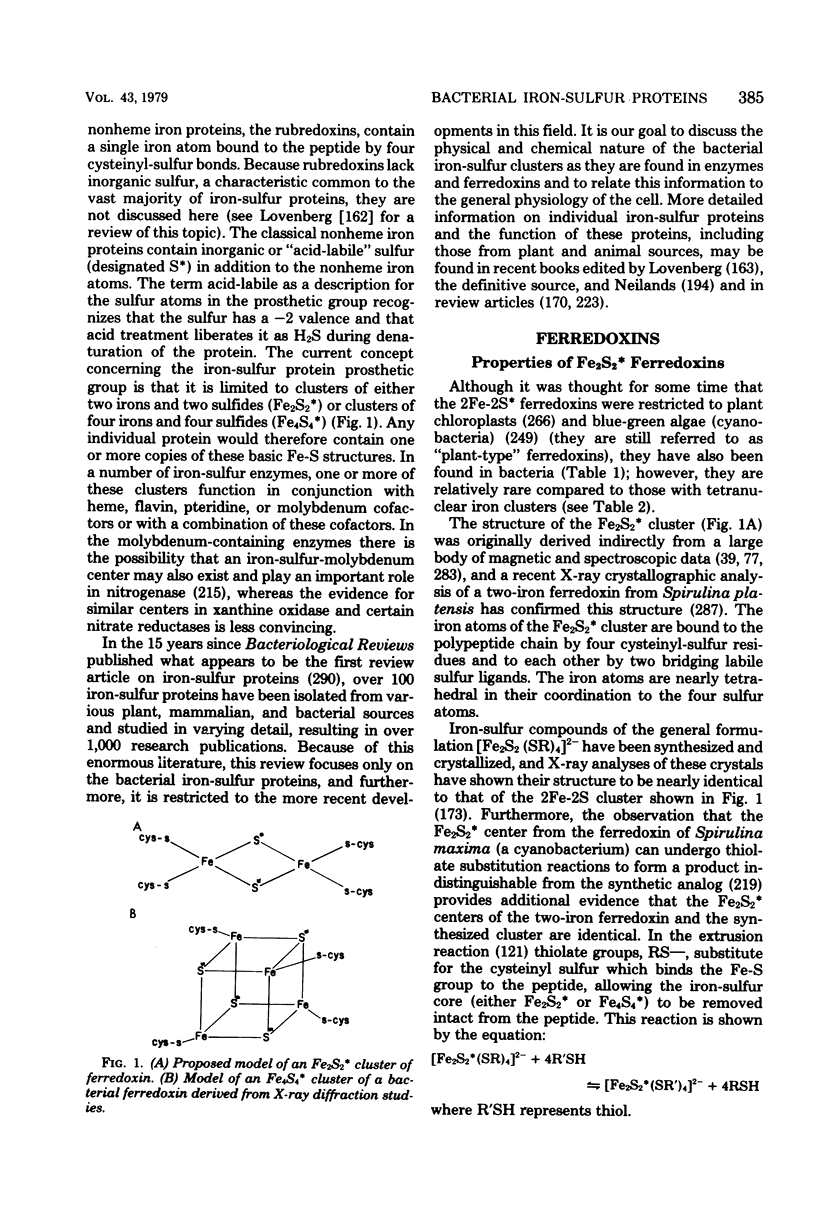
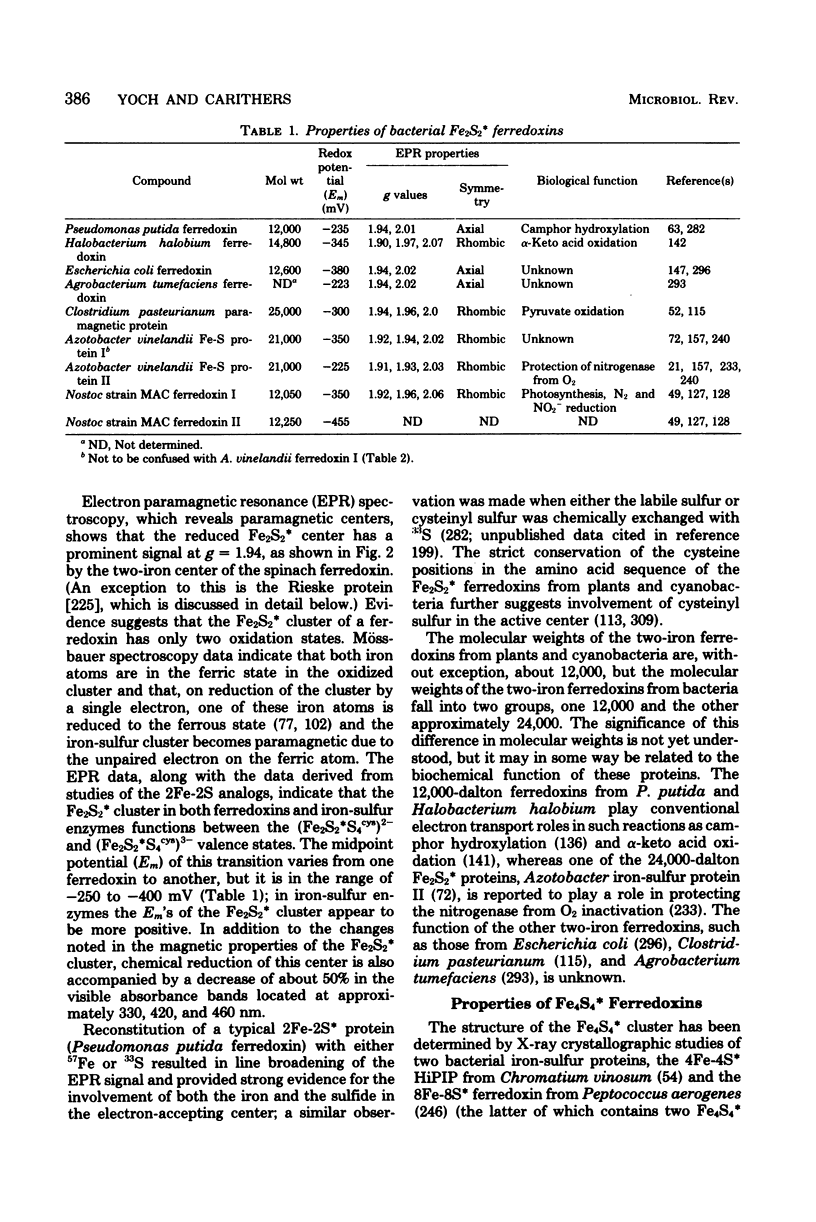
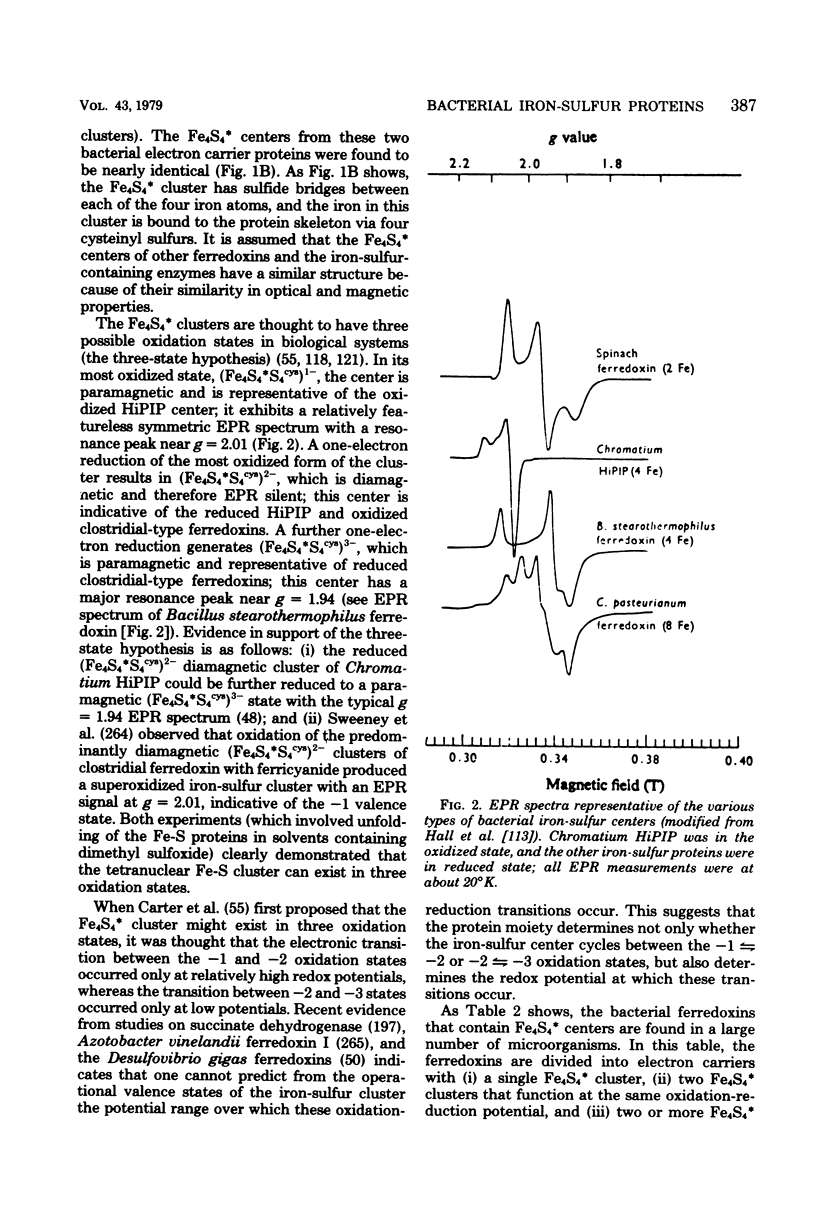
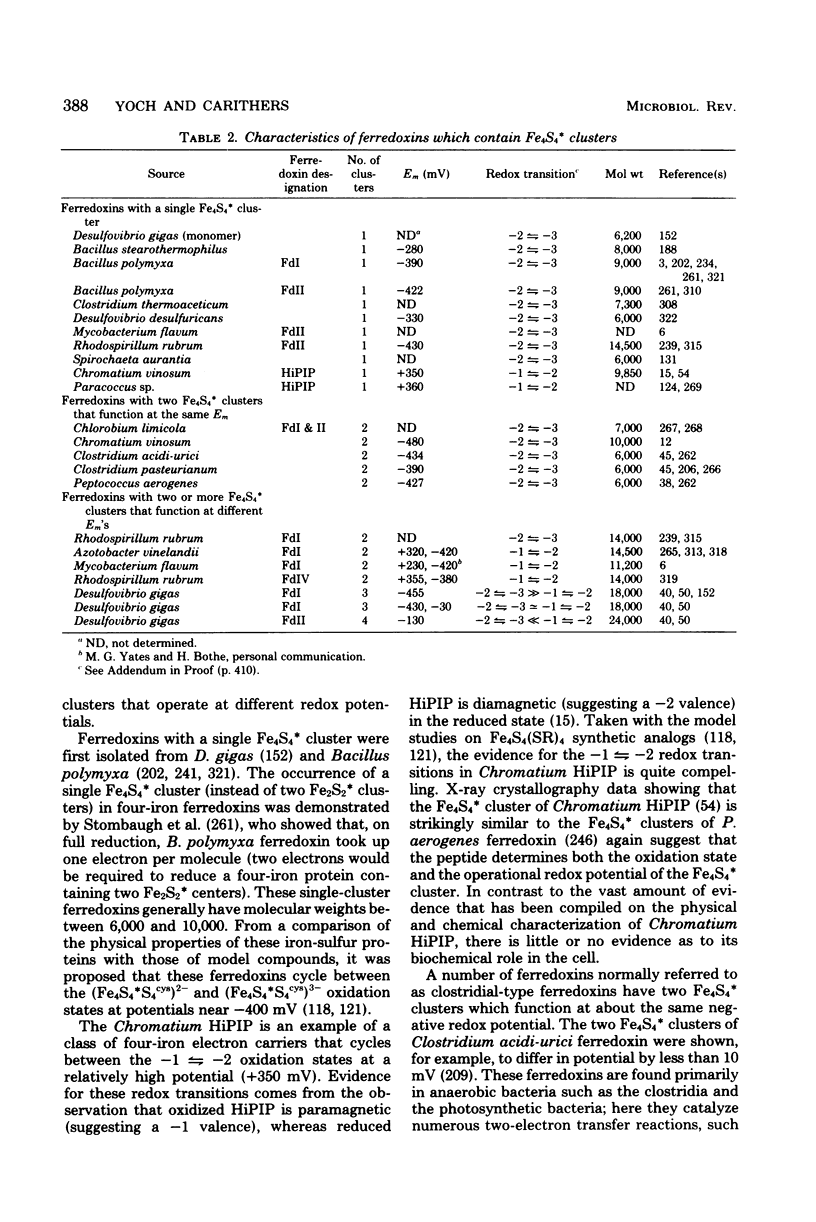
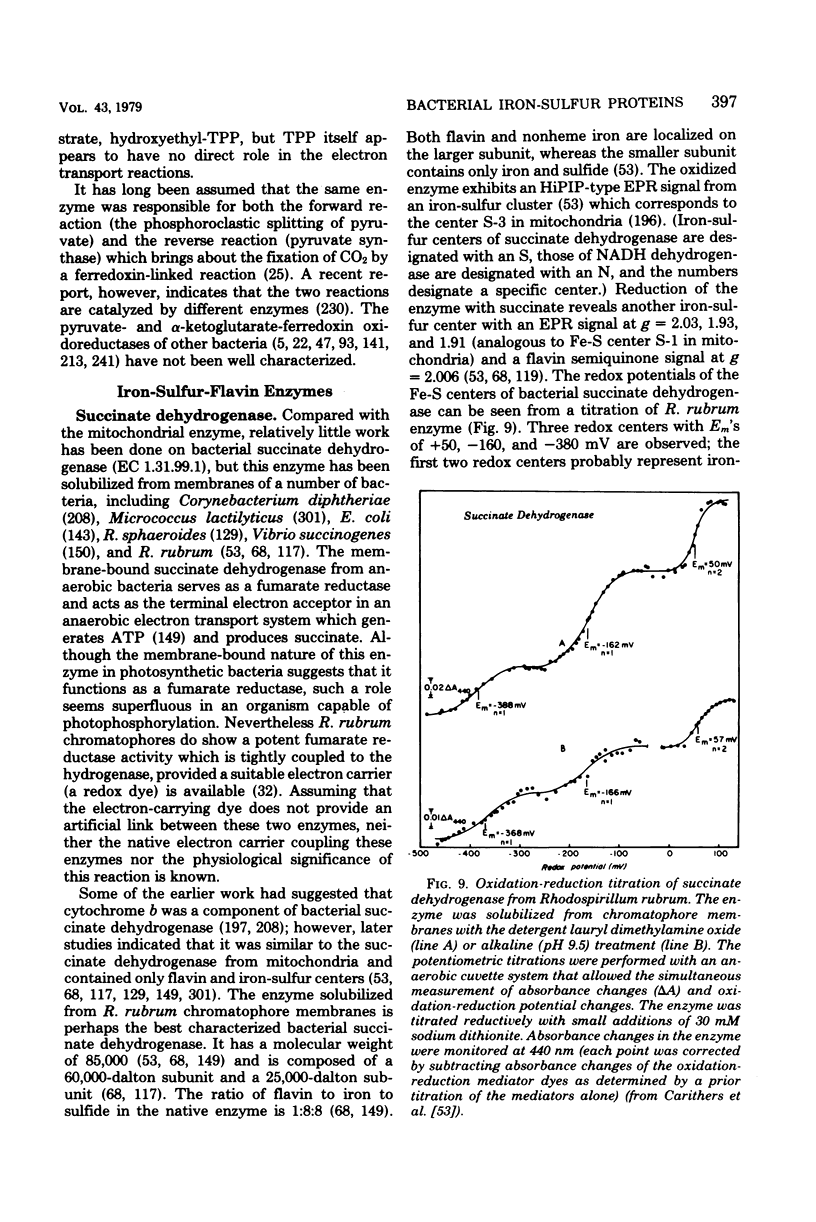
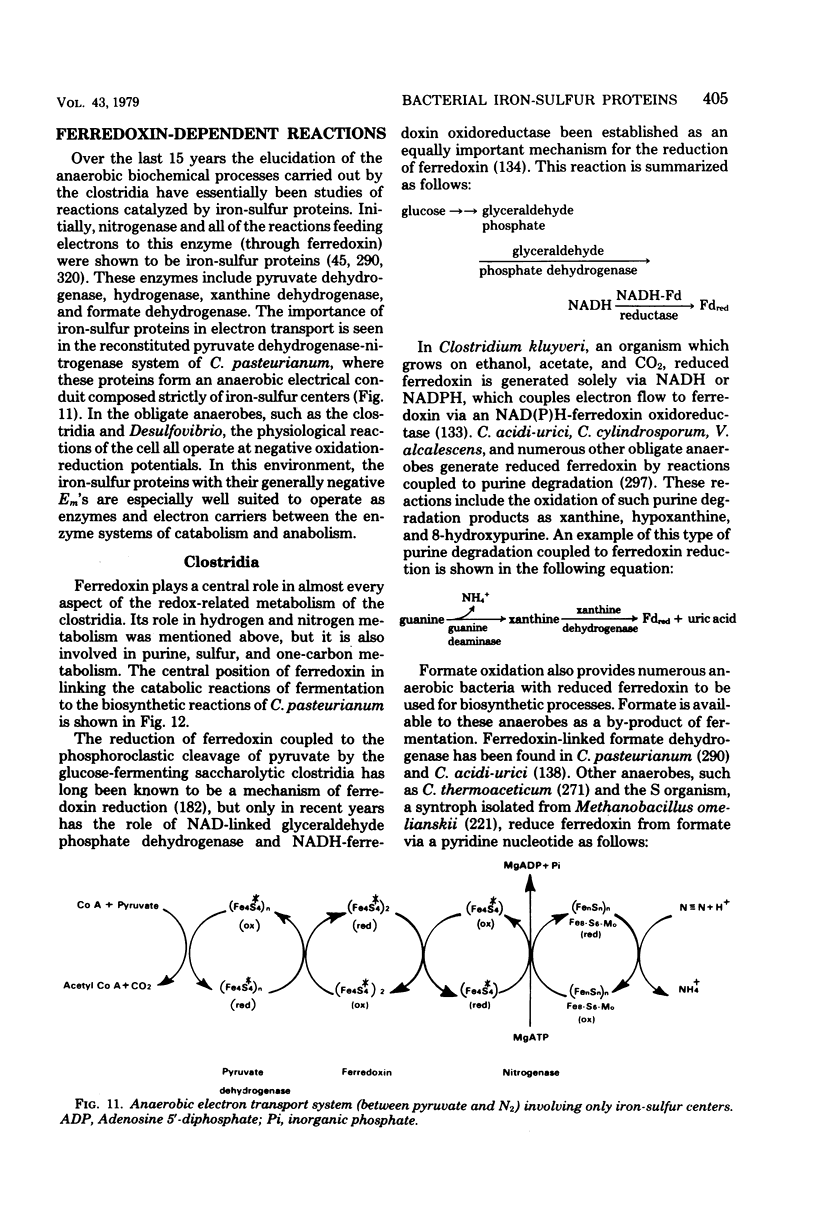
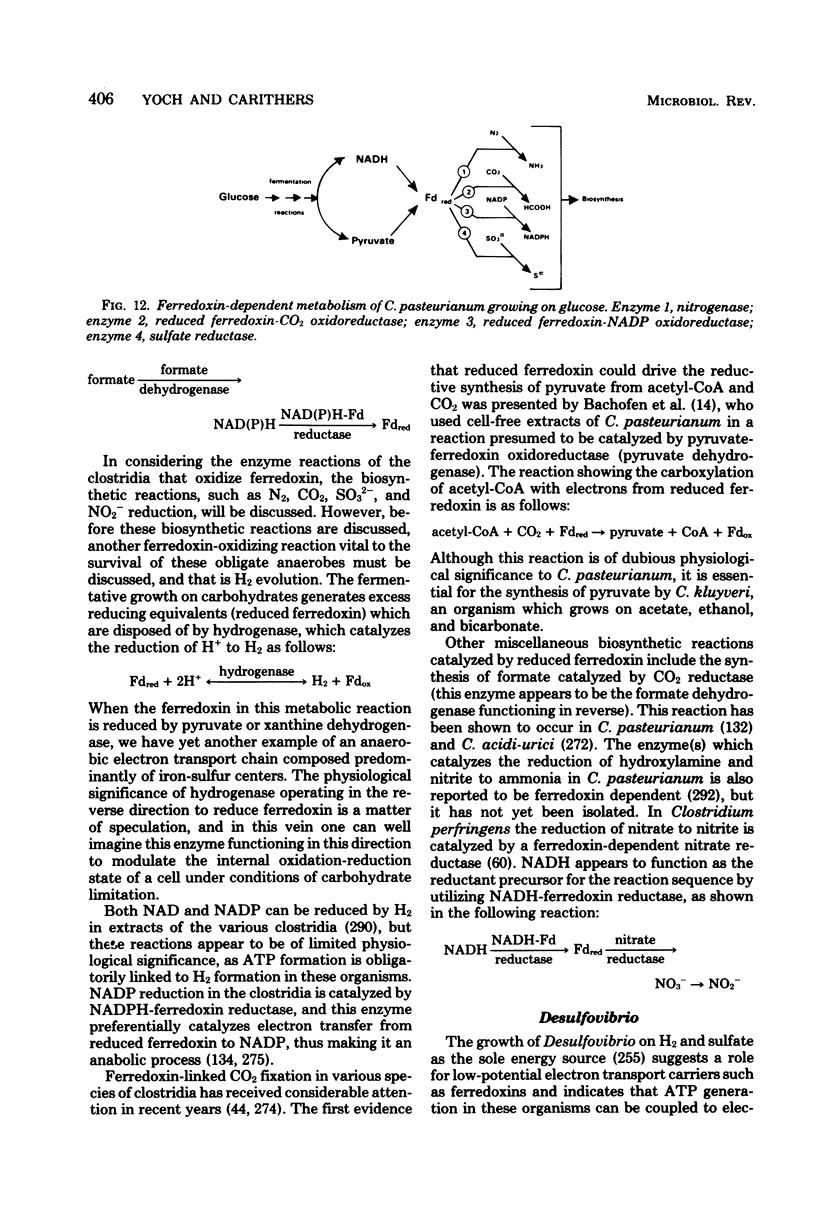
Full text
PDF


























Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. W., Hall D. O. Isolation of the membrane-bound hydrogenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 25;77(2):730–737. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams M. W., Reeves S. G., Hall D. O., Christou G., Ridge B., Rydon H. N. Biological activity of synthetic tetranuclear iron-sulphur analogues of the active sites of ferredoxins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 21;79(4):1184–1191. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
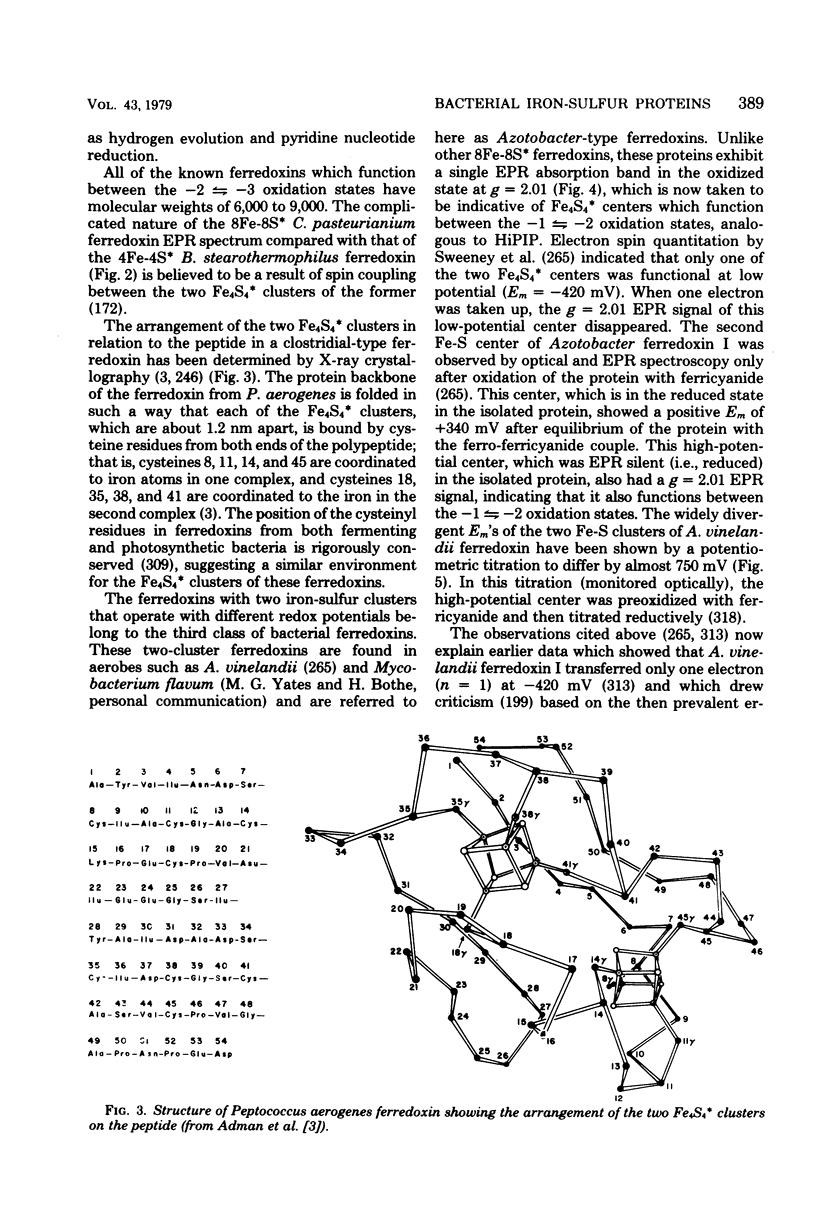
- Adman E. T., Sieker L. C., Jensen L. H. Structure of a bacterial ferredoxin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3987–3996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akagi J. M. Electron carries for the phosphoroclastic reaction of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 25;242(10):2478–2483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akagi J. M. The participation of a ferredoxin of Clostridium nigrificans in sulfite reduction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Oct 8;21(1):72–77. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht S. L., Evans M. C. Measurement of the oxidation reduction potential of the EPR detectable active centre of the molybdenum iron protein of Chromatium nitrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 10;55(3):1009–1014. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aleman V., Handler P. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase. I. General properties. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 25;242(18):4087–4096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aleman V., Handler P., Palmer G., Beinert H. Studies on dihydroorotate dehydrogenase by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. 3. Kinetic studies by rapid freezing. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 25;243(10):2569–2578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aleman V., Handler P., Palmer G., Beinert H. Studies on dihydroorotate dehydrogenase by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. II. Electron paramagnetic resonance and optical spectra and titrations. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 25;243(10):2560–2568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison M. J., Peel J. L. The biosynthesis of valine from isobutyrate by peptostreptococcus elsdenii and Bacteroides ruminicola. Biochem J. 1971 Feb;121(3):431–437. doi: 10.1042/bj1210431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison M. J., Robinson I. M. Biosynthesis of alpha-ketoglutarate by the reductive carboxylation of succinate in Bacteroides ruminicola. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):50–56. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.50-56.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreesen J. R., Ljungdahl L. G. Formate dehydrogenase of Clostridium thermoaceticum: incorporation of selenium-75, and the effects of selenite, molybdate, and tungstate on the enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):867–873. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.867-873.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACHOFEN R., BUCHANAN B. B., ARNON D. I. FERREDOXIN AS A REDUCTANT IN PYRUVATE SYNTHESIS BY A BACTERIAL EXTRACT. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Apr;51:690–694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.4.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEINERT H., HEINEN W., PALMER G. Applications of combined low temperature optical and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy to the study of oxidative enzymes. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1962 Dec;15:229–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOSE S. K., GEST H. Hydrogenase and light-stimulated electron transfer reactions in photosynthetic bacteria. Nature. 1962 Sep 22;195:1168–1171. doi: 10.1038/1951168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachofen R., Arnon D. I. Crystalline ferredoxin from the photosynthetic bacterium Chromatium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 8;120(2):259–265. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90345-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beinert H., Ackrell B. A., Kearney E. B., Singer T. P. Iron-sulfur components of succinate dehydrogenase: stoichiometry and kinetic behavior in activated preparations. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May;54(1):185–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. R., LeGall L., Peck H. D. Evidence for the periplasmic location of hydrogenase in Desulfovibrio gigas. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):994–997. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.994-997.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benemann J. R., Yoch D. C., Valentine R. C., Arnon D. I. The electron transport system in nitrogen fixation by azotobacter. 3. Requirements for NADPH-supported nitrogenase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 2;226(2):205–212. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergersen F. J., Turner G. L. Kinetic studies of nitrogenase from soya-bean root-nodule bacteroids. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;131(1):61–75. doi: 10.1042/bj1310061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhardt F. H., Erdin N., Staudinger H., Ullrich V. Interactions of substrates with a purified 4-methoxybenzoate monooxygenase system (O-demethylating) from Pseudomonas putida. Eur J Biochem. 1973 May;35(1):126–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhardt F. H., Nastainczyk W., Seydewitz V. Kinetic studies on a 4-methoxybenzoate O-demethylase from Pseudomonas putida. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan 3;72(1):107–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhardt F. H., Pachowsky H., Staudinger H. A 4-methoxybenzoate O-demethylase from Pseudomonas putida. A new type of monooxygenase system. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 1;57(1):241–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhardt F. H., Ruf H. H., Ehrig H. A 4-methoxybenzoate monooxygenase system from Pseudomonas putida. Circular dichroism studies on the iron--sulfur protein. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jul 1;43(1):53–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81103-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhardt F. H., Ruf H. H., Staudinger H. Pufification of a 4-methoxybenzoate O-demethylase from Pseudomonas putida. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Aug;352(8):1091–1099. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1971.352.2.1091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackmore M. A., Quayle J. R. Choice between autotrophy and heterotrophy in Pseudomonas oxalaticus. Growth in mixed substrates. Biochem J. 1968 May;107(5):705–713. doi: 10.1042/bj1070705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattmann P., Rétey J. Stereospecificity of the dihydroorotate-dehydrogenase reaction. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Oct 17;30(1):130–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothe H., Yates M. G. The electron transport to nitrogenase in Mycobacterium flavum. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Feb;107(1):25–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00427863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen T. J., Happold F. C., Taylor B. F. Studies on adenosine-5'-phosphosulphate reductase from Thiobacillus denitrificans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 15;118(3):566–576. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramlett R. N., Peck H. D., Jr Some physical and kinetic properties of adenylyl sulfate reductase from Desulfovibrio vulgaris. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2979–2986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray R. C., Vincent S. P., Lowe D. J., Clegg R. A., Garland P. B. Electron-paramagnetic-resonance studies on the molybdenum of nitrate reductase from Escherichia coli K12. Biochem J. 1976 Apr 1;155(1):201–203. doi: 10.1042/bj1550201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brintzinger H., Palmer G., Sands R. H. On the ligand field of iron in ferredoxin from spinach chloroplasts and related nonheme iron enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Feb;55(2):397–404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruschi M., Hatchikian C., Le Gall J., Moura J. J., Xavier A. V. Purification, characterization and biological activity of three forms of ferredoxin from the sulfate-reducing bacterium Desulfovibrio gigas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 9;449(2):275–284. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P., McBride B. C., Wolfe R. S. Hydrogen-oxidizing methane bacteria. I. Cultivation and methanogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1118–1123. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1118-1123.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P., Wolin E. A., Wolin M. J., Wolfe R. S. Methanobacillus omelianskii, a symbiotic association of two species of bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):20–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00406313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan B. B., Arnon D. I. Ferredoxins: chemistry and function in photosynthesis, nitrogen fixation, and fermentative metabolism. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1970;33:119–176. doi: 10.1002/9780470122785.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan B. B., Bachofen R. Ferredoxin-dependent reduction of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotides with hydrogen gas by subcellular preparations from the photosynthetic bacterium, Chromatium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 26;162(4):607–610. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(68)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan B. B., Evans M. C., Arnon D. I. Ferredoxin-dependent carbon assimilation in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):32–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00406314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan B. B. Role of ferredoxin in the synthesis of alpha-ketobutyrate from propionyl coenzyme A and carbon dioxide by enzymes from photosynthetic and nonphotosynthetic bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 10;244(15):4218–4223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammack R. "Super-reduction" of chromatium high-potential iron-sulphur protein in the presence of dimethyl sulphoxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Sep 18;54(2):548–554. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91457-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammack R., Rao K. K., Bargeron C. P., Hutson K. G., Andrew P. W., Rogers L. J. Midpoint redox potentials of plant and algal ferredoxins. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 15;168(2):205–209. doi: 10.1042/bj1680205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammack R., Rao K. K., Hall D. O., Moura J. J., Xavier A. V., Bruschi M., Le Gall J., Deville A., Gayda J. P. Spectroscopic studies of the oxidation-reduction properties of three forms of ferredoxin from Desulphovibrio gigas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 22;490(2):311–321. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammack R., Tel-or E., Stewart W. D. EPR spectra of photosystem I constituents in heterocyst preparations from Anabaena cylindrica. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov;70(1):241–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80766-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carithers R. P., Yoch D. C., Arnon D. I. Isolation and characterization of bound ion-sulfur proteins from bacterial photosynthetic membranes. II. Succinate dehydrogenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum chromatophores. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7461–7467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C. W., Jr, Freer S. T., Xuong N. H., Alden R. A., Kraut J. Structure of the iron-sulfur cluster in the Chromatius iron protein at 2.25 Angstrom resolution. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1972;36:381–385. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1972.036.01.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C. W., Jr, Kraut J., Freer S. T., Alden R. A., Sieker L. C., Adman E., Jensen L. H. A comparison of Fe 4 S 4 clusters in high-potential iron protein and in ferredoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3526–3529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. S., Blanchard D. K. Isolation and properties of a unidirectional H2-oxidizing hydrogenase from the strictly anaerobic N2-fixing bacterium Clostridium pasteurianum W5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 30;84(4):1144–1150. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91703-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. S., Mortenson L. E., Palmer G. The iron-sulfur centers and the function of hydrogenase from Clostridium pasteurianum. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1976;74:68–82. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3270-1_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. S., Mortenson L. E. Purification and properties of hydrogenase from Clostridium pasteurianum W5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 18;371(2):283–298. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba S., Ishimoto M. Ferredoxin-linked nitrate reductase from Clostridium perfringens. J Biochem. 1973 Jun;73(6):1315–1318. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg R. A. Purification and some properties of nitrate reductase (EC 1.7.99.4) from Escherichia coli K12. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 1;153(3):533–541. doi: 10.1042/bj1530533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codd G. A., Rowell P., Stewart W. D. Pyruvate and nitrogenase activity in cell-free extracts of the blue-green alga Anabaena cylindrica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Nov 27;61(2):424–431. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90974-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman D. W., Tsai R. L., Gunsalus I. C. The ferroprotein component of a methylene hydroxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Mar 9;26(5):577–583. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cárdenas J., Mortenson L. E., Yoch D. C. Purification and properties of paramagnetic protein from Clostridium pasteurianum W5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 20;434(1):244–257. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton H., Lowe D. J., Pawlik T., Bray R. C. Studies by electron-paramagnetic-resonance spectroscopy on the mechanism of action of xanthine dehydrogenase from Veillonella alcalescens. Biochem J. 1976 Feb 1;153(2):287–295. doi: 10.1042/bj1530287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton H., Morris J. A., Ward M. A., Mortenson L. E. Purification and some properties of molybdoferredoxin, a component of nitrogenase from Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochemistry. 1971 May 25;10(11):2066–2072. doi: 10.1021/bi00787a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dancey G. F., Levine A. E., Shapiro B. M. The NADH dehydrogenase of the respiratory chain of Escherichia coli. I. Properties of the membrane-bound enzyme, its solubilization, and purification to near homogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5911–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dancey G. F., Shapiro B. M. The NADH dehydrogenase of the respiratory chain of Escherichia coli. II. Kinetics of the purified enzyme and the effects of antibodies elicited against it on membrane-bound and free enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5921–5928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis K. A., Hatefi Y., Crawford I. P., Baltscheffsky H. Purification, molecular properties, and amino acid composition of the subunits of Rhodospirillum rubrum succinate dehydrogenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Apr 30;180(2):459–464. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dervartanian D. V., Bramlett R. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies of 95Mo-enriched NADH dehydrogenase isolated from iron-deficient Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 16;220(3):443–448. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dervartanian D. V., Shethna Y. I., Beinert H. Purification and properties of two iron-sulfur proteins from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 23;194(2):548–563. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90117-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth M. J. Acetylene reduction by nitrogen-fixing preparations from Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 31;127(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90383-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. O. Hydrogenase in legume root nodule bacteroids: occurrence and properties. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;85(3):193–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00408844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drozd J., Postgate J. R. Effects of oxygen on acetylene reduction, cytochrome content and respiratory activity of Azotobacter chroococcum. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Sep;63(1):63–73. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-1-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham W. R., Palmer G., Sands R. H., Bearden A. J. On the structure of the iron-sulfur complex in the two-iron ferredoxins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 7;253(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton P. L., Leigh J. S. Electron spin resonance characterization of Chromatium D hemes, non-heme irons and the components involved in primary photochemistry. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 31;314(2):178–190. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton P. L., Wilson D. F. Redox potentiometry in mitochondrial and photosynthetic bioenergetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 31;346(2):165–212. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(74)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Kennedy C., Smith B. E., Thorneley R. N., Yates G., Postgate J. R. Nitrogenase in Azotobacter chroococcum and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biochem Soc Trans. 1975;3(4):488–492. doi: 10.1042/bst0030488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Smith B. E., Cook K. A., Postgate J. R. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Purification and properties of the component proteins. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):655–675. doi: 10.1042/bj1280655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D., Massey V., Palmer G., Beacham L. M., 3rd, Elion G. B. The resolution of active and inactive xanthine oxidase by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 10;247(5):1597–1604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmerich C., Aubert J. P. Synthesis of glutamate by a glutamine: 2-oxo-glutarate amidotransferase (NADP oxidoreductase) in Bacillus megaterium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Feb 5;42(3):371–376. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90380-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely B., Amarasinghe A. B., Bender R. A. Ammonia assimilation and glutamate formation in Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):225–230. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.225-230.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch H. G., Lester R. L. The purification and properties of formate dehydrogenase and nitrate reductase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6693–6705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch H. G., Lester R. L. The role of a novel cytochrome b-containing nitrate reductase and quinone in the in vitro reconstruction of formate-nitrate reductase activity of E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1234–1241. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80416-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erbes D. L., Burris R. H., Orme-Johnson W. H. On the iron-sulfur cluster in hydrogenase from Clostridium pasteurianum W5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4795–4799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. H., Cammack R. Properties of the primary electron acceptor complex of photosystem I in the blue green alga Chlorogloea fritschii. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 23;68(4):1212–1218. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Albrecht S. L. Determination of the applied oxidation-reduction potential required for substrate reduction by Chromatium nitrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1187–1192. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Buchanan B. B. Photoreduction of ferredoxin and its use in carbon dioxide fixation by a subcellular system from a photosynthetic bacterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jun;53(6):1420–1425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.6.1420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C. Ferredoxin dependent synthesis of alpha-ketoglutarate and pyruvate by extracts of the green photosynthetis bacterium Chloropseudoonas ethylicum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Oct 10;33(1):146–150. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90269-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Lord A. V., Reeves S. G. The detection and characterization by electron-paramagnetic-resonance spectroscopy of iron-sulphur proteins and other electron-transport components in chromatophores from the purple bacterium Chromatium. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;138(2):177–183. doi: 10.1042/bj1380177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Reeves S. G., Telfer A. The detection of a bound ferredoxin in the photosynthetic lamellae of blue-green algae and other oxygen evolving photosynthetic organisms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 2;51(3):593–596. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91355-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Telfer A., Smith R. V. The purification and some properties of the molybdenum-iron protein of Chromatium nitrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 15;310(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90114-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMANN H. C., VENNESLAND B. Crystalline dihydroorotic dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1960 May;235:1526–1532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faeder E. J., Davis P. S., Siegel L. M. Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-sulfite reductase of enterobacteria. V. Studies with the Escherichia coli hemoflavoprotein depleted of flavin mononucleotide: distinct roles for the flavin adenine dinucleotide and flavin mononucleotide prosthetic groups in catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1599–1609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigenblum E., Krasna A. I. Solubilization and properties of the hydrogenase of Chromatium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 11;198(2):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forget P., Dervartanian D. V. The bacterial nitrate reductases: EPR studies on nitrate reductase A from Micrococcus denitrificans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;256(2):600–606. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forget P. The bacterial nitrate reductases. Solubilization, purification and properties of the enzyme A of Escherichia coli K 12. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Mar 1;42(2):325–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz J., Anderson R., Fee J., Palmer G., Sands R. H., Tsibris J. C., Gunsalus I. C., Orme-Johnson W. H., Beinert H. The iron electron-nuclear double resonance (ENDOR) of two-iron ferredoxins from spinach, parsley, pig adrenal cortex and Pseudomonas putida. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Nov 2;253(1):110–133. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90239-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY C. T., GEST H. BIOLOGICAL FORMATION OF MOLECULAR HYDROGEN. Science. 1965 Apr 9;148(3667):186–192. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3667.186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geary L. E., Meister A. On the mechanism of glutamine-dependent reductive amination of alpha-ketoglutarate catalyzed by glutamate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3501–3508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring U., Arnon D. I. Ferredoxin-dependent phenylpyruvate synthesis by cell-free preparations of photosynthetic bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 25;246(14):4518–4522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum W. O., Mortenson L. E., Chen J. S., Holm R. H. Quantitative extrusions of the Fe4S4 cores of the active sites of ferredoxins and the hydrogenase of Clostridium pasteurianum. J Am Chem Soc. 1977 Jan 19;99(2):584–595. doi: 10.1021/ja00444a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlitz P. H., Krasna A. I. Structural and catalytic properties of hydrogenase from Chromatium. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 17;14(12):2561–2568. doi: 10.1021/bi00683a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogotov I. N., Laurinavichene T. V. Rol' ferredoksina v metabolizme vodoroda u Rhodospirillum rubrum. Mikrobiologiia. 1975 Jul-Aug;44(4):581–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogotov I. N., Zorin N. A., Serebriakova L. T., Kondratieva E. N. The properties of hydrogenase from Thiocapsa roseopersicina. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 12;523(2):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero M. G., Vega J. M., Leadbetter E., Losada M. Preparation and characterization of a soluble nitrate reductase from Azotobacter chroococcum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Jun 25;91(4):287–304. doi: 10.1007/BF00425049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman M., Schejter A., Avi-Dor Y. The preparation and properties of the membranal DPNH dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 26;162(4):506–517. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(68)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORI K. Electron transporting components participating in nitrate and oxygen respirations from a halotolerant Micrococcus. II. Properties of cytochrome c551 and brown protein. J Biochem. 1961 Dec;50:481–485. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaker H., Veeger C. Involvement of the cytoplasmic membrane in nitrogen fixation by Azotobacter vinelandii. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 1;77(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall D. O., Rao K. K., Cammack R. The iron-sulphur proteins: structure, function and evolution of a ubiquitous group of proteins. Sci Prog. 1975 Summer;62(246):285–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatchikian E. C., Bruschi M., Le Gall J. Characterization of the periplasmic hydrogenase from Desulfovibrio gigas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 May 30;82(2):451–461. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90896-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatefi Y., Davis K. A., Baltscheffsky H., Baltscheffsky M., Johansson B. C. Isolation and properties of succinate dehydrogenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Oct;152(2):613–618. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90257-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskovitz T., Averill B. A., Holm R. H., Ibers J. A., Phillips W. D., Weiher J. F. Structure and properties of a synthetic analogue of bacterial iron--sulfur proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2437–2441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuti T., Shiga T., Kakuno T., Horio T. Studies on ESR spectra of chromatophores from Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Biochem. 1974 Jun;75(6):1363–1371. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. L., Steenkamp D. J., Holm R. H., Singer T. P. Identification of the iron-sulfur center in trimethylamine dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):547–551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. B., Lorsbach T., Que L. Iron-sulfur clusters and cysteine distribution in a ferredoxin from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 17;70(2):582–588. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91087-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. C., Zumft W. G., Mortenson L. E. Structure of the molybdoferredoxin complex from Clostridium pasteurianum and isolation of its subunits. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):884–890. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.884-890.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson K. G., Rogers L. J., Haslett B. G., Boulter D., Cammack R. Comparative studies on two ferredoxins from the cyanobacterium Nostoc strain MAC. Biochem J. 1978 Jun 15;172(3):465–477. doi: 10.1042/bj1720465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höpner T., Trautwein A. Some properties of formate dehydrogenase. Z Naturforsch B. 1972 Sep;27(9):1075–1076. doi: 10.1515/znb-1972-0923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingledew W. J., Prince R. C. Thermodynamic resolution of the iron-sulfur centers of the succinic dehydrogenase of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jan 15;178(1):303–307. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90195-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel D. W., Howard R. L., Evans H. J., Russell S. A. Purification and characterization of the molybdenum-iron protein component of nitrogenase from soybean nodule bacteroids. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):500–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. W., Canale-Parola E. Properties of rubredoxin and ferredoxin isolated from spirochetes. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973;89(4):341–353. doi: 10.1007/BF00408901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungermann K., Kirchniawy H., Thauer R. K. Ferredoxin dependent CO-2 reduction to formate in Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Nov 9;41(3):682–689. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90067-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungermann K., Rupprecht E., Ohrloff C., Thauer R., Decker K. Regulation of the reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-ferredoxin reductase system in Clostridium kluyveri. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 25;246(4):960–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungermann K., Thauer R. K., Leimenstoll G., Decker K. Function of reduced pyridine nucleotide-ferredoxin oxidoreductases in saccharolytic Clostridia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 30;305(2):268–280. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakuno T., Kaplan N. O., Kamen M. D. Chromatium hydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):861–863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri M., Ganguli B. N., Gunsalus I. C. A soluble cytochrome P-450 functional in methylene hydroxylation. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3543–3546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke B., Bulen W. A., Shaw E. R., Breeze R. H. Determination of oxidation-reduction potentials by spectropolarimetric titration: application to several iron-sulfur proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 May;162(1):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearny J. J., Sagers R. D. Formate dehydrogenase from Clostridium acidiurici. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):152–161. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.152-161.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keister D. L., Yike N. J. Energy-linked reactions in photosynthetic bacteria. I. Succinatelinked ATP-driven NAD reduction by Rhodospirillum rubrum chromatophores. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Aug;121(2):415–422. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerscher L., Oesterhelt D., Cammack R., Hall D. O. A new plant-type ferredoxin from halobacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Dec;71(1):101–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb11094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerscher L., Oesterhelt D. Ferredoxin is the coenzyme of alpha-ketoacid oxidoreductases in Halobacterium halobium. FEBS Lett. 1977 Nov 15;83(2):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)81004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim I. C., Bragg P. D. Some properties of the succinate dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli. Can J Biochem. 1971 Oct;49(10):1098–1104. doi: 10.1139/o71-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura T., Hauber J., Singer T. P. Studies on succinate dehydrogenase. 13. Reversible activation of the mammalian enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 10;242(21):4987–4993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D., Chen C. H. Physical and chemical properties of the nitrogenase proteins form Azotobacter vinelandii. Arch Mikrobiol. 1974 Jun 7;98(1):93–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00425272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaff D. B., Malkin R. Iron-sulfur proteins of the green photosynthetic bacterium Chlorobium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 14;430(2):244–252. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90082-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoell H. E., Knappe J. Escherichia coli ferredoxin, an iron-sulfur protein of the adrenodoxin type. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Dec 16;50(1):245–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch B., Wong P., Russell S. A., Howard R., Evans H. J. Purification and some properties of a non-haem iron protein from the bacteroids of soya-bean (Glycine max Merr) nodules. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;118(5):773–781. doi: 10.1042/bj1180773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröger A. Fumarate as terminal acceptor of phosphorylative electron transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 23;505(2):129–145. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(78)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupfer D. G., Canale-Parola E. Pyruvate metabolism in Sarcina maxima. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):984–990. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.984-990.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARA F. J. The succinic dehydrogenase of Propionibacterium pentosaceum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jun;33(2):565–567. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINNANE A. W., WRIGLEY C. W. FRAGMENTATION OF THE ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. PREPARATION OF A SOLUBLE FORMATE DEHYDROGENASE-CYTOCHROME B1 COMPLEX. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Nov 8;77:408–418. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90515-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laishley E. J., Travis J., Peck H. D., Jr Amino acid composition of ferredoxin and rubredoxin isolated from Desulfovibrio gigas. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):302–303. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.302-303.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam Y., Nicholas D. J. A nitrate reductase from Micrococcus denitrificans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Apr 22;178(2):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Gall J., Dragoni N. Dependance of sulfite reduction on a crystallized ferredoxin from Desulfovibrio gigas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Apr 19;23(2):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90519-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. P., LeGall J., Peck H. D., Jr Isolation of assimilatroy- and dissimilatory-type sulfite reductases from Desulfovibrio vulgaris. J Bacteriol. 1973 Aug;115(2):529–542. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.2.529-542.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. P., Peck H. D., Jr Purification of the enzyme reducing bisulfite to trithionate from Desulfovibrio gigas and its identification as desulfoviridin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov 5;45(3):583–589. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90457-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L. F., Ljungdahl L., Wood H. G. Properties of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate-Dependent Formate Dehydrogenase from Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;92(2):405–412. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.2.405-412.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljones T., Burris R. H. ATP hydrolysis and electron transfer in the nitrogenase reaction with different combinations of the iron protein and the molybdenum-iron protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 12;275(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljones T., Burris R. H. Evidence for one-electron transfer by the Fe protein of nitrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jan 13;80(1):22–25. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund K., DeMoss J. A. Association-dissociation behavior and subunit structure of heat-released nitrate reductase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 25;251(8):2207–2216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER R. W., MASSEY V. DIHYDROOROTIC DEHYDROGENASE. I. SOME PROPERTIES OF THE ENZYME. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1453–1465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor C. H. Anaerobic cytochrome b1 in Escherichia coli: association with and regulation of nitrate reductase. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1111–1116. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1111-1116.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor C. H., Schnaitman C. A., Normansell D. E. Purification and properties of nitrate reductase from Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5321–5327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor C. H. Solubilization of Escherichia coli nitrate reductase by a membrane-bound protease. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1102–1110. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1102-1110.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magasanik B., Prival M. J., Brenchley J. E., Tyler B. M., DeLeo A. B., Streicher S. L., Bender R. A., Paris C. G. Glutamine synthetase as a regulator of enzyme synthesis. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1974;8(0):119–138. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152808-9.50010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin R., Bearden A. J. Membrane-bound iron-sulfur centers in photosynthetic systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Oct 23;505(2):147–181. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(78)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey V., Edmondson D. On the mechanism of inactivation of xanthine oxidase by cyanide. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 25;245(24):6595–6598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews R., Charlton S., Sands R. H., Palmer G. On the nature of the spin coupling between the iron-sulfur clusters in the eight-iron ferredoxins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4326–4328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayerle J. J., Frankel R. B., Holm R. H., Ibers J. A., Phillips W. D., Weiher J. F. Synthetic analogs of the active sites of iron-sulfur proteins. Structure and properties of bis(o-xylyldithiolato-m2-sulfidoferrate (3)), an analog of the 2Fe-2S proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2429–2433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh A. R., Chu M., Bolton J. R. Flash photolysis electron spin resonance studies of the electron acceptor species at low temperatures in photosystem I of spinach subchloroplast particles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 17;376(2):308–314. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna E. J., Coon M. J. Enzymatic omega-oxidation. IV. Purification and properties of the omega-hydroxylase of Pseudomonas oleovorans. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 10;245(15):3882–3889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna E. J., Kallio R. E. The biology of hydrocarbons. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1965;19:183–208. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.19.100165.001151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. E., Stadtman E. R. Glutamate synthase from Escherichia coli. An iron-sulfide flavoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7407–7419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortenson L. E., Morris J. A., Jeng D. Y. Purification, metal composition and properties of molybdoferredoxin and azoferredoxin, two of the components of the nitrogen-fixing system of Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Aug 29;141(3):516–522. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortenson L. E., Zumpft W. G., Palmer G. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies on nitrogenase. 3. Function of magnesium adenosine 5'-triphosphate and adenosine 5'-diphosphate in catalysis by nitrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 22;292(2):422–435. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moura J. J., Xavier A. V., Bruschi M., Le Gall J., Hall D. O., Cammack R. A molybdenum-containing iron-sulphur protein from Desulphovibrio gigas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 4;72(3):782–789. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80201-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moura J. J., Xavier A. V., Cookson D. J., Moore G. R., Williams R. J. Redox states of cytochrome c3 in the absence and presence of ferredoxin. FEBS Lett. 1977 Sep 15;81(2):275–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80534-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moura J. J., Xavier A. V., Hatchikian E. C., Le Gall J. Structural control of the redox potentials and of the physiological activity by oligomerization of ferredoxin. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 1;89(1):177–179. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80549-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullinger R. N., Cammack R., Rao K. K., Hall D. O., Dickson D. P., Johnson C. E., Rush J. D., Simopoulos A. Physicochemical characterization of the four-iron-four-sulphide ferredoxin from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochem J. 1975 Oct;151(1):75–83. doi: 10.1042/bj1510075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. J., Siegel L. M. Siroheme and sirohydrochlorin. The basis for a new type of porphyrin-related prosthetic group common to both assimilatory and dissimilatory sulfite reductases. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6911–6919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münck E., Rhodes H., Orme-Johnson W. H., Davis L. C., Brill W. J., Shah V. K. Nitrogenase. VIII. Mössbauer and EPR spectroscopy. The MoFe protein component from Azotobacter vinelandii OP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 21;400(1):32–53. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90124-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatani H., Shimizu M., Valentine R. C. The mechanism of ammonia assimilation in nitrogen fixing Bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;79(2):164–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00424923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakos G., Mortenson L. E. Structural properties of hydrogenase from Clostridium pasteurianum W5. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2442–2449. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakos G., Mortenson L. Purification and properties of hydrogenase, an iron sulfur protein, from Clostridium pasteurianum W5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 10;227(3):576–583. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C. A., Handler P. Preparation of bovine xanthine oxidase and the subunit structures of some iron flavoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 25;243(20):5368–5373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi T., Lim J., Winter D. B., King T. E. Thermodynamic and EPR characteristics of a HiPIP-type iron-sulfur center in the succinate dehydrogenase of the respiratory chain. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2105–2109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi T., Salerno J. C. Thermodynamic and EPR characteristics of two ferredoxin-type iron-sulfur centers in the succinate-ubiquinone reductase segment of the respiratory chain. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2094–2104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. S., Ballou D. P., Palmer G., Massey V. The mechanism of action of xanthine oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4363–4382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme-Johnson N. R., Hansen R. E., Beinert H. Electron paramagnetic resonance-detectable electron acceptors in beef heart mitochondria. Reduced diphosphopyridine nucleotide ubiquinone reductase segment of the electron transfer system. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 25;249(6):1922–1927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme-Johnson W. H., Hamilton W. D., Jones T. L., Tso M. Y., Burris R. H., Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Electron paramagnetic resonance of nitrogenase and nitrogenase components from Clostridium pasteurianum W5 and Azotobacter vinelandii OP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3142–3145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme-Johnson W. H. Iron-sulfur proteins: structure and function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42(0):159–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PACKER L., VISHNIAC W. The specificity of a diphosphopyridine nucleotide-linked hydrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 May;17(1):153–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90339-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PECK H. D., Jr, DEACON T. E., DAVIDSON J. T. STUDIES ON ADENOSINE 5'-PHOSPHOSULFATE REDUCTASE FROM DESULFOVIBRIO DESULFURICANS AND THIOBACILLUS THIOPARUS. I. THE ASSAY AND PURIFICATION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Mar 22;96:429–446. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90561-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PECK H. D., Jr Evidence for oxidative phosphorylation during the reduction of sulfate with hydrogen by Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. J Biol Chem. 1960 Sep;235:2734–2738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEEL J. L. The breakdown of pyruvate by cell-free extracts of the rumen micro-organism LC. Biochem J. 1960 Mar;74:525–541. doi: 10.1042/bj0740525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer E. L., Sternlicht H. The use of 13C nuclear magnetic resonance of aromatic amino acid residues to determine the midpoint oxidation-reduction potential of each iron-sulfur cluster of Clostridium acidi-urici and Clostridium pasteurianum ferredoxins. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):2062–2072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer G., Multani J. S., Cretney W. C., Zumft W. G., Mortenson L. E. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies on nitrogenase. I. The properties of molybdoferredoxin and azoferredoxin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Nov;153(1):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90452-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer G., Sands R. H., Mortenson L. E. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies on the ferredoxin from Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 May 25;23(4):357–362. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90733-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papa S., Lorusso M., Guerrieri F. Mechanism of respiration-driven proton translocation in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Analysis of proton translocation associated with oxidation of endogenous ubiquinol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 17;387(3):425–440. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck H. D., Jr, Bramlett R., Der Vartanian D. V. On the mechanism of adenylyl sulfate reductase for the sulfate-reducing bacterium, Desulfovibrio vulgaris. Z Naturforsch B. 1972 Sep;27(9):1084–1086. doi: 10.1515/znb-1972-0928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. A., Kusunose M., Kusunose E., Coon M. J. Enzymatic omega-oxidation. II. Function of rubredoxin as the electron carrier in omega-hydroxylation. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 10;242(19):4334–4340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pienkos P. T., Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Molybdenum cofactors from molybdoenzymes and in vitro reconstitution of nitrogenase and nitrate reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5468–5471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. C., Lindsay J. G., Dutton P. L. The Rieske iron-sulfur center in mitochondrial and photosynthetic systems: Em/pH relationships. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 1;51(1):108–111. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80864-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince R. G., Dutton P. L. Further studies on the Rieske iron-sulfur center in mitochondrial and photosynthetic systems: a pK on the oxidized form. FEBS Lett. 1976 May 15;65(1):117–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80634-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Que L., Jr, Holm R. H., Mortenson L. E. Letter: Extrusion of Fe2S2 and Fe4S4 cores from the active sites of ferredoxin proteins. J Am Chem Soc. 1975 Jan 22;97(2):463–464. doi: 10.1021/ja00835a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIESKE J. S., ZAUGG W. S., HANSEN R. E. STUDIES ON THE ELECTRON TRANSFER SYSTEM. LIX. DISTRIBUTION OF IRON AND OF THE COMPONENT GIVING AN ELECTRON PARAMAGNETIC RESONANCE SIGNAL AT G = 1.90 IN SUBFRACTIONS OF COMPLEX 3. J Biol Chem. 1964 Sep;239:3023–3030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings J., Shah V. K., Chisnell J. R., Brill W. J., Zimmermann R., Münck E., Orme-Johnson W. H. Novel metal cluster in the iron-molybdenum cofactor of nitrogenase. Spectroscopic evidence. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1001–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy C. A., Bryant M. P., Wolin M. J. Ferredoxin-dependent conversion of acetaldehyde to acetate and H 2 in extracts of S organism. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):133–138. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.133-138.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieske J. S. Composition, structure, and function of complex III of the respiratory chain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 27;456(2):195–247. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(76)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salerno J. C., Ohnishi T. Tetranuclear and binuclear iron-sulfur clusters in succinate dehydrogenase: a method of iron quantitation by formation of paramagnetic complexes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Dec 6;73(3):833–840. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90884-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer F. D., Bush R. S., Stevenson I. L. The separation of pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase from Clostridium pasteurianum into two enzymes catalyzing different reactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 14;445(2):518–520. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer F. D., Erfle J. D., Mahadevan S. Amino acid biosynthesis in mixed rumen cultures. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;150(3):357–372. doi: 10.1042/bj1500357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer P. A., Thauer R. K. Purification and properties of reduced ferredoxin: CO2 oxidoreductase from Clostridium pasteurianum, a molybdenum iron-sulfur-protein. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(1):125–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider K., Schlegel H. G. Identification and quantitative determination of the flavin component of soluble hydrogenase from Alcaligenes eutrophus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 16;84(3):564–571. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90743-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider K., Schlegel H. G. Localization and stability of hydrogenases from aerobic hydrogen bacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Apr 1;112(3):229–238. doi: 10.1007/BF00413086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. H., DeMoss J. A. Formation of the formate-nitrate electron transport pathway from inactive components in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):478–486. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.478-486.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Isolation of an iron-molybdenum cofactor from nitrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3249–3253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Davis L. C., Brill W. J. Nitrogenase. VI. Acetylene reduction assay: Dependence of nitrogen fixation estimates on component ratio and acetylene concentration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 19;384(2):353–359. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam K. T., Buchanan B. B., Arnon D. I. Ferredoxins in light- and dark-grown photosynthetic cells with special reference to Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;256(2):477–486. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90076-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shethna Y. I., DerVartanian D. V., Beinert H. Non heme (iron-sulfur) proteins of Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jun 28;31(6):862–868. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90531-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shethna Y. I., Stombaugh N. A., Burris R. H. Ferredoxin from Bacillus polymyxa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Mar 19;42(6):1108–1116. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Davis P. S., Kamin H. Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-sulfite reductase of enterobacteria. 3. The Escherichia coli hemoflavoprotein: catalytic parameters and the sequence of electron flow. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1572–1586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Davis P. S. Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-sulfite reductase of enterobacteria. IV. The Escherichia coli hemoflavoprotein: subunit structure and dissociation into hemoprotein and flavoprotein components. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1587–1598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Faeder E. J., Kamin H. Flavin interaction in NADPH-sulfite reductase. Z Naturforsch B. 1972 Sep;27(9):1087–1089. doi: 10.1515/znb-1972-0929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Murphy M. J., Kamin H. Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-sulfite reductase of enterobacteria. I. The Escherichia coli hemoflavoprotein: molecular parameters and prosthetic groups. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):251–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieker L. C., Adman E., Jensen L. H. Structure of the Fe-S complex in a bacterial ferredoxin. Nature. 1972 Jan 7;235(5332):40–42. doi: 10.1038/235040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sin I. L. Purification and properties of xanthine dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas acidovorans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 20;410(1):12–20. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90203-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirevåg R., Ormerod J. G. Carbon dioxide fixation in green sulphur bacteria. Biochem J. 1970 Nov;120(2):399–408. doi: 10.1042/bj1200399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smillie R. M. Isolation of two proteins with chloroplast ferredoxin activity from a blue-green alga. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Sep 8;20(5):621–629. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., Lang G. Mössbauer spectroscopy of the nitrogenase proteins from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Structural assignments and mechanistic conclusions. Biochem J. 1974 Feb;137(2):169–180. doi: 10.1042/bj1370169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith B. E., Lowe D. J., Bray R. C. Studies by electron paramagnetic resonance on the catalytic mechanism of nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biochem J. 1973 Oct;135(2):331–341. doi: 10.1042/bj1350331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. A., Hill S., Yates M. G. Inhibition by acetylene of conventional hydrogenase in nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Nature. 1976 Jul 15;262(5565):209–210. doi: 10.1038/262209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. V., Noy R. J., Evans M. C. Physiological electron donor systems to the nitrogenase of the blue-green alga Anabaena cylindrica. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Nov 2;253(1):104–109. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90238-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. T., Rajagopalan K. V., Handler P. Purification and properties of xanthine dehydroganase from Micrococcus lactilyticus. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 25;242(18):4108–4117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorokin Y. I. Role of carbon dioxide and acetate in biosynthesis by sulphate-reducing bacteria. Nature. 1966 Apr 30;210(5035):551–552. doi: 10.1038/210551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stasny J. T., Burns R. C., Korant B. D., Hardy R. W. Electron microscopy of the Mo-Fe protein from Azotobacter nitrogenase. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jan;60(1):311–316. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.1.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenkamp D. J., Mallinson J. Trimethylamine dehydrogenase from a methylotrophic bacterium. I. Isolation and steady-state kinetics. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 13;429(3):705–719. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenkamp D. J., Singer T. P. On the presence of a novel covalently bound oxidation-reduction cofactor, iron and labile sulfur in trimethylamine dehydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):1289–1295. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90794-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenkamp D. J., Singer T. P. Participation of the iron-sulphur cluster and of the covalently bound coenzyme of trimethylamine dehydrogenase in catalysis. Biochem J. 1978 Feb 1;169(2):361–369. doi: 10.1042/bj1690361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson M. P., Dawes E. A. Pyruvic acid and formic acid metabolism in Sarcina ventriculi and the role of ferredoxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Dec;69(3):331–343. doi: 10.1099/00221287-69-3-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strombaugh N. A., Burris R. H., Orme-Johnson W. H. Ferredoxins from Bacillus polymyxa. Low potential iron-sulfur proteins which appear to contain single four iron, four sulfur centers accepting a single electron on reduction. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7951–7956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh B., Akagi J. M. Formation of thiosulfate from sulfite by Desulfovibrio vulgaris. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):210–215. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.210-215.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney W. V., Bearden A. J., Rabinowitz J. C. The electron paramagnetic resonance of oxidized clostridial ferredoxins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jul 10;59(1):188–194. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80192-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney W. V., Rabinowitz J. C., Yoch D. C. High and low reduction potential 4Fe-4S clusters in Azotobacter vinelandii (4Fe-4S) 2ferredoxin I. Influence of the polypeptide on the reduction potentials. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7842–7847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Synthesis and sideedness of membrane-bound respiratory nitrate reductase (EC1.7.99.4) in Escherichia coli lacking cytochromes. Biochem J. 1975 May;148(2):329–333. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAGAWA K., ARNON D. I. Ferredoxins as electron carriers in photosynthesis and in the biological production and consumption of hydrogen gas. Nature. 1962 Aug 11;195:537–543. doi: 10.1038/195537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Haniu M., Yasunobu K. T., Evans M. C., Rao K. K. Amino acid sequence of ferredoxin from a photosynthetic green bacterium, Chlorobium limicola. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 2;13(14):2953–2959. doi: 10.1021/bi00711a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Haniu M., Yasunobu K. T., Evans M. C., Rao K. K. The amino acid sequence of ferredoxin II from Chlorobium limicola, a photosynthetic green bacterium. Biochemistry. 1975 May 6;14(9):1938–1943. doi: 10.1021/bi00680a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedro S. V., Meyer T. E., Kamen M. D. Primary structure of a high potential iron sulfur protein from a moderately halophilic denitrifying coccus. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7826–7833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tel-Or E., Luijk L. W., Packer L. Hydrogenase in N2-fixing cyanobacteria. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jan 15;185(1):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K. CO 2 reduction to formate in Clostridium acidi-urici. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):443–444. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.443-444.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K. CO(2)-reduction to formate by NADPH. The initial step in the total synthesis of acetate from CO(2) in Clostridium thermoaceticum. FEBS Lett. 1972 Oct 15;27(1):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80421-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Fuchs G., Jungermann K. Reduced ferredoxin: CO2 oxidoreductase from Clostridium pasteurianum: its role in formate metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):758–760. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.758-760.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Rupprecht E., Ohrloff C., Jungermann K., Decker K. Regulation of the reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-ferredoxin reductase system in Clostridium kluyveri. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 25;246(4):954–959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele H. H. Sulfur metabolism in Thiorhodaceae. V. Enzymes of sulfur metabolism in Thiocapsa floridana and Chromatium species. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1968;34(3):350–356. doi: 10.1007/BF02046457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorneley R. N., Eady R. R. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae: evidence for an adenosine triphosphate-induced association of the iron-sulphur protein. Biochem J. 1973 Jun;133(2):405–408. doi: 10.1042/bj1330405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotta P. P., Platzer K. E., Haschemeyer R. H., Meister A. Glutamine-binding subunit of glutamate synthase and partial reactions catalyzed by this glutamine amidotransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4607–4611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trudinger P. A. Carbon monoxide-reacting pigment from Desulfotomaculum nigrificans and its possible relevance to sulfite reduction. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):158–170. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.158-170.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsibris J. C., Tsai R. L., Gunsalus I. C., Orme-Johnson W. H., Hansen R. E., Beinert H. The number of iron atoms in the paramagnetic center (G =1.94) of reduced putidaredoxin, a nonheme iron protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):959–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso M. Y., Burris R. H. The binding of ATP and ADP by nitrogenase components from Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 6;309(2):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso M. Y., Ljones T., Burris R. H. Purification of the nitrogenase proteins from Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 23;267(3):600–604. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso M. Y. Some properties of the nitrogenase proteins from Clostridium pasteurianum. Molecular weight, subunit structure, isoelectric point and EPR spectra. Arch Microbiol. 1974;99(1):71–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00696223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda K., Rabinowitz J. C. Pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase. 3. Purification and properties of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3111–3119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda K., Rabinowitz J. C. Pyruvate-ferredoxin oxidoreductase. IV. Studies on the reaction mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3120–3125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENTINE R. C. BACTERIAL FERREDOXIN. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Dec;28:497–517. doi: 10.1128/br.28.4.497-517.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALENTINE R. C., JACKSON R. L., WOLFE R. S. Role of ferredoxin in hydrogen metabolism of Micrococcus lactilyticus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Jun 4;7:453–456. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90334-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van 't Riet J., Planta R. J. Purification, structure and properties of the respiratory nitrate reductase of Klebsiella aerogenes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 30;379(1):81–94. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandecasteele J. P., Burris R. H. Purification and properties of the constituents of the nitrogenase complex from Clostridium pasteurianum. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):794–801. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.794-801.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetter H., Jr, Knappe J. Flavodoxin and ferredoxin of Escherichia coli. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Mar;352(3):433–446. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1971.352.1.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogels G. D., Van der Drift C. Degradation of purines and pyrimidines by microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Jun;40(2):403–468. doi: 10.1128/br.40.2.403-468.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARRINGA M. G., GIUDITTA A. Studies on succinic dehydrogenase. IX. Characterization of the enzyme from Micrococcus lactilyticus. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jan;230(1):111–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WITTENBERGER C. L., REPASKE R. Studies on hydrogen oxidation in cell-free extracts of Hydrogenomonas eutropha. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Mar 4;47:542–552. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90549-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. A., Mortenson L. E. An effect of magnesium adenosine 5'-triphosphate on the structure of azoferredoxin from Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 6;53(3):904–909. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. A., Mortenson L. E. Effect of magnesium adenosine 5'-triphosphate on the accessibility of the iron of clostridial azoferredoxin, a component of nitrogenase. Biochemistry. 1974 May 21;13(11):2382–2388. doi: 10.1021/bi00708a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. N., Mortenson L. E. Evidence for the existence of a fully reduced state of molybdoferredoxin during the functioning of nitrogenase, and the order of electron transfer from reduced ferredoxin. J Biol Chem. 1974 Oct 10;249(19):6356–6358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt G. D., Bulen W. A., Burns A., Hadfield K. L. Stoichiometry, ATP/2e values, and energy requirements for reactions catalyzed by nitrogenase from Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochemistry. 1975 Sep 23;14(19):4266–4272. doi: 10.1021/bi00690a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong J. Y., Meyer E., Switzer R. L. Glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase from Bacillus subtilis. A novel iron-sulfur protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7424–7426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi T., Honya M., Tamiya N. Purification and properties of hydrogenases of different origins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 2;153(3):699–705. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(68)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi T., Kimura K., Daidoji H., Sakai F., Tamura S. Properties of purified hydrogenase from the particulate fraction of Desulfovibrio vulgaris, Miyazaki. J Biochem. 1976 Mar;79(3):661–671. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. S., Ljungdahl L. G., LeGall J. A four-iron, four-sulfide ferredoxin with high thermostability from Clostridium thermoaceticum. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1084–1090. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1084-1090.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Arnon D. I. Comparison of two ferredoxins from Rhodospirillum rubrum as electron carriers for the native nitrogenase. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):743–745. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.743-745.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Arnon D. I., Sweeney W. V. Characterization of two soluble ferredoxins as distinct from bound iron-sulfur proteins in the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8330–8336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Arnon D. I. The nitrogen fixation system of photosynthetic bacteria. II. Chromatium nitrogenase activity linked to photochemically generated assimilatory power. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 3;197(2):180–184. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Arnon D. I. Two biologically active ferredoxins from the aerobic nitrogen-fixing bacteriu, Azotobacter vinelandii. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4514–4520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Benemann J. R., Arnon D. I., Valentine R. C., Russell S. A. An endogenous electron carrier for the nitrogenase system of Rhizobium bacteroids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Mar 12;38(5):838–842. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90795-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Benemann J. R., Valentine R. C., Arnon D. I. The electron transport system in nitrogen fixation by Azotobacter. II. Isolation and function of a new type of ferredoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1404–1410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Carithers R. P., Arnon D. I. Isolation and characterization of bound ion-sulfur proteins from bacterial photosynthetic membranes. I. Ferredoxins III and IV from Rhodospirillum rubrum chromatophores. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7453–7460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Carithers R. P. Potentiometric titration of the high- and low-potential 4Fe-4S* centers of Azotobacter vinelandii ferredoxin I. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):822–824. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.822-824.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C. Purification and properties of two ferredoxins from the nitrogen-fixing bacterium Bacillus polymyxa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Oct;158(2):633–640. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90555-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Valentine R. C. Ferredoxins and flavodoxins of bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1972;26:139–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.26.100172.001035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Valentine R. C. Four-iron (sulfide) ferredoxin from Bacillus polymyxa. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1211–1213. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1211-1213.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubieta J. A., Mason R., Postgate J. R. A four-iron ferredoxin from Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;133(4):851–854. doi: 10.1042/bj1330851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumft W. G., Cretney W. C., Huang T. C., Mortenson L. E., Palmer G. On the structure and function of nitrogenase from Clostridium pasteurianum W5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 26;48(6):1525–1532. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90887-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumft W. G., Mortenson L. E., Palmer G. Electron-paramagnetic-resonance studies on nitrogenase. Investigation of the oxidation-reduction behaviour of azoferredoxin and molybdoferredoxin with potentiometric and rapid-freeze techniques. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Aug 1;46(3):525–535. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03646.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumft W. G., Mortenson L. E. The nitrogen-fixing complex of bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 31;416(1):1–52. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(75)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumft W. G., Palmer G., Mortenson L. E. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies on nitrogenase. II. Interaction of adenosine 5'-triphosphate with azoferredoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 22;292(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90047-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Beeumen J., de Ley J. A ferrodoxin from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. FEBS Lett. 1975 Nov 15;59(2):146–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80362-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Riet J., van Ed J. H., Wever R., van Gelder B. F., Planta R. J. Characterization of the respiratory nitrate reductase of Klebsiella aerogenes as a molybdenum-containing iron-sulfur enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 20;405(2):306–317. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Westen H. M., Mayhew S. G., Veeger C. Separation of hydrogenase from intact cells of Desulfovibrio vulgaris. Purification and properties. FEBS Lett. 1978 Feb 1;86(1):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


