Abstract
Background
Alcohol use is frequently implicated as a factor in nonadherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). There have not been efforts to systematically evaluate findings across studies. This meta-analysis provides a quantitative evaluation of the alcohol-adherence association by aggregating findings across studies and examining potential moderators.
Methods
Literature searches identified 40 qualifying studies totaling over 25,000 participants. Studies were coded on several methodological variables.
Results
In the combined analysis, alcohol drinkers were approximately 50–60% as likely to be classified as adherent [OR = 0.548, 95% CI: 0.490–0.612] compared to abstainers (or those who drank relatively less). Effect sizes for problem drinking, defined as meeting the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) criteria for at-risk drinking or criteria for an alcohol use disorder, were greater [OR = 0.474, 95% CI = 0.408–0.550] than those reflecting any or global drinking [OR = 0.604, 95% CI = 0.531–0.687]. Several variables moderated the alcohol-adherence association.
Conclusions
Results support a significant and reliable association of alcohol use and medication nonadherence. Methodological variables appear to moderate this association and could contribute to inconsistencies across studies. Future research would benefit from efforts to characterize theoretical mechanisms as well as mediators and moderators of the alcohol-adherence association.
Keywords: alcohol, antiretroviral therapy, HIV/AIDS, medication adherence, meta-analysis, review
Introduction
Since its widespread introduction in 1996, highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) has led to marked improvements in immunologic and virologic outcomes, quality of life and longevity among individuals living with HIV.1,2 However, the optimal benefits of HAART are closely tied to adherence.3 The implications of nonadherence for disease progression are well documented and include adverse consequences for the individual as well as public health.4–6 Improving the ability to identify and remediate barriers to HAART adherence is therefore a clear priority of behavioral HIV/AIDS research. 7
Among the most frequently studied correlates of HAART nonadherence is substance use.8 Historically, most attention has focused on injection drug use (IDU),9–11 but studies focusing on alcohol have been emerging with increasing frequency. A focus on drinking behavior in the context of HAART is warranted for several reasons. Alcohol use is prevalent among HIV-positive individuals; 10, 12–14 is cited by patients as a reason for nonadherence; 15–18 and is associated with nonadherence in numerous studies. Evidence also suggests a deleterious influence of alcohol use on markers of immunological functioning and viral suppression, 9,19–22 effects that could be partly mediated by nonadherence.9 Given these findings and the fact that alcohol use is a modifiable behavior, interventions targeting alcohol use among those living with HIV/AIDS have the potential to improve disease management and perhaps to delay disease progression. 16,18,22,23
Although alcohol use has been associated with HAART nonadherence in numerous studies, the nature, strength and consistency of this association remain unclear. A number of null findings have been reported, leading to a somewhat equivocal literature.8,24 Additionally, the question of whether adherence is progressively compromised as drinking levels increase (i.e., a “dose-response” effect) has not been systematically evaluated, in part due to the use of dichotomous drinking variables in most studies. Of the few studies to examine multiple levels of alcohol use, some have found a positive and linear relationship between drinking and medication nonadherence 9,25,26 whereas others have found similar adherence rates across moderate and high drinking levels.14, 22, 27 Finally, some evidence suggests that the relation of alcohol use and nonadherence could be moderated by demographic or methodological variables, including gender 28,29 and how adherence is defined.16,30–32 There have not been systematic efforts to evaluate hypothesized moderators of the alcohol-adherence association.
There are several potential explanations for heterogeneous findings across studies, including insufficient power in smaller studies and variable methodological and measurement approaches across investigations. 24 Discrepant findings could also reflect the influence of moderating variables that have yet to be systematically evaluated. It is also noteworthy that existing studies are largely based on retrospective survey data 33 and have often used alcohol and adherence measures that were not temporally concurrent. These methodological features are significant barriers to inferring causal associations 34 and leave open the possibility that some reported findings reflect the influence of third variables.16 In sum, a detrimental influence of alcohol use on HAART adherence, though plausible and supported by some empirical data, has yet to be clearly, convincingly or reliably characterized. A causal effect of alcohol consumption on HAART adherence could be better substantiated if this relationship proved consistent and robust across studies, especially given the varied methods reported in the literature.
The current study provides a meta-analytic review of published studies examining the association of alcohol use and antiretroviral adherence. Meta-analytic techniques are well suited for maximizing statistical power by aggregating effect sizes across studies and allowing examination of effect moderators at the aggregate level. This study had the following specific aims: (1) to provide a descriptive account of studies examining alcohol-adherence associations; (2) to provide quantitative estimates of the magnitude and stability of alcohol-adherence associations across studies; (3) to provide an aggregate evaluation of “dose-response” effects by examining effect sizes across objectively defined categories of consumption; and (4) to evaluate methodological and demographic variables as moderators of the alcohol-adherence association.
Method
Study selection
We aimed to identify published, peer-reviewed studies that reported on the association of alcohol consumption and HAART nonadherence. Both electronic and manual literature searches were conducted to identify candidate studies published from 1996 through the end of 2007. Searches of electronic databases (MEDLINE, PubMed, PsycInfo) were conducted by crossing terms related to HIV (HIV; human immunodeficiency virus; AIDS; acquired immunodeficiency syndrome), antiretroviral therapy (HAART; highly active antiretroviral therapy; antiretroviral therapy; ARV; ART; combination therapy; HIV treatment), medication adherence (i.e., adherence, nonadherence, compliance, noncompliance), and alcohol (i.e., alcohol, drinking, substance use, drug use, AOD). All resulting abstracts were screened. Candidate studies were defined as those that reported results from a data-based study and indicated that adherence and alcohol or substance use were assessed.
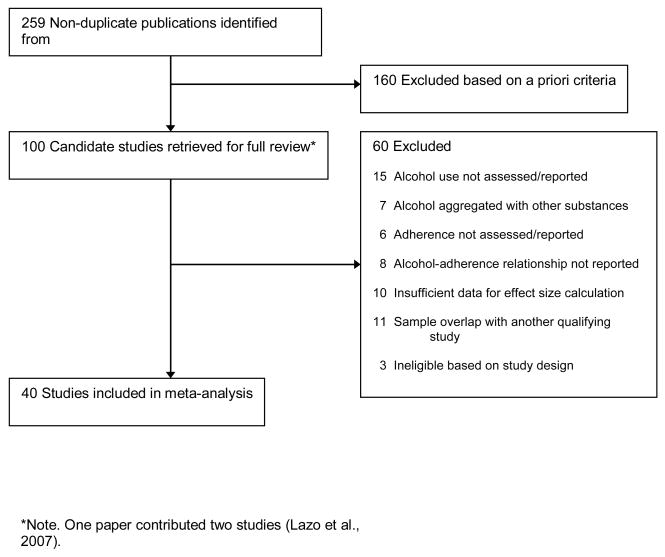
Results of the study selection process are depicted in Figure 1. All candidate studies were retrieved for full review and studies were retained for inclusion in the meta-analysis if they met the following criteria: (a) a measure of antiretroviral adherence was included in the study; (b) a measure of participants’ alcohol use was included; (c) reported a quantitative test of the association of alcohol use and adherence; (d) provided sufficient statistical information for deriving an effect size; and (e) reported on a sample that did not overlap with that of another qualifying study. Studies that combined measures of alcohol with other substance use, or that combined measures of antiretroviral adherence with other medication adherence, were not considered for inclusion. In cases where two or more studies had overlapping samples only one study was retained; we used sample size and specificity of drinking measures as the primary criteria for choosing among them. After arriving at an initial list of qualifying studies we implemented two manual search strategies, which consisted of reviewing references cited in each of the qualifying studies (as defined above) and consulting review papers on correlates of antireteroviral adherence to identify additional candidate studies. Forty published studies were retained for the meta-analysis (denoted with asterisks in the references section).
Figure 1.
Results of study selection process.
Data abstraction and coding
All studies were coded on attributes within three categories: descriptive characteristics, characteristics of adherence measurement, and characteristics of alcohol use measurement. Descriptive characteristics included study location and year; gender composition; study aim (defined as whether alcohol/substance use was assessed as a primary or ancillary aim of the study); and sample size for the alcohol-adherence analysis. In cases where the number of participants for the alcohol-adherence analysis was smaller than that of the overall sample, sample size was coded based on the former. Studies from the U.S. were coded on racial composition of the sample using the two most commonly reported demographic groups (i.e., % African American and % White). Non-U.S. studies typically lacked data on race/ethnicity. Given the association of IDU with HAART adherence we also estimated the proportion of each sample that reported IDU using available indicators; these varied across studies (e.g., past-month IDU; lifetime IDU; IDU as the mode of HIV transmission).
For adherence measurement, studies were coded based on the assessment method (self-report, MEMS, etc.) and the length of time over which adherence was recalled or otherwise measured (e.g., 3 days, 7 days, etc.). Studies also were coded based on whether adherence was analyzed as a continuous (e.g., % adherence) or dichotomous (e.g., adherent vs. non-adherent) outcome. For dichotomous outcomes, criterion cutoffs for adherence (e.g., 95%) were recorded. With regard to alcohol use, studies were coded on the length of the alcohol use assessment period and whether the authors reported use of a previously validated measure to assess alcohol use or alcohol use disorders. The most frequently reported instruments/methods used to infer alcohol use disorders were the CAGE35 (4 studies), the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT)36 (4 studies), and DSM-IV criteria (2 studies). Each effect size was coded based on the type of drinking examined in relation to adherence. Specifically, effect sizes were categorized as assessing (a) drinking frequency (e.g., days per week); (b) drinking quantity (e.g., drinks per drinking day); (c) drinking frequency and quantity (e.g., 3+ drinks at least twice a week).
Our aim to examine a possible “dose response” effect of alcohol on adherence was complicated by the fact that the majority of studies used dichotomous drinking categories with highly variable cutoffs and/or definitions. Therefore, we created an objective index of drinking severity that was standardized across studies. Each effect size was coded on a variable reflecting drinking intensity, which included three levels— problem drinking, moderate drinking, and any or global drinking. A three-level variable was a chosen to allow evaluation of possible “dose-response” effects while retaining enough effect sizes per category for meaningful comparisons.
An effect size was coded as assessing problem drinking if it was derived from a dichotomous measure of alcohol use with a threshold that (a) met or exceeded the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) definition of at-risk drinking, using the threshold for men (> 14 drinks per week or > 4 drinks in a day)37, or (b) met criteria for a probable alcohol use disorder based on diagnostic or screening criteria. For instance, a study that categorized participants based on whether they drank at least five drinks per drinking occasion, consumed at least 20 drinks per week, had a CAGE score of 2+ or an AUDIT score of 8+ would contribute an effect size to the problem drinking category. Effect sizes were coded as assessing moderate drinking when based on a dichotomous outcome with a clearly defined threshold that reflected moderate drinking levels that did not exceed NIAAA criteria for at-risk drinking. For example, studies that categorized participants on whether they drank at least 2 times per week or at least 10 drinks per month were assigned to this category because these levels fall below NIAAA-defined at-risk drinking. Effect sizes were coded as any or global drinking if they (a) used categories that were exceedingly broad (e.g., any alcohol use in the past month vs. none), (b) used a single, continuous drinking measure of drinking (e.g., drinking days in the past two months), or (c) used indicators that were so vague as to preclude clear assignment to another category. A separate category for heavy episodic (“binge”) drinking (e.g., 5+ drinks on one occasion) was not included because few studies reported this outcome and because our problem drinking category encompassed this definition.
Some studies had more than one effect size because they compared more than two drinking patterns/categories. In these instances, we selected the effect size that represented the most extreme comparison between drinking levels for the primary analysis in order to avoid violating the independence of effect sizes. However, we also conducted separate analyses that included (a) the least extreme comparison per study and (b) an average effect size for those studies with multiple effect sizes (described below).
Studies were also coded based on whether the reported alcohol-adherence association was determined using unadjusted or adjusted odds ratios because these relations could differ after controlling for other variables. Finally, studies were coded based on the degree of temporal overlap among the alcohol use and adherence measurements (i.e., the degree to which these variables were assessed over the same time interval). This variable was included because temporal contiguity between the predictor and outcome variable has important implications for inferring causal relationships and could influence the pattern of effect sizes across studies. Temporal overlap was coded from 0–3. A score of 0 indicated that the alcohol and adherence measures had no overlap (or it was impossible to determine overlap based on the study description). A code of 1 indicated some but minimal overlap among assessment intervals. A code of 2 was used if there was evidence that the measures overlapped at least partially, and a code of 3 indicated that the assessment intervals were identical or almost identical.
Descriptive information
The 40 studies included in the meta-analysis spanned a 10-year period (1998–2007) and totaled over 25,000 participants. Most studies (33) were conducted in the U.S.; other locations were France (3), Canada (1), Brazil (1), India (1) and Italy (1). Examining alcohol/substance use was identified as a primary study aim in 9 studies. Typically, alcohol use was one of several demographic or behavioral variables that were assessed and was not a major focus of the report. Twenty-one studies were derived from prospective cohort investigations, 16 from cross-sectional studies and 3 from clinical trials. Of 24 studies derived from prospective designs (prospective cohort or clinical trial), 9 used prospective data to test the alcohol-adherence association. Table 1 presents descriptive information and results of the alcohol-adherence analysis for each study.
Table 1.
Study characteristics and findings
| Source Author Date |
Sample Location Setting Sample size % Male % MSM % AA % LAT % WH |
Study Design Inclusion Criteria |
Medication Adherence Definition Measure/Timeframe Used in Analyses Adherence Rate for Sample |
Alcohol Use Definition Measure/Timeframe Used in Analyses Prevalence in Sample |
Adherence × Alcohol Rates Primary Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Berg et al. 2004 | Bronx, NY, USA Methadone maintenance program N= 113 57% Male 22% AA 66% LAT 12% WH |
Prospective cohort Previous participation in HIV Epidemiologic Research on Outcomes (HERO) study, currently prescribed HAART, willing to use EDM |
Measured as continuous variable EDM measured at 6 research visits at 4-week intervals (#openings/prescribed doses) Median adherence rate 62% |
Alcohol use while in the study Number of drinks and frequency of drinking 6 month timeframe of the study “Problem alcohol use” defined as 1+ of the following: (a) more than 5 drinks on one occasion, or (b) drinking “everyday” or “several days per week” at any time during the study 30% problem alcohol use |
Bivariate: participants reporting problem alcohol use had a median adherence 29% lower than those without problem alcohol use; non-significant trend (40 vs 69%, p<.07). Problem alcohol use was not associated with adherence for men. Women endorsing problem alcohol use reported significantly lower median adherence (25 vs. 57%, p=.003) |
| Bonolo et al. 2005 | Belo Horizonte, Brazil Public AIDS referral centers N = 306 65% Male 22% endorsed male-male sex as transmission route 74% African descent 26% WH |
Prospective cohort Patients initiating ART: ART naive, 18+ years, signed written informed consent, had their antiretroviral drugs dispensed in one of the centers |
>95% of prescribed doses taken Number of prescribed doses for the 3 days prior to each follow-up visit Self-report via interview. Follow-up visits at 1st, 4th, and 7th month after initiating HAART 63% adherent |
Any alcohol use in the month prior to the baseline interview Self-report of use lifetime and past month 38% past month 89% lifetime |
Bivariate: significant effect of alcohol on adherence for the full sample (p=.018). Multivariate: alcohol use in the month preceding baseline was associated with non-adherence (hazard ratio 2.27, CI 1.58–3.25, p<.001). |
| Catz et al. 2001 | Baltimore MD, & Milwaukee, WI, USA AIDS Service Organizations N = 113 (total) N=84 (on HAART) 75% Male 51% gay, 13% bi 36% AA 7% LAT 48% WH |
Cross-sectional Late middle-aged & older adults: 45+ years old, HIV+ |
No skipped or late doses Self-report via questionnaire (likert- scale) past 7 days 69% adherent |
Number of days alcohol was used Self-report via questionnaire in past two months (60 days) N/R alcohol rate |
Bivariate: Older adults who adhered more consistently to HIV treatment regimens used alcohol less frequently (r= −.27, p< .01) Multivariate: significant for full sample, fewer drinking days in past 60 days predicted more consistent treatment adherence (OR=.88, CI .79–.98, p=.03). |
| Chander et al. 2006 | Baltimore, MD, USA University-based HIV Clinic N= 1957 (subsample on HAART) 64% Male 24% MSM 81% AA 19% WH/Other |
Prospective cohort On HAART, attending clinic |
< 2 Missed Doses (dichotomous) Self-report via survey Past two weeks N/R adherent |
NIAAA-defined hazardous drinking, based on mean quantity and frequency per week in previous 6-months Self-report via interview Assessed in approx 6- month intervals 46% use alcohol 35% moderate (any use below NIAAA definiton) 11% hazardous (meeting NIAAA definition) |
Bivariate: both moderate (OR .78, CI .63–.92) and hazardous (OR .43, CI .32–.57) drinkers were less likely to be adherent than nondrinkers Multivariate: hazardous drinkers (adj OR .46, CI .57–.99) and moderate drinkers (adj OR .78, CI .64–.95) were less likely to be adherent than nondrinkers |
| Cook et al. 2001 | Pennsylvania, USA 1 University-based HIV clinic 1 Community-based HIV clinic N=219 72% Men 48% gay/bisexual 24% AA 15% LAT 58% WH |
Cross-sectional HIV+ pts who attended clinic during study enrollment period |
No doses missed in previous 24 hours and no doses taken off schedule in past 7 days Self-report via questionnaire (likert- scale) 86% adherent (24 hours) 70% adherent (7 day) |
Drinking patterns examined: Binge [5+ (women) or 6+ (men) drinks in one sitting at least monthly]; Heavy (12+ (women) or 16+ (men) drinks/week in past month; Hazardous: AUDIT of 8+ AUDIT (past year) and 2 Q/F questions (past month) 52% alcohol use in past year 19% problem drinking (hazardous, heavy, or binge) 33% mild-moderate drinking (do not meet criteria for problem use) |
Bivariate: No significant associations found between any category of problem drinking and missed doses. Multivariate: Problem drinkers (hazardous, heavy or binge drinking) were more likely to have taken a dose off schedule in the past 7 days (adj OR 2.64, CI 1.07–6.53, & adj OR 4.70, CI 1.49–14.84, respectively). No association of alcohol with missed dose in past 24 hours. |
| De Jong et al. 2005 | California, USA Public Health Clinics N=168 75% Men 30% AA 29% LAT 35% WH |
Cross-Sectional N/R explicitly; pts on HAART attending clinics |
No missed doses in past 7 days Self-report via questionnaire 66% adherent |
Use in past month (yes/no) Self-report via questionnaire, past month 47% use in past month 14% heavy drinkers (not defined) |
Statistically significant for the sample. 58% of adherent and 42% of non-adherent pts used alcohol in past month (crude OR .51, CI .27–.98, p=.045). |
| Eldred et al. 1998 | Baltimore, MD, USA HIV Outpatient Clinic N=244 63.1% Men 19.7% MSM 85.2% AA 14.8% WH |
Cross-sectional 18+ years, enrolled in state medical assistance, at least one clinic visit in past 6 months, prescription of ART for at least 6 months |
Percent of prescribed pills taken in past week and percent of days in which at least one dose was taken in past two weeks (>80% doses taken = adherent) Self-report via structured interview and medical record review of # pills prescribed Self-Report 60% adherent (dose) 74% medication days |
Frequency and quantity of alcohol consumption Self-report via interview (timeframe N/R) N/R alcohol rate |
Adherence and alcohol were not associated in bivariate analyses. The sample was queried about reasons for missing doses, and 16% of the sample endorsed “alcohol or drug use” as the primary reason. |
| Golin et al. 2002 | USA Public hospital HIV clinic N=117 80% Men N/R MSM 27% AA 47% LAT 16% WH |
Prospective Cohort Speak English or Spanish, initiating ART medication (PI or NNRTI) |
Percent of prescribed doses taken in past four weeks (continuous measure) Composite score: EDM data, pill counts, & self- report (every 4 weeks) Summed over 48 weeks 71% adherent 4% classified as >95% adherent |
Any use in past 30 days (yes/no) 37% alcohol use |
Bivariate: alcohol use and adherence significantly associated for full sample (p=.008). Multivariate: alcohol use is a significant predictor of non-adherence; non-drinkers report 75% of doses taken compared to 66% for drinkers (p<.01). |
| Heckman et al. 2004 | Multiple rural sites in 12 states, USA N=329 N=272 (on HAART) 72% Men 74% gay/bisexual 18% AA 3% LAT 74% WH |
Baseline data from RCT of phone delivered intervention HIV+, 18+ years, living in rural location, accessing health or social services from participating agencies |
No missed doses in past week Self-report via questionnaire (1 item, Likert-type scale) 50% adherent |
Number of drinking days in past 2 months Self-report via questionnaire Mean 7.7 drinking days in past two months |
Bivariate: non-significant trend. Adherent pts reported avg of 6.2 drinking days in past 2 months; non-adherent reported 9.1 (OR .64, CI .39–1.03, p=.07). |
| Hicks et al. 2007 | Multiple Sites, USA HIVRN Cohort N=659 70% Men 36% MSM 3% MSM/IDU 51% AA 14% LAT 31% WH |
Cross-sectional N/R explicitly; HIV+, in care |
>95% adherence to all medications in past 2 weeks ACTG; number of missed doses in past 2 weeks for each drug prescribed 67% adherent |
Used NIAAA criteria; quantity and freq of drinking Self-report via questionnaire Past 4 weeks 58% - no drinking 31% - social drinking (any consumption other than hazardous/binge) 11% - hazardous (7+ drinks/wk for women; 14 drinks/wk for men) or binge (5+ drinks per occasion) |
Bivariate: no association between social drinking and adherence. Significant effect of hazardous/binge drinking on adherence (OR .45, CI .26–.76). |
| Hinkin et al. 2004 | Los Angeles, CA, USA Community agencies/ Medical Centers N=148 83% Men 70% AA 9% LAT 17% WH |
Cross-sectional HIV+ adults |
>95% of prescribed doses EDM data Past four weeks 81% adherent |
DSM-IV alcohol abuse/dependence criteria SCID-Substance Use Module N/R alcohol rate |
Bivariate: 77% of pts with DSM-IV AUD were non- adherers; approximately 65% without AUD were non-adherers (ns). |
| Holmes et al. 2007 | Pennsylvania, USA University-affiliated HIV Clinics N=116 81% Men 43% MSM 66% AA N/R LAT N/R WH |
Prospective Cohort 18+, VL less than 75, on 2 or 3 ARVs |
>95% of doses taken EDM data (modified with diaries kept to record erroneous openings, etc.) 3 months prior to participant completion 52% adherent |
Any use in past year Measure N/R 58% alcohol use in past year |
Bivariate: association between alcohol use and adherence was statistically significant for full sample. More high- than low-adherence pts reported no current alcohol use (53 vs. 30%; p<0.01). |
| Holstad et al. 2006 | Georgia, USA 2 urban HIV clinics N=120 65% Men 46% gay, 12% bi 66% AA 3% LAT 27% WH |
Cross-sectional Speak English, on HAART for at least one month |
% of doses taken (continuous) Self-report via AGAS scale (5 items, Likert- scale) Past month Mean 83% adherent 43% perfect adherence |
No use, past use, weekly use, occasional use Measure N/R Dichotomized into current vs. no current use 44% no use 7% past use 44% occasional use 5% weekly use |
Multivariate: Current alcohol users had slightly lower mean adherence scores (81%) than non- current drinkers (85%) but this difference was a non-significant trend (stdzd B = −.177, p=.065). |
| Howard et al. 2002 | Multiple Sites, USA Multi-center cohort study N=161 0& Men 69% AA 14% LAT 16% WH |
Prospective cohort Already participating in AGR/HER study, taking 2+ HAART meds |
% of doses taken EDM data (# openings/# doses prescribed) modified by interview data about errors Monthly rates over 6 months 64% adherent, month 1 45% adherent, month 6 |
One day or more per week versus no use during study period Self-report measure, 6 months prior to enrollment 17% 1+ drinking day/week (baseline) 25% 1+ drinking day/week (6 months) |
Bivariate: significant effect of alcohol use on adherence for women only. Women who reported 1+ drinking days per week had a lower mean adherence rate (43%) compared to women who drank less frequently (56%; p=.02). Multivariate: 1+ drinking days/week was a significant predictor of lower adherence (p=.04) |
| Johnson et al. 2003 | Multiple Sites, USA Multi-center study (Healthy Living Project) N=2765 74% Men 43% gay, 12% bi 49% AA 18% LAT 26% WH |
Cross-sectional 18+, provided informed consent, documented HIV+, no severe neuropsych impairments, not involved in another behavioral HIV intervention |
>90% prescribed doses Self-report via computer assisted interview (#doses skipped) Past 3 days 68% adherent |
Use in past three months (none, less than daily, daily) Measure N/R N/R alcohol rate |
Bivariate: significant alcohol effects on adherence (X2 = 17.49, p<.001) by frequency of use category; no use, 71% adherent; less than daily, 69% adherent; daily, 43% adherent. Multivariate: not significant. Significant factors in the multivariate model examining contextual factors include black/African American ethnicity, being in a primary relationship, history of homelessness or living in a housing shelter, history of IV drug use, and current crack cocaine use. |
| Kalichman & Rompa 2003 | Georgia, USA HIV treatment/social services N=255 (analytic sample) 70% Men 53% gay, 11% bi 71% AA N/R LAT 24% WH |
Cross-sectional HIV+, on HAART |
No missed doses Self-report of missed doses Past 7 days 56% adherent |
Use in past three months (yes/no) Measure N/R 46% used alcohol in the past 3 months |
Bivariate: results not significant. Alcohol use in past 3 months did not differ for adherers (43%) vs. non- adherers (54%). |
| Kleeberger et al. 2001 | Multiple Sites, USA MACS, multi-center AIDS cohort study N=539 100% Men 100% MSM 84%WH |
Prospective cohort MACS pts with adherence data from visit 30 |
100% of doses taken Self-report measure adapted from ACTG survey (# missed doses/# prescribed) Past four days 78% adherent |
>14 vs. ≤ 14 drinks per week Measure N/R N/R alcohol rate |
Bivariate: no significant effect of alcohol on adherence for more vs. less drinking groups (70 vs. 79% adherence rates). |
| Lazo et al. 2007 | Multiple sites, USA MACS (Men) N= 640 WIHS (Women) N=1304 MACS/Men 100% MSM 19% AA 7% LAT 73% WH WIHS/Women 52% AA 30% LAT 15% WH |
Prospective cohort On HAART for whom adherence data were available |
100% of doses taken Self-report/ACTG 4 days (men); 3 days (women). Reported outcome as change in adherence over time (increasing vs. decreasing). N/R adherent (men) 77% adherent (women) |
Quantity and frequency of alcohol use, grouped into: Low: 0–2/day (men); 0–1/day (women) Moderate/Heavy: 3–4 at least 3 times a month; or >5 less than once a month (men & women) Binge: >5 at least once per month (men); >4 at least once per month (women) Past 6 months Measure N/R Men: 55% low, 15% heavy, 7% binge Women: 28% low, 8% heavy, 4% binge |
Bivariate: any drinking was positively and significantly related to decreasing adherence over time for women only: Binge – OR 1.75, CI 1,17–2.64 Mod/Heavy – OR 1.47, CI 1.08–1.99 Low – OR 1.28, CI 1.05–1.54 Drinking was negatively related to increasing adherence over time for women only: Binge – OR .38, CI .21–.72 Low – OR .74, CI .57–.97 Multivariate: drinking was a significant predictor of decreasing adherence over time for women only: Binge – OR 1.81, CI 1.20–2.72 Mod/Heavy – OR 1.52, CI 1.11–2.07 Low – OR 1.29, CI 1.06–1.57 As well as to increasing adherence over time for women only: Binge – OR .41, CI .21–.78 Low – OR .73, CI .57–.95 For women, a dose-response associated was found. Low-to-moderate, moderate-to-heavy, and binge drinking associated with 29%, 52%, and 81% higher odds of decreasing adherence over time, respectively. Alcohol was not associated with adherence among men. |
| Liu et al. 2006 | Los Angeles, CA, USA Community-based clinics, county hospitals, ethnic- and AIDS-specific organizations N=148 0% Men 54% AA 40% LAT 6% WH |
Cross-sectional (baseline data from an intervention study) HIV+, history of CSA |
>90% of doses taken / 100% doses taken Self report via questionnaire Past 1, 2, 3, and 14 days from baseline 91% adherent, past day 91% adherent, past 2 days 93% adherent, past 3 days 88% adherent, past 14 days |
Problem drinking = AUDIT score ≥ 8 Self report via AUDIT (past year); current drinking (past 4 weeks) 7% met criteria for problem drinking AUDIT mean 2.3 (SD 5.5) |
Current drug use, problem drinking, and current alcohol use were not significantly associated with adherence. |
| Martini et al. 2004 | Italy Multi-center study N=214 | Cross-sectional case control 18+, on HAART |
No errors in adherence behavior: errors include missed doses, off- schedule dose, not following special instructions, etc. <2 errors (high adh) 3–4 errors (med adh) ≥ 5 errors (low adh) N/R adherent |
Greater than 6 units (~4 standard drinks) per day Measure N/R 9% report alcohol use of 6+U/day |
No significant effects of alcohol use on adherence. |
| Moatti et al. 2000 | France MANIF study Hospital Clinics N=164 68% Male |
Prospective cohort Pts enrolled in MANIF cohort: 18+, CDC 300+, no opportunistic infections, HIV- infected through IV drug use |
>80% of total prescribed HAART doses Self-report via nurse interview (# pills taken/# prescribed) Past 7 days 65% adherent |
Mean number of glasses per month. Reported that one glass was equivalent to 2 units (~1–2 standard drinks) Measure N/R Past 6 months N/R alcohol rate |
Multivariate: alcohol use was a significant predictor of nonadherence. The non-adherent group reported drinking more drinks/month on average (56) compared to the adherent group (33), adj OR 1.20, CI 1.04–1.41. |
| Mohammed et al. 2004 | Louisiana, USA Rural HIV clinics N=273 71% Male 60% AA |
Cross-sectional 18+, rural residence | No missed doses Self-report via interview Past 7 days 66% adherent |
Problem drinking, past month: 2+/4 items on CAGE or binge drinking (5+ drinks per sitting) Self-report via interview Past month 13% problem drinking 13% binge drinking |
Bivariate: significant effect of problem drinking on adherence (OR 2.60, CI 1.13–2.60, p=.02). Adherent pts reported significantly lower rates of problem drinking (9% binge, 6% CAGE+) vs. non-adherent pts (19% binge, 23% CAGE+). In problem drinkers, mean adherence was 37% vs. 70% in non-problem drinkers. |
| Moss et al. 2004 | San Francisco, CA, USA Homeless services N=102 (analytic sample who remained on HAART during the study) 86% Male 55% MSM 38% AA 5% LAT 44% WH (demographics of N=56 pts who remained on HAART) |
Prospective cohort Homeless or marginally housed, HIV+ |
Percentage of pills taken out of total pills prescribed (continuous) 3 methods: unannounced pill count at home visits, self-report, EDM Mean adherence rates (pill count) across visits: Full sample: 67% Continued HAART: 74% Discontinued HAART: 51% |
Consuming 5+ drinks a day (yes/no) Self-report Timeframe N/R 13% full sample 11% of those continuing HAART |
Bivariate: alcohol use did not predict discontinuation of HAART, nor was there a significant association between alcohol use and adherence rates (drinkers vs. nondrinkers, 71 vs. 74% adherent). |
| Mugavero et al. 2007 | Multiple sites, USA CHASE cohort N=474 71% Male 35% MSM 33% WH |
Prospective cohort Participation in larger study, on HAART |
No missed doses Self-report based on ACTG Past 7 days 76% adherent |
ASI composite alcohol score Self-report via interview Past 30 days N/R alcohol rate |
Bivariate: 10-point increase in ASI alcohol score was significantly associated with non-adherence (OR 1.71, CI 1.18–2.45, p<.01). Multivariate: 10-point increase in ASI alcohol score was an predictor of non-adherence (OR 1.57, CI 1.06–2.32, p=.02). |
| Murphy et al. 2002 | California, USA PACT study cohort N=46 0% Male 0% MSM 59% AA 24% LAT 7% WH |
Prospective cohort Female PACT participants on HAART |
>95% of doses taken on schedule 4 outcomes: 3 self-report via questionnaire (3- and 7-day dose adherence, 3- day schedule adherence) and a 4-week pill count Past 3 & 7 days, past 4 weeks Dose: 56% 3-day, 50% 7- day Schedule: 50% 3-day \ Pill count: 43% |
Any alcohol use Self report via the NIDA Risk Behavior Assessment (quantity/freq, past 3 months) 50% alcohol use in past month |
Bivariate: significant effect of alcohol use on schedule (but not dose) adherence (OR .20, CI N/R, p<.05). |
| Murphy et al. 2004 | Los Angeles, CA, USA HIV clinic N=115 85% Male 52% MSM 50% AA 20% LAT 24% WH |
Cross-sectional 18+, on HAART, non-adherent to regimen, CD4 >100, no opportunistic infections/past month, no active psychiatric condition, no participation in another clinical or adherence study |
No missed doses Self-report via modified ACTG questionnaires (on CASI) 3 day, 7 day, past month 3-day, 58% adherent 7 day, 35% adherent Past month, 26% adherent |
Frequency of recent drinking (ordinal) Self-report via CASI Past three months Measure N/R 37% no use 19% weekly use 4% daily use |
Multivariate: more frequent alcohol use associated with non-adherence in the past month (OR .51, CI .33–.79). |
| Murphy et al. 2005 | Multiple Sites, USA REACH study pts N=231 27% Men 75% AA 11% LAT 14% WH |
Prospective cohort Adolescents on HAART |
Reported taking meds “most of the time” or “all of the time” Self-report via interview Past month, preceding weekday, preceding Saturday 70% adherent, past month 69% adherent, preceding weekend 63% adherent, preceding Saturday |
Intensity of alcohol use (past 3 months) Problem alcohol use (ever) CAGE (2+ items = problem drinking) Self-report via questionnaire 5-point Likert scale assessing frequency in past 3 months N/R alcohol rate |
Bivariate: higher intensity of alcohol use was significantly associated with lower adherence rates for adherence on the preceding Saturday (adj OR .67, CI .55–.82, p<.05) and in the past month (adj OR .80, CI .66–.98, p<.05). Both associations remained significant in multivariate analyses. Other alcohol variables were not associated with adherence outcomes. |
| Parsons et al. 2007b | New York, USA HIV clinics N = 272 (N=154 with adherence data) 78% Men 48% gay, 12% bi 58.% AA 25% LAT 11% WH |
Randomized controlled intervention trial HIV+ problem drinkers: 18+, score of 8+ on AUDIT, currently on HAART |
>95% doses taken % Adherence among those without perfect adherence (continuous) Self-report via TLFB 14 days 43% adherent |
Composite alcohol factor comprising three measures of alcohol use/problems: AUDIT (30-day timeframe) DrinC (90 days) TLFB (30 days) N/R alcohol rate |
Multivariate: the alcohol factor significantly predicted dichotomous non-adherence (B = −.593, p<.001) as well as continuous non-adherence (with pts reporting 100% adherence removed; B = −.214, p<.021). Also, number of drinks in the past 30 days was a significant negative predictor of perfect adherence (B=.834, p=.002). |
| Peretti-Watel et al. 2006 | France Hospital HIV depts N=2484 74% Men 41% Gay/bi |
Cross-sectional On HAART |
Perfect adherence Self-report via 4 dichotomous interview questions 7 days 60% adherent |
Regular use (2x/week or more) Regular binge drinking (drinking 5+ drinks in a row 2x/month or more), Potential alcohol abuse (2+ items on CAGE) Self-report via computer-assisted interview; quantity/frequency and CAGE 12 months 31% regular drinking 9% binge drinking 12% potential abuse |
Bivariate: significant effects of alcohol use on adherence for all alcohol use groups, including: Regular drinkers, 36% low adh vs. 28% high adh (p<.001) Binge drinkers, 14% low adh vs. 6% high adh (p<.001) Potential alcohol abusers, 19% low adh vs. 8% high adh (p=.003) Multivariate: alcohol abuse was a significant predictor of nonadherence (OR 2.55, 2.00–3.26). |
| Rothlind et al. 2005 | San Francisco, CA, USA VA Medical Center N = 268 (N=126 HIV+ subset) 95% Men 78% gay/bi 20% AA 7% LAT |
Prospective cohort HIV+, English speaking, no psychiatric disorders, non-alcohol substance use disorders, or head injuries |
Composite measure: sum of formula on a scale of 0 (no doses taken) to 1 (100% doses taken) Self-report, based on Chesney (2000), assessed 12 reasons for missing doses & ordinal freq measures for each reason (timeframe N/R) N/R adherent |
Mean # of drinks per month Categorized into light drinkers: 45 (men)/35 (women) drinks or less per month and no past or current dependence or significant periods of drinking more than 45 drinks per month; and heavy drinkers: at least 100 (men)/80 (women) drinks per month for the prior 3 years and current active drinking SCID, lifetime LDH, past week 56% light drinkers 44% heavy drinkers |
Bivariate: significant effect of heavy alcohol use on adherence. Mean adherence (0–1) for heavy drinkers was .68 and .78 for light drinkers (inferential test N/R). |
| Samet et al. 2004 | Boston, MA, USA Community/Medical Centers N= 267 (on HAART) 81% Male 42% AA 23%Other 35% WH |
Prospective cohort HIV+, history of alcohol related problems, English or Spanish speaking, MMSE score >20, no plans to move from Boston in next 2 years |
No missed doses Self-report via ACTG survey Past 3 days 66% adherent |
Used NIAAA criteria for at-risk drinking (men: >14 drinks/wk or >4 drink/day; women: >7 drinks/wk or >3 drinks/day) Self-report via ASI Past 6 months At baseline (N=205): 60% abstinent 24% moderate (any drinking below at-risk) 16% at-risk |
Bivariate: significant effects of drinking level on 100% 3-day adherence; 76% of abstinent, 57% moderate drinkers, 42% of at-risk drinkers (p=.0004). Multivariate: abstinent group was more likely to report 100% adherence compared to at-risk group (adj OR 3.6, CI 2.1–6.2) and compared to moderate group (adj OR 3.0, CI 2.0-4.5) No significant difference in adherence between moderate and at-risk groups |
| Shannon et al. 2005 | Vancouver, Canada High-risk community sample N=184 66% Male 39% Aboriginal |
Prospective cohort In CHASE cohort (engaged in drug treatment), had data available |
Percent of months during follow-up in which refills were picked up (>95% = adherent) Monthly pharmacy refill compliance (from medical records 35 months 30% adherent |
Frequent of alcohol use (defined as daily or most days) Self-report via questionnaire (timeframe unclear) N/R prevalence |
Bivariate: no significant association of alcohol use with adherence (non-adherent, 11% frequent drinkers; adherent, 7% frequent drinkers). |
| Sharma et al. 2007 | India Hospital/Clinic N=226 97.8% Male |
Cross-sectional On ART, current or previous IV drug use |
No missed doses/never discontinued medication Measure N/R N/R adherence rate |
Any use (yes/no) Self-report Past month/year 10% past month 31% past year |
Bivariate: significant effect of alcohol use on adherence. Of pts reporting missing a dose, 18% were current drinkers. Of those who never missed a dose, 5% were current drinkers (p=.003). The proportion of current drinkers was significantly higher among those who did (16%) vs. those who did not (7%) discontinue medication use (p=.031). |
| Spire et al. 2002 | France Hospitals N=445 78% Male 45% male-male HIV transmission |
Prospective cohort APROCO patients who had necessary data |
100% of doses taken and “totally followed” regimen Self-report # of doses taken; ordinal freq of how often regimen followed Past 4 days 73% adherent |
>1 unit (~.5 – 1 standard drinks) per day Measure N/R Past month 26% reported 1+ unit/day |
Bivariate: greater alcohol use marginally associated with being non-adherent (p=.09). Increased use of alcohol (increasing >1 unit/day) from baseline to 4 month follow-up associated with increased likelihood of non-adherence (adj OR 2.24, CI 1.35–3.71). |
| Sullivan et al. 2007 | Multiple Sites, USA Health centers N=5,887 74% Male 40% MSM 51% AA 21% LAT 24% WH |
Cross-sectional 18+, in SHAS study, on HAART |
>95% of prescribed doses taken Self-report via interview (measure N/R) 48 Hours 84% adherent |
Any alcohol use in past year CAGE 12 months N/R alcohol prevalence |
Bivariate: significant effect of alcohol on adherence. Pts who reported alcohol use in the past year were more likely to be <95% adherent (OR 1.3, CI 1.1–1.5). |
| Tesoriero et al. 2003 | Multiple sites, USA Hospitals/clinics N=435 61% Male 48% AA 32% LAT 13% WH |
Prospective cohort Enrolled in TADP, on HAART at baseline |
100% doses taken Self-report ACTG (# of doses missed) Past 3 days 65% adherent at baseline 46% adherent across all time points |
3+ drinks/day (yes/no) Self-report Past 3 months 22% drank 3+ drinks/day |
Bivariate: significant effect of alcohol on adherence only for pts who transitioned from non-frequent to frequent drinking over time (adj OR 2.92, CI 1.18–7.25, p<.05). |
| Tucker et al. 2003 | Multiple sites, USA HIV service organizations N=1,910 (on HAART) 78% Male 32% AA 15% LAT |
Prospective cohort HCSUS pts: data from all three interviews & on HAART at second follow-up |
No missed doses, taken as directed “all the time” Self-report via interview Past week 46% adherent |
Quantity/freq of alcohol use: no drinking; non-heavy drinking (always <5 drinks per day), heavy drinking (5+ drinks on 1–4 occasions); frequent heavy drinking (5+ drinks on 5+ occasions). Self-report via interview (measure N/R) Past 4 weeks 5% frequent/heavy 9% heavy 38% non-heavy |
Bivariate: significant effect of alcohol on adherence. Among pts reporting no alcohol use, 52% were adherent; non-heavy, 43% adherent; heavy, 39% adherent; frequent heavy, 31% adherent (p<.001). Multivariate: significant effect of drinking category on nonadherence. Non-heavy, adj OR 1.6, CI 1.3–2.0, p<.001 Heavy, adj OR 1.7, CI 1.3–2.3, p<.001 Freq heavy, adj OR 2.7, CI 1.7–4.5, p<.001 |
| Wagner et al. 2002 | Multiple sites, USA VA Infectious Disease Clinics (Veterans Aging Cohort Study; VACS3) N=793 (on HAART) Demographics N/R |
Observational cohort VACS3 pts on HAART |
Perfect (100%) adherence ACTG survey & provider report Past 4 days 27% perfect adh 46% intermediate adh 25% poor adh |
Problem drinking (8+ on AUDIT) AUDIT & provider-reported current alcohol use N/R alcohol rate |
Bivariate: among pts reporting current drinking, 26% of perfect adherers drank, 39% of intermediate adherers drank, and 58% of poor adherers drank (p<.001). Multivariate: current drinkers vs. non-drinkers were more likely to report missed doses (OR 1.88, CI 1.4–2.5, p<.001). |
| Wilson et al. 2002 | Multiple sites, USA WIHS study cohort N=766 0% Male 0% MSM 53% AA 26% LAT 19% WH |
Prospective cohort On HAART for >1 month, not enrolled in ACTG study, not pregnant |
>95% doses taken Self-report via interview 6 Months 76% adherent |
# of drinks per week Mean # of drinks per week in the previous 6 months N/R alcohol rate |
Bivariate: no significant effect of alcohol use on likelihood of reporting >95% adherence. Adherent group reported mean 2.2 drinks/week, non-adherent group reported 3.8 drinks/week. |
Note. N/R = Not reported. Pts = Participants. MSM = Men who have sex with men. Bi = bisexual. Adh = adherence. AA = African American. LAT = Latino. WH = White/Caucasian. EDM = Electronic drug monitoring. ASI = Addiction Severity Index measure. Freq = frequency. Avg = average. HAART = highly active antiretroviral therapy. CSA = childhood sexual abuse. TLFB = timeline follow-back interview method. SCID = Structured Clinical Interview for the DSM-IV. LDH = Lifetime Drinking History questionnaire. ACTG = AIDS Clinical Trials Group. AGAS = Antiretroviral General Adherence Scale.
Effect size abstraction
Effect size data were entered and standardized prior to analysis. Odds ratios (ORs) were chosen for the effect size metric because the majority of studies compared two categories of alcohol use (e.g., drinkers vs. nondrinkers; 72.5% of studies,) on a dichotomous adherence indicator variable (e.g., adherent vs. nonadherent, 77.5% of studies). Nine studies (20.5%) included multiple comparisons involving an alcohol-related indicator (e.g., any use vs. none in addition to problematic vs. nonproblematic use or none). In order not to violate the assumption of independence of effect sizes, we did not include more than one comparison per study per analysis. Two alternative ways to extract effect sizes from these studies were explored: selecting the least extreme comparison (Alternative 1; e.g., any vs. no alcohol) and computing the average effect size (Alternative 2). When studies included multiple adherence outcomes (e.g., proportion of doses and timing of doses), one measure reflecting proportion of doses taken was selected because this was the primary outcome for most studies. If more than one adherence cutoff (e.g., 90% and 100%) was evaluated in relation to drinking the more stringent cutoff was used.
For each effect size estimate we computed a 95% confidence interval (CI), Z-statistic and p-value. Figure 2 presents the effect size data and the forest plot. For each study, the forest plot indicates the point estimate for the study’s effect size (OR) and its 95% confidence interval. The size of the point represents the weight of the study in the context of the present meta-analysis. An OR of one indicates no effect of alcohol on adherence, ORs greater than one would indicate a benefit of alcohol on adherence, and ORs less than one indicate a detriment of alcohol on adherence. An initial test of homogeneity of variance indicated heterogeneity across samples, Q(39) = 82.235, p < .001; therefore, random effects models were used. The core analysis yielded an estimate of the overall effect. A sensitivity analysis was conducted whereby the overall effect was computed with each study removed in turn. A stratification analysis was conducted to examine the 3-level variable reflecting drinking intensity (any/global use, moderate use, problem drinking). Moderator variables were tested using linear meta-regression. Finally, for the overall effect, publication bias was evaluated via inspection of a funnel plot and Duvall and Tweedie’s “Trim and Fill” method38.
Figure 2.
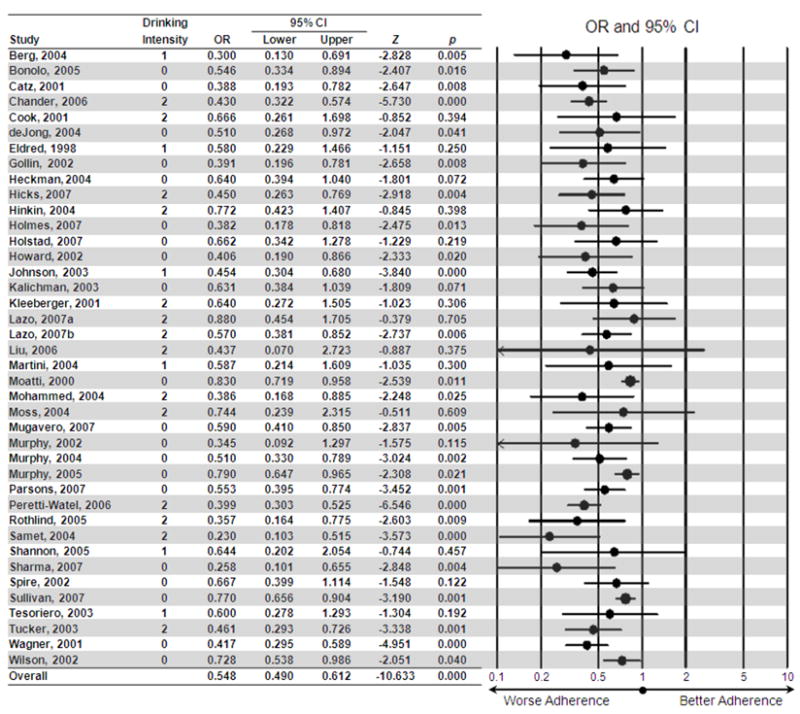
Forest plot indicating the effect size contributed by each study, using the most extreme comparison per study. Drinking intensity: 0 = global (e.g., any use vs. none), 1 = moderate drinking (that did not exceed the NIAAA definition of at-risk drinking or constitute an alcohol use disorder) vs. nonuse, 2 = problem drinking (that met the NIAAA definition for at-risk drinking or criteria for an alcohol use disorder) vs. nonproblem use/nonuse.
Results
Core and Sensitivity Analyses
Under the random effects model, the point estimate and 95% confidence interval for the combined studies was 0.548 (0.490, 0.612), Z = −10.633, p < .001, indicating that those who used alcohol, or who drank relatively more, were 0.548 times as likely to be classified as adherent as compared to nonusers, or those who drank relatively less. Sensitivity analysis found no individual effect size to unduly influence the estimate of the overall effect; therefore, all were retained. The primary analysis used the most extreme comparison for those that included comparison of multiple drinking levels. As might be expected, alternative methods of effect size extraction altered the estimate of the overall effect. Using Alternative 1, the overall OR was estimated to be 0.628 (0.568, 0.695), Z = −9.042, p < .001, indicating that when using the least extreme comparison per study, drinkers were 0.628 times as likely to be classified as adherent compared to nonusers. Using Alternative 2, the overall OR was estimated to be 0.586 (0.531, 0.647), Z = −10.647, p < .001, indicating that, when collapsing across multiple comparisons per study, alcohol users were 0.586 times as likely to be classified as adherent as nonusers.
Stratification Analysis of the Effect of Drinking Intensity
Participants classified as problem drinkers, defined in accordance with NIAAA guidelines for at-risk drinking or based on meeting diagnostic criteria for a probable alcohol use disorder, were 0.474 (0.408, 0.550) times as likely as non-problem drinkers or abstainers to be classified as adherent (14 effect sizes, Q(13) = 13.034, Z = −9.803, p < .001). Among studies examining drinking thresholds classified as moderate (i.e., falling short of problem drinking criteria), drinkers were 0.480 (0.360, 0.639) times as likely as abstainers, or those who consumed less, be adherent (6 effect sizes, Q(5) = 2.180, Z = −5.021, p < .001). Among studies examining any or global alcohol use (e.g., any use in the past year vs. none), the combined OR was 0.604 (0.531, 0.687) (20 effect sizes, Q(19) = 17.312, Z = −7.704, p < .001). Overlap in the confidence intervals for the effect sizes by level of drinking intensity indicates that, although the effect sizes are significantly different from zero, they are not significantly different from each other.
Moderator Analyses
Results of univariate moderator analyses are shown in Table 2. Findings indicate that the effect of alcohol on adherence was significantly moderated by a number of variables. Greater alcohol-related decrements in adherence were associated with higher proportions of men in study samples, lower proportions of participants reporting IDU, higher adherence criteria, nonuse of a self-report measure of adherence, nonuse of a dichotomous measure of adherence, assessing alcohol/substance use as a primary study aim, dichotomization of the alcohol variable, using an alcohol variable that took into account both quantity and frequency, use of a standardized alcohol measure, and use of the AUDIT in particular.
Table 2.
Results of univariate analyses of potential moderators of the association of alcohol and adherence.
| k | B | SE | Z | Q | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion of sample male (%) | 40 | −0.003 | 0.001 | −2.301 | 5.293 | 0.021 |
| Proportion of sample White (%) | 27 | −0.001 | 0.003 | −0.267 | 0.071 | 0.789 |
| Proportion of sample African American (%) | 31 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.971 | 0.943 | 0.332 |
| Proportion of sample reporting IDU (%) | 23 | 0.008 | 0.003 | 2.772 | 7.682 | 0.006 |
| Effect size based on adjusted odds ratio* | 40 | −0.113 | 0.119 | −0.947 | 0.897 | 0.344 |
| Temporal overlap for alcohol and adherence† | 38 | −0.049 | 0.038 | −1.293 | 1.672 | 0.196 |
| Design of alcohol-adherence analysis‡ | 40 | −0.083 | 0.118 | −0.707 | 0.500 | 0.480 |
| Adherence criterion (% doses) | 30 | −0.022 | 0.005 | −4.751 | 22.573 | 0.000 |
| Length of adherence recall period (days) | 35 | −0.001 | 0.001 | −1.111 | 1.234 | 0.267 |
| Used self-report measure of adherence* | 40 | 0.340 | 0.150 | 2.264 | 5.126 | 0.024 |
| Used MEMS to assess adherence* | 40 | −0.235 | 0.179 | −1.314 | 1.727 | 0.189 |
| Used a dichotomous measure of adherence* | 40 | 0.384 | 0.121 | 3.179 | 10.104 | 0.001 |
| Assessing alcohol was a primary study aim* | 40 | −0.415 | 0.083 | −4.996 | 24.964 | 0.000 |
| Length of alcohol recall period (days) | 31 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.389 | 1.930 | 0.165 |
| Alcohol assessed as a continuous variable* | 40 | 0.214 | 0.068 | 3.160 | 9.987 | 0.002 |
| Alcohol variable reflected frequency and quantity* | 40 | −0.340 | 0.095 | −3.596 | 12.930 | 0.000 |
| Reported use of a standardized alcohol measure* | 40 | −0.411 | 0.075 | −5.514 | 30.403 | 0.000 |
| Used the AUDIT* | 40 | −0.372 | 0.126 | −2.954 | 8.726 | 0.003 |
Note. Negative Bs indicate the higher the moderator, the lower the odds ratio, i.e., the stronger the deleterious effect of alcohol on adherence. Variables were continuous unless otherwise noted. k = number of effect sizes.
Coded 0=no, 1=yes.
Coded 0= no/unclear, 1=some/very broad, 2=fair/moderate, 3=good/extensive overlap in assessment periods for alcohol use and adherence.
Coded 1=cross-sectional, 2=prospective.
Publication Bias
Inspection of a funnel plot revealed slight asymmetry, which is an indicator of publication bias. The Trim and Fill Method38 indicated missing studies to the right of the mean. Eight studies were identified for trimming; the imputed point estimate was 0.638 (0.600, 0.679). Since the imputed estimate is very close to observed estimate, 0.624 (0.585, 0.664), and their confidence intervals overlap considerably, publication bias appears to have been minimal.
Discussion
This study provides the first meta-analytic evaluation of the association of alcohol use and antiretroviral adherence. Effect sizes for the combined studies suggested that those who used alcohol were 50–60% as likely (OR = 0.548, 95% CI: 0.490–0.612) to be classified as adherent compared to those who abstained (or drank relatively less). Alcohol use that met or exceeded an objective threshold for problem drinking (defined as meeting NIAAA criteria for at-risk drinking or diagnostic criteria for an alcohol use disorder) was associated with the largest effect (OR = 0.474, 95% CI = 0.408, 0.550), whereas the overall effect was smaller among studies examining any or global alcohol use (OR = 0.604, 95% CI = 0.531, 0.687). Although these effect sizes were not significantly different from each other, they were significantly different from zero and the point estimates can be viewed as broadly consistent with “dose-response” effects reported in previous studies.9,14,25,27
Several variables moderated the alcohol-adherence association. This association was stronger in samples that included a higher proportion of men, a finding that is inconsistent with previous reports suggesting that alcohol’s effects on adherence are more prominent among women. 28,29 The alcohol-adherence association was also stronger in samples with a lower reported prevalence of IDU. Given the established association of IDU with lower adherence, it is possible that any effects of alcohol on adherence are obscured in the context of IDU. The observation that effects were stronger in studies with larger samples presumably reflects greater statistical power. Aspects of alcohol use measurement also moderated the effects. Studies assessing both drinking quantity and frequency, as well as those using the AUDIT (which assesses quantity and frequency) showed stronger effect sizes. A recent study found that when disaggregating the NIAAA at-risk drinking criteria into its two components (> 4 drinks per day or > 14 drinks per week), only the former predicted reduced adherence. 26 Taken together, the available evidence suggests that drinking quantity is a more robust and important predictor of adherence than drinking frequency, a finding that appears consistent with dose-related alcohol effects on adherence.14,27 Dichotomous (compared to continuous) drinking outcomes were also associated with stronger effects, perhaps because studies using continuous measures tended to rely on global variables (e.g., drinks per week) that did not index drinking quantity.
With respect to adherence assessment, moderator analyses indicated greater alcohol-related decrements in adherence in studies where adherence was defined using a higher criterion (e.g., 100% versus 90%). This result is consistent with event-level findings suggesting that alcohol’s effects are more evident under more difficult adherence requirements39 and suggests that alcohol use might be particularly detrimental to achieving perfect or near-perfect adherence. The alcohol-adherence association was also stronger when using continuous adherence measures. Continuous measures presumably afford greater statistical power and have been shown to explain the most variance in viral load.40 Incorporating continuous measures might allow more sensitive evaluation of alcohol-adherence associations in future studies. Finally, alcohol’s effects on adherence were stronger when using assessment approaches other than self-report. Similarly, research on illicit drug use and adherence suggests that this association might be more reliable when using MEMS compared to self-report.41 Use of MEMS specifically was not a significant moderator in this study, perhaps due to low power given that only four studies used MEMS. Objective measures might be more likely to detect significant associations due to fewer sources of measurement error, including social desirability influences.40 Readers are referred elsewhere for comprehensive reviews of adherence assessment approaches.40, 42, 43
In addition to establishing provisional effect size estimates, this study offers a basis for discussing methodologic and conceptual issues in research on alcohol and HAART adherence. A primary concern is the substantial heterogeneity in the measurement and definition of alcohol use across studies, which makes it difficult to compare and aggregate findings. Researchers are encouraged to use standardized assessment approaches that include validated and multidimensional measures of alcohol use. The AUDIT36 is a particularly useful measure given its brevity (10 items), established validity44 and inclusion of items assessing drinking frequency, quantity, heavy episodes, and symptoms of alcohol dependence. Moreover, this measure is the recommended standard in primary care settings.37 Timeline Followback (TLFB) approaches, while relatively more time consuming, are extremely useful for providing nuanced assessments of the daily covariation among drinking and adherence.25,26 Other event-level methods that permit fine-grained analyses45 warrant consideration in future studies. Relying solely on diagnostic criteria is probably less useful because traditional diagnostic schemes (as well as some brief screening methods) omit measures of drinking quantity, which is a significant limitation.46 Consistent with this reasoning, a recent study showed that drinking quantity/frequency, but not alcohol-related problems, predicted reduced adherence.47
Although the association of alcohol use and nonadherence is replicable and reliable, it remains difficult to speak to the causal nature of this association. The majority of studies included in this review were cross-sectional reports that evaluated global associations using retrospective measures of drinking and adherence. In a substantial proportion of studies there was little or no overlap among the alcohol use and adherence assessment intervals. These limitations restrict the ability to infer causal effects and leave open the possibility that these associations could be attributable to other variables. If alcohol use is embedded in a broader context of problematic behaviors that also influence adherence, including IDU or other substance use, spurious associations could emerge (the association of tobacco use with nonadherence24 likely reflects this phenomenon). The possibility that alcohol use is simply a marker for broader substance use involvement cannot be ruled out based on the current analyses; however, our finding that the alcohol-adherence association was significantly stronger in the context of lower IDU argues against this possibility and suggests a unique association of alcohol with adherence. Moreover, recent studies using sophisticated measurement approaches25, 26, 39 provide compelling evidence that that alcohol use is closely associated with decreased adherence. Continued use of these approaches would increase the ability to speak to causal associations. Researchers have also begun to examine specific intrapersonal and situational moderators of alcohol’s effects on adherence.26,39 We suggest that future research should continue to evaluate potential moderators in order to clarify the conditions under which alcohol use is likely to influence adherence. Because the association of alcohol and nonadherence appears significant and reliable across studies, further efforts to evaluate global associations may do little to extend knowledge in this area. That noted, there is a dearth of research on this issue in developing countries and establishing basic associations of alcohol and adherence in these settings would be useful.
A notable aspect of this literature is the omission of theoretical frameworks for understanding alcohol’s association with adherence. Of the studies included in this review, the vast majority did not discuss possible mechanisms for these effects. One intuitive mechanism is cognitive impairment, such that acute intoxication might interfere with one’s capacity to plan for or remember dosing requirements.26 However, additional explanations are possible. Alcohol users might have decreased access to HAART,48 or may use alcohol to reduce or avoid HIV-related negative affect,49,50 a motive that could also lead one to neglect adherence requirements. It is also important to note that some patients intentionally skip medication doses when drinking due to misperceptions about possible toxic interactions.15,18, 51 These various explanations each have unique theoretical and clinical implications for research and intervention at the intersection of alcohol and adherence. An important direction for future research is to specify mechanisms that explain the link between drinking and nonadherence, which should aid in identifying intervention targets. Such mechanisms are likely to involve cognitive factors such as alcohol-related beliefs, expectancies, and motives, in addition to environmental and event-level factors.
The present study has several limitations. Given that the measurement and definitions of drinking and adherence varied considerably across studies, effect sizes should be considered provisional and interpreted as relative (rather than absolute) estimates of the likelihood of nonadherence in the context of alcohol use. While we imposed a relatively objective measure of drinking intensity in the stratification analyses, there was still heterogeneity within categories due to measurement differences across studies and these analyses relied on a modest number of effect sizes. Results concerning significant moderators should also be interpreted with caution. Another limitation is the omission unpublished studies, although there was minimal evidence of publication bias.
The current findings support the need for interventions that address alcohol use in the context of HAART. 14,23 Given reported associations of alcohol use and immunologic function among those living with HIV/AIDS,9,19,20,22 successful alcohol interventions could potentially show salutary effects on disease progression and, theoretically, life expectancy.52 Few such interventions have been tested and more are needed.12 In one recent study, 23 an alcohol/adherence intervention did not influence drinking but nonetheless led to improved adherence, decreased viral load and increased CD4 cell counts, suggesting that adherence and biological outcomes can be improved even in the context of continued alcohol use. Similarly, meta-analytic research suggests that drug users often maintain adequate adherence, especially in the context of medical and psychosocial support.11 Interventions might therefore aim not only to reduce alcohol use, but also to promote strategies for maximizing adherence among those who are unlikely or unwilling to cease drinking. These efforts will benefit from an improved characterization of alcohol’s relation to adherence and identification of factors that mediate or moderate this association.
Acknowledgments
Work on this study was supported by National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) grant F31AA016440. The authors thank Jacqueline M. Otto for her assistance with literature reviews.
Footnotes
Portions of this study were presented at the Presented at the XVII International AIDS Conference, Mexico City, August 2008.
References
* = Study included in the meta-analysis
- 1.Amico KR, Harman JJ, Johnson BT. Efficacy of antiretroviral therapy adherence interventions – research synthesis of trials, 1996 to 2004. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2006;41:285–297. doi: 10.1097/01.qai.0000197870.99196.ea. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Palella FJ, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, Loveless MO, Fuhrer J, Satten GA, et al. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–860. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199803263381301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bartlett JA. Addressing the challenges of adherence. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2002;29:S2–S10. doi: 10.1097/00126334-200202011-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bangsberg DR, Hecht FM, Charlebois ED, Zolopa AR, Holodniy M, Sheiner L, et al. Adherence to protease inhibitors, HIV-1 viral load, and development of drug resistance in an indigent population. AIDS. 2000;14:357–366. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200003100-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bangsberg DR, Perry S, Charlebois ED, Clark RA, Roberston M, Zolopa AR, Moss A. Non-adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy predicts progression to AIDS. AIDS. 2001;15:1181–1183. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200106150-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Quinn TC, Wawer MJ, Sewankambo N, Serwadda D, Li CJ, Wabwire-Mangen F, et al. Viral load and heterosexual transmission of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:921–929. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200003303421303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Simoni JM, Amico KR, Pearson CR, Malow R. Strategies for promoting adherence to antiretroviral therapy: a review of the literature. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2008;10:515–21. doi: 10.1007/s11908-008-0083-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ammassari A, Trotta MP, Murri R, Castelli F, Narciso P, Noto P, et al. Correlates and predictors of adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy: Overview of published literature. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2002;31 (Suppl 3):S123–7. doi: 10.1097/00126334-200212153-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9*.Chander G, Lau B, Moore RD. Hazardous alcohol use: A risk factor for non-adherence and lack of suppression in HIV infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2006;43:411–417. doi: 10.1097/01.qai.0000243121.44659.a4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Conigliaro J, Justice AC, Gordon AJ, Bryant K, GVABCR Role of alcohol in determining human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-relevant outcomes: A conceptual model to guide the implementation of evidence-based interventions into practice. Med Care. 2006;44:S1–S6. doi: 10.1097/01.mlr.0000223659.36369.cf. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Malta M, Magnanini MMF, Strathdee SA, Bastos FI. Adherence to antiretroviral therapy among HIV-infected drug users: A meta-analysis. Aids Behav. doi: 10.1007/s10461-008-9489-7. in press. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bryant KJ. Expanding research on the role of alcohol consumption and related risks in the prevention and treatment of HIV/AIDS. Subst Use Misuse. 2006;41:1465–1507. doi: 10.1080/10826080600846250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Galvan FH, Bing EG, Fleishman JA, London AS, Caetano R, Burnam MA, et al. The prevalence of alcohol consumption and heavy drinking among people with HIV in the United States: Results from the HIV cost and services utilization study. J Stud Alcohol. 2002;63:179–186. doi: 10.15288/jsa.2002.63.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14*.Samet JH, Horton NJ, Meli S, Freedberg KA, Palepu A. Alcohol consumption and antiretroviral adherence among HIV-infected persons with alcohol problems. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2004;28:572–577. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000122103.74491.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Brigido LFM, Rodrigues R, Casseb J, Oliveira D, Rossetti M, Menezes P, Duarte AJS. Impact of adherence to antiretroviral therapy in HIV-1-infected patients at a university public service in Brazil. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2001;15:587–593. doi: 10.1089/108729101753287685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16*.Cook RL, Sereika SM, Hunt SC, Woodward WC, Erlen JA, Conigliaro J. Problem drinking and medication adherence among persons with HIV infection. J Gen Intern Med. 2001;16:83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1497.2001.00122.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17*.Eldred LJ, Wu AW, Chaisson RE, Moore RD. Adherence to antiretroviral and Pneumocystis prophylaxis in HIV disease. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1998;18:117–125. doi: 10.1097/00042560-199806010-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sankar A, Wunderlich T, Neufeld S, Luborsky M. Sero-positive African Americans’ Beliefs about alcohol and their impact on anti-retroviral adherence. AIDS Behav. 2007;11:195–203. doi: 10.1007/s10461-006-9144-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Miguez MJ, Shor-Posner G, Morales G, Rodriguez A, Burbano X. HIV treatment in drug abusers: impact of alcohol use. Addict Biol. 2003;8:33–37. doi: 10.1080/1355621031000069855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Palepu A, Tyndall MW, Li K, Yip B, O’Shaughnessy MV, Schechter MT, et al. Alcohol use and incarceration adversely affect HIV-1 RNA suppression among injection drug users starting antiretroviral therapy. J Urban Health. 2003;80:667–675. doi: 10.1093/jurban/jtg073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pence BW, Miller WC, Gaynes BN, Eron JJ. Psychiatric illness and virologic response in patients initiating highly active antiretroviral therapy. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007;44:159–166. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e31802c2f51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Samet JH, Cheng DM, Libman H, Nunes DP, Alperen JK, Saitz R. Alcohol consumption and HIV disease progression. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007;46:194–199. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e318142aabb. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Parsons JT, Golub SA, Rosof E, Holder C. Motivational interviewing and cognitive-behavioral intervention to improve HIV medication adherence among hazardous drinkers: A randomized controlled trial. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007;46:443–450. doi: 10.1097/qai.0b013e318158a461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24*.Peretti-Watel P, Spire B, Lert F, Obadia Y, Grp V. Drug use patterns and adherence to treatment among HIV-positive patients: evidence from a large sample of French outpatients (ANRS-EN12-VESPA 2003) Drug Alcohol Depend. 2006;82:S71–S79. doi: 10.1016/s0376-8716(06)80012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Braithwaite RS, McGinnis KA, Conigliaro J, Maisto SA, Crystal S, Day N, et al. A temporal and dose-response association between alcohol consumption and medication adherence among veterans in care. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005;29:1190–1197. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000171937.87731.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Braithwaite RS, Conigliaro J, McGinnis KA, Maisto SA, Bryant K, Justice AC. Adjusting alcohol quantity for mean consumption and intoxication threshold improves prediction of nonadherence in HIV patients and HIV-negative controls. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2008;32:1645–1651. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2008.00732.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27*.Tucker JS, Burnam MA, Sherbourne CD, Kung FY, Gifford AL. Substance use and mental health correlates of nonadherence to antiretroviral medications in a sample of patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Am J Med. 2003;114:573–580. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(03)00093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28*.Berg KM, Demas PA, Howard AA, Schoenbaum EE, Gourevitch MN, Arnsten JH. Gender differences in factors associated with adherence to antiretroviral therapy. J Gen Intern Med. 2004;19:1111–1117. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1497.2004.30445.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29*.Lazo M, Gange SJ, Wilson TE, Anastos K, Ostrow DG, Witt MD, Jacobson LP. Patterns and predictors of changes in adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy: Longitudinal study of men and women. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45:1377–1385. doi: 10.1086/522762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30*.Murphy DA, Greenwell L, Hoffman D. Factors associated with antiretroviral adherence among HIV-infected women with children. Women Health. 2002;36:97–111. doi: 10.1300/J013v36n01_07. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31*.Murphy DA, Marelich WD, Hoffman D, Steers WN. Predictors of antiretroviral adherence. Aids Care. 2004;16:471–484. doi: 10.1080/09540120410001683402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32*.Murphy DA, Belzer M, Durako SJ, Sarr M, Wilson CM, Muenz LR. Longitudinal antiretroviral adherence among adolescents infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2005;159:764–770. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.159.8.764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33*.Spire B, Duran S, Souville M, Leport C, Raffi F, Moatti JP, Grp ACS. Adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapies (HAART) in HIV-infected patients: from a predictive to a dynamic approach. Soc Sci Med. 2002;54:1481–1496. doi: 10.1016/s0277-9536(01)00125-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cook TD, Campbell DT. Quasi-experimentation: Design and analysis issues for field settings 1979. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company; 1979. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ewing JA. Detecting alcoholism: The CAGE questionnaire. JAMA. 1984;252:1905–7. doi: 10.1001/jama.252.14.1905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Babor TF, Biddle-Higgins JC, Saunders JB, Monteiro MG. AUDIT: The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test: Guidelines for Use in Primary Health Care. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 37.National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Helping Patients Who Drink Too Much. A Clinician’s Guide. 2005. Washington, DC: National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Duval SJ, Tweedie RL. Trim and fill: A simple funnel plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics. 2000;56:276–284. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341x.2000.00455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Parsons JT, Rosof E, Mustanski B. The temporal relationship between alcohol consumption and HIV-medication adherence: A multilevel model of direct and moderating effects. Health Psychol. 2008;27:628–637. doi: 10.1037/a0012664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hinkin CH, Barclay TR, Castellon SA, Levine AJ, Durvasula RS, Marion SD, et al. Drug use and medication adherence among HIV-1 infected individuals. AIDS Behav. 2007;11:185–194. doi: 10.1007/s10461-006-9152-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pearson CR, Simoni JM, Hoff P, Kurth AE, Martin DP. Assessing antiretroviral adherence via electronic drug monitoring and self-report: An examination of key methodological issues. AIDS Behav. 2007;11:161–173. doi: 10.1007/s10461-006-9133-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bova CA, Fennie KP, Knafl GJ, Dieckhaus KD, Watrous E, Williams AB. Use of electronic monitoring devices to measure antiretroviral adherence: Practical considerations. AIDS Behav. 2005;9:103–110. doi: 10.1007/s10461-005-1685-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Simoni JM, Kurth AE, Pearson CR, Pantalone DW, Merrill JO, Frick PA. Self-report measures of antiretroviral adherence: A review with recommendations for HIV research and clinical management. AIDS Behav. 2006;10:227–245. doi: 10.1007/s10461-006-9078-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Reinert DF, Allen JP. The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test: An update of research findings. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2007;31:185–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2006.00295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Stone AA, Shiffman S. Ecological momentary assessment (EMA) in behavorial medicine. Ann Behav Med. 1994;16:199–202. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Martin CS, Chung T, Langenbucher JW. How should we revise diagnostic criteria for substance use disorders in the DSM-V? J Abnorm Psychol. 2008;117:561–575. doi: 10.1037/0021-843X.117.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47*.Parsons JT, Rosof E, Mustanski B. Patient-related factors predicting HIV medication adherence among men and women with alcohol problems. J Health Psychol. 2007;12:357–370. doi: 10.1177/1359105307074298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tucker JS, Orlando M, Burnam MA, Sherbourne CD, Kung FY, Gifford AL. Psychosocial mediators of antiretroviral nonadherence in HIV-positive adults with substance use and mental health problems. Health Psychol. 2004;23:363–70. doi: 10.1037/0278-6133.23.4.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.McKirnan DJ, Ostrow DG, Hope B. Sex, drugs and escape: A psychological model of HIV-risk sexual behaviours. AIDS Care. 1996;8:655–669. doi: 10.1080/09540129650125371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Nemeroff CJ, Hoyt MA, Huebner DM, Proescholdbell RJ. The cognitive escape scale: Measuring HIV-related thought avoidance. AIDS Behav. 2008;12:305–320. doi: 10.1007/s10461-007-9345-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kalichman SC, Amaral CM, White D, Swetsze C, Pope H, Kalichman MO, et al. Prevalence and clinical implications of interactive toxicity beliefs regarding mixing alcohol and antiretroviral therapies among people living with HIV/AIDS. AIDS Patient Care STDS. doi: 10.1089/apc.2008.0184. in press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Braithwaite RS, Conigliaro J, Roberts MS, Shechter S, Schaefer A, McGinnis K, et al. Estimating the impact of alcohol consumption on survival for HIV+ individuals. AIDS Care. 2007;19:459–66. doi: 10.1080/09540120601095734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53*.Bonolo PD, Cesar CC, Acurcio FA, Ceccato MDB, de Padua CAM, Alvares J, et al. Non-adherence among patients initiating antiretroviral therapy: a challenge for health professionals in Brazil. AIDS. 2005;19:S5–S13. doi: 10.1097/01.aids.0000191484.84661.2b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54*.Catz SL, Heckman TG, Kochman A, DiMarco M. Rates and correlates of HIV treatment adherence among late middle-aged and older adults living with HIV disease. Psychol Health Med. 2001;6:47–58. [Google Scholar]
- 55*.de Jong BC, Prentiss D, McFarland W, Machekano R, Israelski DM. Marijuana use and its association with adherence to antiretroviral therapy among HIV-infected persons with moderate to severe nausea. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2005;38:43–46. doi: 10.1097/00126334-200501010-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56*.Golin CE, Liu HH, Hays RD, Miller LG, Beck CK, Ickovics J, et al. A prospective study of predictors of adherence to combination antiretroviral medication. J Gen Intern Med. 2002;17:756–765. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.2002.11214.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57*.Heckman BD, Catz SL, Heckman TG, Miller JG, Kalichman SC. Adherence to antiretroviral therapy in rural persons living with HIV disease in the United States. AIDS Care. 2004;16:219–230. doi: 10.1080/09540120410001641066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58*.Hicks PL, Mulvey KP, Chander G, Fleishman JA, Josephs JS, Korthuis PT, et al. The impact of illicit drug use and substance abuse treatment on adherence to HAART. AIDS Care. 2007;19:1134–1140. doi: 10.1080/09540120701351888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59*.Hinkin CH, Hardy DJ, Mason KI, Castellon SA, Durvasula RS, Lam MN, Stefaniak M. Medication adherence in HIV-infected adults: effect of patient age, cognitive status, and substance abuse. AIDS. 2004;18(Suppl 1):S19–S25. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200418001-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60*.Holmes WC, Bilker WB, Wang H, Chapman J, Gross R. HIV/AIDS-Specific quality of life and adherence to Antiretroviral therapy over time. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007;46:323–327. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e31815724fe. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61*.Holstad MKM, Pace JC, De AK, Ura DR. Factors associated with adherence to antiretroviral therapy. J Assoc Nurses AIDS Care. 2006;17:4–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jana.2006.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62*.Howard AA, Arnsten JH, Li YT, Vlahov D, Rich JD, Schuman P, et al. A prospective study of adherence and viral load in a large multi-center cohort of HIV-infected women. AIDS. 2002;16:2175–2182. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200211080-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63*.Johnson MO, Catz SL, Remien RH, Rotheram-Borus MJ, Morin SF, Charlebois E, et al. Theory-guided, empirically supported avenues for intervention on HIV medication nonadherence: Findings from the healthy living project. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2003;17:645–656. doi: 10.1089/108729103771928708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64*.Kalichman SC, Rompa D. HIV treatment adherence and unprotected sex practices in people receiving antiretroviral therapy. Sex Transm Infect. 2003;79:59–61. doi: 10.1136/sti.79.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65*.Kleeberger CA, Phair JP, Strathdee SA, Detels R, Kingsley L, Jacobson LP. Determinants of heterogeneous adherence to HIV-antiretroviral therapies in the multicenter AIDS cohort study. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2001;26:82–92. doi: 10.1097/00126334-200101010-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66*.Liu H, Longshore D, Williams JK, Rivkin I, Loeb T, Warda US, et al. Substance abuse and medication adherence among HIV-positive women with histories of child sexual abuse. AIDS Behav. 2006;10:279–286. doi: 10.1007/s10461-005-9041-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67*.Martini M, Recchia E, Nasta P, Castanotto D, Chiaffarino F, Parazzini F, Agnoletto V. Illicit drug use: Can it predict adherence to antiretroviral therapy? Eur J Epidemiol. 2004;19:585–587. doi: 10.1023/b:ejep.0000032353.03967.ef. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68*.Moatti JP, Carrieri MP, Spire B, Gastaut JA, Cassuto JP, Moreau J, Manif Study G. Adherence to HAART in French HIV-infected injecting drug users: the contribution of buprenorphine drug maintenance treatment. AIDS. 2000;14:151–155. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200001280-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69*.Mohammed H, Kieltyka L, Richardson-Alston G, Magnus M, Fawal H, Vermund SH, et al. Adherence to HAART among HIV-infected persons in rural Louisiana. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2004;18:289–296. doi: 10.1089/108729104323076025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70*.Moss AR, Hahn JA, Perry S, Charlebois ED, Guzman D, Clark RA, Bangsberg DR. Adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy in the homeless population in San Francisco: A prospective study. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2004;39:1190–1198. doi: 10.1086/424008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71*.Mugavero M, Ostermann J, Whetten K, Leserman J, Swartz M, Stangl D, et al. Barriers to antiretroviral adherence: The importance of depression, abuse, and other traumatic events. AIDS Patient Care STDS. 2006;20:418–428. doi: 10.1089/apc.2006.20.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72*.Rothlind JC, Greenfield TM, Bruce AV, Meyerhoff DJ, Flenniken DL, Lindgren JA, Weiner MW. Heavy alcohol consumption in individuals with HIV infection: Effects on neuropsychological performance. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2005;11:70–83. doi: 10.1017/S1355617705050095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73*.Shannon K, Kerr T, Lai C, Ishida T, Wood E, Montaner JS, et al. Nonadherence to antiretroviral therapy among a community with endemic rates of injection drug use. J Int Assoc Physicians AIDS Care. 2005;4:66–72. doi: 10.1177/1545109705284353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74*.Sharma M, Singh RR, Laishram P, Kumar B, Nanao H, Sharma C, Ahmed T. Access, adherence, quality and impact of ARV provision to current and ex-injecting drug users in Manipur (India): An initial assessment. Inl J Drug Policy. 2007;18:319–325. doi: 10.1016/j.drugpo.2007.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75*.Sullivan PS, Campsmith ML, Nakamura GV, Begley EB, Schulden J, Nakashima AK. Patient and regimen characteristics associated with self-reported nonadherence to antiretroviral therapy. PLoS ONE. 2007;2:e552. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76*.Tesoriero J, French T, Weiss L, Waters M, Finkelstein R, Agins B. Stability of adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy over time among clients enrolled in the treatment adherence demonstration project. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2003;33:484–493. doi: 10.1097/00126334-200308010-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77*.Wagner JH, Justice AC, Chesney M, Sinclair G, Weissman S, Rodriguez-Barradas M, Team VP. Patient- and provider-reported adherence: toward a clinically useful approach to measuring antiretroviral adherence. J Clin Epidemiol. 2001;54:S91–S98. doi: 10.1016/s0895-4356(01)00450-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78*.Wilson TE, Barron Y, Cohen M, Richardson J, Greenblatt R, Sacks HS, et al. Adherence to Antiretroviral therapy and its association with sexual behavior in a national sample of women with human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34:529–53. doi: 10.1086/338397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]