Full text
PDF

























Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER H. E., KOCH G., MOUNTAIN I. M., SPRUNT K., VAN DAMME O. Infectivity of ribonucleic acid of poliovirus on HeLa cell mono-layers. Virology. 1958 Feb;5(1):172–173. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham G., Cooper P. D. Relations between poliovirus polypeptides as shown by tryptic peptide analysis. J Gen Virol. 1975 Nov;29(2):215–221. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-29-2-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amako K., Dales S. Cytopathology of Mengovirus infection. II. Proliferation of membranous cisternae. Virology. 1967 Jun;32(2):201–215. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90270-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambros V., Pettersson R. F., Baltimore D. An enzymatic activity in uninfected cells that cleaves the linkage between poliovirion RNA and the 5' terminal protein. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1439–1446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. A., Edmonds M., Nakazato H., Phillips B. A., Vaughn M. H. Polyadenylic acid sequences in the virion RNA of poliovirus and Eastern Equine Encephalitis virus. Science. 1972 May 5;176(4034):526–528. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4034.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins J. F., Steitz J. A., Anderson C. W., Model P. Binding of mammalian ribosomes to MS2 phage RNA reveals an overlapping gene encoding a lysis function. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):247–256. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachrach H. L., Swaney J. B., Vande Woude G. F. Isolation of the structural polypeptides of foot-and-mouth disease virus and analysis of their C-terminal sequences. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):520–528. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90347-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C., Simili M., Shafritz D. A. Initiation activity of EMC virus RNA, binding to initiation factor eIF-4B and shut-off of host cell protein synthesis. Nature. 1978 Sep 21;275(5677):240–243. doi: 10.1038/275240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft J. B. The self-assembly of spherical plant viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1970;16:99–134. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxt B., Grubman M. J., Bachrach H. L. The relation of poly(A) length to specific infectivity of viral RNA: a comparison of different types of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):480–483. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90573-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beremand M. N., Blumenthal T. Overlapping genes in RNA phage: a new protein implicated in lysis. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berghe D. V., Boeyé A. A new species of poliovirus top component. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;41(1):138–142. doi: 10.1007/BF01249940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz K., Egger D., Rasser Y., Bossart W. Kinetics and location of poliovirus macromolecular synthesis in correlation to virus-induced cytopathology. Virology. 1980 Jan 30;100(2):390–399. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90530-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeyé A. A comparative study of fibril formation from Coxsackie B 1 and other picornaviruses. Brief report. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1972;37(2):285–287. doi: 10.1007/BF01268014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond C. W., Swim H. E. Factors affecting composition and thermostability of mengovirus virions. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1256–1261. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1256-1261.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond C. W., Swim H. E. Physiological characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of mengovirus. J Virol. 1975 Feb;15(2):288–296. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.2.288-296.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boublik M., Drzeniek R. Demonstration of a core in poliovirus particles by electron microscopy. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jun;31(3):447–449. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boublik M., Drzeniek R. Structural subunits of poliovirus particles by electron microscopy. J Gen Virol. 1977 Oct;37(1):127–134. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-1-127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowles S. A., Tershak D. R. Proteolysis of noncapsid protein 2 of type 3 poliovirus at the restrictive temperature: breakdown of noncapsid protein 2 correlates with loss of RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):443–448. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.443-448.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breese S. S., Jr, Trautman R., Bachrach H. L. Rotational Symmetry in Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus and Models. Science. 1965 Dec 3;150(3701):1303–1305. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3701.1303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breindl M. VP 4, the D-reactive part of poliovirus. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):962–964. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown F., Newman J., Stott J., Porter A., Frisby D., Newton C., Carey N., Fellner P. Poly(C) in animal viral RNAs. Nature. 1974 Sep 27;251(5473):342–344. doi: 10.1038/251342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burness A. T., Clothier F. W. Particle weight and other biophysical properties of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Gen Virol. 1970 Mar;6(3):381–393. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-6-3-381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burness A. T., Fox S. M., Pardoe I. U. The polypeptide composition of the encephalomyocarditis virus particle. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jun;23(3):225–236. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-23-3-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burness A. T., Pardoe I. U., Duffy E. M., Bhalla R. B., Goldstein N. O. The size and location of the poly(A) tract in EMC virus RNA. J Gen Virol. 1977 Feb;34(2):331–344. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-2-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burness A. T., Pardoe I. U., Fox S. M. Evidence for the lack of glycoprotein in the encephalomyocarditis virus particle. J Gen Virol. 1973 Jan;18(1):33–49. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-18-1-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burness A. T., Walter D. S. Protein components of encephalomyocarditis virus. Nature. 1967 Sep 23;215(5108):1350–1352. doi: 10.1038/2151350a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrell C. J., Cooper P. D. N-terminal aspartate, glycine and serine in poliovirus capsid protein. J Gen Virol. 1973 Dec;21(3):443–451. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-21-3-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E. A comparison of the virus-specific polypeptides of encephalomyocarditis virus, human rhinovirus-1A, and poliovirus. Virology. 1973 Dec;56(2):439–453. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Korant B. D. Characterization of the large picornaviral polypeptides produced in the presence of zinc ion. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):282–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.282-291.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Rueckert R. R. Kinetics of synthesis and cleavage of encephalomyocarditis virus-specific proteins. Virology. 1972 Nov;50(2):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90405-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth B. E., Shimshick E. J., Yin F. H. Association of the polioviral RNA polymerase complex with phospholipid membranes. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):457–466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.457-466.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLTER J. S., BIRD H. H., MOYER A. W., BROWN R. A. Infectivity of ribonucleic acid isolated from virus-infected tissues. Virology. 1957 Dec;4(3):522–532. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Compans R. W. The formation of poliovirus particles in association with the RNA replication complexes. J Gen Virol. 1973 Oct;21:99–108. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-21-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Mosser A. G. Proteins associated with the poliovirus RNA replication complex. Virology. 1971 Nov;46(2):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. Characterization of poliovirus-specific structures associated with cytoplasmic membranes. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):112–122. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. The role of cytoplasmic membranes in poliovirus biosynthesis. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):100–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew P., Martin S. J. The iodination of bovine enterovirus particles. J Gen Virol. 1974 Sep;24(3):525–534. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-3-525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celma M. L., Ehrenfeld E. Translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro: detection of two different initiation sites. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 15;98(4):761–780. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan V. F., Black F. L. Uncoating of poliovirus by isolated plasma membranes. J Virol. 1970 Mar;5(3):309–312. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.3.309-312.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. B., Goldberg I. H., Herner A. E. Inhibition by pactamycin of the initiation of protein synthesis. Effect on the 30S ribosomal subunit. Biochemistry. 1969 Apr;8(4):1327–1335. doi: 10.1021/bi00832a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole C. N. Defective interfering (di) particles of poliovirus. Prog Med Virol. 1975;20:180–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D. A genetic map of poliovirus temperature-sensitive mutants. Virology. 1968 Aug;35(4):584–596. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90287-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D., Steiner-Pryor A., Wright P. J. A proposed regulator for poliovirus: the equestron. Intervirology. 1973;1(1):1–10. doi: 10.1159/000148826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D., Summers D. F., Maizel J. V. Evidence for ambiguity in the posttranslational cleavage of poliovirus proteins. Virology. 1970 Jul;41(3):408–418. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90161-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowell R. L., Philipson L. Specific alterations of coxsackievirus B3 eluted from HeLa cells. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):509–515. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.509-515.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALES S., EGGERS H. J., TAMM I., PALADE G. E. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF POLIOVIRUS. Virology. 1965 Jul;26:379–389. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase: a soluble enzyme able to initiate copying of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Zabel P., Baltimore D. Dependence of the activity of the poliovirus replicase on the host cell protein. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):423–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90516-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Sena J., Mandel B. Studies on the in vitro uncoating of poliovirus. I. Characterization of the modifying factor and the modifying reaction. Virology. 1976 Apr;70(2):470–483. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90288-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Sena J., Mandel B. Studies on the in vitro uncoating of poliovirus. II. Characteristics of the membrane-modified particle. Virology. 1977 May 15;78(2):554–566. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Sena J., Torian B. Studies on the in vitro uncoating of poliovirus. III. Roles of membrane-modifying and -stabilizing factors in the generation of subviral particles. Virology. 1980 Jul 15;104(1):149–163. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90373-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denoya C. D., Scodeller E. A., Vasquez C., La Torre J. L. Foot and mouth disease virus. II. Endoribonuclease activity within purified virions. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90040-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denoya C. D., Scodeller E. A., Vasquez C., La Torre J. L. Ribonuclease activities associated with purified foot and mouth disease virus. Arch Virol. 1978;57(2):153–159. doi: 10.1007/BF01315676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsch-Häsler K., Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Replication of picornaviruses. I. Evidence from in vitro RNA synthesis that poly(A) of the poliovirus genome is genetically coded. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1512–1517. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1512-1517.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downer D. N., Sunderland S., Colter J. S. Isolation and partial characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of Mengo virus. Virology. 1976 Mar;70(1):190–194. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90250-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drzeniek R., Bilello P. Absence of glycoproteins in poliovirus particles. J Gen Virol. 1974 Oct;25(1):125–132. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-25-1-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drzeniek R., Bilello P. Reconstitution of poliovirus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):719–724. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80199-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K., Rueckert R. R. Fragments generated by pH dissociation of ME-virus and their relation to the structure of the virion. J Mol Biol. 1971 May 28;58(1):217–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
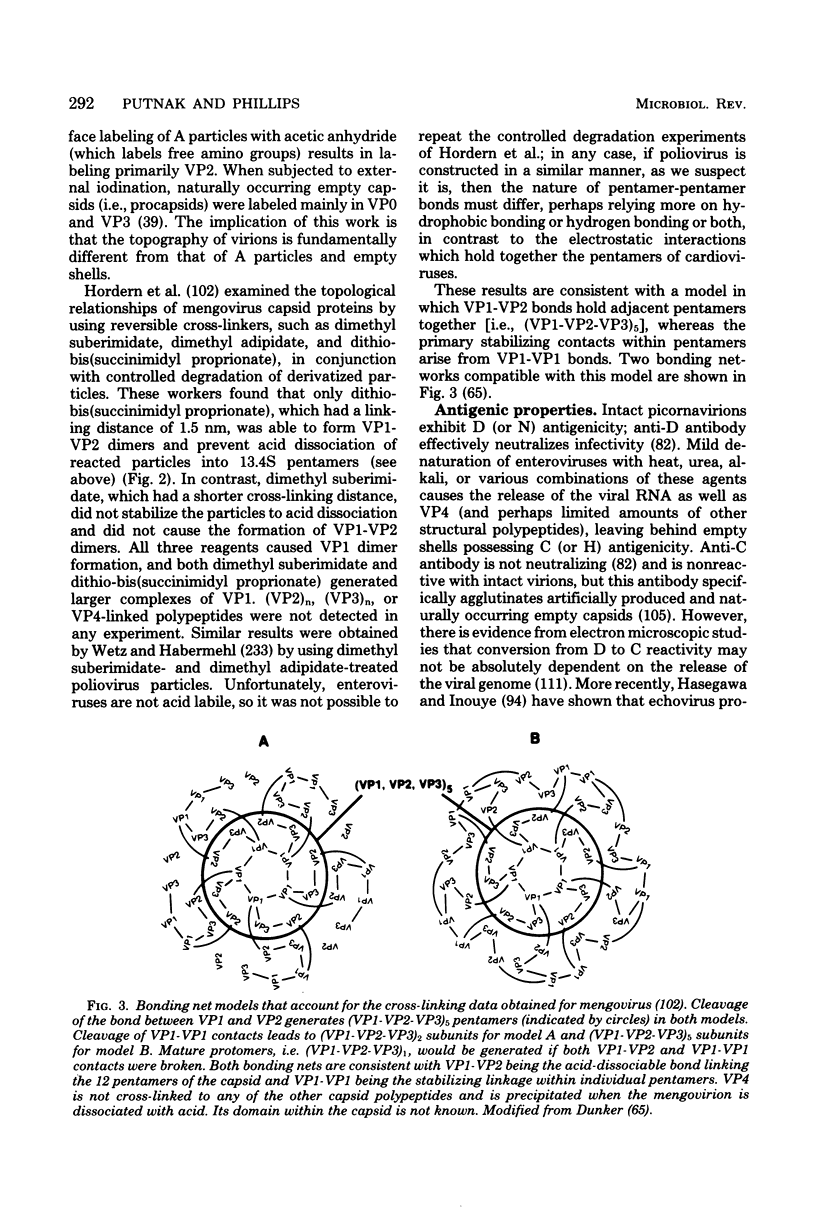
- Dunker A. K. The structure of picornaviruses: classification of the bonding networks. Virology. 1979 Aug;97(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENWICK M. L., COOPER P. D. Early interactions between poliovirus and ERK cells: some observations on the nature and significance of the rejected particles. Virology. 1962 Oct;18:212–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINCH J. T., KLUG A. Structure of poliomyelitis virus. Nature. 1959 Jun 20;183(4677):1709–1714. doi: 10.1038/1831709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennell R., Phillips B. A. Polypeptide composition of urea- and heat-resistant mutants of poliovirus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1974 Oct;14(4):821–833. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.4.821-833.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick M. L. The effect of reaction with formaldehyde on the sedimentation rates of ribonucleic acids. Biochem J. 1968 May;107(6):851–859. doi: 10.1042/bj1070851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Muñoz R., Lavi U. 5' termini of poliovirus RNA: difference between virion and nonencapsidated 35S RNA. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):820–824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.820-824.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Tomas C. B., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus. II. Demonstration of a new intermediate, the proviron. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):1122–1130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.1122-1130.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Tomas C. B., Guttman N., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus 3. Formation of provirion in cell-free extracts. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):1181–1183. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.1181-1183.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiszman M., Reynier M., Bucchini D., Girard M. Thermosensitive block of the Sabin strain of poliovirus type I. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1143–1151. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1143-1151.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus-specific primer-dependent RNA polymerase able to copy poly(A). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3677–3680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisby D. P., Cotter R. I., Richards B. M. Structural studies of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA both in situ and in free solution. J Gen Virol. 1977 Nov;37(2):311–322. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-2-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisby D., Smith J., Jeffers V., Porter A. Size and location of poly (A) in encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2789–2810. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauntt C. J. Fragmentation of RNA in virus particles of rhinovirus type 14. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):762–764. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.762-764.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghendon Y. Z., Yakobson E. A. Antigenic specificity of poliovirus-related particles. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):589–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.589-590.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghendon Y., Yakobson E., Mikhejeva A. Study of some stages of poliovirus morphogenesis in MiO cells. J Virol. 1972 Aug;10(2):261–266. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.2.261-266.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golini F., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. The genome-linked protein of picornaviruses. IV. Difference in the VPg's of encephalomyocarditis virus and poliovirus as evidence that the genome-linked proteins are virus-coded. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golini F., Semler B. L., Dorner A. J., Wimmer E. Protein-linked RNA of poliovirus is competent to form an initiation complex of translation in vitro. Nature. 1980 Oct 16;287(5783):600–603. doi: 10.1038/287600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granboulan N., Girard M. Molecular weight of poliovirus ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1969 Oct;4(4):475–479. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.4.475-479.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubman M. J., Baxt B., Bachrach H. L. Foot-and-mouth disease virion RNA: studies on the relation between the length of its 3'-poly(A) segment and infectivity. Virology. 1979 Aug;97(1):22–31. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90369-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttman N., Baltimore D. A plasma membrane component able to bind and alter virions of poliovirus type 1: studies on cell-free alteration using a simplified assay. Virology. 1977 Oct 1;82(1):25–36. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttman N., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus. IV. existence of particles sedimenting at 150S and having the properties of provirion. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):363–367. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.363-367.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., HOYER B. H. Early stages of enterovirus infection. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:101–112. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J. Irreversible eclipse of poliovirus by HeLa cells. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:163–176. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90292-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMELER K., ANDERSON T. F., BROWN R. A. Identification of poliovirus particles of different antigenicity by specific agglutination as seen in the electron microscope. Virology. 1962 Jan;16:84–90. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L., Rueckert R. R. Infection of mouse fibroblasts by cardioviruses: premature uncoating and its prevention by elevated pH and magnesium chloride. Virology. 1971 Jan;43(1):152–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halperen S., Stone H. O., Korant B. D. Isolation of glucosamine from the capsids of a picornavirus. J Gen Virol. 1973 Sep;20(3):267–276. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-20-3-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamann A., Reichel C., Wiegers K. J., Drzeniek R. Isoelectric points of polypeptides of standard poliovirus particles of different serological types and of empty capsids and dense particles of poliovirus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1978 Mar;38(3):567–570. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-3-567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamann A., Wiegers K. J., Drzeniek R. Isoelectric focusing and 2D-analysis of poliovirus proteins. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):359–362. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. J., Brown F. Biochemical analysis of a virulent and an avirulent strain of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jan;34(1):87–105. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa A., Inouye S. Antigenicity and polypeptide composition of native and heated echovirus type 7 procapsids. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jan;42(1):119–125. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-42-1-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey E. M., Martin S. J. A possible precursor containing RNA of a bovine enterovirus: the provirion 11. J Gen Virol. 1974 Sep;24(3):515–524. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-3-515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter H., Monstein H. J., Weissmann C. The readthrough protein A1 is essential for the formation of viable Q beta particles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 6;374(2):238–251. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90366-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Doyle M., Perrault J., Kingsbury D. T., Etchison J. Proteinase activity in purified animal viruses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):634–639. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80187-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Kiehn E. D. Specific cleavage of viral proteins as steps in the synthesis and maturation of enteroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):1015–1022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hordern J. S., Leonard J. D., Scraba D. G. Structure of the mengo virion. VI. Spatial relationships of the capsid polypeptides as determined by chemical cross-linking analyses. Virology. 1979 Aug;97(1):131–140. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Roberts W. K. Encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. III. Presence of a genome-associated protein. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):413–415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.413-415.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Roberts W. K. Encephalomyocarditis virus RNA: variations in polyadenylic acid content and biological activity. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):325–330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.325-330.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries S., Knauert F., Ehrenfeld E. Capsid protein precursor is one of two initiated products of translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):481–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.481-488.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Asso J., Baltimore D. Further evidence on the formation of poliovirus proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 14;49(3):657–669. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90289-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus. I. Association of the viral RNA with coat protein. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Polypeptide cleavages in the formation of poliovirus proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):77–84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. D., Martin S. J. Capsid and procapsid proteins of a bovine enterovirus. J Gen Virol. 1971 May;11(2):71–79. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-11-2-71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M. CELLULAR SUSCEPTIBILITY TO ENTEROVIRUSES. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Dec;28:382–390. doi: 10.1128/br.28.4.382-390.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri S., Hinuma Y., Ishida N. Biophysical properties of poliovirus particles irradiated with ultraviolet light. Virology. 1967 Jun;32(2):337–343. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90282-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khesin Y. E., Amchenkova A. M., Sovjetova G. P. Group G chromosomes and the susceptibility of cells of human origin to Coxsackie B viruses. J Gen Virol. 1974 Apr;23(1):17–22. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-23-1-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauert F., Ehrenfeld E. Translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro: studies on n-formylmethionine-labeled polypeptides initiated in cell-free extracts prepared from poliovirus infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1979 Mar;93(2):537–546. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90256-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D., Butterworth B. E. Inhibition by zinc of rhinovirus protein cleavage: interaction of zinc with capsid polypeptides. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):298–306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.298-306.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D. Cleavage of viral precursor proteins in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):751–759. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.751-759.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B. D., Halperen S. Electrophoretic analysis of capsid and non-capsid polypeptides of echovirus 12, and selective inhibtion of the formation of virus particles by actinomycin D. J Gen Virol. 1975 Mar;26(3):239–248. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-26-3-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korant B., Chow N., Lively M., Powers J. Virus-specified protease in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2992–2995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. How do eucaryotic ribosomes select initiation regions in messenger RNA? Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1109–1123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LE BOUVIER G. L. The D to C change in poliovirus particles. Br J Exp Pathol. 1959 Dec;40:605–620. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence C., Thach R. E. Identification of a viral protein involved in post-translational maturation of the encephalomyocarditis virus capsid precursor. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):918–928. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.918-928.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus L. H., Barzilai R. Association of foot-and-mouth disease virus replicase with RNA template and cytoplasmic membranes. J Gen Virol. 1974 May;23(2):213–218. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-23-2-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Colter J. S. Further characterization of Mengo subviral particles: a new hypothesis for picornavirus assembly. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):266–274. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90338-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Kitamura N., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. Sequence studies of poliovirus RNA. IV. Nucleotide sequence complexities of poliovirus type 1, type 2 and two type 1 defective interfering particles RNAs, and fingerprint of the poliovirus type 3 genome. J Gen Virol. 1979 Aug;44(2):311–322. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-2-311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Detjen B. M., Wimmer E. A protein covalently linked to poliovirus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner A. M., Bailey E. J., Tillotson J. R. Enterovirus hemagglutination: inhibition by several enzymes and sugars. J Immunol. 1965 Dec;95(6):1111–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Butterworth B. E. Investigation of the structure of polio- and human rhinovirions through the use of selective chemical reactivity. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Korant B. D. Early interaction of rhinoviruses with host cells. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):29–40. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.29-40.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K. The effects of concanavalin A on the early events of infection by rhinovirus type 2 and poliovirus type 2. J Gen Virol. 1975 Sep;28(3):313–327. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-28-3-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J. Cleavage of mengovirus polyproteins in vivo. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):261–269. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.261-269.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund G. A., Scraba D. G. The isolation of Mengo virus stable non-capsid polypeptides from infected L cells and preliminary characterization of an RNA polymerase activity associated with polypeptide E. J Gen Virol. 1979 Aug;44(2):391–403. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-2-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund G. A., Ziola B. R., Salmi A., Scraba D. G. Structure of the Mengo virion. V. Distribution of the capsid polypeptides with respect to the surface of the virus particle. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist R. E., Ehrenfeld E., Maizel J. V., Jr Isolation of a viral polypeptide associated with poliovirus RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4773–4777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAIZEL J. V., Jr PREPARATIVE ELECTROPHORESIS OF PROTEINS IN ACRYLAMIDE GELS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:382–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnaughton M. R., Dimmock N. J. Polyadenylic acid sequences in rhinovirus RNA species from infected human diploid cells. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):745–748. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.745-748.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr, Summers D. F. Evidence for differences in size and composition of the poliovirus-specific polypeptides in infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1968 Sep;36(1):48–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak T. W., Colter J. S., Scraba D. G. Structure of the Mengo virion. II. Physicochemical and electron microscopic analysis of degraded virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak T. W., O'Callaghan D. J., Colter J. S. Studies of the pH inactivation of three variants of Mengo encephalomyelitis virus. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel B. Characterization of type 1 poliovirus by electrophoretic analysis. Virology. 1971 Jun;44(3):554–568. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90369-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel B. The relationship between penetration and uncoating of poliovirus in HeLa cells. Virology. 1967 Apr;31(4):702–712. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapoles J. E., Anderegg J. W., Rueckert R. R. Properties of poliovirus propagated in medium containing cesium chloride: implications for picornaviral structure. Virology. 1978 Oct 1;90(1):103–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheka H. D., Bachrach H. L. N-terminal amino acid sequences in the major capsid proteins of foot-and-mouth disease virus types A, O, and C. J Virol. 1975 Nov;16(5):1248–1253. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.5.1248-1253.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor S. Evidence for the existence of protomers in the assembly of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1107–1120. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1107-1120.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor S., Rueckert R. R. Picornaviral capsid assembly: similarity of rhinovirus and enterovirus precursor subunits. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):548–553. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.548-553.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren L. C., Scaletti J. V., James C. G. Isolation and properties of enterovirus receptors. Wistar Inst Symp Monogr. 1968;8:123–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean C., Matthews T. J., Rueckert R. R. Evidence of ambiguous processing and selective degradation in the noncapsid proteins of rhinovirus 1A. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):903–914. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.903-914.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikhejeva A., Yakobson E., Ghendon Y. Z. Studies on temperature-sensitive events in synthesis of poliovirus ts mutants. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;43(4):352–358. doi: 10.1007/BF01556152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser A. G., Caliguiri L. A., Scheid A. S., Tamm I. Chemical and enzymatic characteristics of cytoplasmic membranes of poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1972 Jan;47(1):30–38. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser A. G., Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. Incorporation of lipid precursors into cytoplasmic membranes of poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1972 Jan;47(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90236-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEURATH H. MECHANISM OF ZYMOGEN ACTIVATION. Fed Proc. 1964 Jan-Feb;23:1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair C. N., Lonberg-Holm K. K. Infectivity and sedimentation of rhinovirus ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1971 Feb;7(2):278–280. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.2.278-280.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Kitamura N., Golini F., Wimmer E. The 5'-terminal structures of poliovirion RNA and poliovirus mRNA differ only in the genome-linked protein VPg. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5345–5349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Lee Y. F., Wimmer E. The 5' end of poliovirus mRNA is not capped with m7G(5')ppp(5')Np. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):375–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENMAN S., BECKER Y., DARNELL J. E. A CYTOPLASMIC STRUCTURE INVOLVED IN THE SYNTHESIS AND ASSEMBLY OF POLIOVIRUS COMPONENTS. J Mol Biol. 1964 Apr;8:541–555. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmenberg A. C., Pallansch M. A., Rueckert R. R. Protease required for processing picornaviral coat protein resides in the viral replicase gene. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):770–778. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.770-778.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paucha E., Seehafer J., Colter J. S. Synthesis of viral-specific polypeptides in Mengo virus-infected L cells: evidence for asymmetric translation of the viral genome. Virology. 1974 Oct;61(2):315–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90269-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Leaky UAG termination codon in tobacco mosaic virus RNA. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):469–471. doi: 10.1038/272469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Synthesis and proteolytic processing of cowpea mosaic virus proteins in reticulocyte lysates. Virology. 1979 Jul 30;96(2):463–477. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vitro yields an active proteolytic processing enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):457–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlin M., Phillips B. A. In vitro assembly of polioviruses. 3. Assembly of 14 S particles into empty capsids by poliovirus-infected HeLa cell membranes. Virology. 1973 May;53(1):107–114. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90469-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlin M., Phillips B. A. In vitro assembly of polioviruses. IV. Evidence for the existence of two assembly steps in the formation of empty capsids from 14 S particles. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):505–511. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R. F., Ambros V., Baltimore D. Identification of a protein linked to nascent poliovirus RNA and to the polyuridylic acid of negative-strand RNA. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):357–365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.357-365.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson R. F., Flanegan J. B., Rose J. K., Baltimore D. 5'-Terminal nucleotide sequences of polio virus polyribosomal RNA and virion RNA are identical. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):270–272. doi: 10.1038/268270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A., Fennell R. Polypeptide composition of poliovirions, naturally occurring empty capsids, and 14S precursor particles. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):291–299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.291-299.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A. In vitro assembly of poliovirus. II. Evidence for the self-assembly of 14 S particles into empty capsids. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):307–316. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90262-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A. In vitro assembly of polioviruses. I. Kinetics of the assembly of empty capsids and the role of extracts from infected cells. Virology. 1969 Dec;39(4):811–821. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A., Lundquist R. E., Maizel J. V., Jr Absence of subviral particles and assembly activity in HeLa cells infected with defective-interfering (DI) particles of poliovirus. Virology. 1980 Jan 15;100(1):116–124. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90557-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A., Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr In vitro assembly of poliovirus-related particles. Virology. 1968 Jun;35(2):216–226. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A. The morphogenesis of poliovirus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1972;58:157–174. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65357-5_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. A., Wiemert S. In vitro assembly of poliovirus. V. Evidence that the self-assembly activity of 14 S particles is independent of extract assembly factor(s) and host proteins. Virology. 1978 Jul 1;88(1):92–104. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. G., Fellner P., Black D. N., Rowlands D. J., Harris T. J., Brown F. 3'-Terminal nucleotide sequences in the genome RNA of picornaviruses. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):298–301. doi: 10.1038/276298a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. G., Merregaert J., Van Emmelo J., Fiers W. Sequence of 129 nucleotides at the 3'-terminus of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jul 3;87(3):551–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A., Carey N., Fellner P. Presence of a large poly(rC) tract within the RNA of encephalomyocarditis virus. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):675–678. doi: 10.1038/248675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poyton R. O., McKemmie E. Post-translational processing and transport of the polyprotein precursor to subunits IV to VII of yeast cytochrome c oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6772–6780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROIZMAN B., MAYER M. M., RAPP H. J. Immunochemical studies of poliovirus. III. Further studies on the immunologic and physical properties of poliovirus particles produced in tissue culture. J Immunol. 1958 Nov;81(5):419–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUECKERT R. R. STUDIES ON THE STRUCTURE OF VIRUSES OF THE COLUMBIA SK GROUP. II. THE PROTEIN SUBUNITS OF ME-VIRUS AND OTHER MEMBERS OF THE COLUMBIA SK GROUP. Virology. 1965 Jun;26:345–358. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90282-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radloff R. J. Isolation and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):182–192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.182-192.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rekosh D. M., Lodish H., Baltimore D. Protein synthesis in Escherichia coli extracts programmed by poliovirus RNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):327–340. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90433-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Trachsel H., Leong K., Baltimore D. Inhibition of translation by poliovirus: inactivation of a specific initiation factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2732–2736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenwirth B., Eggers H. J. Early processes of echovirus 12-infection: elution, penetration, and uncoating under the influence of rhodanine. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):241–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg P. G., Harris T. J., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. O4-(5'-uridylyl)tyrosine is the bond between the genome-linked protein and the RNA of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4868–4872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roumiantzeff M., Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr In vitro protein synthetic activity of membrane-bound poliovirus polyribosomes. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90257-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. J., Harris T. J., Brown F. More precise location of the polycytidylic acid tract in foot and mouth disease virus RNA. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):335–343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.335-343.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands D. J., Sangar D. V., Brown F. A comparative chemical and serological study of the full and empty particles of foot-and mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1975 Mar;26(3):227–238. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-26-3-227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
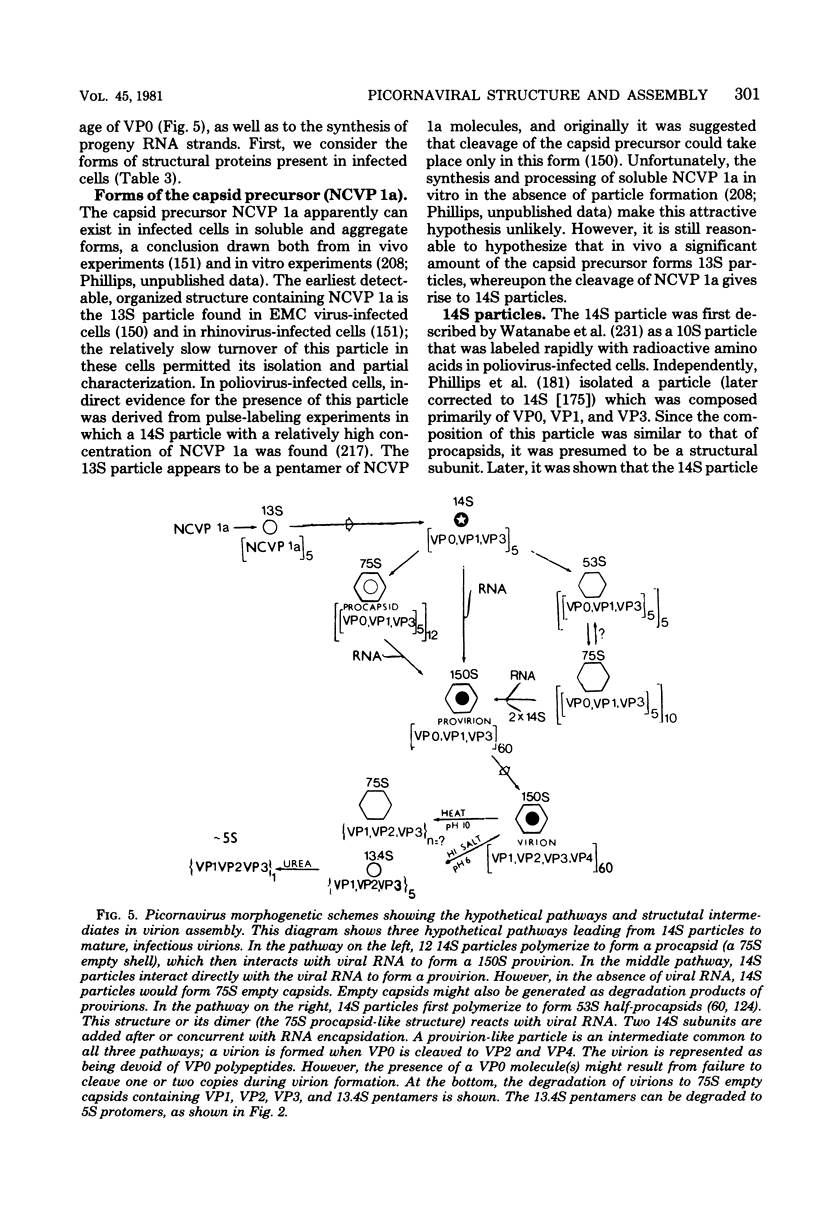
- SCHARFF M. D., MAIZEL J. V., Jr, LEVINTOW L. PHYSICAL AND IMMUNOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF A SOLUBLE PRECURSOR OF THE POLIOVIRUS CAPSID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Feb;51:329–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangar D. V., Rowlands D. J., Harris T. J., Brown F. Protein covalently linked to foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA. Nature. 1977 Aug 18;268(5621):648–650. doi: 10.1038/268648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangar D. V., Rowlands D. J., Smale C. J., Brown F. Reaction of glutaraldehyde with food-and-mouth disease virus. J Gen Virol. 1973 Nov;21(2):399–406. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-21-2-399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangar D. V. The replication of picornaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1979 Oct;45(1):1–13. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki S. G., Jelinek W., Darnell J. E. 3'-Terminal addition to HeLa cell nuclear and cytoplasmic poly (A). J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):219–235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller H. C., Rau T., Bode H. Epithelial cells in nerve-free hydra produce morphogenetic substances. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):589–591. doi: 10.1038/283589a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scraba D. G., Kay C. M., Colter J. S. Physico-chemical studies of three variants of Mengo virus and their constituent ribonucleates. J Mol Biol. 1967 May 28;26(1):67–79. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90261-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafritz D. A., Weinstein J. A., Safer B., Merrick W. C., Weber L. A., Hickey E. D., Baglioni C. Evidence for role of m7G5'-phosphate group in recognition of eukaryotic mRNA by initiation factor IF-M3. Nature. 1976 May 27;261(5558):291–294. doi: 10.1038/261291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. Capping of eucaryotic mRNAs. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Kew O., Pallansch M., Rueckert R., Kaesberg P. Cell-free synthesis and processing of the proteins of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5807–5811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih D. S., Shih C. T., Zimmern D., Rueckert R. R., Kaesberg P. Translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in reticulocyte lysates: kinetic analysis of the formation of virion proteins and a protein required for processing. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):472–480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.472-480.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E. The initiation of protein synthesis directed by the RNA from encephalomyocarditis virus. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Mar 1;33(2):301–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02684.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Morgan M. A., Merrick W. C., Shatkin A. J. A polypeptide in eukaryotic initiation factors that crosslinks specifically to the 5'-terminal cap in mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4843–4847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N., Rupprecht K. M., Hecht S. M., Shatkin A. J. Eukaryotic mRNA cap binding protein: purification by affinity chromatography on sepharose-coupled m7GDP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4345–4349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Polyadenylic acid on poliovirus RNA. II. poly(A) on intracellular RNAs. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1418–1431. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1418-1431.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Requirement of 3'-terminal poly(adenylic acid) for the infectivity of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2983–2987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus C. M., Rueckert R. Capsid polypeptides of mouse Elberfeld virus. I. Amino acid compositions and molar ratios in the virion. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):347–355. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.347-355.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su R. T., Taylor M. W. Morphogenesis of picornaviruses: characterization and assembly of bovine enterovirus subviral particles. J Gen Virol. 1976 Mar;30(3):317–328. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-30-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr Evidence for virus-specific noncapsid proteins in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):505–513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr Determination of the gene sequence of poliovirus with pactamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2852–2856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr Evidence for large precursor proteins in poliovirus synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):966–971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Shaw E. N., Stewart M. L., Maizel J. V., Jr Inhibition of cleavage of large poliovirus-specific precursor proteins in infected HeLa cells by inhibitors of proteolytic enzymes. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):880–884. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.880-884.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMM I., EGGERS H. J. SPECIFIC INHIBITION OF REPLICATION OF ANIMAL VIRUSES. Science. 1963 Oct 4;142(3588):24–33. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3588.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taber R., Rekosh D., Baltimore D. Effect of pactamycin on synthesis of poliovirus proteins: a method for genetic mapping. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):395–401. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.395-401.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S., Steiner D. F. Peptide hormones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):509–538. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.002453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. A., Gibbs A. J., Cooper P. D. A re-examination of the molecular weight of poliovirus RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 23;38(2):298–304. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90712-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd D., Martin S. J. Determination of the molecular weight of bovine enterovirus RNA by nuclease digestion. J Gen Virol. 1975 Jan;26(1):121–129. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-26-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub A., Duskin B., Rosenberg H., Kalmar E. Isolation and properties of the replicase of encephalomyocarditis virus. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):375–382. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.375-382.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Elsen A., Boeyé A., Teuchy H. Formation of fibrillar structures from poliovirus by alkaline disruption and other treatments. Virology. 1968 Nov;36(3):511–514. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90179-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasquez C., Denoya C. D., La Torre J. L., Palma E. L. Structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus capsid. Virology. 1979 Aug;97(1):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90387-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Komaroff L., McDowell M., Baltimore D., Lodish H. F. Translation of reovirus mRNA, poliovirus RNA and bacteriophage Qbeta RNA in cell-free extracts of mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:709–723. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE Y., WATANABE K., HINUMA Y. Synthesis of poliovirus-specific proteins in HeLa cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Dec 31;61:976–977. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Weber K. Natural read-through at the UGA termination signal of Q-beta coat protein cistron. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 15;234(50):206–209. doi: 10.1038/newbio234206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetz K., Habermehl K. O. Topographical studies on poliovirus capsid proteins by chemical modification and cross-linking with bifunctional reagents. J Gen Virol. 1979 Aug;44(2):525–534. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-2-525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegers K. J., Yamaguchi-Koll U., Drzeniek R. A complex between poliovirus RNA and the structural polypeptide VP1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):1308–1312. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90797-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer E. Sequence studies of poliovirus RNA. I. Characterization of the 5'-terminus. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 28;68(3):537–540. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90106-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wouters M., Vandekerckhove J. Amino acid composition of the poliovirus capsid polypeptides isolated as fluorescamine conjugates. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):529–533. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wouters M., Vanden Berghe D., Boeyé A. Composition of poliovirus fibrils. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;43(1):25–33. doi: 10.1007/BF01249345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright P. J., Cooper P. D. Poliovirus proteins associated with the replication complex in infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1976 Jan;30(1):63–71. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-30-1-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Davidson N., Wimmer E. An electron microscope study of the proteins attached to polio virus RNA and its replicative form (RF). Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Dec;5(12):4711–4723. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.12.4711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yafal A. G., Palma E. L. Morphogenesis of foot-and-mouth disease virus. I. Role of procapsids as virion Precursors. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):643–649. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.643-649.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi-Koll U., Wiegers K. J., Drzeniek R. Isolation and characterization of 'dense particles' from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Gen Virol. 1975 Mar;26(3):307–319. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-26-3-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin F. H. Involvement of viral procapsid in the RNA synthesis and maturation of poliovirus. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Poly (A) and poly (U) in poliovirus double stranded RNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 11;242(119):171–174. doi: 10.1038/newbio242171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Polyadenylic acid at the 3'-terminus of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1877–1882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Sequence studies of poliovirus RNA. III. Polyuridylic acid and polyadenylic acid as components of the purified poliovirus replicative intermediate. J Mol Biol. 1975 Mar 5;92(3):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90292-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmern D., Kaesberg P. 3'-terminal nucleotide sequence of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA determined by reverse transcriptase and chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4257–4261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziola B. R., Scraba D. G. Structure of the Mengo virion. IV. Amino- and carboxyl-terminal analyses of the major capsid polypeptides. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziola B. R., Scraba D. G. Structure of the mengo virion. III. Purification and amino acid compositions of the major capsid polypeptides. Virology. 1975 Mar;64(1):228–235. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]