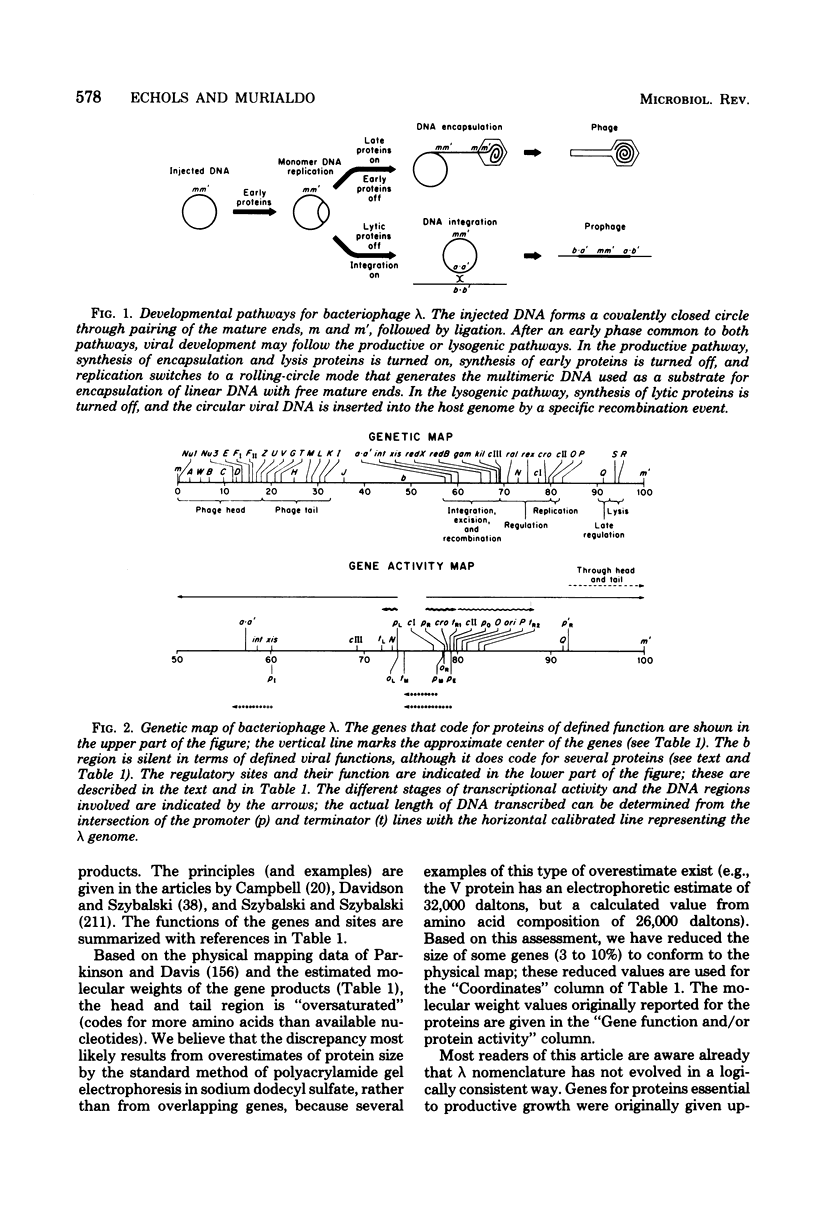
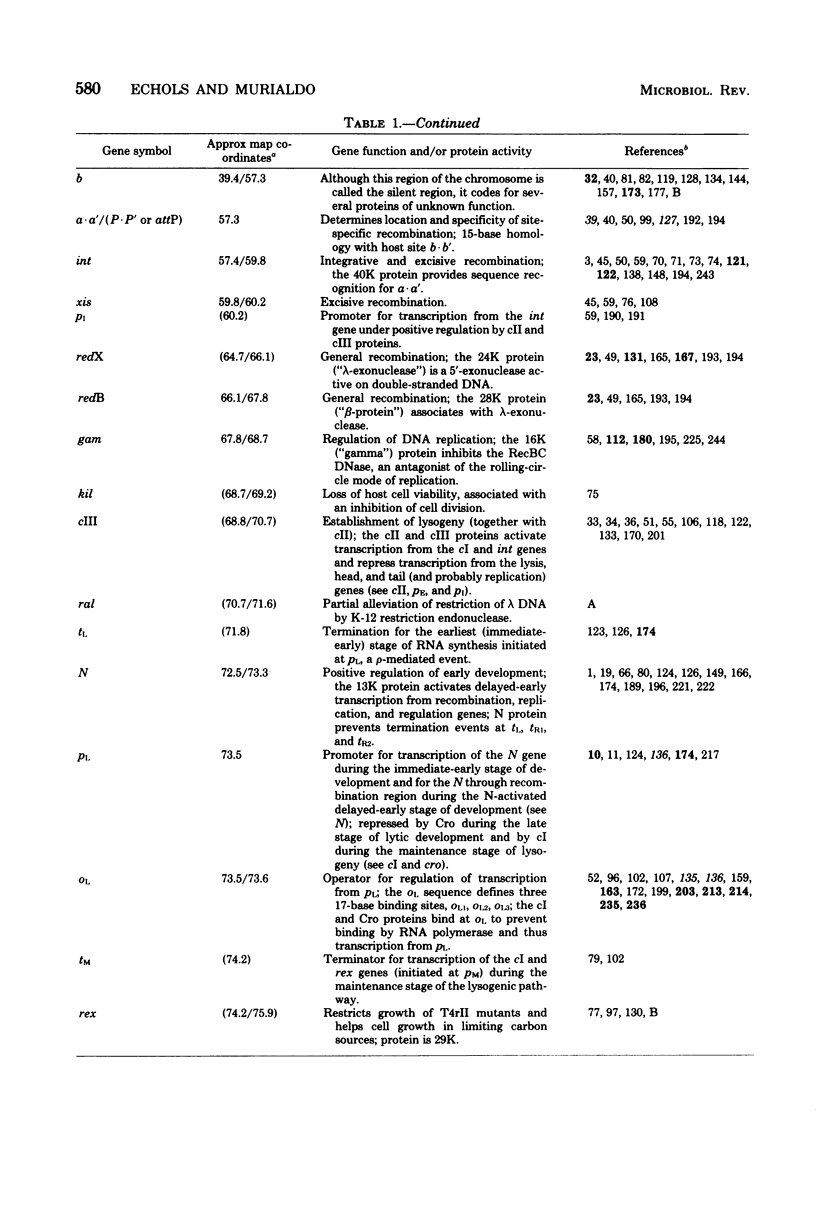
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M., De Crombrugghe B. Release of polarity in Escherichia coli by gene N of phage lambda: termination and antitermination of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2534–2538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausubel F. M. Radiochemical purification of bacteriophage lambda integrase. Nature. 1974 Jan 18;247(5437):152–154. doi: 10.1038/247152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer M. E., Bocharov A. F. The capsid structure of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1973 Aug;54(2):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90157-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker A., Gold M. Isolation of the bacteriophage lambda A-gene protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):581–585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker A., Marko M., Gold M. Early events in the in vitro packaging of bacteriophage lambda DNA. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):291–305. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker A., Murialdo H., Gold M. Studies on an in vitro system for the packaging and maturation of phage lambda DNA. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):277–290. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black L. W., Hogness D. S. The lysozyme of bacteriophage lambda. I. Purification and molecular weight. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):1968–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Dahlberg J. E. RNA synthesis startpoints in bacteriophage lambda: are the promoter and operator transcribed? Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 21;237(77):227–232. doi: 10.1038/newbio237227a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Fiandt M., Hass K. K., Twose P. A., Szybalski W. Deletions and insertions in the immunity region of coliphage lambda: revised measurement of the promoter-startpoint distance. Virology. 1974 Dec;62(2):458–471. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90407-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode V. C. Incomplete lambda bacteriophage heads produced by a gene F mutant. J Virol. 1971 Sep;8(3):349–351. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.3.349-351.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode V. C., Kaiser A. D. Changes in the structure and activity of lambda DNA in a superinfected immune bacterium. J Mol Biol. 1965 Dec;14(2):399–417. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80190-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boklage C. E., Wong E. C., Bode V. C. Functional abnormality of lambda phage particles from complemented FII-mutant lysates. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):22–28. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90238-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boklage C. E., Wong E. C., Bode V. C. The lambda F mutants belong to two cistrons. Genetics. 1973 Oct;75(2):221–230. doi: 10.1093/genetics/75.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchwald M., Murialdo H., Siminovitch L. The morphogenesis of bacteriophage lambda. II. Identification of the principal structural proteins. Virology. 1970 Oct;42(2):390–400. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90282-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchwald M., Siminovitch L. Production of serum-blocking material by mutants of the left arm of the lambda chromosome. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL A., DELCAMPILLO-CAMPBELL A. MUTANT OF LAMBDA BACTERIOPHAGE PRODUCING A THERMOLABILE ENDOLYSIN. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1202–1207. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1202-1207.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL A. Sensitive mutants of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1961 May;14:22–32. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90128-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calef E., Neubauer Z. Active and inactive states of the CI gene in some lambda defective phages. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:765–767. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter D. M., Radding C. M. The role of exonuclease and beta protein of phage lambda in genetic recombination. II. Substrate specificity and the mode of action of lambda exonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2502–2512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casjens S. R., Hendrix R. W. Locations and amounts of major structural proteins in bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):535–545. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90500-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casjens S. Bacteriophage lambda FII gene protein: role in head assembly. J Mol Biol. 1974 Nov 25;90(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90252-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casjens S., Hendrix R. Comments on the arrangement of the morphogenetic genes of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1974 Nov 25;90(1):20–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casjens S., Hohn T., Kaiser A. D. Morphological proteins of phage lambda: identification of the major head protein as the product of gene E. Virology. 1970 Oct;42(2):496–507. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casjens S., Horn T., Kaiser A. D. Head assembly steps controlled by genes F and W in bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 14;64(3):551–563. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90082-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattoraj D. K., Inman R. B. Location of DNA ends in P2, 186, P4 and lambda bacteriophage heads. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 25;87(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90556-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury M. R., Dumbar S., Becker A. Induction of an endonuclease by some substitution and deletion variants of phage lambda. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):314–318. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S., Echols H. Positive regulation of integrative recombination by the cII and cIII genes of bacteriophase lambda. Virology. 1977 Jun 15;79(2):312–319. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Court D., Campbell A. Gene regulation in N mutants of bacteriophage lambda. J Virol. 1972 Jun;9(6):938–945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.6.938-945.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Court D., Green L., Echols H. Positive and negative regulation by the cII and cIII gene products of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):484–491. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W., Schreier P. H., Buchel D. E. Nucleotide sequence of the attachment site of coliphage lambda. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):757–760. doi: 10.1038/270757a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. W., Parkinson J. S. Deletion mutants of bacteriophage lambda. 3. Physical structure of att-phi. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):403–423. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90473-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denniston-Thompson K., Moore D. D., Kruger K. E., Furth M. E., Blattner F. R. Physical structure of the replication origin of bacteriophage lambda. Science. 1977 Dec 9;198(4321):1051–1056. doi: 10.1126/science.929187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dove W. F. Action of the lambda chromosome. I. Control of functions late in bacteriophage development. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(1):187–201. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echolas H., Gingery R. Mutants of bacteriophage lambda defective in vegetative genetic recombination. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):239–249. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90249-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H., Court D., Green L. On the nature of cis-acting regulatory proteins and genetic organization in bacteriophage: the example of gene Q of bacteriophage lambda. Genetics. 1976 May;83(1):5–10. doi: 10.1093/genetics/83.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H. Developmental pathways for the temperate phage: lysis vs lysogeny,. Annu Rev Genet. 1972;6(0):157–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.06.120172.001105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H., Gingery R., Moore L. Integrative recombination function of bacteriophage lambda: evidence for a site-specific recombination enzyme. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90250-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H., Green L. Establishment and maintenance of repression by bacteriophage lambda: the role of the cI, cII, and c3 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2190–2194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H., Green L., Oppenheim A. B., Oppenheim A., Honigman A. Role of the cro gene in bacteriophage lambda development. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 25;80(2):203–216. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90167-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H. Integrative and excisive recombination by bacteriophage lambda: evidence for an excision-specific recombination protein. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):575–583. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90324-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H., Pilarski L., Xcheng P. Y. In vitro repression of phage lambda DNA transcription by a partially purified repressor from lysogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):1016–1023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan J. B., Hogness D. S. The topography of lambda DNA: isolation of ordered fragments and the physical mapping of point mutations. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 14;71(2):363–381. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90357-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen H. A., Fuerst C. R., Siminovitch L., Thomas R., Lambert L., Pereira da Silva L., Jacob F. Genetics and physiology of defective lysogeny in K12 (lambda): studies of early mutants. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):224–241. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen H., Brachet P., Pereira da Silva L., Jacob F. Regulation of repressor expression in lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):855–862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons S. W. Bacteriophage lambda derivatives carrying two copies of the cohesive end site. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar 15;83(4):511–525. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90511-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Skalka A. Replication of bacteriophage lambda DNA dependent on the function of host and viral genes. I. Interaction of red, gam and rec. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):185–212. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Weisberg R. A. A genetic analysis of the att-int-xis region of coliphage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr;111(2):97–120. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiss M., Bublitz A. Polarized packaging of bacteriophage lambda chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jun 5;94(4):583–594. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90323-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiss M., Campbell A. Duplication of the bacteriophage lambda cohesive end site: genetic studies. J Mol Biol. 1974 Mar 15;83(4):527–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90512-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkmanis A., Maltzman W., Mellon P., Skalka A., Echols H. The essential role of the cro gene in lytic development by bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1977 Sep;81(2):352–362. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkmanis A., Takeda Y., Simuth J., Gussin G., Echols H. Purification and properties of a DNA-binding protein with characteristics expected for the Cro protein of bacteriophage lambda, a repressor essential for lytic growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2249–2253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin N. C. Altered reading of genetic signals fused to the N operon of bacteriophage lambda: genetic evidence for modification of polymerase by the protein product of the N gene. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):33–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Blattner F. R., McLeester C., Dove W. F. Genetic structure of the replication origin of bacteriophage lambda. Science. 1977 Dec 9;198(4321):1046–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.929186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. Formation of covalent circles of lambda DNA by E. coli extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jan;57(1):148–155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.1.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingery R., Echols H. Integration, excision, and transducing particle genesis by bacteriophage lambda. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:721–727. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingery R., Echols H. Mutants of bacteriophage lambda unable to integrate into the host chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1507–1514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. R., Howe M. New mutations in the S cistron of bacteriophage lambda affecting host cell lysis. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):200–202. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. E., Yarmolinsky M. B. Integration-negative mutants of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):487–505. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90423-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. E., Yarmolinsky M. B. The integration and excision of the bacteriophage lambda genome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:735–747. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer H. The kil gene of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1975 Aug;66(2):589–604. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90231-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarneros G., Echols H. New mutants of bacteriophage lambda with a specific defect in excision from the host chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):565–574. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gussin G. N., Peterson V. Isolation and properties of rex - mutants of bacteriophage lambda. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):760–765. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.760-765.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERSHEY A. D., BURGI E. COMPLEMENTARY STRUCTURE OF INTERACTING SITES AT THE ENDS OF LAMBDA DNA MOLECULES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:325–328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes S., Szybalski W. Control of short leftward transcripts from the immunity and ori regions in induced coliphage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Nov 22;126(4):275–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00269438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D., Weil J. A mutant of Escherichia coli that prevents growth of phage lambda and is bypassed by lambda mutants in a nonessential region of the genome. Virology. 1976 Jun;71(2):546–559. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix R. W., Casjens S. R. Assembly of bacteriophage lambda heads: protein processing and its genetic control in petit lambda assembly. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 15;91(2):187–199. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90159-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix R. W., Casjens S. R. Protein cleavage in bacteriophage lambda tail assembly. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):156–159. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90250-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix R. W., Casjens S. R. Protein fusion during the assembly of phage lambda heads. J Supramol Struct. 1974;2(2-4):329–336. doi: 10.1002/jss.400020222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix R. W., Casjens S. R. Protein fusion: a novel reaction in bacteriophage lambda head assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1451–1455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. Control of gene expression in bacteriophage lambda. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:289–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I., Signer E. R. A site essential for expression of all late genes in bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. DNA as substrate for packaging into bacteriophage lambda, in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 15;98(1):93–106. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn T., Flick H., Hohn B. Petit lambda, a family of particles from coliphage lambda infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 15;98(1):107–120. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80104-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn T., Hohn B. A minor pathway leading to plaque-forming particles in bacteriophage lambda. Studies on the function of gene D. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 5;79(4):649–662. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn T., Katsura I. Structure and assembly of bacteriophage lambda. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1977;78:69–110. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66800-5_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn T., Morimasa T., Tsugita A. The capsid protein of bacteriophage lambda and of its prehead. J Mol Biol. 1976 Aug 5;105(2):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90117-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn T., Wurtz M., Hohn B. Capsid transformation during packaging of bacteriophage lambdaDNA. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Nov 30;276(943):51–61. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1976.0097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. D. Phage lambda mutants deficient in r-II exclusion. Science. 1967 Dec 22;158(3808):1588–1589. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3808.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howatson A. F., Kemp C. L. The structure of tubular head forms of bacteriophage lambda; relation to the capsid structure of petit lambda and normal lambda heads. Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):80–84. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90405-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hradecna Z., Szybalski W. Electron micrographic maps of deletions and substitutions in the genomes of transducing coliphages lambda dg and lambda bio. Virology. 1969 Jul;38(3):473–477. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90160-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang M. W., Cole R. D., Takeda Y., Echols H. Amino acid sequence of Cro regulatory protein of bacteriophage lambda. Nature. 1977 Nov 17;270(5634):275–277. doi: 10.1038/270275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huntley G. H., Kemp C. L. Isolation and protein composition of normal and petit capsids of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1971 Nov;46(2):298–309. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jara L., Murialdo H. Isolation of nonsense mutants in the morphogenetic region of the bacteriophage lambda chromosome. Virology. 1975 Mar;64(1):264–268. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A., Meyer B. J., Ptashne M. Mechanism of action of the cro protein of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1783–1787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyner A., Isaacs L. N., Echols H., Sly W. S. DNA replication and messenger RNA production after induction of wild-type lambda bacteriophage and lambda mutants. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(1):174–186. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAISER A. D., JACOB F. Recombination between related temperate bacteriophages and the genetic control of immunity and prophage localization. Virology. 1957 Dec;4(3):509–521. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAISER A. D. Mutations in a temperate bacteriophage affecting its ability to lysogenize Escherichia coli. Virology. 1957 Feb;3(1):42–61. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER G., ZICHICHI M. L., WEIGLE J. A mutation affecting the DNA content of bacteriophage lambda and its lysogenizing properties. J Mol Biol. 1961 Aug;3:399–408. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser A. D., Masuda T. Evidence for a prophage excision gene in lambda. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):557–564. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D., Masuda T. In vitro assembly of bacteriophage Lambda heads. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):260–264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D., Syvanen M., Masuda T. DNA packaging steps in bacteriophage lambda head assembly. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 15;91(2):175–186. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D., Syvanen M., Masuda T. Processing and assembly of the head of bacteriophage lambda. J Supramol Struct. 1974;2(2-4):318–328. doi: 10.1002/jss.400020221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karu A. E., Sakaki Y., Echols H., Linn S. The gamma protein specified by bacteriophage gamma. Structure and inhibitory activity for the recBC enzyme of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7377–7387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsura I., Kühl P. W. A regulator protein for the length determination of bacteriophage lambda tail. J Supramol Struct. 1974;2(2-4):239–253. doi: 10.1002/jss.400020217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsura I., Kühl P. W. Morphogenesis of the tail of bacteriophage lambda. II. In vitro formation and properties of phage particles with extra long tails. Virology. 1975 Jan;63(1):238–251. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90388-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsura I., Kühl P. W. Morphogenesis of the tail of bacteriophage lambda. III. Morphogenetic pathway. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 25;91(3):257–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90379-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsura I. Morphogenesis of bacteriophage lambda tail. Polymorphism in the assembly of the major tail protein. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov 5;107(3):307–326. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsura I., Tsugita A. Purification and characterization of the major protein and the terminator protein of the bacteriophage lambda tail. Virology. 1977 Jan;76(1):129–145. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90290-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzir N., Oppenheim A., Belfort M., Oppenheim A. B. Activation of the lambda int gene by the cii and ciii gene products. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):324–331. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90339-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotewicz M., Chung S., Takeda Y., Echols H. Characterization of the integration protein of bacteriophage lambda as a site-specific DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1511–1515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kourilsky P., Marcaud L., Sheldrick P., Luzzati D., Gros F. Studies of the messenger RNA of bacteriophage lambda, I. Various species synthesized early after induction of the prophage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Nov;61(3):1013–1020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.3.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Bovre K., Guha A., Hradecna Z., Maher V. R., Szybalski W. Orientation and control of transcription in E. coli phage lambda. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):823–825. doi: 10.1038/221823a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kül P. W., Katsura I. Morphogenesis of the tail of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1975 Jan;63(1):221–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landy A., Ross W. Viral integration and excision: structure of the lambda att sites. Science. 1977 Sep 16;197(4309):1147–1160. doi: 10.1126/science.331474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman J. F. Lambda site-specific recombination: local transcription and an inhibitor specified by the b2 region. Mol Gen Genet. 1974 Jun 27;130(4):333–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00333873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lickfeld K. G., Menge B. Morphogenesis of bacteriophage lambda: electron microscopy of thin sections. J Mol Biol. 1976 May 15;103(2):299–318. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90314-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin L., Bitner R., Edlin G. Increased reproductive fitness of Escherichia coli lambda lysogens. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):554–559. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.554-559.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W. An exonuclease induced by bacteriophage lambda. II. Nature of the enzymatic reaction. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):679–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone R. E., Chattoraj D. K. The role of Chi mutations in the Spi- phenotype of phage lambda: lack of evidence for a gene delta. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Dec 30;143(1):35–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00269418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Ptashne M., Backman K., Kield D., Flashman S., Jeffrey A., Maurer R. Recognition sequences of repressor and polymerase in the operators of bacteriophage lambda. Cell. 1975 Jun;5(2):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Ptashne M., Barrell B. G., Donelson J. Sequence of a repressor-binding site in the DNA of bacteriophage lamda. Nature. 1974 Aug 2;250(465):394–397. doi: 10.1038/250394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure S. C., MacHattie L., Gold M. A sedimentation analysis of DNA found in Escherichia coli infected with phage lambda mutants. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90109-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMacken R., Mantei N., Butler B., Joyner A., Echols H. Effect of mutations in the c2 and c3 genes of bacteriophage lambda on macromolecular synthesis in infected cells. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 14;49(3):639–655. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90288-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer B. J., Kleid D. G., Ptashne M. Lambda repressor turns off transcription of its own gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4785–4789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Nash H. A. Restriction assay for integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda DNA in vitro: requirement for closed circular DNA substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3524–3528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount D. W., Harris A. W., Fuerst C. R., Siminovitch L. Mutations in bacteriophage lambda affecting particle morphogenesis. Virology. 1968 May;35(1):134–149. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90313-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murialdo H., Becker A. Assembly of biologically active proheads of bacteriophage lambda in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):906–910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murialdo H., Ray P. N. Model for arrangement of minor structural proteins in head of bacteriophage lambda. Nature. 1975 Oct 30;257(5529):815–817. doi: 10.1038/257815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murialdo H., Siminovitch L. The morphogenesis of bacteriophage lambda. IV. Identification of gene products and control of the expression of the morphogenetic information. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):785–823. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murialdo H., Siminovitch L. The morphogenesis of phage lambda. V. Form-determining function of the genes required for the assembly of the head. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):824–835. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K., Murray N. E., Bertani G. Base changes in the recognition site for ter functions in lambdoid phage DNA. Nature. 1975 Mar 20;254(5497):262–265. doi: 10.1038/254262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray K., Murray N. E. Terminal nucleotide sequences of DNA from temperate coliphages. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 30;243(126):134–139. doi: 10.1038/newbio243134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Purification of bacteriophage lambda Int protein. Nature. 1974 Feb 22;247(5442):543–545. doi: 10.1038/247543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijkamp H. J., Bovre K., Szybalski W. Controls of rightward transcription in coliphage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 28;54(3):599–604. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90130-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K. I., Sakakibara Y., Tomizawa J. I. Regulation of transcription of the lambda bacteriophage genome. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):901–918. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa T., Tomizawa J. Replication of bacteriophage DNA. I. Replication of DNA of lambda phage defective in early functions. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec 14;38(2):217–225. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90407-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim A. B., Neubauer Z., Calef E. The antirepressor: a new element in the regulation of protein synthesis. Nature. 1970 Apr 4;226(5240):31–32. doi: 10.1038/226031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim A., Katzir N., Oppenheim A. B. The product on gene P of coliphage lambda. Virology. 1977 Jun 15;79(2):437–441. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90369-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Davis R. W. A physical map of the left arm of the lambda chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):425–428. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90474-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Genetics of the left arm of the chromosome of bacteriophage lambda. Genetics. 1968 Jul;59(3):311–325. doi: 10.1093/genetics/59.3.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Huskey R. J. Deletion mutants of bacteriophage lambda. I. Isolation and initial characterization. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):369–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90471-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pero J. Location of the phage lambda gene responsible for turning off lambda-exonuclease synthesis. Virology. 1970 Jan;40(1):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V. Sequence of the OR operator of phage lambda. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):114–117. doi: 10.1038/254114a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Backman K., Humayun M. Z., Jeffrey A., Maurer R., Meyer B., Sauer R. T. Autoregulation and function of a repressor in bacteriophage lambda. Science. 1976 Oct 8;194(4261):156–161. doi: 10.1126/science.959843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Hopkins N. The operators controlled by the lambda phage repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1282–1287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. ISOLATION OF THE lambda PHAGE REPRESSOR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):306–313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raab C., Klein A., Kluding H., Hirth P., Fuchs E. Cell free synthesis of bacteriophage lambda replication proteins. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 15;80(2):275–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80456-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M., Echols H. The role of the N gene of phage lambda in the synthesis of two phage-specific proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jun;60(2):707–712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.2.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M., Shreffler D. C. Regulation of lambda exonuclease. II. Joint regulation of exonuclease and a new lambda antigen. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(2):251–261. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. The role of exonuclease and beta protein of bacteriophage lambda in genetic recombination. I. Effects of red mutants on protein structure. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 28;52(3):491–499. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90415-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambach A. Replicator mutants of bacteriophage lambda: characterization of two subclasses. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):270–277. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90136-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P., Murialdo H. The role of gene Nu3 in bacteriophage lambda head morphogenesis. Virology. 1975 Mar;64(1):247–263. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt L. F. Control of bacteriophage lambda repressor synthesis after phage infection: the role of the N, cII, cIII and cro products. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 5;93(2):267–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt L. F. Control of bacteriophage lambda repressor synthesis: regulation of the maintenance pathway of the cro and cI products. J Mol Biol. 1975 Apr 5;93(2):289–309. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt L., Kaiser A. D. Control of lambda repressor synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2185–2189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades M., Meselson M. An endonuclease induced by bacteriophage lambda. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):521–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W. Transcription termination and late control in phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3300–3304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. M., Shimatake H., Brady C., Rosenberg M. Sequence of Cro gene of bacteriophage lambda. Nature. 1977 Nov 17;270(5634):274–275. doi: 10.1038/270274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehrdanz R. L., Dove W. F. A factor in the b2 region affecting site-specific recombinations in lambda. Virology. 1977 Jun 1;79(1):40–49. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90332-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D., Shimatake H., Brady C., Wulff D. L. The relationship between function and DNA sequence in an intercistronic regulatory region in phage lambda. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):414–423. doi: 10.1038/272414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRACK H. B., KAISER A. D. ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE ENDS OF LAMBADA DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:36–49. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80280-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saigo K., Uchida H. Connection of the right-hand terminus of DNA to the proximal end of the tail in bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1974 Oct;61(2):524–536. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90287-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaki Y., Karu A. E., Linn S., Echols H. Purification and properties of the gamma-protein specified by bacteriophage lambda: an inhibitor of the host RecBC recombination enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2215–2219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Air G. M., Barrell B. G., Brown N. L., Coulson A. R., Fiddes C. A., Hutchison C. A., Slocombe P. M., Smith M. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage phi X174 DNA. Nature. 1977 Feb 24;265(5596):687–695. doi: 10.1038/265687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer R. T., Anderegg R. Primary structure of the lambda repressor. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 21;17(6):1092–1100. doi: 10.1021/bi00599a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scandella D., Arber W. Phage lambda DNA injection into Escherichia coli pel- mutants is restored by mutations in phage genes V or H. Virology. 1976 Jan;69(1):206–215. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G., Hobom G., Kössel H. DNA base sequence of the po promoter region of phage lamdba. Nature. 1977 Jan 13;265(5590):117–121. doi: 10.1038/265117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnös M., Inman R. B. Position of branch points in replicating lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 14;51(1):61–73. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90270-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz E., Scherer G., Hobom G., Kössel H. Nucleotide sequence of cro, cII and part of the O gene in phage lambda DNA. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):410–414. doi: 10.1038/272410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. C., Walker J. E., Northrop F. D., Barrell B. G., Godson G. N., Fiddes J. C. Gene K, a new overlapping gene in bacteriophage G4. Nature. 1978 Apr 6;272(5653):510–515. doi: 10.1038/272510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. E., Jones B. B., Pearson M. L. Identification of the N gene protein of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2225–2229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Campbell A. Int-constitutive mutants of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):237–241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Campbell A. Lysogenization and curing by int-constitutive mutants of phage lambda. Virology. 1974 Jul;60(1):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90373-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M. J., Hallick L. M., Echols H., Signer E. R. Properties of recombination-deficient mutants of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 28;52(3):501–520. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90416-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Gottesman M. Attachment site mutants of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 25;81(4):461–482. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90517-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signer E. R., Weil J. Recombination in bacteriophage lambda. I. Mutants deficient in general recombination. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):261–271. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90251-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sironi G., Bialy H., Lozeron H. A., Calendar R. Bacteriophage P2: interaction with phage lambda and with recombination-deficient bacteria. Virology. 1971 Nov;46(2):387–396. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalka A., Butler B., Echols H. Genetic control of transcription during development of phage gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):576–583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalka A., Poonian M., Bartl P. Concatemers in DNA replication: electron microscopic studies of partially denatured intracellular lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 14;64(3):541–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar J., Yot P., Weissman S. M. Determination of genes, restriction sites, and DNA sequences surrounding the 6S RNA template of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1817–1821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman W. G., Reichardt L. F., Yaniv M., Heinemann S. F., Kaiser A. D., Eisen H. Bidirectional transcription and the regulation of Phage lambda repressor synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3156–3160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman W. G. Two states of expression of genes cl, rex, and N in lambda. Virology. 1971 Jan;43(1):16–33. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl F. W., Murray N. E. The evolution of gene clusters and genetic circularity in microorganisms. Genetics. 1966 Mar;53(3):569–576. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A., Ptashne M. In vitro repression of RNA synthesis by purified lambda phage repressor. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 17;230(11):76–80. doi: 10.1038/newbio230076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N. A genetic analysis of bacteriophage lambda head assembly. Virology. 1976 Jun;71(2):568–582. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90382-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N., Weisberg R. Packaging of coliphage lambda DNA. I. The role of the cohesive end site and the gene A protein. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 15;117(3):717–731. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N., Weisberg R. Packaging of coliphage lambda DNA. II. The role of the gene D protein. J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 15;117(3):733–759. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90067-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N., Weisberg R. Packaging of prophage and host DNA by coliphage lambda. Nature. 1975 Jul 10;256(5513):97–103. doi: 10.1038/256097a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syvanen M. Processing of bacteriophage lambda DNA during its assembly into heads. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 15;91(2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90157-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szybalski E. H., Szybalski W. Physical mapping of the att-N region of coliphage lambda: apparent oversaturation of coding capacity in the gam-ral segment. Biochimie. 1974;56(11-12):1497–1503. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(75)80272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS R. ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE GENETIC SEGMENT CONTROLLING IMMUNITY IN TEMPERATE BACTERIOPHAGES. J Mol Biol. 1964 Feb;8:247–253. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80134-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S. Role of genes O and P in the replication of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):385–396. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90209-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Folkmanis A., Echols H. Cro regulatory protein specified by bacteriophage lambda. Structure, DNA-binding, and repression of RNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):6177–6183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Matsubara K., Ogata K. Regulation of early gene expression in bacteriophage lambda: effect of tof mutation on strand-specific transcriptions. Virology. 1975 Jun;65(2):374–384. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. Endopeptidase activity of phage lamba-endolysin. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 1;234(48):144–145. doi: 10.1038/newbio234144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor K., Hradecna Z., Szybalski W. Asymmetric distribution of the transcribing regions on the complementary strands of coliphage lambda DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1618–1625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O. Chemical linkage of the tail to the right-hand end of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 25;87(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90555-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. Control of development in temperate bacteriophages. 3. Which prophage genes are and which are not trans-activable in the presence of immunity? J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 28;49(2):393–404. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90252-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R., Leurs C., Dambly C., Parmentier D., Lambert L., Brachet P., Lefebvre N., Mousset S., Porcheret J., Szpirer J. Isolation and characterization of new sus (amber) mutants of bacteriophage lambda. Mutat Res. 1967 Nov-Dec;4(6):735–741. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(67)90082-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa J., Ogawa T. Replication of phage lambda DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:533–551. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. C., Echols H., Clark A. J. Interaction of the recombination pathways of bacteriophage lambda and host Escherichia coli: effects on lambda recombination. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 14;70(3):531–537. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90557-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake R. G., Kaiser A. D., Inman R. B. Isolation and structure of phage lambda head-mutant DNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 14;64(3):519–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz A., Pirrotta V. Sequence of the PR promoter of phage lambda. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):118–121. doi: 10.1038/254118a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C., Davidson N. Cyclization of phage DNAs. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1968;33:409–415. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1968.033.01.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C., Kaiser A. D. Evidence that the cohesive ends of mature lambda DNA are generated by the gene A product. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 3;241(105):16–17. doi: 10.1038/newbio241016a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel P. H., Englund P. T., Murray K., Old R. W. The 3'-terminal nucleotide sequences of bacteriophage lambda DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1151–1155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle J. Assembly of phage lambda in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1462–1466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil J., Signer E. R. Recombination in bacteriophage lambda. II. Site-specific recombination promoted by the integration system. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Richards K. E. Letter: Capsid structure of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):547–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90501-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. M., Ghosh S., Echols H. Repression by the cI protein of phage lambda: interaction with RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):423–432. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90460-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. M., Ghosh S., Echols H., Spiegelman W. G. Repression by the cI protein of phage lambda: in vitro inhibition of RNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):407–421. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90459-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Kaiser A. D. Structure and base sequence in the cohesive ends of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Aug 14;35(3):523–537. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R., Taylor E. Nucleotide sequence analysis of DNA. II. Complete nucleotide sequence of the cohesive ends of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 14;57(3):491–511. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Gette W. R., Furth M. E., Nomura M. Effects of ribosomal mutations on the read-through of a chain termination signal: studies on the synthesis of bacteriophage lambda O gene protein in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):689–693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen K. M., Gussin G. N. Genetic characterization of a prm- mutant of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1973 Nov;56(1):300–312. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90308-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary A., Simon L. D., Litwin S. Lambda head morphogenesis as seen in the electron microscope. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):429–442. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90172-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zissler J. Integration-negative (int) mutants of phage lambda. Virology. 1967 Jan;31(1):189–189. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90030-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


