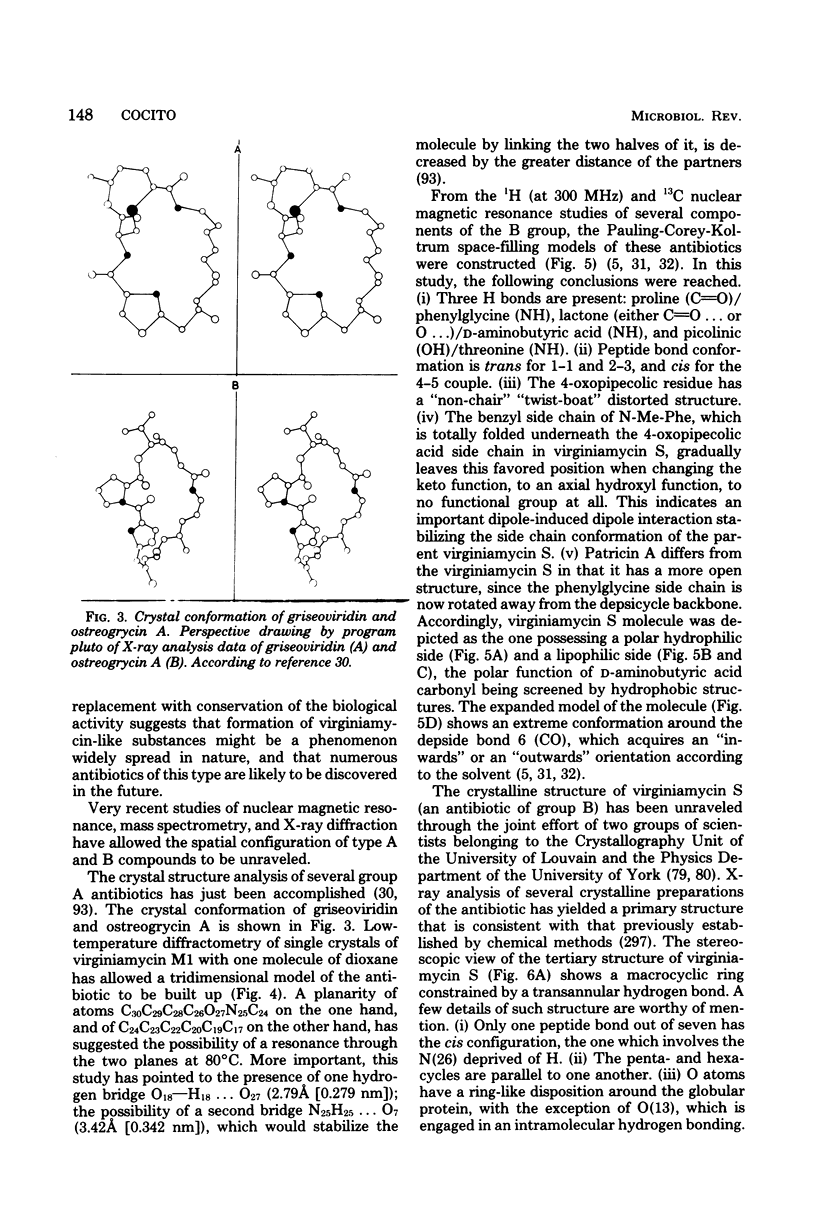
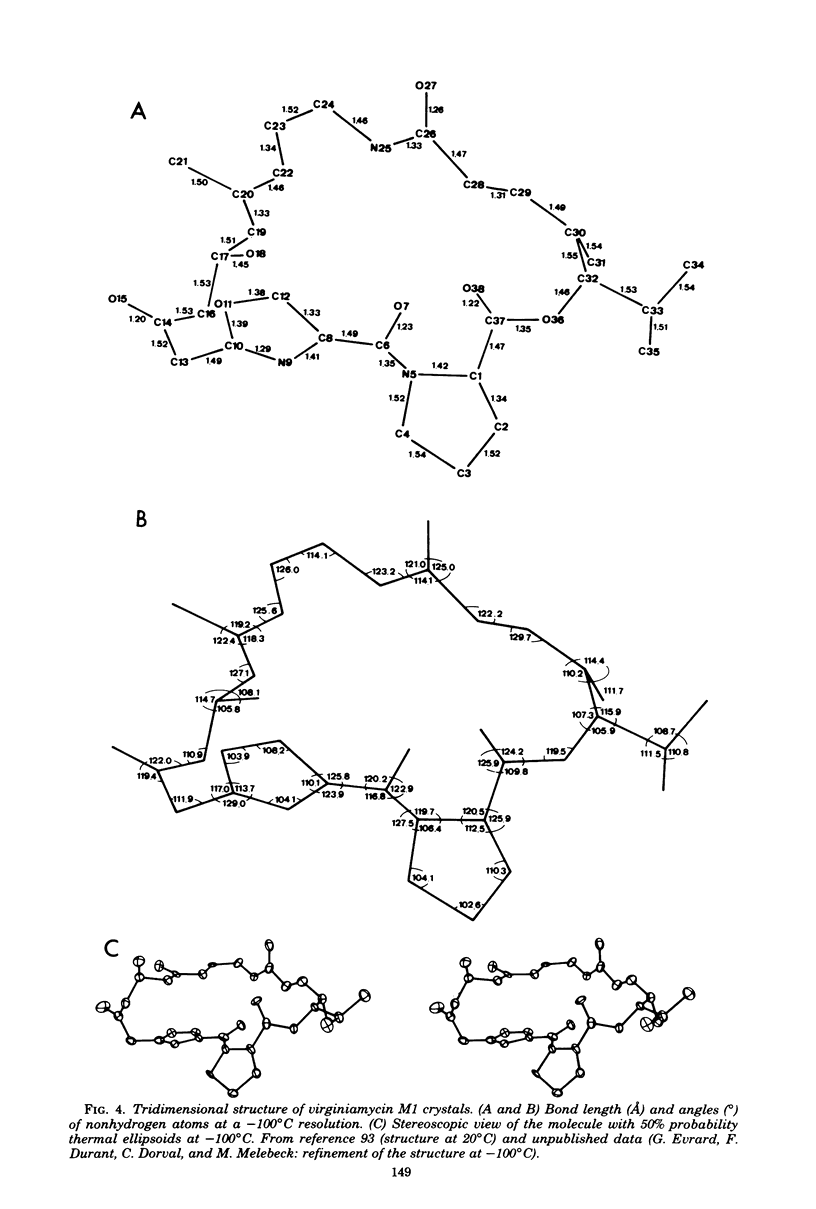
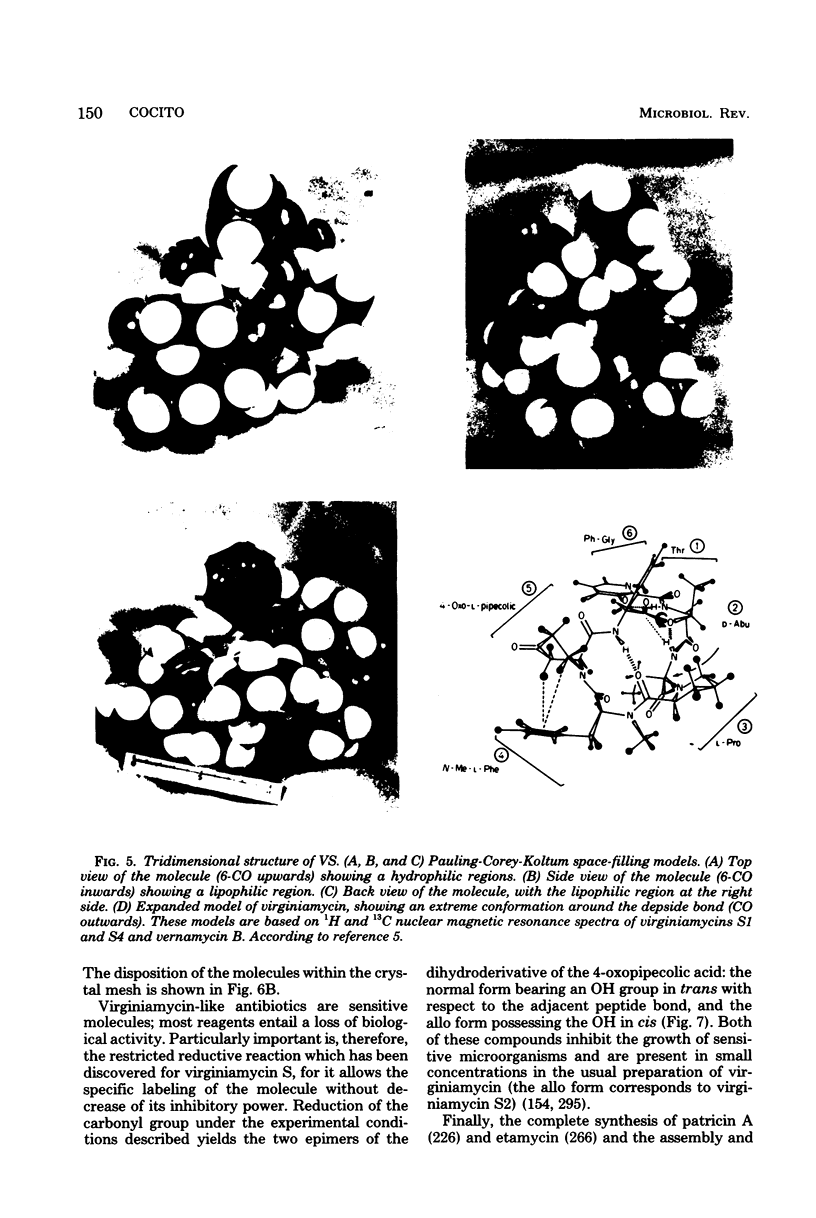
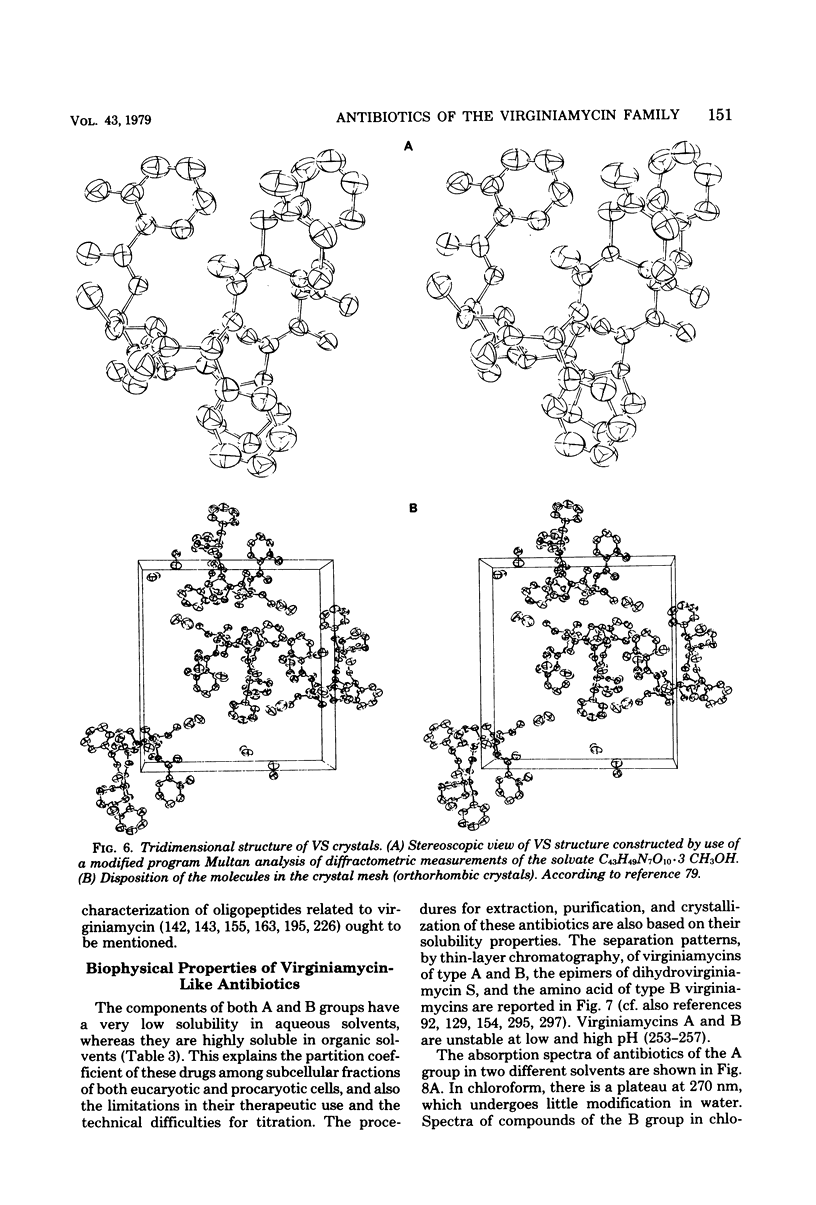
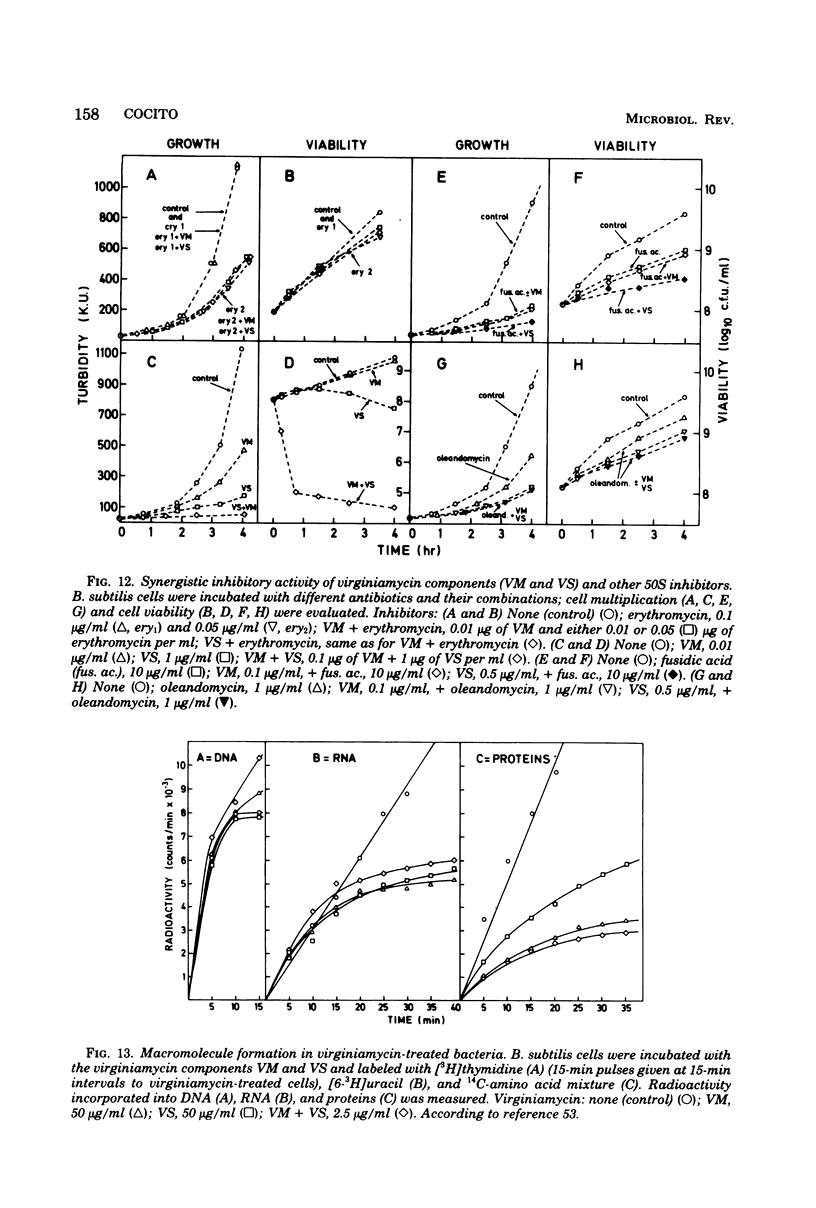
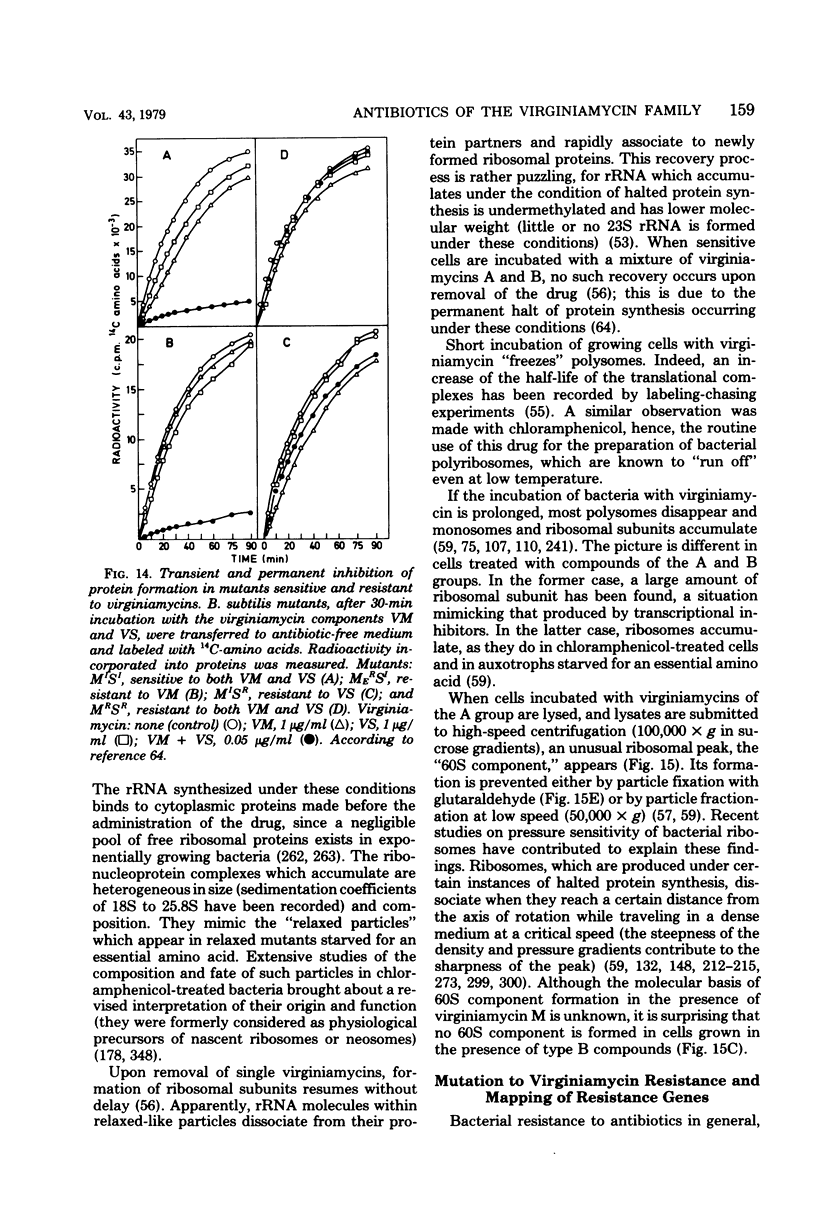
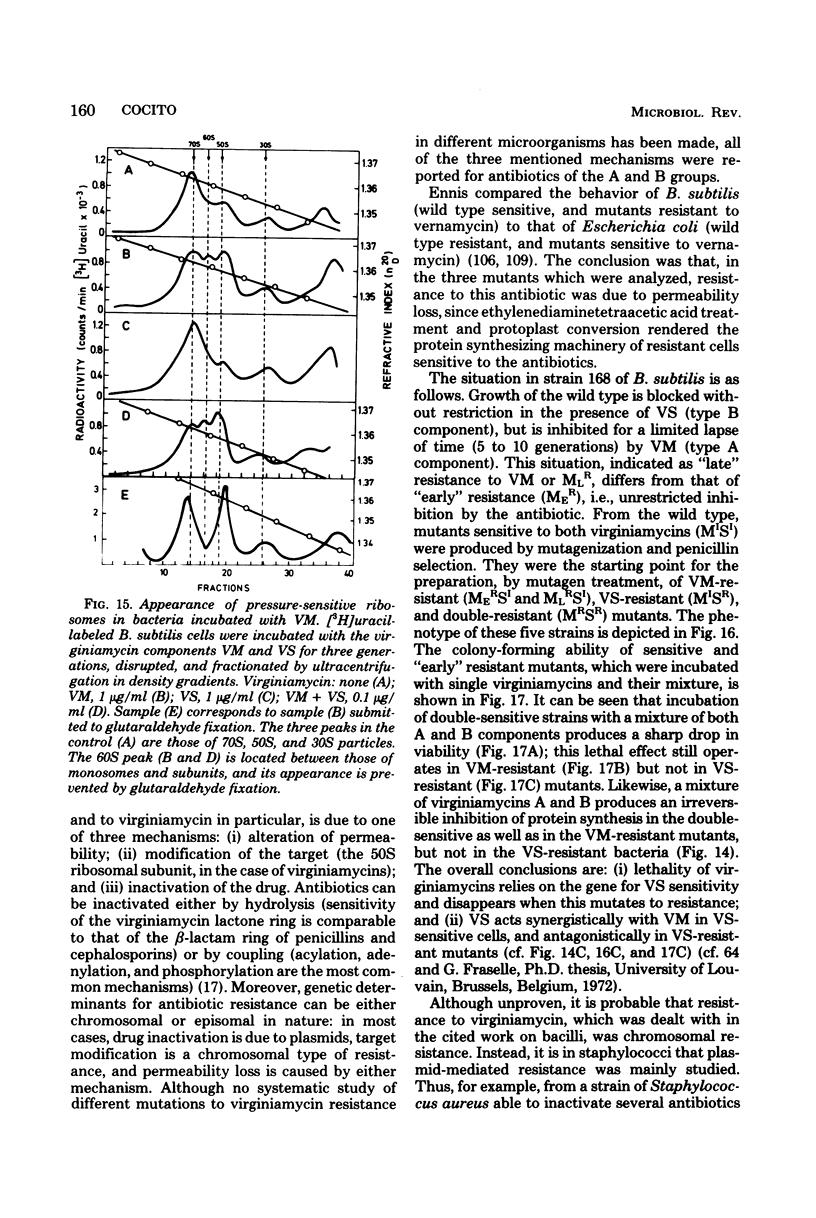
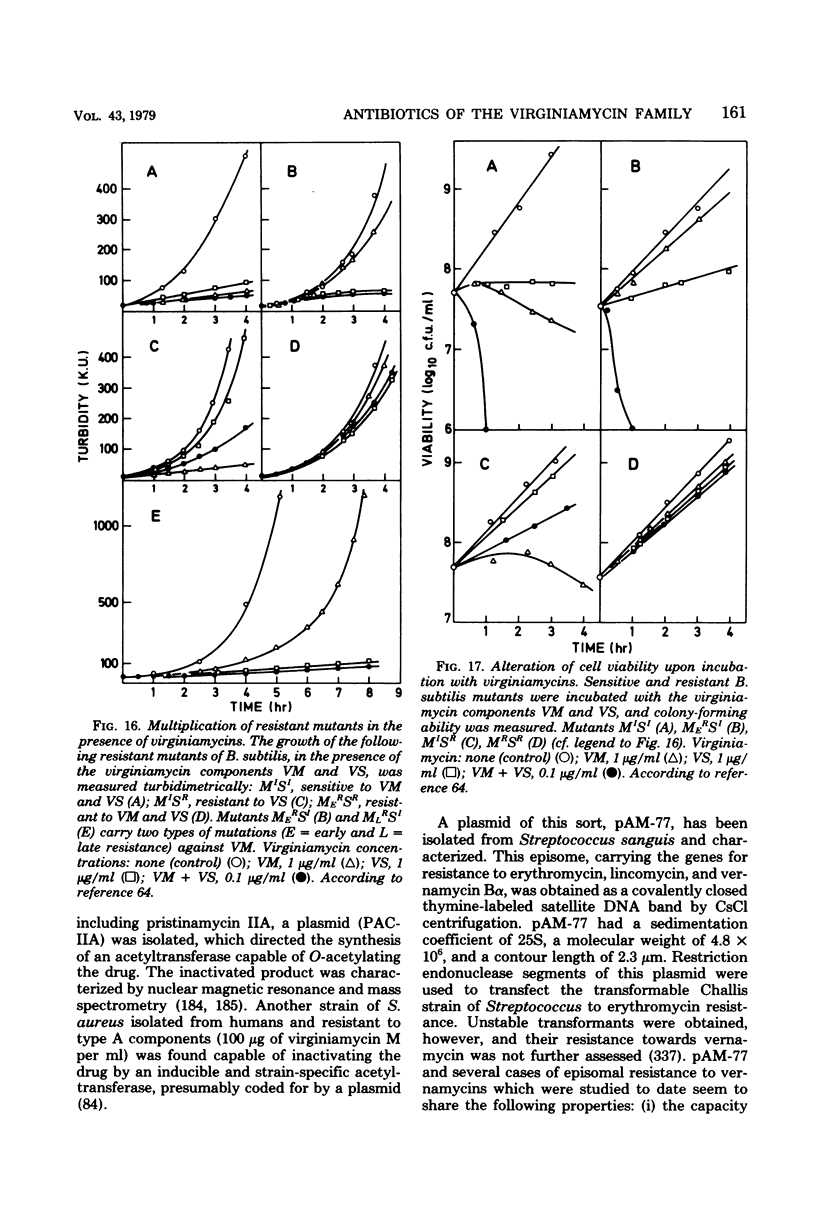
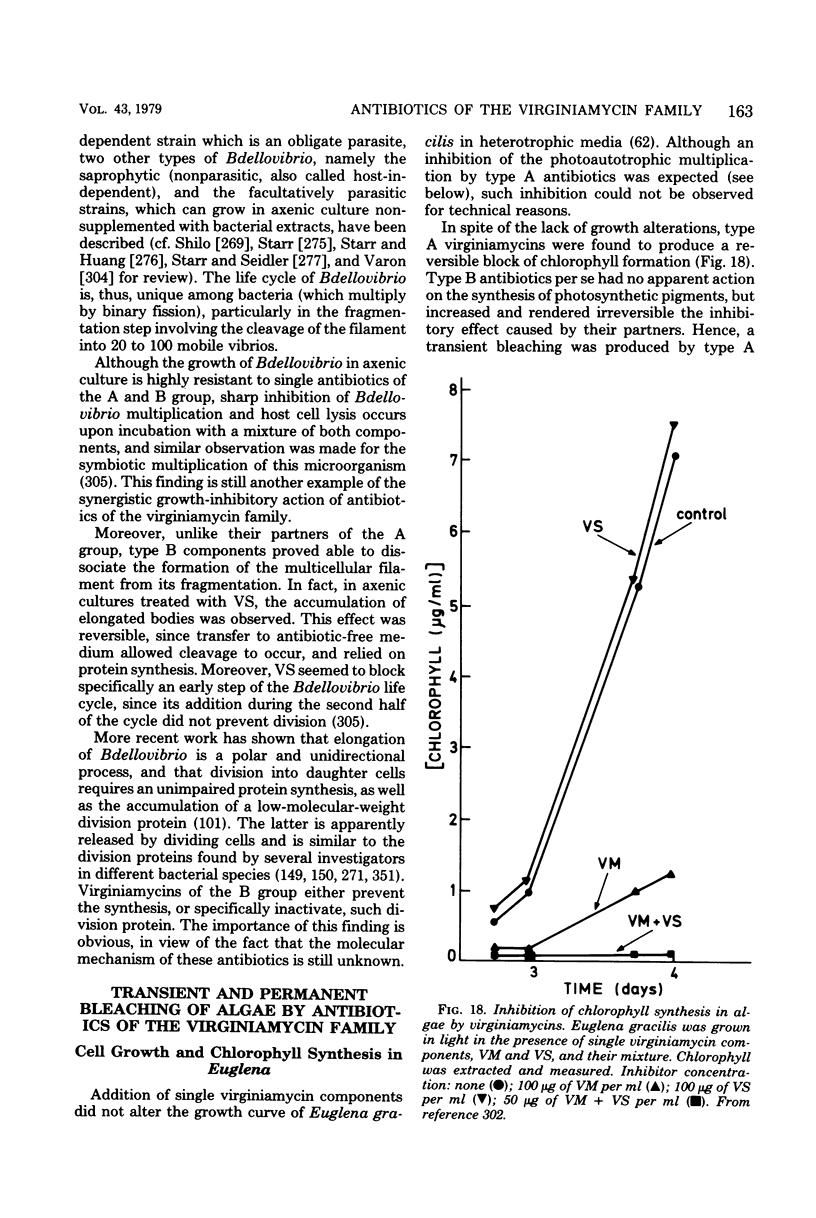
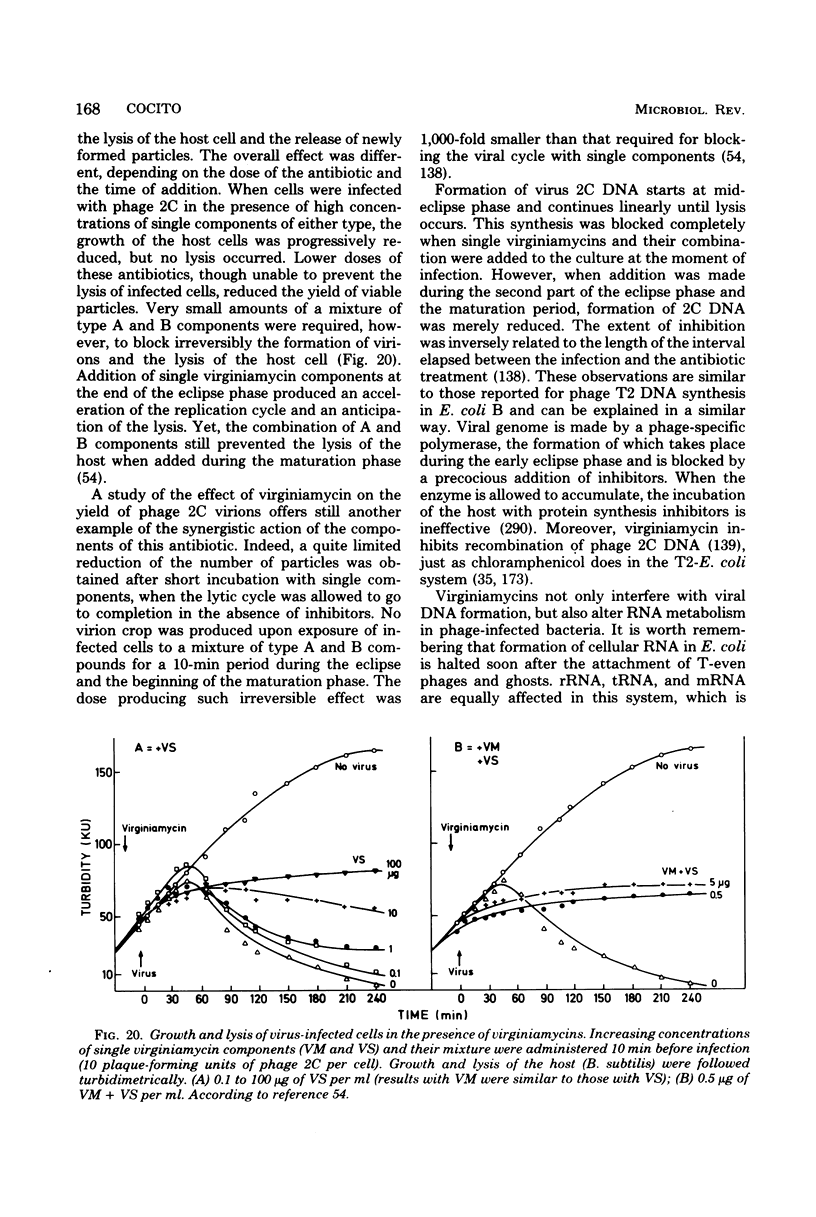
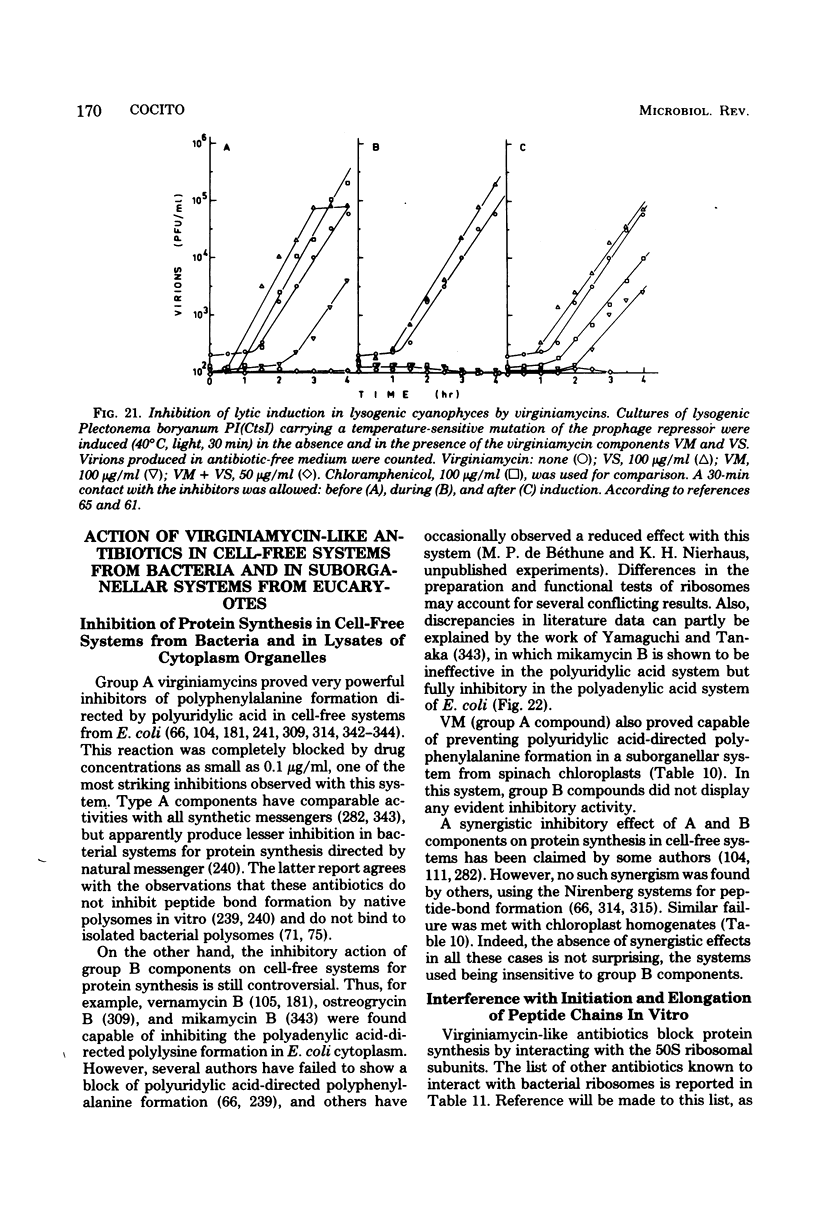
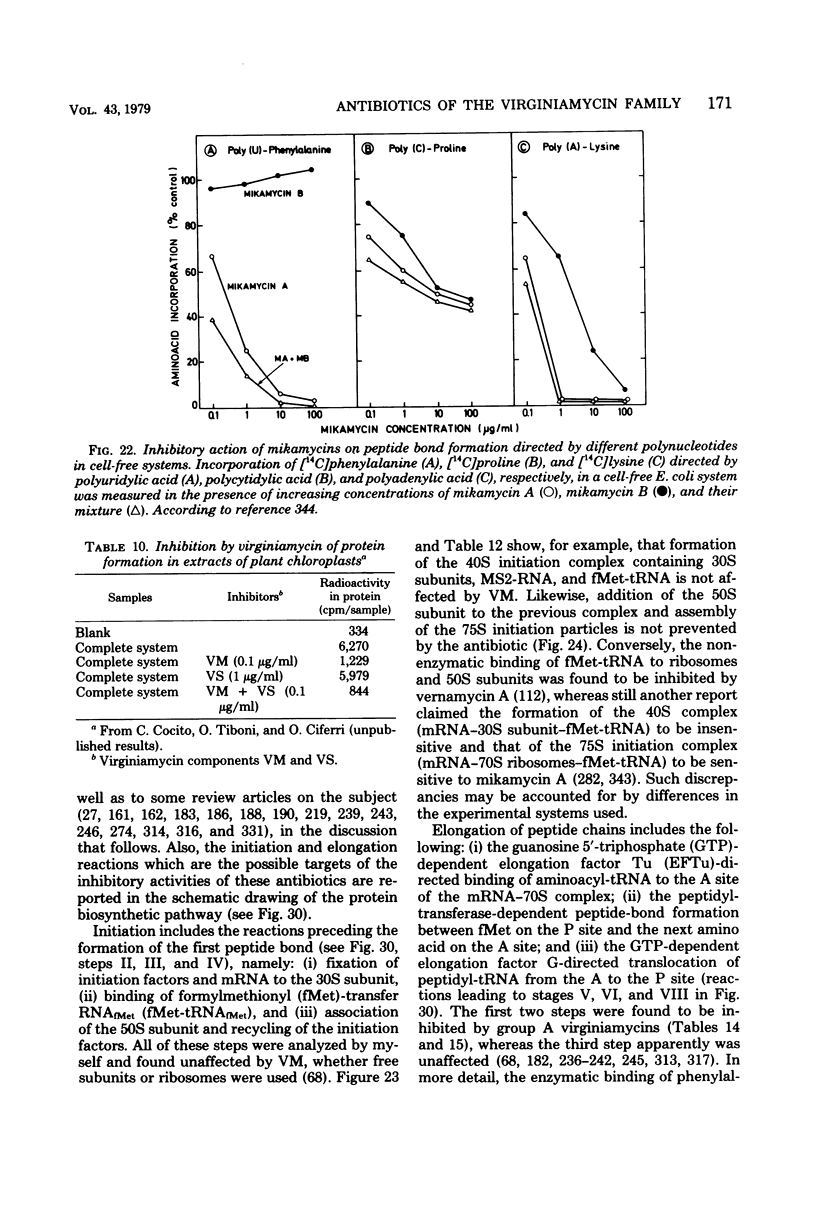
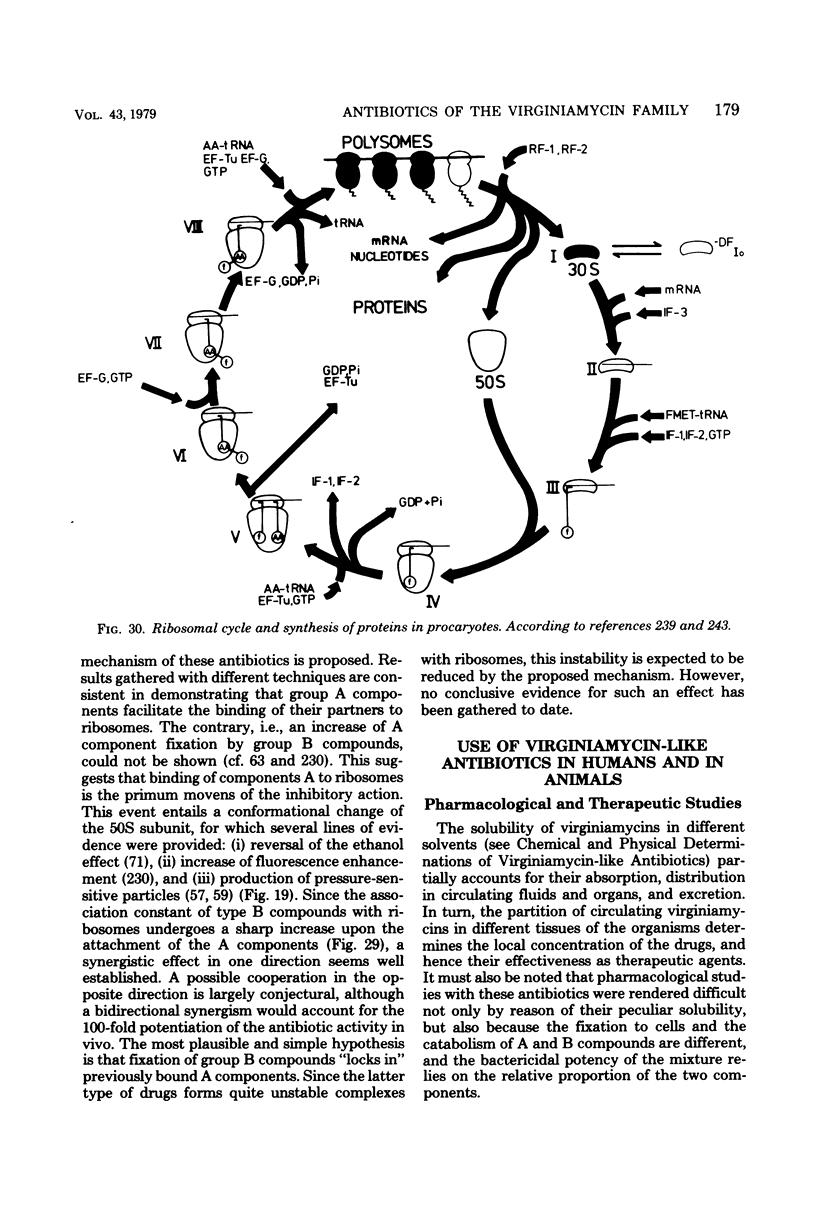
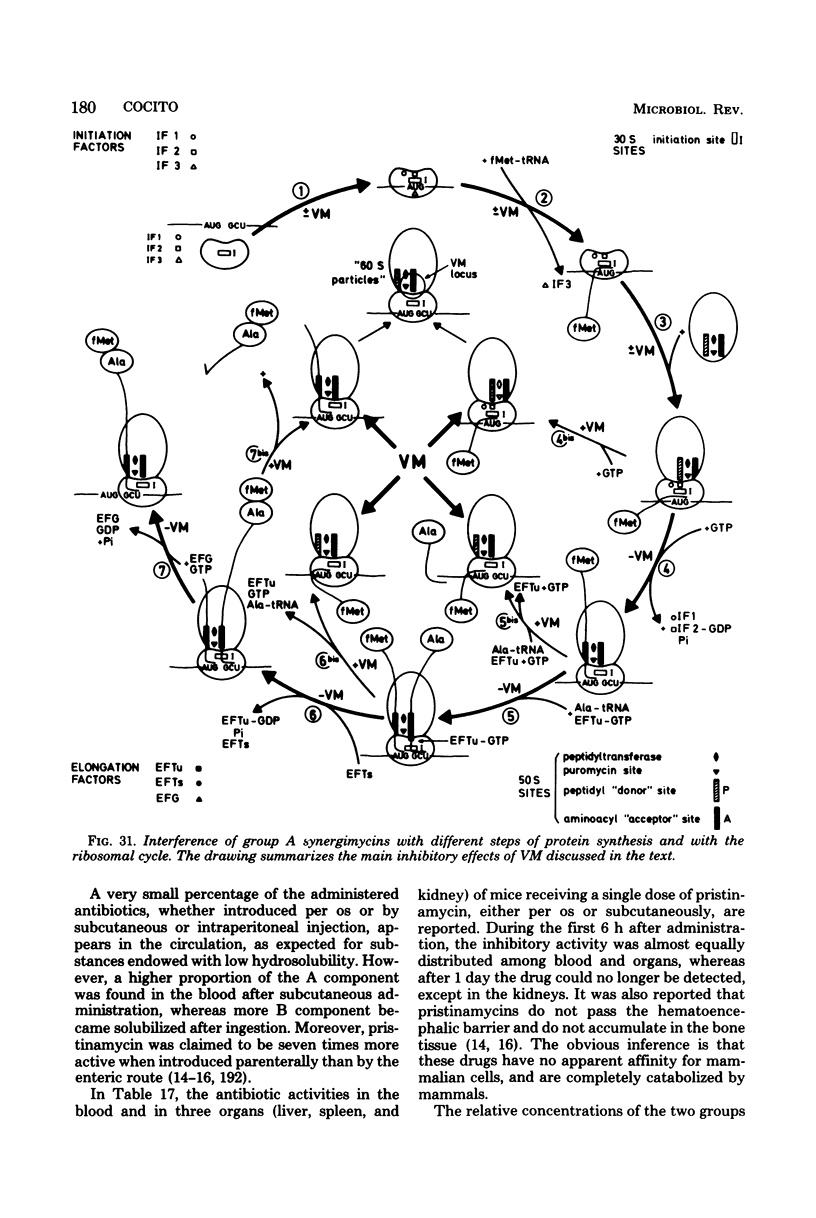
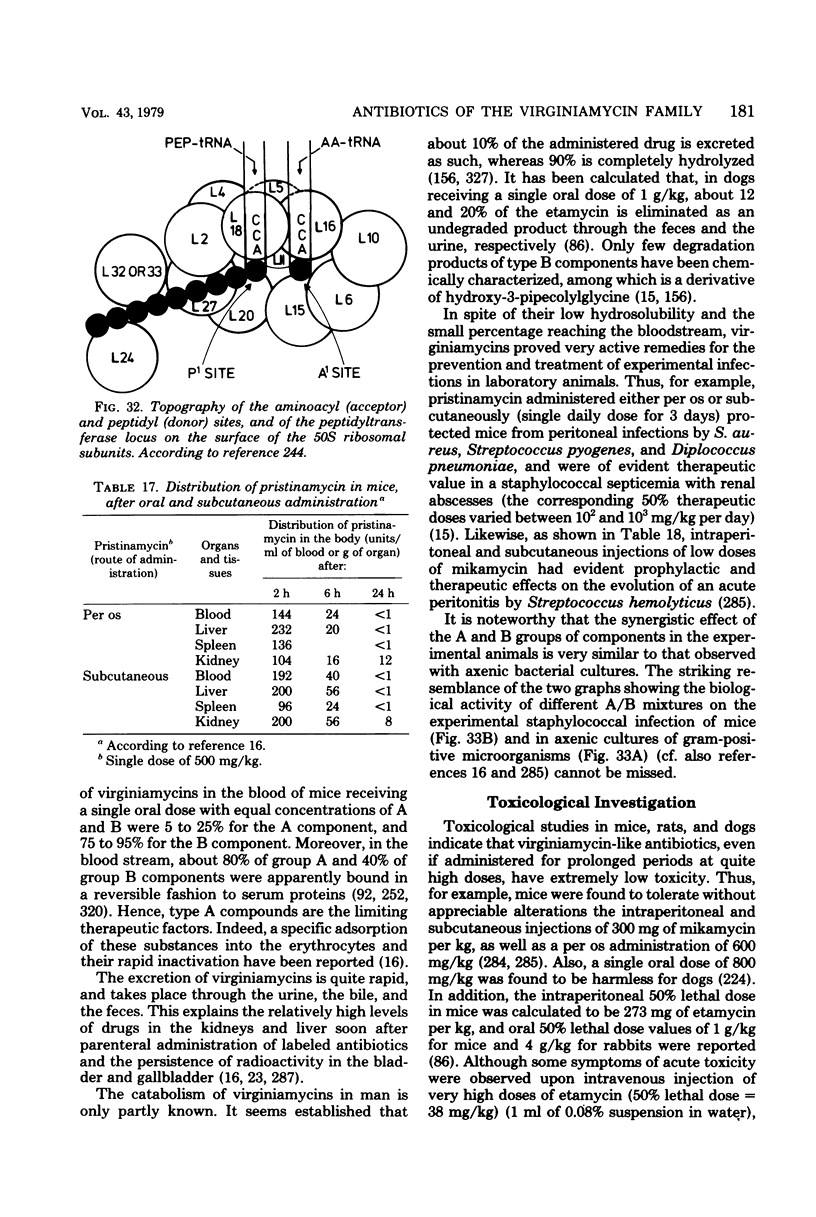
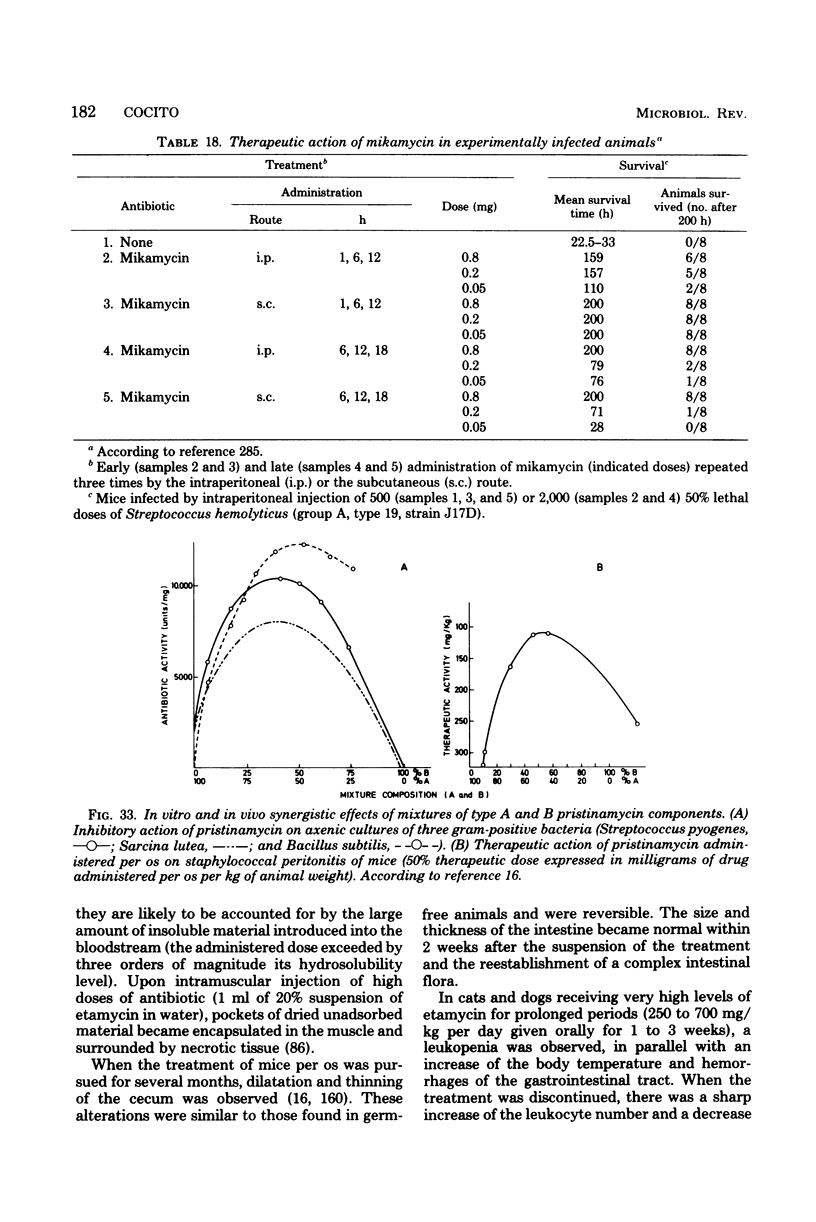
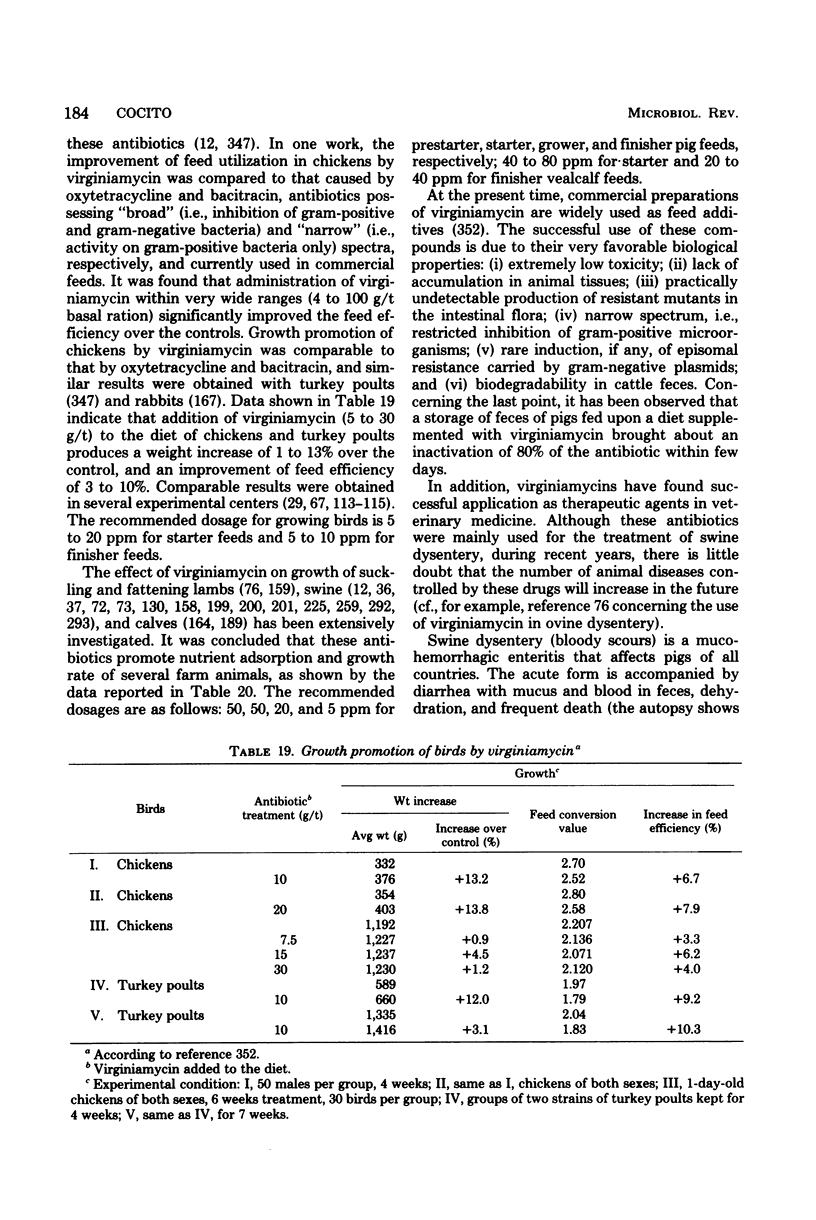
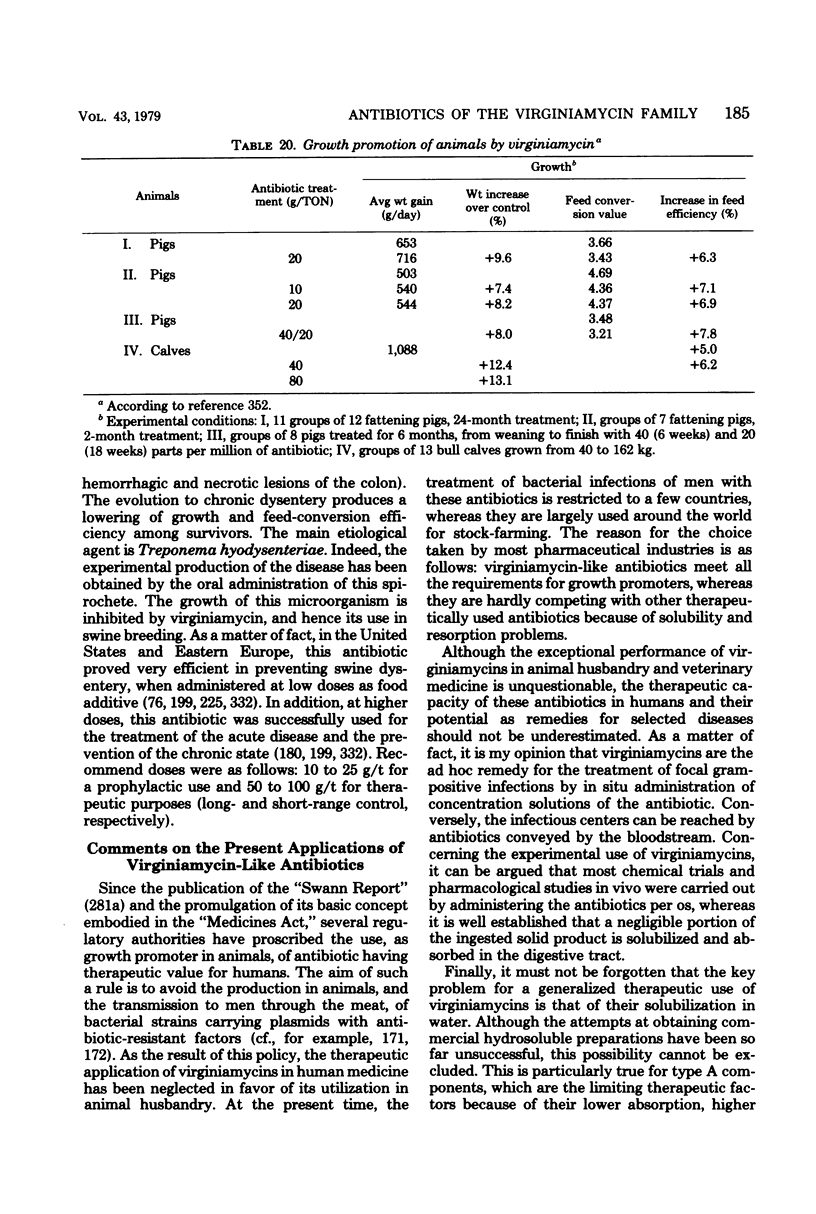
Full text
PDF
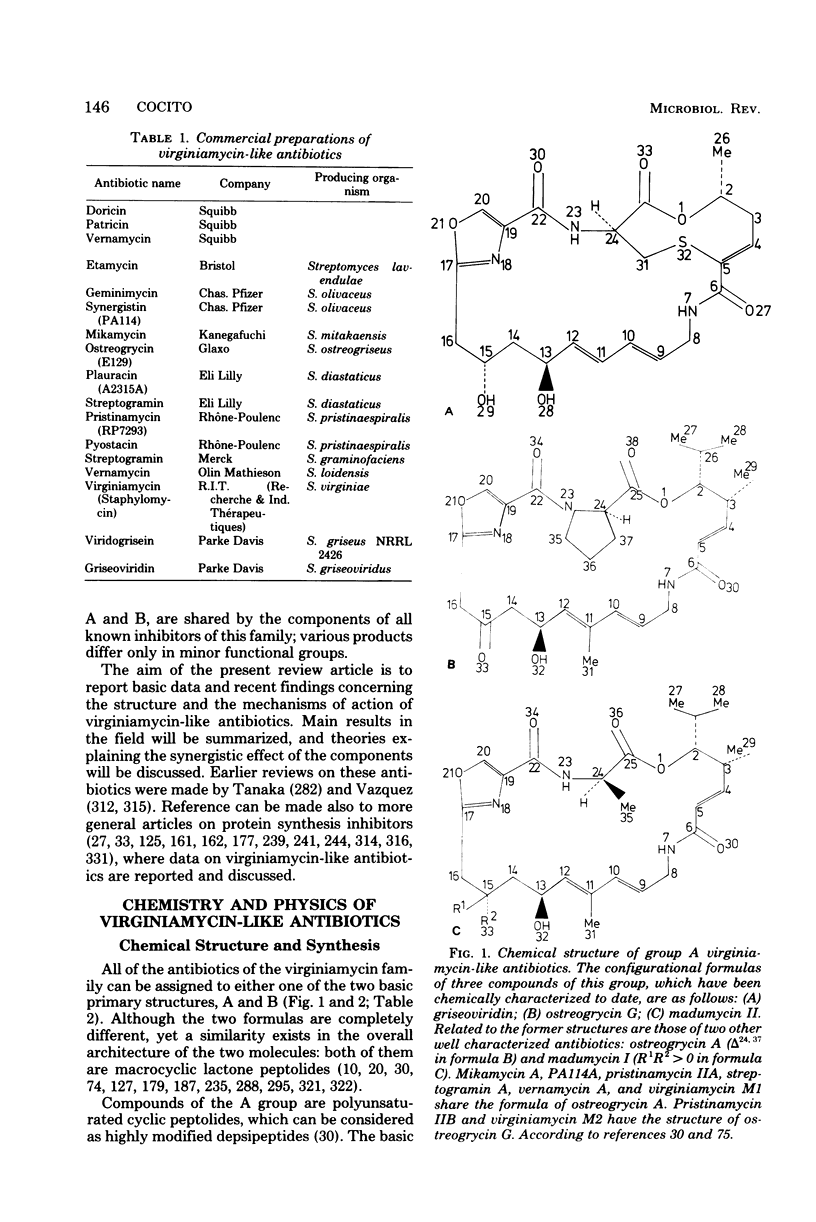
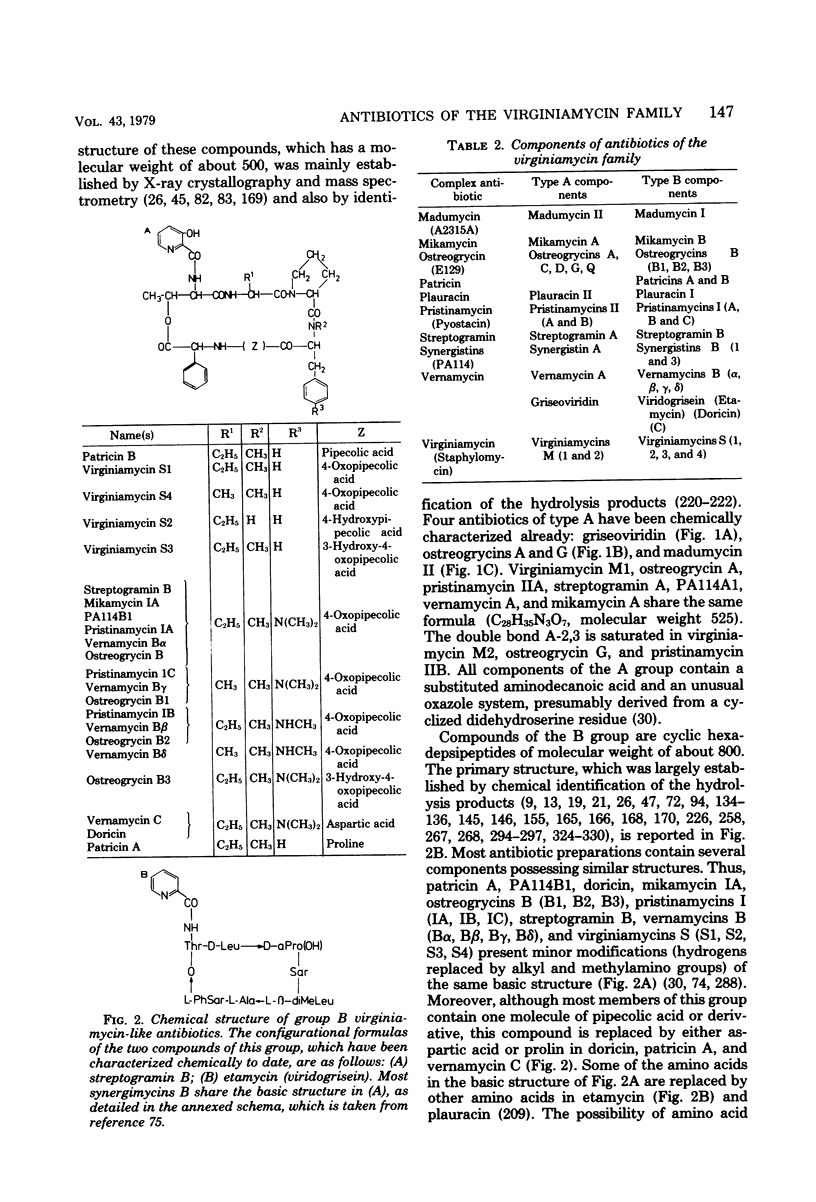

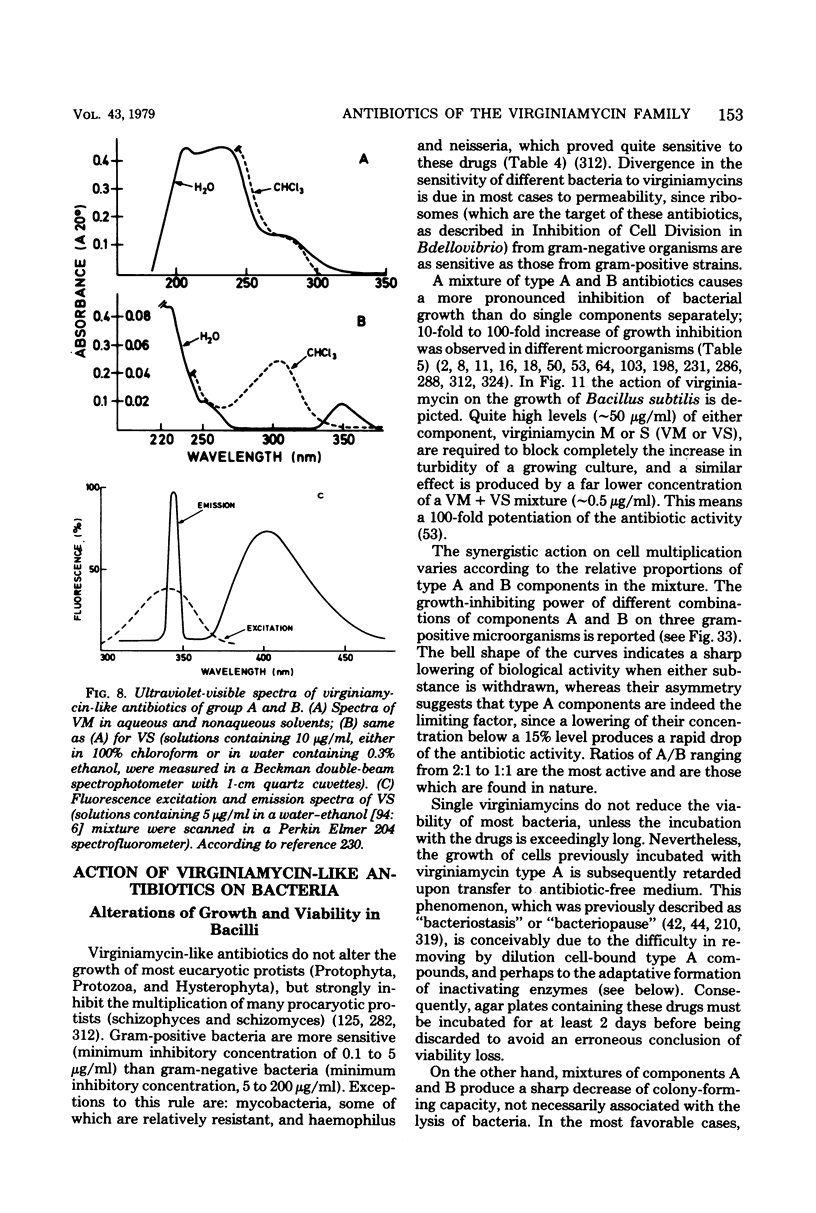
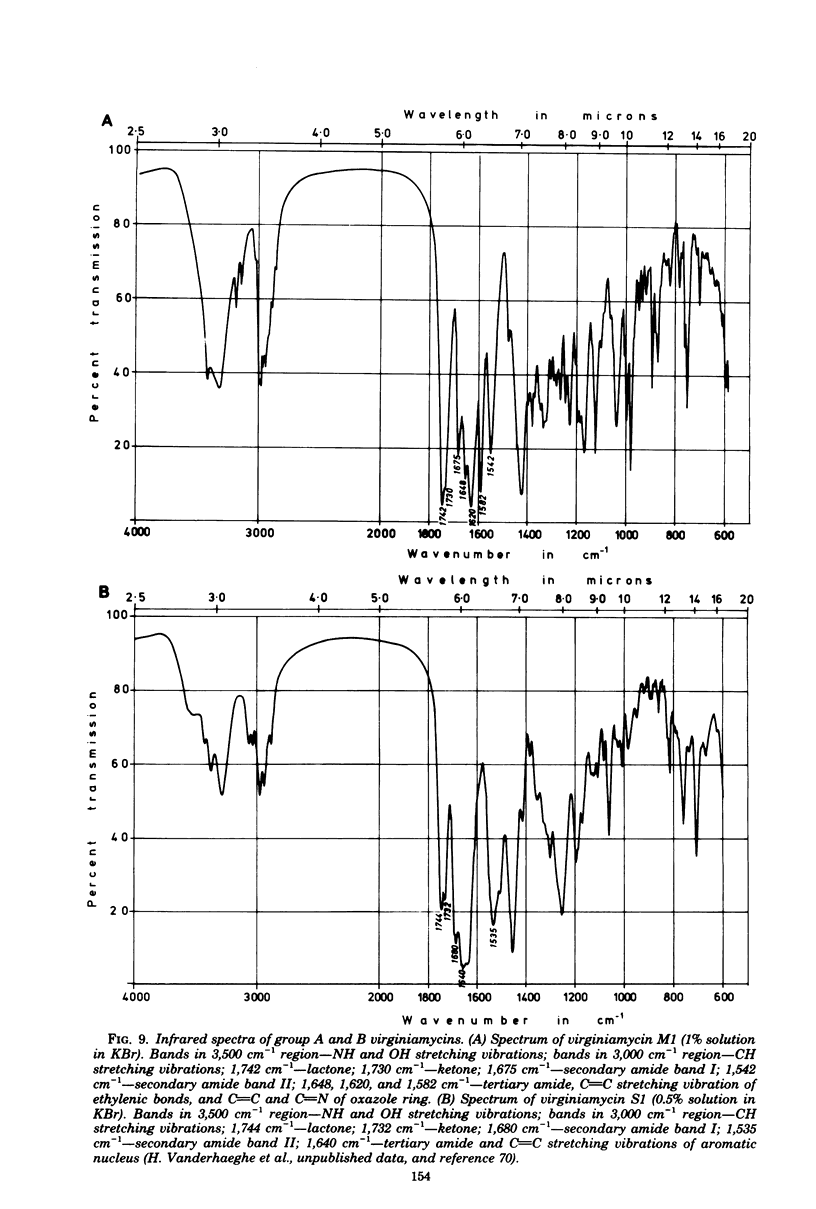
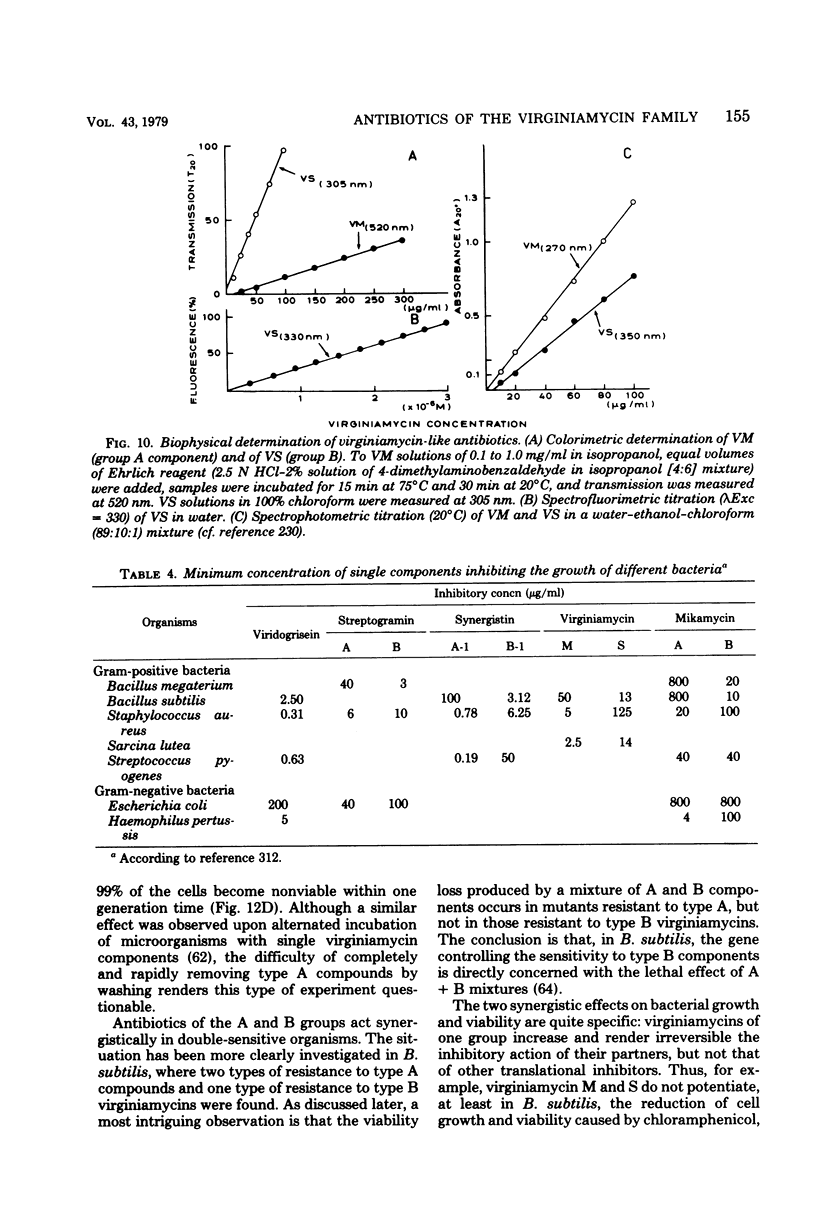

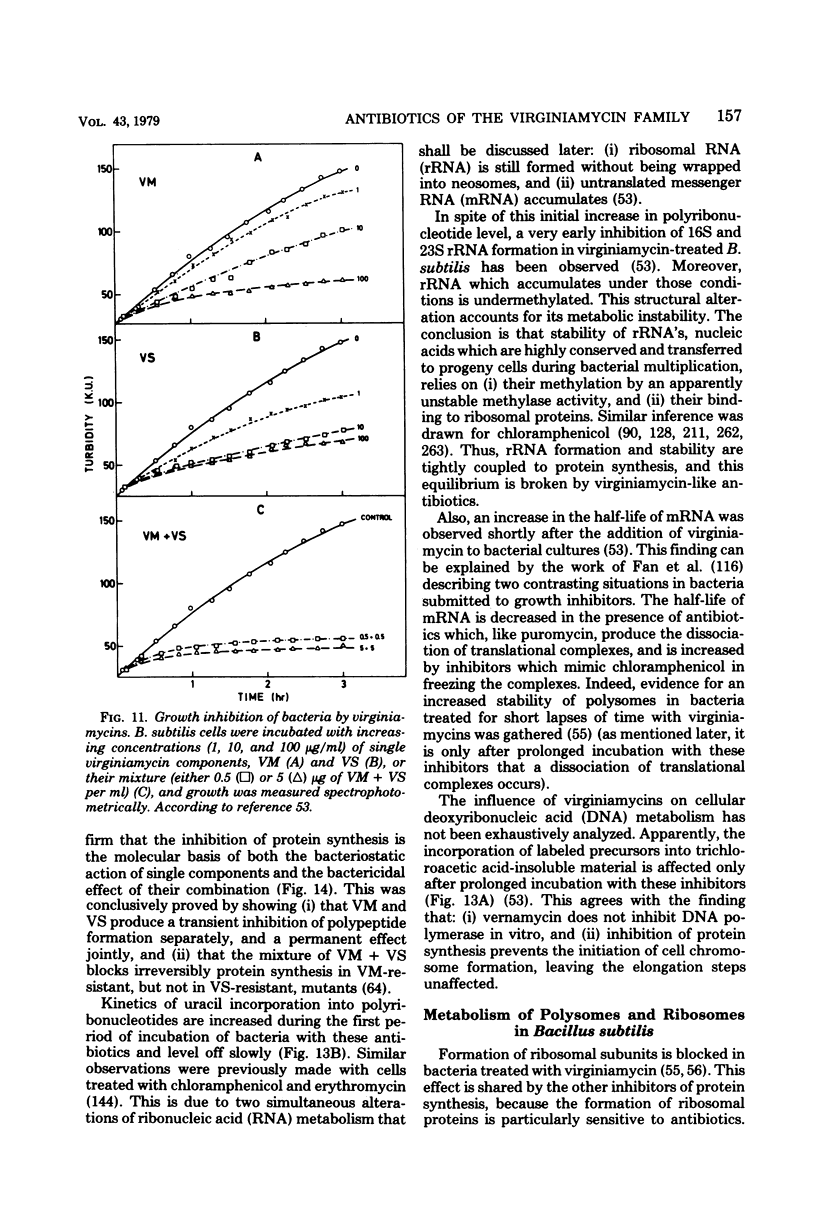























Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARAI M., FUKUHARA K., NAKAMURA S., SAKAGAMI Y., YONEHARA H. A new antibiotic, mikamycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1956 Sep;9(5):193–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARAI M., KARASAWA K., NAKAMURA S., YONEHARA H., UMEZAWA H. Studies on mikamycin. I. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1958 Jan;11(1):14–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARAI M., OKABE K., YONEHARA H., UMEZAWA H. Studies on mikamycin. II. Comparative studies on mikamycin with streptogramin and the antibiotic No. 899. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1958 Jan;11(1):21–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achard, Boudon L'utilisation de la pristinamycine en odonto-stomatologie. Inf Dent. 1969 Sep 11;51(37):3308–3311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen N. E. Macrolide resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: inducers of macrolide resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):669–674. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen N. E. Macrolide resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: induction of macrolide-resistant protein synthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):661–668. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anteunis M. J., Callens R. E., Tavernier D. K. Solution conformation of virginiamycins (staphylomycins). Eur J Biochem. 1975 Oct 15;58(2):259–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBER M., WATERWORTH P. M. ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF LINCOMYCIN AND PRISTINAMYCIN: A COMPARISON WITH ERYTHROMYCIN. Br Med J. 1964 Sep 5;2(5409):603–606. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5409.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENAZET F., BOURAT G. ETUDE AUTORADIOGRAPHIQUE DE LA R'EPARTITION DU CONSTITUANT I-A DE LA PRISTINAMYCINE (7.293 R.P.) CHEZ LA SOURIS. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 1;260:2622–2625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENAZET F., COSAR C. ETUDE CHEZ L'ANIMAL DES CONSTITUANTS DE LA PRISTINAMYCINE (7 293 R.P.) Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Aug;109:281–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOURDIAL J., NATALI R., GUERIN C. EMPLOI DE LA STAPHYLOMYCINE EN O.-R.-L. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac. 1964 Jul-Aug;81:502–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodanszky M., Perlman D. Peptide antibiotics. Science. 1969 Jan 24;163(3865):352–358. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3865.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon B., Gilbert M., Lamy F. Etude des taux plasmatiques et urinaires de la virginiamycine chez l'homme. Therapie. 1973 Mar-Apr;28(2):367–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouanchaud D. H., Fouace J. M., Bieth G. Physical studies of a Staphylococcus aureus plasmid mediating resistance to streptogramins, lincosamins and aminoglycosides. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1977 Nov-Dec;128B(4):431–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R., Nierhaus K. H., Garrett R. A., Wittmann H. G. The ribosome of Escherichia coli. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;18:1-44, 323-5. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60585-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. M., Jr Algal viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1972;17:243–277. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60752-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CELMER W. D., SOBIN B. A. The isolation of two synergistic antibiotics from a single fermentation source. Antibiot Annu. 1955;3:437–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHABBERT Y. A., ACAR J. F. INTERACTIONS BACT'ERIOSTATIQUES ET BACT'ERICIDES CHEZ LES ANTIBIOTIQUES DU GROUPE DE LA STREPTOGRAMINE. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Dec;107:777–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHASSAGNE P., CRUVEILLER J., BOCQUET L., GUIBERT C. LE TRAITEMENT DE LA COQUELUCHE PAR LA STAPHYLOMYCINE. ETUDE DE 88 OBSERVATIONS. Therapie. 1963 Jul-Aug;18:969–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHENG L., VAN STRATEN S., SNELL J. F. Studies in metabolic spectra. VI. An evaluation of the synergistic action between PA 114 A and B in vitro. Antibiot Chemother. 1960 Nov;10:671–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon R. E., Shane M. S. The effect of antibiotic stress on protein synthesis in the establishment of lysogeny of Plectonema boryanum. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):130–133. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson K., Kozinski A. W. Parent-to-progeny transfer and recombination of T4rII bacteriophage. J Virol. 1970 Sep;6(3):344–352. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.3.344-352.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celma M. L., Monro R. E., Vazquez D. Substrate and antibiotic binding sites at the peptidyl transferase centre of E. coli ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1970 Feb 16;6(3):273–277. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80076-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celma M. L., Monro R. E., Vazquez D. Substrate and antibiotic binding sites at the peptidyl transferase centre of E. coli ribosomes: Binding of UACCA-Leu to 50 S subunits. FEBS Lett. 1971 Mar 16;13(4):247–251. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80546-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabbert Y. A., Courvalin P. Synergie des composants des antibiotiques du groupe de la streptogramine. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1971 Jun-Jul;19(11):613–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin J. W., Chen S. A2315, new antibiotics produced by Actinoplanes philippinensis. 2. Structure of A2315A. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Mar;30(3):197–201. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Siddhikol C., Weisblum B. Subunit localization studies of antibiotic inhibitors of protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Aug 20;186(2):396–398. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles-Sigler R., Gil-Av E. Gas chromatographic determination of the configuration of amino acids in antibiotics of the vernamycin B group. Tetrahedron Lett. 1966 Sep;35:4231–4238. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(00)76042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinali G., Wolf H., Parmeggiani A. Effect of kirromycin on elongation factor Tu. Location of the catalytic center for ribosome-elongation-factor-Tu GTPase activity on the elongation factor. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):55–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11503.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Franke A. E. Characterization of a plasmid determining resistance to erythromycin, lincomycin, and vernamycin Balpha in a strain Streptococcus pyogenes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 May;5(5):534–537. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.5.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C. G., Bronchart R., Van Pel B. Phenotypic and genotypic changes induced in eucaryotic cells by protein inhibitors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 25;46(4):1688–1694. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90804-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C., Di Giambattista M. The in vitro binding of virginiamycin M to bacteria ribosomes and ribosomal subunits. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Oct 25;166(1):53–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00379729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C. Formation and decay of polyribosomes and ribosomes during the inhibition of protein synthesis and recovery. Biochimie. 1971;53(9):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(71)80067-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C. Formation of ribosomal particles in virginiamycin sensitive and resistant mutants of Bacillus subtilis. Biochimie. 1973;55(2):153–161. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(73)80387-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C., Fraselle G. The properties of virginiamycin-resistant mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 May;76(1):115–125. doi: 10.1099/00221287-76-1-115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C., Goldstein D. Inhibition of lytic induction in lysogenic cyanophyces. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):483–491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.483-491.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C., Kaji A. Virginiamycin M, a specific inhibitor of the acceptor site of ribosomes. Biochimie. 1971;53(6):763–770. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(71)80117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C. Metabolism of macromolecules in bacteria treated with virginiamycin. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Aug;57(2):179–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-57-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C. Origin and metabolic properties of the RNA species formed during the replication cycle of virus 2C. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1482–1493. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1482-1493.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C. Pressure dissociation of bacterial ribosomes and reassociation of ribosomal subunits. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jun 1;162(1):43–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00333849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C., Shilo M. Macromolecule metabolism and photosynthetic functions in blue-green algae treated with virginiamycin, an inhibitor of protein synthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Aug;6(2):136–143. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.2.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C. The action of virginiamycin on nucleic acid and protein synthesis in Bacillus subtilis infected with bacteriophage 2C. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Aug;57(2):195–206. doi: 10.1099/00221287-57-2-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C. The ribosomal cycle in bacteria treated with an inhibitor of protein synthesis. Biochimie. 1973;55(3):309–316. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(73)80130-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C., Vanlinden F. Polysomes and ribosome metabolism in virus 2C multiplication. Biochimie. 1978;60(4):399–402. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(78)80673-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocito C., Voorma H. O., Bosch L. Interference of virginiamycin M with the initiation and the elongation of peptide chains in cell-free systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 27;340(3):285–298. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90274-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras A., Vázquez D. Synergistic interaction of the streptogramins with the ribosome. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Apr 15;74(3):549–551. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crooy P., De Neys R. Virginiamycin: nomenclature. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Jun;25(6):371–372. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cundliffe E. Antibiotics and polyribosomes. II. Some effects of lincomycin, spiramycin, and streptogramin A in vivo. Biochemistry. 1969 May;8(5):2063–2066. doi: 10.1021/bi00833a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOST M., PASCAL C. M'ETHODES DE DOSAGE DES CONSTITUANTS DE LA PRISTINAMYCINE DANS LES LIQUIDES BIOLOGIQUES. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Aug;109:290–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Meester C., Rondelet J. Microbial acetylation of M factor of virginiamycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 Dec;29(12):1297–1305. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delpierre G. R., Eastwood F. W., Gream G. E., Kingston D. G., Sarin P. S., Todd L., Williams D. H. Antibiotics of the ostreogrycin complex. II. Structure of ostreogrycin A. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1966;19:1653–1669. doi: 10.1039/j39660001653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delpierre G. R., Eastwood F. W., Gream G. E., Kingston D. G., Sarin P. S., Todd L., Williams D. H. Antibiotics of the ostreogrycin complex. II. Structure of ostreogrycin A. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1966;19:1653–1669. doi: 10.1039/j39660001653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delpierre G. R., Eastwood F. W., Gream G. E., Kingston D. G., Sarin P. S., Todd L., Williams D. H. The structure of ostreogrycin A. Tetrahedron Lett. 1966 Jan;(4):369–372. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(00)72948-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCuollo C. J., Miller J. A., Miller C. R. Tissue residue studies in swine treated with virginiamycin. J Agric Food Chem. 1973 Sep-Oct;21(5):818–821. doi: 10.1021/jf60189a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon H., Kellerman G. M., Linnane A. W. XXIV. Effect of mikamycin, carbomycin, spiramycin, erythromycin, and paromomycin on growth and respiration of HeLa cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Oct;152(2):869–875. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90283-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon H., Kellerman G. M., Mitchell C. H., Towers N. H., Linnane A. W. Mikamycin, an inhibitor of both mitochondrial protein synthesis and respiration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 May 21;43(4):780–786. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90684-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubin D. T., Elkort A. T. A direct demonstration of the metabolic turnover of chloramphenicol RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jun 8;103(2):355–358. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90180-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dublanchet A., Soussy C. J., Squinazi F., Duval J. Résistance de Staphylococcus aureus aux streptogramines. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1977 Apr;128A(3):277–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGLISH A. R., HALSEMA G. V., MCBRIDE T. J. Biologic studies on the PA 114 group of antibiotics. Antibiot Annu. 1955;3:442–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebringer L. Are plastids derived from prokaryotic micro-organisms? Action of antibiotics on chloroplasts of Euglena gracilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Jun;71(1):35–52. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-1-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebringer L. Macrolide antibiotics as bleaching factors for Euglena gracillis. Naturwissenschaften. 1965 Dec;52(24):666–666. doi: 10.1007/BF00589640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H. Developmental pathways for the temperate phage: lysis vs lysogeny,. Annu Rev Genet. 1972;6(0):157–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.06.120172.001105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman M., Swinton D., Schiff J. A., Epstein H. T., Zeldin B. Deoxyribonucleic Acid of the blue-green algae (cyanophyta). Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):315–331. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.315-331.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eksztejn M., Varon M. Elongation and cell division in Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Aug 26;114(2):175–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00410781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis H. L. Bacterial resistance to the synergistic antibiotics of the PA 114, streptogramin, and vernamycin complexes. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1881–1887. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1881-1887.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis H. L. Binding of the antibiotic vernamycin in Balpha to Escherichia coli ribosomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Feb;160(2):394–401. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90413-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis H. L., Duffy K. E. Vernamycin A inhibits the non-enzymatic binding of fMet-tRNA to ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 29;281(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90191-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis H. L. Inhibition of protein synthesis by polypeptide antibiotics. 3. Ribosomal site of inhibition. Mol Pharmacol. 1966 Sep;2(5):444–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis H. L. Inhibition of protein synthesis by polypeptide antibiotics. I. Inhibition in intact bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):1102–1108. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.1102-1108.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis H. L. Inhibition of protein synthesis by polypeptide antibiotics.. II. In vitro protein synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1965 Oct;90(4):1109–1119. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.4.1109-1119.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis H. L. Interaction of vernamycin A with Escherichia coli ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 30;10(7):1265–1270. doi: 10.1021/bi00783a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis H. L. Mutants of Escherichia coli sensitive to antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1971 Aug;107(2):486–490. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.2.486-490.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis H. L. Polysome metabolism in Escherichia coli: effect of antibiotics on polysome stability. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Mar;1(3):197–203. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.3.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAN D. P., HIGA A., LEVINTHAL C. MESSENGER RNA DECAY AND PROTECTION. J Mol Biol. 1964 Feb;8:210–222. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80130-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINLAND M., JONES W. F., Jr, NICHOLS R. L. Development of resistance and cross-resistance in vitro to erythromycin, carbomycin, spiramycin, oleandomycin and streptogramin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Nov;93(2):388–393. doi: 10.3181/00379727-93-22766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREY H., MEYER H. J., NIEVERGELT J. [Therapeutic trials with the antibiotic staphylomycin]. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1962 Jun 23;92:785–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Munoz R., Monro R. E., Torres-Pinedo R., Vazquez D. Substrate- and antibiotic-binding sites at the peptidyl-transferase centre of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Studies on the chloramphenicol. lincomycin and erythromycin sites. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Nov 11;23(1):185–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouace J., Bouanchaud D. H., Duval J. Propriétés génétiques d'un plasmide de staphylocoque codant pour la résistance à cinq aminosides et aux streptogramines. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1977 May-Jun;128A(4):371–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freymuth F., Moulin M. A., Morel C., Savini E. C. Contribution à l'élaboration du spectre antibactérien des antibiotiques: rifamycines, gentamycine, fusidate de sodium, kitasamycine, virginiamycine, pristinamycine, mikamycine, amfomycine. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1970;164(11):2244–2249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARCIA-MENDOZA C. STUDIES ON THE MODE OF ACTION OF ETAMYCIN (VIRIDOGRISEIN). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Feb 15;97:394–396. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARROD L. P., WATERWORTH P. M. Behaviour in vitro of some new antistaphylococcal antibiotics. Br Med J. 1956 Jul 14;2(4984):61–65. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4984.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON J., BOMAN H. G., ISAKSSON L. A. IN VIVO INHIBITION OF RNA METHYLATION IN THE PRESENCE OF CHLORAMPHENICOL. J Mol Biol. 1964 Sep;9:831–833. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80190-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOSSELINCKX F., PARMENTIER G. CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATION OF THE COMPONENTS OF STAPHYLOMYCIN. J Pharm Belg. 1963 Sep-Oct;18:419–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett R. A., Wittmann H. G. Structure of bacterial ribosomes. Adv Protein Chem. 1973;27:277–347. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60450-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goffic F. L., Capmau M. L., Bonnet D., Cerceau C., Soussy C., Dublanchet A., Duval J. Plasmid-mediated pristinamycin resistance. PAC IIA: a new enzyme which modifies pristinamycin IIA. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Aug;30(8):665–669. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBBS D. C., CELMER W. D. Structure of the antibiotics PA 114B-1 and PA114B-3. Nature. 1960 Aug 13;187:598–599. doi: 10.1038/187598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOSOKAWA K., NOMURA M. INCOMPLETE RIBOSOMES PRODUCED IN CHLORAMPHENICOL- AND PUROMYCIN-INHIBITED ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:225–241. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80296-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hapke B., Noll H. Structural dynamics of bacterial ribosomes. IV. Classification of ribosomes by subunit interaction. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 25;105(1):97–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90196-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoet P. P., Fraselle G., Cocito C. Discontinuous duplication of both strands of virus 2C DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Mar 9;171(1):43–51. doi: 10.1007/BF00274013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoet P., Coene M., Cocito C. Synthesis of phage 2C-DNA in permeabilized B. subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jan 17;158(3):297–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00267201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoet P., Fraselle G., Cocito C. Recombinational-type transfer of viral DNA during bacteriophage 2C replication in Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):718–726. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.718-726.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoet P., Fraselle G., Cocito C. Transfer to progeny of both DNA strands of phage 2C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 2;66(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook D. J., Vining L. C. Biosynthetic precursors of etamycin, a peptidolactone antibiotic from Streptomyces griseoviridus. Can J Biochem. 1973 Dec;51(12):1630–1637. doi: 10.1139/o73-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou C. T., Perlman D. Microbial transformations of peptide antibiotics. V. Purification and properties of the actinomycin lactonase from Actinoplanes missouriensis. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 25;245(6):1289–1295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou C. T., Perlman D., Schallock M. R. Microbial transformation of peptide antibiotics. VI. Purification and properties of a peptide lactonase hydrolyzing dihydrostaphylomycin S. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Jan;23(1):35–42. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell N., Molloy P. L., Linnane A. W., Lukins H. B. Biogenesis of mitochondria 34. The synergistic interaction of nuclear and mitocohondrial mutations to produce resistance to high levels of mikamycin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;128(1):43–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00267293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infante A. A., Baierlein R. Pressure-induced dissociation of sedimenting ribosomes: effect on sedimentation patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1780–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L. O., Fisher W. D. Mechanism for the regulation of cell division in Agmenellum. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):1006–1014. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.1006-1014.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L. O., Fisher W. D. Novel mutant impaired in cell division: evidence for a positive regulating factor. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):999–1005. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.999-1005.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANBON M., BRUNEL D., BERTRAND A., MICHEL-BRIAND Y. [Effectiveness of a new antistaphylococcal agent (7293 RP) in acute osteomyelitis in children]. Arch Fr Pediatr. 1962 Dec;19:1409–1412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janbon M., Bertrand A., Pourquier M. Etude comparée de l'activité de divers antibiotiques à l'égard du staphylocoque doré pathogène. Chemotherapy. 1965;10(4):229–244. doi: 10.1159/000220412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen G., Anne J., Vanderhaeghe H. Preparation and properties of derivatives of virginiamycin S. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Feb;30(2):141–145. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolles F., Terlain B., Thomas J. P. Metabolic investigations on pristinamycin. Nature. 1965 Jul 10;207(993):199–200. doi: 10.1038/207199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURLAND C. G., NOMURA M., WATSON J. D. The physical properties of the chloromycetin particles. J Mol Biol. 1962 May;4:388–394. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji H. Intraribosomal environment of the nascent peptide chain. Int Rev Cytol. 1970;29:169–211. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamal F., Katz E. Studies of etamycin biosynthesis employing short-term experiments with radiolabeled precursors. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1976 Sep;29(9):944–949. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.29.944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. H., Otake N., Yonehara H. Studies on mikamycin B lactonase. I. Degradation of mikamycin B by Streptomyces mitakaensis. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1974 Dec;27(12):903–908. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.27.903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. O. The feeding of virginiamycin to growing rabbits. Vet Rec. 1971 Dec 25;89(26):677–679. doi: 10.1136/vr.89.26.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston D. G., Sarin P. S., Todd L., Williams D. H. Antibiotics of the ostreogrycin complex. IV. The structure of ostreogrycin G. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1966;20:1856–1860. doi: 10.1039/j39660001856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston D. G., Todd L., Williams D. H. Antibiotics of the ostreogrycin complex. 3. The structure of ostreogrycin A. Evidence based on nuclear magnetic double resonance experiments and high-resolution mass spectrometry. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1966;19:1669–1676. doi: 10.1039/j39660001669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knothe H. A review of the medical considerations of the use of tylosin and other macrolide antibiotics as additives in animal feeds. Infection. 1977;5(3):183–187. doi: 10.1007/BF01639755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knothe H. Medical implications of macrolide resistance and its relationship to the use of tylosin in animal feeds. Infection. 1977;5(3):137–139. doi: 10.1007/BF01639747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozinski A. W., Kozinski P. B., Shannon P. REPLICATIVE FRAGMENTATION IN T4 PHAGE: INHIBITION BY CHLORAMPHENICOL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Oct;50(4):746–753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.4.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota K., Okuyama A., Tanaka N. Differential effects of antibiotics on peptidyl transferase reactions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 9;47(5):1196–1202. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90961-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland C. G. Ribosome structure and function emergent. Science. 1970 Sep 18;169(3951):1171–1177. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3951.1171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland C. G. Structure and function of the bacterial ribosome. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:173–200. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küchler E. Chemical methods of studying ribosome structure. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1976 Sep;15(9):533–542. doi: 10.1002/anie.197605331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUCKEY T. D. Antibiotic action in adaptation. Nature. 1963 Apr 20;198:263–265. doi: 10.1038/198263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskin A. I., Chan W. M. Effects of vernamycins on aminoacyl-transfer ribonucleic acid binding to Escherichia coli ribosomes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1965;5:321–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Goffic F., Capmau M. L., Abbe J., Cerceau C., Dublanchet A., Duval J. Plasmid mediated pristinamycin resistance: PH 1A, a pristinamycin 1A hydrolase. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1977 Nov-Dec;128B(4):471–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P. The elongation reactions in protein synthesis. Adv Protein Chem. 1973;27:213–242. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60448-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipmann F. Polypeptide chain elongation in protein biosynthesis. Science. 1969 May 30;164(3883):1024–1031. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3883.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas I. A. The use of antibiotics as feed additives for farm animals. Proc Nutr Soc. 1972 May;31(1):1–8. doi: 10.1079/pns19720003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAILLARD M. A., PELLERAT J. COMPORTEMENT DE LA PRISTINAMYCINE DANS LE SANG HUMAIN. COMPARAISON AVEC QUELQUES AUTRES ANTIBIOTIQUES. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Aug;109:314–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASSIAS P. [Use of staphylomycin in orthopedic surgery]. Presse Med. 1962 Dec 29;70:2827–2828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madan V., Kumar H. D. Action of nalidixic acid and hydroxyurea on two blue-green algae. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1971;11(6):495–499. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630110605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino F., Tsuzuki J. Absence of histone in the blue-green alga Anabaena cylindrica. Nature. 1971 Jun 18;231(5303):446–447. doi: 10.1038/231446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauger A. B. Peptide antibiotic biosynthesis: a new approach. Experientia. 1968 Oct 15;24(10):1068–1072. doi: 10.1007/BF02138755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May P., May E., Granboulan P., Granboulan N., Marmur J. Ultrastructure du bactériophage 2C et propriétés de son DNA. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1968 Dec;115(6):1029–1046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Rohn J. Experimentelle Erfahrungen mit Staphylomycin. Arzneimittelforschung. 1965 May;15(5):477–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. R., Philip J. R., Free S. M., Jr, Landis L. M. Virginiamycin for prevention of swine dysentery. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1972 Nov;67(11):1246–1248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnier J., Bourse R. Résistance croisée chez les macrolides et les groupes apparentés. Pathol Biol. 1967 Dec;15(23):1179–1187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E. Catalysis of peptide bond formation by 50 S ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 28;26(1):147–151. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90271-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E., Celma M. L., Vazquez D. Action of sparsomycin on ribosome-catalysed peptidyl transfer. Nature. 1969 Apr 26;222(5191):356–358. doi: 10.1038/222356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E., Marcker K. A. Ribosome-catalysed reaction of puromycin with a formylmethionine-containing oligonucleotide. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 28;25(2):347–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E., Staehelin T., Celma M. L., Vazquez D. The peptidyl transferase activity of ribosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:357–368. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monro R. E., Vazquez D. Ribosome-catalysed peptidyl transfer: effects of some inhibitors of protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 28;28(1):161–165. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEIDHARDT F. C., GROS F. Metabolic instability of the ribonucleic acid synthesized by Escherichia coli in the presence of chloromycetin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Sep;25(3):513–520. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90521-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOMURA M., OKAMOTO K., ASANO K. RNA metabolism in Escherichia coli infected with bacteriophage T4. Inhibition of host ribosomal and soluble RNA synthesis by phage and effect of chloromycetin. J Mol Biol. 1962 May;4:376–387. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Hapke B., Noll H. Structural dynamics of bacterial ribosomes. II. Preparation and characterization of ribosomes and subunits active in the translation of natural messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 5;80(3):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90419-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Hapke B., Schreier M. H., Noll H. Structural dynamics of bacterial ribosomes. I. Characterization of vacant couples and their relation to complexed ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):281–294. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Noll H. Structural dynamics of bacterial ribosomes. III. Quantitative conversion of vacant ribosome couples into an initiation complex with R17 RNA as messenger. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 5;90(2):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Noll H. Structural dynamics of bacterial ribosomes. V. Magnesium-dependent dissociation of tight couples into subunits: measurements of dissociation constants and exchange rates. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 25;105(1):111–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Witten C., Mantei N., Echols H. Inhibition of host nucleic acid synthesis by bacteriophage T4: effect of chloramphenicol at various multiplicities of infection. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):273–278. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKABE K. Studies on mikamycin. III. Characterization and hydrolysis. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1959 May;12(3):86–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKABE K., YONEHARA H., UMEZAWA H. Alkaline hydrolysis of mikamycin A. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1959 Jul;12:192–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKAMOTO K., SUGINO Y., NOMURA M. Synthesis and turnover of phage messenger RNA in E. coli infected with bacteriophage T4 in the presence of chloromycetin. J Mol Biol. 1962 Nov;5:527–534. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obbink D. J., Spithill T. W., Maxwell R. J., Linnane A. W. Biogenesis of mitochondria 48: mikamycin resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae--a mitochondrial mutation conferring resistance to an antimycin A-like contaminant in mikamycin. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Mar 7;151(2):127–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00338687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa S. Translation of the genetic message. Naturwissenschaften. 1968 Nov;55(11):505–514. doi: 10.1007/BF00660121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson L. D., Rodabaugh D. E. Evaluation of virginiamycin in feed for treatment and retreatment of swine dysentery. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Oct;38(10):1485–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondetti M. A., Thomas P. L. Synthesis of a peptide lactone related to vernamycin B-alpha. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Oct 5;87(19):4373–4380. doi: 10.1021/ja00947a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTE J. C., HIRSCH H., CHABBERT Y. Etude des courbes d'effet baçtériostatique des associations d'antibiotiques. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1958 May;94(5):621–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PREUDHOMME J., BELLOC A., CHARPENTIE Y., TARRIDEC P. UN ANTIBIOTIQUE FORM'E DE DEUX GROUPES DE COMPOSANTS 'A SYNERGIE D'ACTION: LA PRISTINAMYCINE. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1965 Jan 25;260:1309–1312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRINGUET R. [Local treatment of cutaneous staphylococcal infections with staphylomycin (78 cases)]. Presse Med. 1962 Dec 8;70:2573–2574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Shilo M. Cyanophages-viruses attacking blue-green algae. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):343–370. doi: 10.1128/br.37.3.343-370.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Shilo M., Oppenheim A. B. Lysogeny of the blue-green alga Plectonema boryanum by LPP2-SPI cyanophage. Virology. 1972 Feb;47(2):525–526. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parfait R., de Béthune M. P., Cocito C. A spectrofluorimetric study of the interaction between virginiamycin S and bacterial ribosomes. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Oct 25;166(1):45–51. doi: 10.1007/BF00379728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Antibiotics as probes of ribosome structure: binding of chloramphenicol and erythromycin to polyribosomes; effect of other antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):255–267. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Hintikka H. Studies on the formation of ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. XVI. Effect of ribosomal translocation inhibitors on polyribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7723–7730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Insights into protein biosynthesis and ribosome function through inhibitors. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;17:217–245. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60071-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. 8. Survey of the effect of antibiotics of N-acetyl-phenylalanyl-puromycin formation: possible mechanism of chloramphenicol action. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Jan;136(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. IX. Effect of antibiotics on translocation and peptide bond formation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Jan;136(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90330-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. XI. Antibiotic effects on phenylalanyl-oligonucleotide binding to ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):709–714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. XIX. Effect of antibiotics on peptidyl puromycin synthesis on polyribosoms from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4669–4678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preud'homme J., Tarridec P., Belloc A. 90. Pristinamycine isolement, caractérisation et identification des constituants. Bull Soc Chim Fr. 1968 Feb;2:585–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J. J. Host macromolecular synthesis in bacteriophage-infected Bacillus subtilis. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 1):379–386. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pène J. J., Marmur J. Deoxyribonucleic acid replication and expression of early and late bacteriophage functions in Bacillus subtilis. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):86–91. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.86-91.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimon A., Oppenheim A. B. Heat induction of the blue-green alga Plectonema boryanum lysogenic for the cyanophage SPlcts1. Virology. 1975 Apr;64(2):454–463. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90123-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberfroid M. B., Dumont P. A. Absorption and metabolism of tritium-labelled factor M 1 of virginiamycin by oral and parenteral administration. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Jan;25(1):30–38. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollmann B., Rondelet J. Etude spectrophotométrique de la transformation du facteur M de la viriginiamycine en milieu acide. Pharm Acta Helv. 1972 Nov-Dec;47(11):698–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollmann B., Rondelet J. Influence du pH sur la vitesse de l'altération du facteur S de la virginiamycine en milieu aqueux. Pharm Acta Helv. 1975;50(12):455–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollmann B., Rondelet J. La transformation du facteur M de la virginiamycine en milieu acide. Etude chromatographique. J Pharm Belg. 1973 Jul-Aug;28(4):425–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollmann B., Rondelet J. Transformation en milieu acide du facteur M de la virginiamycine. Déterminatination de paramètres cinétiques. Ann Pharm Fr. 1973 Jun;31(6):451–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rondelet J. A., Froment P. Synthèse et propriétés de la N-(hydroxy-2 éthyl)-4 pipérazinyl carboxyméthyl-1) tétracycline. Ann Pharm Fr. 1968 Jan;26(1):63–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safferman R. S., Morris M. E. Observations on the Occurrence, Distribution, and Seasonal Incidence of Blue-green Algal Viruses. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Sep;15(5):1219–1222. doi: 10.1128/am.15.5.1219-1222.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safferman R. S., Morris M. E., Sherman L. A., Haselkorn R. Serological and electron microscopic characterization of a new group of blue-green algal viruses (LPP-2). Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):775–780. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. F. Origin of chloramphenicol particle protein. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleif R. Control of production of ribosomal protein. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):41–55. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90350-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger D., Apirion D. Escherichia coli ribosomes: recent developments. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:387–426. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.002131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger D. Ribosomes: development of some current ideas. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Dec;33(4):445–453. doi: 10.1128/br.33.4.445-453.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan J. C., Ledis S. L. Total synthesis of a monocyclic peptide lactone antibiotic, etamycin. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Feb 7;95(3):875–879. doi: 10.1021/ja00784a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilo M. Morphological and physiological aspects of the interaction of Bdellovibrio with host bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1969;50:174–204. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46169-9_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. S., Pardee A. B. Accumulation of a protein required for division during the cell cycle of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):901–909. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.901-909.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spirin A. S. On the equilibrium of the association-dissociation reaction of ribosomal subparticles and on the existance of the so-called '60 S intermediate' ('swollen 70 S') during centrifugation of the equilibrium mixture. FEBS Lett. 1971 May 20;14(5):349–353. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80298-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr M. P. Bdellovibrio as symbiont; the associations of Bdellovibrios with other bacteria interpreted in terms of a generalized scheme for classifying organismic associations. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1975;(29):93–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr M. P., Huang J. C. Physiology of the bdellovibrios. Adv Microb Physiol. 1972;8:215–261. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr M. P., Seidler R. J. The Bdellovibros. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:649–678. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.003245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern J. L., Barner H. D., Cohen S. S. The lethality of streptomycin and the stimulation of RNA synthesis in the absence of protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):188–217. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. G., Ferretti J. J. Genetic analysis of antibiotic resistance in Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):852–859. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.852-859.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A. R., Davis B. D. Rapid exchange of subunits between free ribosomes in extracts of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2453–2457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANAKA N., MIYAIRI N., WATANABE K., SHINJO N., NISHIMURA T., UMEZAWA H. Biological studies on mikamycin. II. Laboratory investigations of mikamycin A and mikamycin B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1959 Nov;12:290–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANAKA N., SHINJO N., MIYAIRI N., UMEZAWA H. Biological studies on mikamycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1958 Jul;11(4):127–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANAKA N., YAMAGUCHI H., UMEZAWA H. Biological studies on mikamycin. IV. Blood and tissue levels of tritiated mikamycins A and B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1962 Jan;15:33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAUT R. R., MONRO R. E. THE PUROMYCIN REACTION AND ITS RELATION TO PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Oct;10:63–72. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAZQUEZ D. ANTIBIOTICS WHICH AFFECT PROTEIN SYNTHESIS: THE UPTAKE OF 14C-CHLORAMPHENICOL BY BACTERIA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Aug 14;12:409–413. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAZQUEZ D. Studies on the mode of action of streptogramin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Nov 26;61:849–851. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Assche P. F., De Mey L. E., Descamps J. A. In vitro study of the influence of virginiamycin and spiramycin on the composition and biochemical activities of the gastrointestinal flora of piglets. I. influence on the composition of the flora. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1975;231(1-3):153–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Assche P. F., De Mey L. E., Descamps J. A. In vitro study of the influence of virginiamycin and spiramycin on the composition and biochemical activities of the gastrointestinal flora of piglets. II. Influence on the biochemical activities of the microflora. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1975;231(1-3):163–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Pel B., Bronchart R., Kebers F., Cocito C. Structure and function of cytoplasmic organelles in transiently and permanently bleached Euglena. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Mar 30;78(1):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Pel B., Cocito C. Formation of chloroplast ribosomes and ribosomal RNA in Euglena incubated with protein inhibitors. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Mar 30;78(1):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderhaeghe H., Janssen G., Compernolle F. Bereiding van radioactieve dihydrovirginiamycine S en karakterisering van virginiamycine S componenten. Verh K Vlaam Acad Geneeskd Belg. 1972;34(2):209–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon M., Cocito C., Seijffers J. Effect of virginiamycin on the growth cycle of Bdellovibrio. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):179–188. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon M. The bdellophage three-membered parasitic system. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1974;3(3):221–241. doi: 10.3109/10408417409108751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D. Antibiotics affecting chloramphenicol uptake by bacteria. Their effect on amino acid incorporation in a cell-free system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 21;114(2):289–295. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90310-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D. Binding of chloramphenicol to ribosomes. The effect of a number of antibiotics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 21;114(2):277–288. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90309-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D. Inhibitors of protein synthesis at the ribosome level. Studies on their site of action. Life Sci. 1967 Feb 15;6(4):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D. Inhibitors of protein synthesis. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 23;40(0):suppl–suppl:S84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80689-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D., Monro R. E. Effects of some inhibitors of protein synthesis on the binding of aminoacyl tRNA to ribosomal subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 20;142(1):155–173. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90524-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D. Studies on the mode of action of the streptogramin antibiotics. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jan;42(1):93–106. doi: 10.1099/00221287-42-1-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez D. The binding of chloramphenicol by ribosomes from Bacillus megaterium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Apr 22;15(5):464–468. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90487-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Videau D. La pristinamycine et le phénomène de bactériopause. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 May;108(5):602–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Videau D., Roiron V. Titrages et taux sanguins de la pristinamycine chez l'homme. Presse Med. 1965 Sep 11;73(37):2101–2103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER D. T. Proposed molecular models of gramicidin S and other polypeptides. Nature. 1961 Apr 8;190:120–128. doi: 10.1038/190120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARNER D. T. Proposed molecular models: II. Conformations of staphylomycin and other polypeptides and an possible relation to the structure of water. J Theor Biol. 1961 Oct;1:514–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE K. Studies on mikamycin. IV. The isolation and properties of mikamycin B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1960 Jan;13:57–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE K., YONEHARA H., TANAKA N., UMEZAWA H. Studies on mikamycin B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1959 May;12(3):112–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE K. [Mikamycin]. J Antibiot B. 1962 Jun;15:147–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe K., Yonezawa K., Komai T., Takeuchi T. Biological studies on mikamycin. V. Absorption and excretion of tritiated mikamycins A and B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Aug;23(8):394–400. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisblum B., Davies J. Antibiotic inhibitors of the bacterial ribosome. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 2):493–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. J., Babcock W. E. In vitro susceptibility of Treponema hyodysenteriae to carbadox, virginiamycin, and tylosin. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1976 Jul;71(7):957–959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise E. M., Jr, Park J. T. Penicillin: its basic site of action as an inhibitor of a peptide cross-linking reaction in cell wall mucopeptide synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):75–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Chinali G., Parmeggiani A. Kirromycin, an inhibitor of protein biosynthesis that acts on elongation factor Tu. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4910–4914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Chinali G., Parmeggiani A. Mechanism of the inhibition of protein synthesis by kirromycin. Role of elongation factor Tu and ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):67–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolk C. P. Physiology and cytological chemistry blue-green algae. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Mar;37(1):32–101. doi: 10.1128/br.37.1.32-101.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAGUCHI H. Action mechanism of mikamycins. I. Effects of mikamycins on protein and nucleic acid metabolisms. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1961 Nov;14:313–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAGUCHI H., TANAKA N. SELECTIVE TOXICITY OF MIKAMYCINS, INHIBITORS OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Nature. 1964 Feb 1;201:499–501. doi: 10.1038/201499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAKI H., TANAKA N. EFFECTS OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS INHIBITORS ON THE LETHAL ACTION OF KANAMYCIN AND STREPTOMYCIN. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1963 Nov;16:222–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YATES J. D., SCHAIBLE P. J. Virginiamycin as an antibiotic for poultry feeds. Nature. 1962 Apr 14;194:183–184. doi: 10.1038/194183b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi Y., McLellan T. S., Frez W. A., Clewell D. B. Characterization of a small plasmid determining resistance to erythromycin, lincomycin, and vernamycin Balpha in a strain of Streptococcus sanguis isolated from dental plaque. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 May;13(5):884–887. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.5.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Tanaka H. Site of action of mikamycins A and B in polypeptide synthesizing systems. J Biochem. 1967 Jan;61(1):18–25. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Tanaka N., Umezawa H. Effects of biopolymers and magnesium on the mikamycins inhibition of polyphenylalanine synthesis and the synergistic action of mikamycins A and B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1967 Jan;20(1):41–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Yoshida Y., Tanaka N. Inhibition by mikamycins of polypeptide synthesis directed by native messengers and synthetic polynucleotides. J Biochem. 1966 Sep;60(3):246–255. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Osawa S. Origin of the protein component of chlormaphenicaol particles in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 14;33(3):559–569. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn R. K., Heicke B., Ochs H. G., Tiesler E., Forster W., Hanske W., Walter W., Hollstein H. In vitro inhibition of the synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid by 2-phenyl-ethanol and some of its derivatives. Nature. 1966 Oct 15;212(5059):297–298. doi: 10.1038/212297a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn R. K., Tiesler E., Heicke B., Hanske W., Forster W., Hollstein H., Walter H. Cellular division and cellular volume distribution in the presence of 2-phenyl-ethanol and some of its derivatives. Nature. 1966 Oct 15;212(5059):298–298. doi: 10.1038/212298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman D. R., Inouye M., Pardee A. B. Cell division in Escherichia coli: evidence for regulation of septation by effector molecules. J Mol Biol. 1972 Aug 14;69(1):119–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bethune M. P., Nierhaus K. H. Characterisation of the binding of virginiamycin S to Escherichia coli ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1978 May;86(1):187–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Diggelen O. P., Bosch L. The association of ribosomal subunits of Escherichia coli. 1. Two types of association products differing in their apparent sedimentation coefficient. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 15;39(2):499–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Diggelen O. P., Heinsius H. L., Kalousek F., Bosh L. Formation of 61 s and 70 s particles from ribosomal subunits of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jan 28;55(2):277–281. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]