1 in the supplemental material). Standard PM testing protocols are described in http://www.biolog.com; the conditions are similar to those used here.
Table 1.
Growth advantages in the liaS mutant
| Mode of Action | Compounds |
|---|---|
| Cell wall synthesis | Fosphomycin, Glycine, Cefsulodin, Cetoperazone, cephalosporin, Cefoxitin, Moxalactam, Piperacillin, D-Cycloserine, Ceftriaxone |
| Membrane and ion channel | 4-Aminopyridine, Polymyxin B, Colistin |
| DNA damage | Semicarbazide hydrochloride, Hydroxylamine, Phleomycin |
| DNA synthesis | Nitrofurantoin, Bleomycin |
| DNA unwinding | Norfloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, Oxolinic acid, Lomefloxacin, Ofloxacin, Enoxacin, Nalidixic acid |
| DNA intercalator | 4-Hydroxycoumarin |
| DNA methyltransferase | 5-Azacytidine |
| Nucleic acid analogs | Cytosine arabinoside, 5-Fluorouracil, 5-Fluoro-5′-deoxyuridine |
| Folate antagonist | Sulfachloropyridazine, Sulfanilamide, Sulfamethazine, Sulfamethoxazole, Trimethoprim,, Sulfisoxazole |
| Ribonucletide reductase | Hydroxyurea |
| Thymidylate synthetase | Trifluorothymidine |
| t-RNA synthetase | L-Glutamic-g-Hydroxamate, Glycine Hydroxamate |
| Protein synthesis | Cinoxacin, Capreomycin, Chloramphenicol, Spectinomycin*, Streptomycin, Hygromycin, Geneticin (G418), Tetracycline, Gentamicin, Amikacin, Kanamycin, Minocycline |
| Osmotic sensitivity | 1% NaCl, 3% Sodium Sulfate |
| Oxidizing agents | D,L-ThiocticAcid |
| Respiration | Pentachlorophenol (PCP), Sorbic Acid, Sodium Caprylate, Cinnamic Acid, Sodium azide |
| Toxic anion | Sodium Nitrite, Sodium Metaborate, Sodium Tungstate, Sodium Arsenate, Sodium Dichromate |
| Toxic cation | Cesium chloride, Thallium (I) acetate, Chromium Chloride, Ferric Chloride, Aluminum Sulfate, Boric Acid, Potassium Tellurite, Sodium periodate, Potassium chromate, Sodium metasilicate |
| Chelating agents | Sodium pyrophosphate decahydrate, EGTA, EDTA, Fusaric Acid |
| Others* | 5-Fluoroorotic Acid, Chlorambucil, Thiosalicylate, Ethionamide, Patulin, Apramycin, Triclosan, Chloroxylenol, Aminotriazole, PMSF, Phenylarsine Oxide |
Mode of action includes anti-capsule, antimicrobial, fatty-acid synthesis, histidine biosynthesis, tyrosine phosphatase.
IBS148 contains a spectinomycin resistant gene.
Antibiotic susceptibility stress
Disk inhibition assays were performed as described previously to evaluate antibiotic susceptibility of the S. mutans liaS mutant (Biswas et al., 2008). Antibiotic disks (6 mm in diameter; Becton and Dickinson Laboratories) were placed on THY agar plates inoculated with the wild-type or the liaS mutant strains. Following overnight incubation under microaerophilic conditions, the zones of inhibition were measured. In addition, susceptibilities to selected antimicrobial agents were tested using E-test strips (AB-Biodisk, Solna, Sweden) on THY agar plates.
RESULTS
The LiaSR family of TCS is known to be involved in sensing cell envelope stress. However, the nature of the cell envelope stress and the genes under the control of the LiaSR regulon vary greatly depending on the organism. To better understand the role of LiaS in cell envelop stress response in S. mutans, we performed a complete PM analysis using a previously constructed liaS mutant strain, IBS148 (Chong et al., 2008). This strain was generated by replacing an internal part of the liaS orf with an aad gene encoding spectinomycin-resistance (Chong et al., 2008).
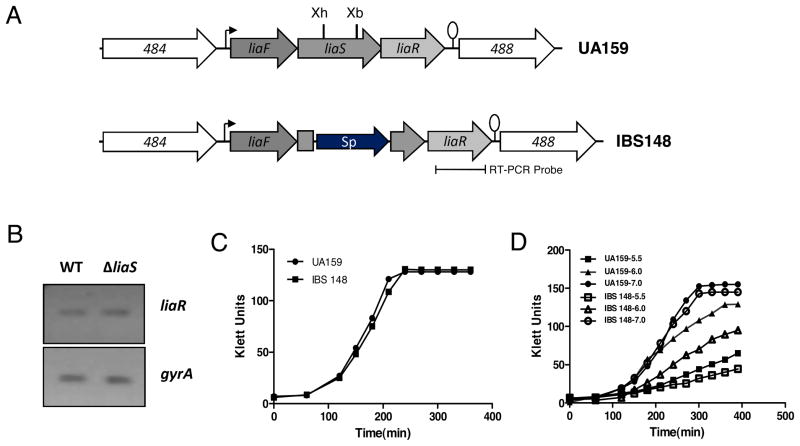
To ensure that the expression of the downstream liaR gene was unaffected in the liaS mutant IBS148, we performed a semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis. RNA was extracted from strains UA159 and IBS148 after growth reached mid-exponential phase. Semiquantitative RT-PCR was performed using liaR specific primers (Chong et al., 2008) to measure the level of liaR expression; the level of gyrA transcript was also measured to ensure equal amounts of RNA were being used in the RT-PCR assay. As expected, the level of liaR transcript in IBS148 was equivalent to that of the wild-type strain UA159 (Fig 1B) indicating that the insertion of the aad gene in liaS has little or no effect on the transcription of the downstream genes.
Figure 1.
A). Schematic diagram of the lia locus in the wild-type UA159 and the liaS mutant strains. Directions of transcription from the open reading frames (orf) are depicted by block arrows with the bent arrow and the lollipop showing putative promoter and rho-independent terminator, respectively. A part of the liaS orf is deleted by XhoI (Xh) and XbaI (Xb) digestion and replaced with a spectinomycin-resistant gene aad (Sp). B). The level of downstream liaR transcription is measured by semi-quantitative RT-PCR in the wild-type (UA159) and liaS mutant (IBS148). C). The growth kinetics of UA159 and IBS148 in rich medium (THY). D). Growth kinetics of UA159 and IBS148 in THY medium buffered with Citrate-phosphate at indicated pHs. Cultures were grown at 37°C under microaerophilic condition. Growth experiments were repeated at least thrice and a representative growth curve is shown here.
Since PM analysis relies on bacterial growth in media containing various growth inhibitors or toxic compounds, we wanted to measure the growth kinetics of IBS148 under nutrient rich standard growth condition. Both IBS148 and wild-type UA159 were grown in THY medium at 37°C under static (microaerophilic) condition. As shown in Fig 1C, the growth kinetics for both UA159 and IBS148 were very similar indicating that there was no obvious growth defect in the liaS mutant.
PM analysis was first performed using metabolic panels (PM1-8). There was no significant difference in the carbon utilization panels (PM1-2, data not shown). This was expected, since LiaS is not involved in sensing nutritional signals (Mascher, 2006; Mascher et al., 2006). The signals for the rest of the metabolic panels (PM3-8) were very low which made the comparison difficult (data not shown). These panels include nitrogen utilization panels (PM3, 6–7), phosphate and sulfate panel (PM4), and nutrient stimulation panel (PM5). The poor growth in these metabolic panels was not surprising since a previous study also demonstrated poor growth of a wild-type NG-8 strain, a different S. mutans strain than the one used in this study (Biswas & Biswas, 2005).
PM analysis in the osmotic panel (PM10) generated mixed results (data not shown). In the majority of the wells, there were no growth advantages for either of the strains. However, UA159 produced stronger signals in media containing 4% urea and 0.2M sodium benzoate. In contrast, IBS148 generated stronger signals in media containing 1% NaCl or 3% sodium sulfate. However, this growth advantage of IBS148 may not be significant since the growth kinetics of both IBS148 and UA159 were similar in THY medium supplemented with 1% NaCl or 3% sodium sulfate (data not shown).
In the pH panel (PM9) there were no signals detected in about half of the wells (data not shown). In the remaining wells, there were no significant differences between the wild-type and the liaS mutant strains. However, it was previously reported that a liaS mutant derivative of an NG-8 strain displayed a growth defect at pH5.0 (Li et al., 2002). Under the PM condition tested, both the UA159 and IBS148 grew equally well at pH5.0, but they both failed to grow below pH5.0 in PM plates. Failure to grow below pH5.0 under the PM condition tested is not a strain-specific phenomenon, since a similar growth defect was previously reported for S. mutans NG-8 strain (Biswas & Biswas, 2005). We have studied further the pH sensitivity of our IBS148 strain by growing the strain in THY medium buffered with Citrate-phosphate buffer (Biswas et al., 2007). As shown in Fig 1D, IBS148 grew poorly compared to the wild-type UA159 in media with pH 6.0. At pH5.5, both the strains grew poorly, whereas at pH7.0, both the strains grew equally well. Thus, taken together, our results show that LiaS is indeed involved in the acid-tolerance response of S. mutans. However, the apparent discrepancy between the growth of the cultures in the PM plate (at pH5.0) and in the THY-buffer broths remain to be examined.
Surprisingly, PM analyses for the chemical sensitivity panels generated many positive differences for the IBS148 strains (Fig. 2). A list of the various inhibitors and toxic substances that produced a growth advantage for IBS148 is compiled in Table 1. IBS148 showed better growth than the wild-type UA159 in the presence of many antibiotics that target cell-wall biosynthesis, such as phosphomycin, D-cycloserine, and cefoxitin (Fig. 2). A growth advantage was also observed for IBS148 in the presence of polymyxin B and colistin, both these chemicals target the cell membrane.
Figure 2.
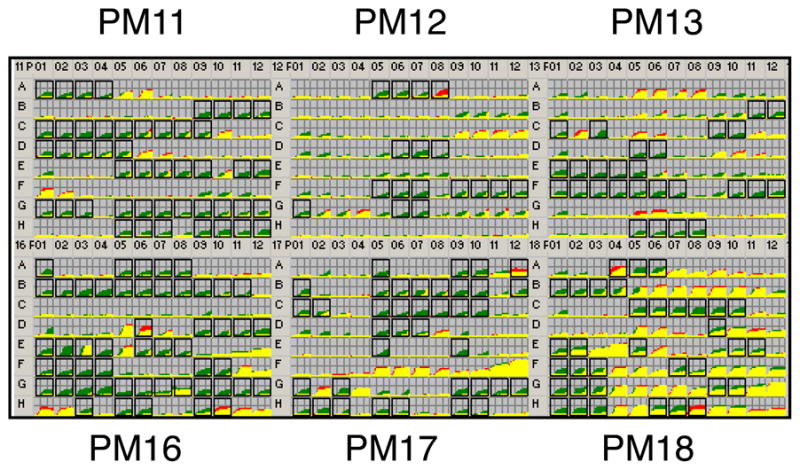
PM analysis for sensitivity to various antibiotics and toxic compounds. A complete catalog of the reagents used in the sensitivity panel (PM11-PM20) is listed in www.biolog.com. The wild-type and the liaS mutant were grown in a 96-well plate under different conditions. Growth kinetics were obtained with the OmniLog instrument, a video-based detection system that detects color development of tetrazolium dye due to bacterial respiration. Growth kinetics of wild-type and liaS mutant are superimposed using OmniLog software. The PM kinetic results show consensus data comparing the liaS mutant (IBS148, green) and its wild-type parental strain (UA159, red). A growth advantage by the parent is indicated by red, while a growth advantage by the liaS mutant is shown by green. When both strains have equal growth response or metabolisms in a well, the red and green kinetics overlaps and produces yellow color. Two independent growth kinetic experiments were performed. A box around a well indicates a difference in response that was observed in both the experiments. The phenotypic changes are listed in Table 1; for a complete list, please refer to Table S1.
Compounds that also produced positive phenotypes for IBS148 strain, but not the wild-type strain, include chemicals that block nucleotide biosynthesis, DNA replication, DNA unwinding, or induce DNA damage. Other chemicals such as folate antagonist, inhibitor of ribonucleotide reductase, and nucleotide analogs were inhibited the growth of the wild-type UA159, but not the growth of IBS148. Similarly, IBS148 was resistant to many protein synthesis inhibitors, including chloramphenicol, gentamycin, and tetracycline. Resistance to spectinomycin was also detected in IBS148 (Table 1), but this was presumably due to the presence of the aad gene used for the disruption of the liaS gene. Resistance was also noted with chemicals that interfere with t-RNA synthesis, such as glycine hydroxamate and L-glutamic-g-hydroxamate.
IBS148 displayed growth advantages in the presence of many toxic anions and cations, such as sodium nitrate, sodium arsenate, and potassium telurite to name a few (Table 1). Several chelating agents, such as EGTA and EDTA, also generated positive results for IBS148. In addition, growth of IBS148 was better in the presence of chlorambucil, thiosalicylate, ethionamide, patulin, apramycin, triclosan, PMSF, and phenylarsine oxide etc. Cellular targets for some of these compounds such as triclosan (fatty acid biosynthesis) and PMSF (protease inhibitor) are known, while cellular targets of the other chemicals in S. mutans are currently unknown.
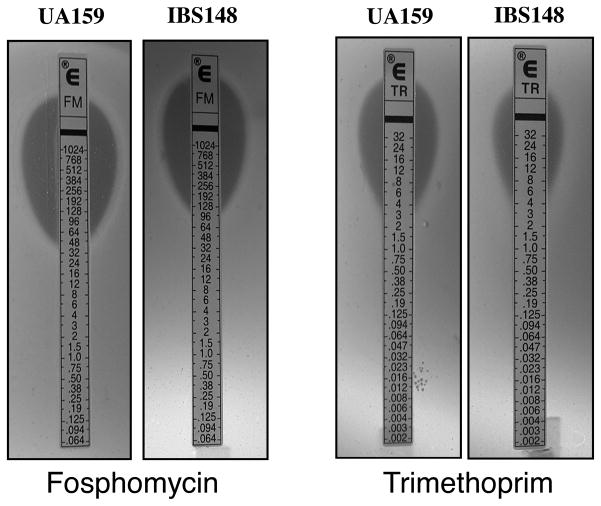
To confirm the PM sensitivity results, some of the key findings were investigated further by performing independent studies (Fig 3). Susceptibilities to some of antibiotics were verified using antibiotic disc diffusion assays and MICs were determined using E-tests. As shown in Fig 3, treatment with fosphomycin (cell wall inhibitor) or trimethoprime (folate antagonist) resulted in a visible difference in growth for IBS148 when compared with UA159. The MIC for ciprofloxaxin (DNA gyrase inhibitor) was also two fold higher in IBS148 (MIC 2.0μg/ml) compared to UA159 (MIC 0.75μg/ml, data not shown). There was no difference in vancomycin resistance observed between the UA159 and IBS148 strains (MIC 2.0μg/ml). Taken together, our results demonstrate that IBS148 is more tolerant to several antibiotics that interfere with cell-wall biosynthesis and to compounds that interfere with the overall DNA replication process.
Figure 3.
Sensitivity to various antibiotics. E-strip tests were performed using either UA159 or IBS148 strains on THY agar plates. Plates were incubated at 37°C under microaerophilic conditions for 20 hrs.
DISCUSSION
In B. subtilis and S. aureus, IM-HKs such as LiaS and other sensor kinases are involved in sensing cell envelope stresses (Jordan et al., 2008; Mascher, 2006). Although the term “cell-envelop stress” is not well defined, it generally indicates a condition that affects the composition and integrity of the cell membrane. These IM-HKs function as a sentinel system to detect conditions that presumably damage the integrity of the envelope or interfere with the cell-wall synthesis. However, the nature of the signals that is detected by LiaS or its homologs can vary depending on the organisms. In B. subtilis, LiaS generally detects damage caused by antibiotics that interfere with lipid II recycling during cell wall biosynthesis, such as bacitracin or vancomycin (Mascher et al., 2003; Mascher et al., 2004); in S. aureus, VraS responds to an even broader spectrum of antibiotics, such as glycopeptides and β-lactams (Kuroda et al., 2003). In contrast to the wealth of knowledge on the role of LiaS in sensing cell-envelope stress in the above mentioned organisms, little is known about its function in other gram-positive pathogens including S. mutans. In this study, we report a comprehensive phenotypic analysis of a liaS mutant of S. mutans where we document several unexpected findings.
Unlike its B. subtilis and S. aureus counterparts, inactivation of liaS in S. mutans produced gain-in-function phenotypes. For example, inactivation of vraS in S. aureus made the bacterium more susceptible to treatment with β-lactams and vancomycin (Kuroda et al., 2003). In contrast, we observed that deletion of the liaS gene in S. mutans resulted in increased tolerance, and not increased sensitivity, to cell-wall damaging antibiotics such as fosphomycin and other β-lactams (Table 1). This is quite surprising since LiaS and VraS are positively involved in sensing cell envelop stresses in B. subtilis and S. aureus, respectively (Mascher, 2006). One explanation could be that LiaS in S. mutans works differently than its counterpart in other bacteria. In S. mutans, it is possible that the primary function of LiaS is to inhibit the activity of LiaR, the cognate response regulator. In the absence of LiaS, LiaR might become constitutively activated (due to a change in phosphorylation status), and allowing the gene expression necessary to survive cell-envelope stresses. The number and nature of the genes regulated by LiaR and its homologs differ greatly. In B. subtilis, LiaR only regulates the expression of two operons, including its own expression. On the other hand, there are approximately 46 genes in S. aureus and about 21 genes in L. lactis that are part of the LiaR regulon (Martinez et al., 2007). Negative regulation of LiaR by LiaS is rather possible in S. mutans, since a recent study shows that a liaR mutant is phenotypically quite similar to its isogenic wild-type parent, while a liaS mutant is not (Chong et al., 2008).
We also observed that two other antibiotics, vancomycin and bacitracin, which are known to be involved in LiaS dependent signaling, have no noticeable effect on the liaS mutant. In B. subtilis, there are at least three different IM-HKs (LiaS, BceS, and YvcQ) that are responsible for sensing different types of cell-envelope stresses. While LiaS can sense many different types of cell-envelope stresses, BceS only responds to bacitracin in B. subtilis (Jordan et al., 2008; Mascher, 2006). In S. mutans, MbrD (SMU.1009), an IM-HK similar to LiaS, is involved in sensing cell envelop stress generated by bacitracin (Tsuda et al., 2002). In addition, another sensor kinase, SMU.1965, also plays a role in bacitracin sensitivity (Biswas et al., 2008). Therefore, it is possible that either of these two sensor kinases, or both, may be involved in sensing cell-envelope stress generated by vancomycin, while LiaS takes part in detecting other cell-envelope stresses. However, based on the sequence homology and the genomic context, neither MbrD nor SMU.1965 appears to be the true homologue of LiaS.
We observed that the liaS mutant was more tolerant to compounds that interfere with nucleotide synthesis, DNA replication, and DNA repair. This is rather surprising, since TCS are not commonly involved in sensing DNA replication status or damage to DNA. It is possible that changes in the cell-envelope structure in the mutant strain may prevent these chemical agents from penetrating into the cell or the efflux systems in the mutant are derepressed and the toxic chemicals are pumped out from the cell more efficiently, thereby making the liaS mutant more resistant to the action of these chemicals. On the other hand, there are a few examples in which TCSs have been shown to be involved in sensing DNA replication blockages or DNA damages. For example, in Caulobacter crescentus, a multi-component signal transduction system involving three sensor kinases (CckA, PleC, and DivJ), along with the master response regulator CtrA and another response regulator, DivK, respond to cell cycle signals and other developmental cues (Jacobs-Wagner, 2004; Jenal, 2000). Moreover, in E. coli, the ArcAB system seems to control initiation of DNA replication (Lee et al., 2001). Thus it is also possible that LiaS either directly or indirectly senses DNA replication blockage or DNA damage.
In bacteria, the process of cell division and DNA replication is highly coordinated (Huisman & D’Ari, 1981; Liu et al., 2001). Interruption of DNA replication or chromosomal segregation interferes with proper cell division that ultimately leads to elongation of cells in rod shaped bacteria such as E. coli and B. subtilis. However, in the case of Enterococcus faecalis, a spherical shaped bacterium similar to S. mutans, inhibition of DNA synthesis by mitomycin C (Higgins et al., 1974) and nalidixic acid (Patel & Weaver, 2006) leads to the inhibition of cell division, and an increase in cell surface area. We speculate that treatment of S. mutans cells with chemicals that block DNA synthesis also leads to improper cell division that causes enlargement of cell shape. This cell shape enlargement disrupts normal cell envelope integrity, which is recognized by LiaS. Interestingly, a recent report indicates that in B. subtilis, a sensor kinase, YycG, co-ordinates cell wall architecture during cell division by co-localizing with FtsZ at the cell division septum and perceiving the signal (Fukushima et al., 2008). S. mutans also encodes a homolog of YycG, known as VicK; inactivation of vicK makes the S. mutans susceptible to many cell-wall targeted antibiotics including β-lactams (Biswas et al., 2008). Whether LiaS or VicK also localize at a particular site on the cell surface for detecting cell envelope stress signals remains to be examined in S. mutans.
The bacterial cell envelope is one of the crucial cellular structures whose integrity needs to be maintained at all time under any circumstances. Various environmental insults such as acidic pH, high osmotic pressure, and toxic chemicals, including antibiotics, can damage the integrity of the cell envelope. To cope with the cell envelope damage, bacteria have evolved various mechanisms to detect perturbations to the envelope. There are at least four different types of signal transduction systems that sense and respond to cell envelope stresses in gram-positive bacteria: TCSs; membrane-anchored anti- σ factor and its corresponding ECF (extracytoplasmic function) σ factor; transmembrane sensory protein BlaR1/MecR1; and a membrane-attached hybrid sensor/transcriptional regulator (Jordan et al., 2008). However, S. mutans does not encode any alternative σ factors, and no BlaR1/MecR1 system has been identified in its genome. Therefore, we speculate that S. mutans primarily relies on TCS to recognize cell envelope stress, and LiaS is one of the most important IM-HKs that plays a significant role in recognizing cell envelope stress in this pathogen.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank members of the Biswas laboratory for critically reading this manuscript. This work was supported in part by funding from NIDCR (DE016686) to I.B.
References
- Ahn SJ, Wen ZT, Burne RA. Multilevel control of competence development and stress tolerance in Streptococcus mutans UA159. Infect Immun. 2006;74:1631–1642. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.3.1631-1642.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ajdic D, McShan WM, McLaughlin RE, et al. Genome sequence of Streptococcus mutans UA159, a cariogenic dental pathogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:14434–14439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.172501299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banas JA, Vickerman MM. Glucan-binding proteins of the oral streptococci. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2003;14:89–99. doi: 10.1177/154411130301400203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas I, Drake L, Biswas S. Regulation of gbpC expression in Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 2007;189:6521–6531. doi: 10.1128/JB.00825-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas I, Drake L, Erkina D, Biswas S. Involvement of sensor kinases in the stress tolerance response of Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 2008;190:68–77. doi: 10.1128/JB.00990-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas S, Biswas I. Role of HtrA in Surface Protein Expression and Biofilm Formation by Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 2005;73:6923–6934. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.10.6923-6934.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas S, Biswas I. Regulation of the glucosyltransferase (gtfBC) operon by CovR in Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 2006;188:988–998. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.3.988-998.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner BR, Gadzinski P, Panomitros E. Phenotype microarrays for high-throughput phenotypic testing and assay of gene function. Genome Res. 2001;11:1246–1255. doi: 10.1101/gr.186501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher BG, Lin YP, Helmann JD. The yydFGHIJ operon of Bacillus subtilis encodes a peptide that induces the LiaRS two-component system. J Bacteriol. 2007;189:8616–8625. doi: 10.1128/JB.01181-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J, Hamilton IR. Metabolic activity of oral bacteria. 2. Copenhagen, Denmark: Munksgaard; 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Chong P, Drake L, Biswas I. LiaS regulates virulence factor expression in Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 2008;76:3093–3099. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01627-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton TL, Scott JR. CovS inactivates CovR and is required for growth under conditions of general stress in Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol. 2004;186:3928–3937. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.12.3928-3937.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Sharoud WM. Two-component signal transduction systems as key players in stress responses of lactic acid bacteria. Sci Prog. 2005;88:203–228. doi: 10.3184/003685005783238381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabret C, Feher VA, Hoch JA. Two-component signal transduction in Bacillus subtilis: how one organism sees its world. J Bacteriol. 1999;181:1975–1983. doi: 10.1128/jb.181.7.1975-1983.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima T, Szurmant H, Kim EJ, Perego M, Hoch JA. A sensor histidine kinase co-ordinates cell wall architecture with cell division in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 2008 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06308.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardete S, Wu SW, Gill S, Tomasz A. Role of VraSR in antibiotic resistance and antibiotic-induced stress response in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:3424–3434. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00356-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas W, Kaushal D, Sublett J, Obert C, Tuomanen EI. Vancomycin stress response in a sensitive and a tolerant strain of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 2005;187:8205–8210. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.23.8205-8210.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S, Slade HD. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980;44:331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins ML, Daneo-Moore L, Boothby D, Shockman GD. Effect of inhibition of deoxyribonucleic acid and protein synthesis on the direction of cell wall growth in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1974;118:681–692. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.681-692.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huisman O, D’Ari R. An inducible DNA replication-cell division coupling mechanism in E. coli. Nature. 1981;290:797–799. doi: 10.1038/290797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idone V, Brendtro S, Gillespie R, et al. Effect of an Orphan Response Regulator on Streptococcus mutans Sucrose-Dependent Adherence and Cariogenesis. Infect Immun. 2003;71:4351–4360. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.8.4351-4360.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs-Wagner C. Regulatory proteins with a sense of direction: cell cycle signalling network in Caulobacter. Mol Microbiol. 2004;51:7–13. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03828.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenal U. Signal transduction mechanisms in Caulobacter crescentus development and cell cycle control. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2000;24:177–191. doi: 10.1016/S0168-6445(99)00035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan S, Junker A, Helmann JD, Mascher T. Regulation of LiaRS-dependent gene expression in bacillus subtilis: identification of inhibitor proteins, regulator binding sites, and target genes of a conserved cell envelope stress-sensing two-component system. J Bacteriol. 2006;188:5153–5166. doi: 10.1128/JB.00310-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan S, Rietkotter E, Strauch MA, Kalamorz F, Butcher BG, Helmann JD, Mascher T. LiaRS-dependent gene expression is embedded in transition state regulation in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology. 2007;153:2530–2540. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/006817-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan S, Hutchings MI, Mascher T. Cell envelope stress response in Gram-positive bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2008;32:107–146. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. Virulence factors of mutans streptococci: role of molecular genetics. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1993;4:159–176. doi: 10.1177/10454411930040020201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda M, Kuroda H, Oshima T, Takeuchi F, Mori H, Hiramatsu K. Two-component system VraSR positively modulates the regulation of cell-wall biosynthesis pathway in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Microbiol. 2003;49:807–821. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee YS, Han JS, Jeon Y, Hwang DS. The arc two-component signal transduction system inhibits in vitro Escherichia coli chromosomal initiation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:9917–9923. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M008629200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemos JA, Abranches J, Burne RA. Responses of cariogenic streptococci to environmental stresses. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2005;7:95–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li YH, Lau PC, Tang N, Svensater G, Ellen RP, Cvitkovitch DG. Novel two-component regulatory system involved in biofilm formation and acid resistance in Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 2002;184:6333–6342. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.22.6333-6342.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu G, Begg K, Geddes A, Donachie WD. Transcription of essential cell division genes is linked to chromosome replication in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 2001;40:909–916. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche WJ. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol Rev. 1986;50:353–380. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.353-380.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez B, Zomer AL, Rodriguez A, Kok J, Kuipers OP. Cell envelope stress induced by the bacteriocin Lcn972 is sensed by the Lactococcal two-component system CesSR. Mol Microbiol. 2007;64:473–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascher T, Margulis NG, Wang T, Ye RW, Helmann JD. Cell wall stress responses in Bacillus subtilis: the regulatory network of the bacitracin stimulon. Mol Microbiol. 2003;50:1591–1604. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascher T, Zimmer SL, Smith TA, Helmann JD. Antibiotic-inducible promoter regulated by the cell envelope stress-sensing two-component system LiaRS of Bacillus subtilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:2888–2896. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.8.2888-2896.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascher T. Intramembrane-sensing histidine kinases: a new family of cell envelope stress sensors in Firmicutes bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006;264:133–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascher T, Helmann JD, Unden G. Stimulus perception in bacterial signal-transducing histidine kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2006;70:910–938. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00020-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel S, Weaver KE. Addiction toxin Fst has unique effects on chromosome segregation and cell division in Enterococcus faecalis and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 2006;188:5374–5384. doi: 10.1128/JB.00513-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda H, Yamashita Y, Shibata Y, Nakano Y, Koga T. Genes involved in bacitracin resistance in Streptococcus mutans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46:3756–3764. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.12.3756-3764.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman RF, Miller SJ, Strampfer MJ, Cunha BA. Streptococcus mutans endocarditis: report of three cases and review of the literature. Heart Lung. 1988;17:209–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verneuil N, Sanguinetti M, Le Breton Y, Posteraro B, Fadda G, Auffray Y, Hartke A, Giard JC. Effects of the Enterococcus faecalis hypR gene encoding a new transcriptional regulator on oxidative stress response and intracellular survival within macrophages. Infect Immun. 2004;72:4424–4431. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.8.4424-4431.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin S, Daum RS, Boyle-Vavra S. VraSR two-component regulatory system and its role in induction of pbp2 and vraSR expression by cell wall antimicrobials in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50:336–343. doi: 10.1128/AAC.50.1.336-343.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou L, Lei XH, Bochner BR, Wanner BL. Phenotype microarray analysis of Escherichia coli K-12 mutants with deletions of all two-component systems. J Bacteriol. 2003;185:4956–4972. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.16.4956-4972.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.