Fig. 8.
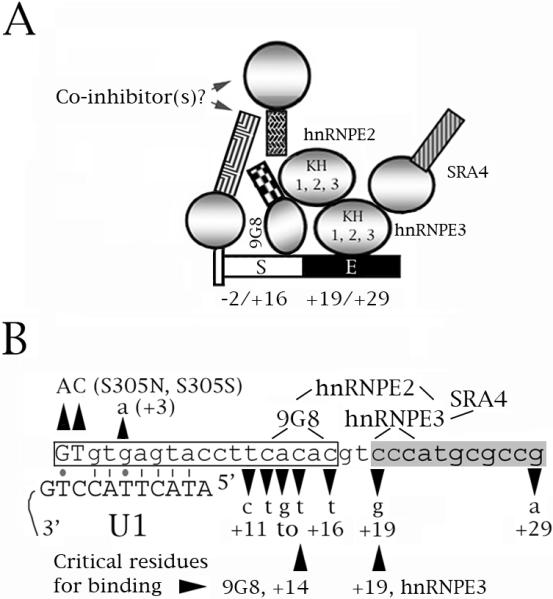
A speculative model of the role of hnRNPE3 in the regulation of tau exon 10 splicing. The model comes from this study, Broderick et al. (2004) and Gao et al. (2007). (A, B) Diagrams of the proximal downstream intron of exon 10. The numbers below the sequence correspond to the residue number within the exon (− numbers) and the intron (+ numbers). 9G8 inhibits exon 10 splicing whereas hnRNPE2, hnRNPE3 and SRA4 activate it. 9G8 and hnRNPE3 bind to the tau pre-mRNA at sites around residues +14 and +19, respectively. hnRNPE2 interacts with 9G8 and hnRNPE3, hnRNPE3 interacts with SRA4. (A) The end of the exon is shown as a narrow tall rectangle, the intron as a narrower rectangle. S=intronic splicing silencer (white), E=intronic splicing enhancer (black). For the factors, circles represent RRM or KH domains, squares represent RS domains. (B) The boxed region is the intronic silencer, the shaded region the intronic enhancer. The exon is shown in uppercase, the intron in lowercase letters. The FTDP mutations are indicated. The lines show which factors interact and the regions of the tau pre-mRNA that interact with 9G8 and hnRNPE3. The two residues critical for binding of 9G8 (+14) and hnRNPE3 (+19) are indicated. Also shown is the base paring of the exon 10 5' splice site with the U1 snRNA. Lines are Crick-Watson pairs, dots G-T base pairs.
