Abstract
Aims/hypothesis
Interleukin-6 is an inflammatory cytokine with pleiotropic effects upon nutrient homeostasis. Many reports show that circulating IL6 correlates with obesity and contributes to insulin resistance; however, IL6 can promote energy expenditure that improves glucose homeostasis.
Methods
We investigated nutrient homeostasis in C57BL/6J mice with sustained circulating human IL6 (hIL6) secreted predominantly from brain and lung (hIL6 tg mice).
Results
The hIL6 tg mice displayed no features of systemic inflammation and were more insulin-sensitive than wild-type mice. On a high-fat diet, hIL6 tg mice were lean, had low leptin concentrations, consumed less food and expended more energy than wild-type mice. Like ob/ob mice, the ob/ob IL6 mice (generated by intercrossing ob/ob and hIL6 tg mice) were obese and glucose-intolerant. However, low-dose leptin injections increased physical activity and reduced both body weight and food intake in ob/ob IL6 mice, but was ineffective in ob/ob mice. Leptin increased hypothalamic signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 phosphorylation in ob/ob IL6 mice, whereas ob/ob mice barely responded.
Conclusions/interpretation
Human IL6 enhanced central leptin action in mice, promoting nutrient homeostasis and preventing diet-induced obesity.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1007/s00125-009-1580-8) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorised users.
Keywords: Diabetes, IL6, Insulin resistance, Leptin, Leptin sensitivity, Obesity
Introduction
Understanding how IL6 regulates central and peripheral nutrient homeostasis is complicated by contradictory and multi-systemic effects under various physiological states [1]. IL6 is best known as a pro-inflammatory cytokine that regulates innate immunity and the acute-phase response. However, IL6 also has tissue-specific effects that can differ in humans and rodents, depending on context and timing of stimulation [2]. IL6 promotes chronic inflammation, whereas it displays anti-inflammatory effects during acute inflammatory stimuli [3].
Obesity and its progression to diabetes are associated with chronic inflammation characterised by secretion of the proinflammatory cytokines resistin, TNFα and IL6 from adipocytes [4]. Epidemiological data confirm that elevated circulating IL6 correlates with adiposity in humans [5]. IL6 is generally thought to promote systemic insulin resistance, especially during obesity, because it is secreted from fat cells of insulin-resistant humans [5]. However, in type 2 diabetes patients the plasma concentrations of IL6 and TNFα may best reflect the level of adiposity rather than insulin sensitivity during the euglycaemic–hyperinsulinaemic clamp [6]. Yet TNFα might also be a principle cause of dysregulated insulin signalling, as it stimulates production of IL6, IL1 and C-reactive peptide [7]. It is possible that IL6 opposes the action of TNFα upon insulin sensitivity, as physical exercise promotes secretion of IL6 from skeletal muscle, while improving insulin sensitivity and nutrient homeostasis [1, 8]. The question of how IL6 integrates multiple signalling cascades to coordinate nutrient homeostasis in mammals remains unanswered.
Cell-based experiments and in vivo studies in rodents show that IL6 promotes insulin resistance [9]. In vivo, 90 min after IL6 injections plasma glucose and insulin concentrations increase [10]. Infusion of IL6 for 3 h causes hepatic and muscle insulin resistance [11, 12]. In addition, hepatic insulin receptor signalling improves in ob/ob mice treated with neutralising antibodies against IL6 [13]. Recently, electrotransfer of murine IL6 cDNA into skeletal muscle promoted liver inflammation and hyperinsulinaemia in mice [14].
Unlike in rodent studies, infusion of recombinant human IL6 (hIL6) to sustain physiological concentrations in healthy individuals or patients with diabetes increases lipolysis in the absence of adverse effects and enhances glucose infusion rates during a euglycaemic–hyperinsulinaemic clamp [15–17]. Moreover, adipose-derived hIL6 can have autocrine effects that increase leptin secretion and fat oxidation, and reduce expression and activity of lipoprotein lipase in human adipose tissues, a phenomenon that might attenuate progression of obesity and diabetes [18]. Human IL6 also displays anti-inflammatory characteristics by inhibiting TNFα and IL1, and activating IL1 receptor antagonist and IL10 [19–21]. Moreover, in rodents IL6 has central effects similar to those of leptin in promotion of nutrient homeostasis and peripheral insulin sensitivity [1, 22]. Thus, the role of IL6 in the regulation of nutrient homeostasis is contradictory and incompletely resolved, possibly confounded by differences between human and murine cytokine action [1].
Leptin is secreted from adipose tissue in proportion to fat stores, informing the central nervous system of the peripheral energy supply. Dysregulated leptin action (ob/ob mice) increases food intake, while reducing energy expenditure. In addition, ob/ob mice display severe obesity and insulin resistance that progresses to diabetes [23]. However, ordinary obesity in mice and humans is associated with elevated leptin concentrations, suggesting leptin resistance in the central nervous system as a principle cause [24, 25]. Interestingly, IL6 might be required for a normal leptin response, as adult Il6 −/− mice develop hyperphagia and obesity, which is difficult to prevent by peripheral leptin injections [26].
To establish the long-term systemic effect of hIL6 upon nutrient homeostasis in mice, we investigated glucose tolerance, energy expenditure and insulin action in transgenic C57BL/6J mice and ob/ob mice that secrete hIL6 constitutively into the circulation. Our results show that hIL6 promotes central leptin action in mice, together with its beneficial effects upon nutrient homeostasis.
Methods
Animals
Treatment of mice involved in this study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Children’s Hospital Boston. IL6 transgenic mice, which have been previously described [27], were generated by ten backcrosses for pure C57BL/6J background. Ob/ob mice were purchased from the Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME, USA). Ob/ob IL6 mice were generated by mating ob +/−/IL6 tg mice with ob +/− mice. Animals were fed either regular chow diet with 9% of energy derived from fat or a high-fat diet (HFD) (Research Diets, New Brunswick, NJ, USA) with 45% of energy derived from fat.
Metabolic analysis
Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test was performed on mice fasted overnight for 16 h. Blood glucose levels were measured on random-fed or overnight-fasted animals in mouse-tail blood using a glucometer (Elite; Bayer, Leverkusen, Germany) and serum samples were collected for insulin measurements. Animals were then injected intraperitoneally with d-glucose (2 g/kg body weight) and blood glucose levels were measured [28]. Blood insulin and leptin levels were determined using rat insulin and mouse leptin ELISA kits (Crystal Chem, Downers Grove, IL, USA). Lean and fat body mass were assessed by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) (GE Lunar, Madison, WI, USA) [28].
Food intake, physical activity and energy expenditure
All measurements were performed over a 72 h period with a comprehensive laboratory animal monitoring system (Oxymax Windows 3.0.3; Columbus Instruments, Columbus, OH, USA). The data presented are average values obtained in these recordings.
Hypothalamic neuropeptide expression
Neuropeptide mRNA was analysed using quantitative real-time PCR with customised primers. Actin gene expression was used to normalise RNA content and the relative gene product amounts were reported as mean ± SEM of several animals.
Western blotting
Mice were fasted overnight (16 h) and then fed for 4 h. Tissues were removed under anaesthetic, homogenised and applied for direct immunoblotting (50 μg) with the indicated antibodies [29]. Antibodies used in this study included: rabbit insulin receptor, IRS1 and IRS2 antibodies (Upstate Biotechnology, Billerica, MA, USA); antibodies against signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3), phospho-specific STAT3 (Tyr307), phospho-Aktser473, Akt and β-actin (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA); monoclonal antibody to suppressor of cytokine signalling (SOCS3) and phospho-tyrosine (Upstate Biotechnology). The intensity of signals was determined using a Kodak molecular imaging system.
Statistical analysis
Unless otherwise stated, mean values ± SEM were used to make comparisons between groups. Logistic regression or generalised linear regression (SPSS version 16; SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA) was used where indicated to establish significant difference (p < 0.05) when multiple categorical predictors were compared across the experiments. A generalised linear model was used to make comparisons across all samples, using the Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons.
Results
The effect of human IL6 on growth and diet-induced obesity in mice
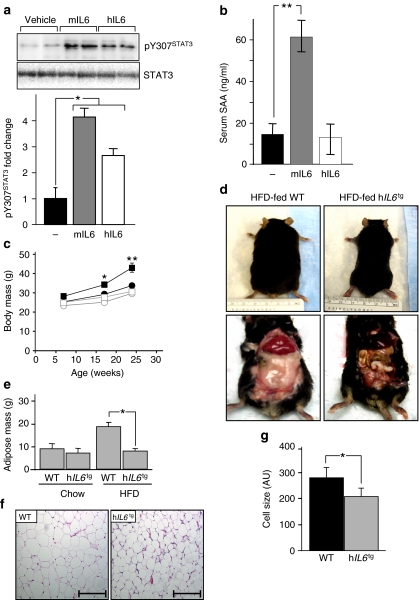
To investigate the effect of hIL6 upon nutrient homeostasis, we created mice with sustained circulating hIL6 secreted predominantly from brain and lung (hIL6 tg mice) by backcrossing wild-type C57BL/6J mice 12 times with MUP/hIL6 mice expressing human IL6 cDNA under the control of a mouse urinary protein gene promoter. The hIL6 transgene is expressed predominantly in the brain and the lung (as demonstrated by RT–PCR), (Electronic supplementary material [ESM] Methods, ESM Fig. 1a) [27]. To verify that hIL6 is active in mice, we compared the biological response of wild-type mice to daily injections (50 ng i.p.) of hIL6 or murine IL6 (mIL6) (circulating IL6 143–180 pg/ml, 150 min after injection). Murine IL6 and hIL6 stimulated STAT3 phosphorylation in liver, although the effect of mIL6 was 1.5-fold greater than that of hIL6 (Fig. 1a). Body weight and blood glucose concentrations were unchanged during 3 days of mIL6 or hIL6 injections; however, circulating insulin increased equally during injections with mIL6 or hIL6 (ESM Fig. 1b–d). As previously shown, serum amyloid A protein, a sensitive marker of hepatic acute-phase reaction in mice, increased significantly after mIL6 injections [14, 30]; despite this, hIL6 had no effect upon serum amyloid A concentrations in mice or cultured mouse hepatocytes (ESM Methods, Fig. 1b, ESM Fig. 1e) [31]. In hIL6 tg mice, circulating hIL6 reached 1,150 pg/ml, which was about tenfold higher than the concentration achieved during injection (ESM Methods, ESM Table 1). Nevertheless, hIL6 tg mice displayed no evidence of inflammatory or immunological disturbances in tissue histology as demonstrated by immunostaining, white blood cell count or serum chemistry (ESM Methods, ESM Figs 1f, 2b–d, ESM Tables 1 and 2). In addition, IL6 transgene expression in different brain regions did not trigger inflammatory responses within the central nervous system, as demonstrated by RT–PCR (ESM Methods, ESM Table 3). Thus, hIL6 is biologically active in mice, but did not promote an acute inflammatory response.
Fig. 1.
The effect of human IL6 on growth and diet-induced obesity in mice. a Western blot and densitometric analysis of pSTAT3 and total STAT3 in liver of C57BL/6 mice after three daily injections of mIL6 (50 ng), hIL6 (50 ng) or vehicle. Intensity of pSTAT3 was normalised to STAT3 (n = 10). b Serum amyloid A (SAA) levels measured from random fed mice 150 min after injection of mIL6, hIL6 or vehicle (n = 10). c Average body weights of male hIL6 tg mice on chow diet (white circles; n = 15) and on HFD (white squares; n = 10), or of wild-type mice on chow diet (black circles; n = 15) and on HFD (black squares; n = 10). d Representative images of 24-week-old mice as labelled. e Body composition of 24-week-old wild-type and hIL6 tg mice on chow and HFD measured by DEXA (n = 10–12). f Representative haematoxylin and eosin staining of epididymal adipose tissue of wild-type and hIL6 tg mice aged 24 weeks. Scale bar, 500 µm. g Morphometric analysis of epididymal adipose tissue (n = 5 animals per genotype). Values (where applicable) are mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 for wild-type vs hIL6 tg mice
The hIL6 tg mice maintained between 4 and 24 weeks of age on regular chow (9% of energy derived from fat) were slightly smaller than wild-type mice (Fig. 1c). By comparison, HFD (45% energy derived from fat) caused significant weight gain in wild-type mice, whereas HFD-fed hIL6 tg mice were slightly smaller than chow-fed wild-type mice (Fig. 1c, d). DEXA confirmed that the lean body mass of 24-week-old wild-type or hIL6 tg mice was not influenced by diet. By comparison, HFD increased adipose mass of wild-type mice twofold, but had no effect on hIL6 tg mice (Fig. 1e). Haematoxylin and eosin staining confirmed that adipocytes were 30% smaller (p < 0.05) in HFD-fed hIL6 tg mice than in wild-type mice (Fig. 1f, g). Thus, hIL6 tg mice were slightly smaller and had less visceral fat on a chow diet, whereas HFD-induced obesity was prevented.
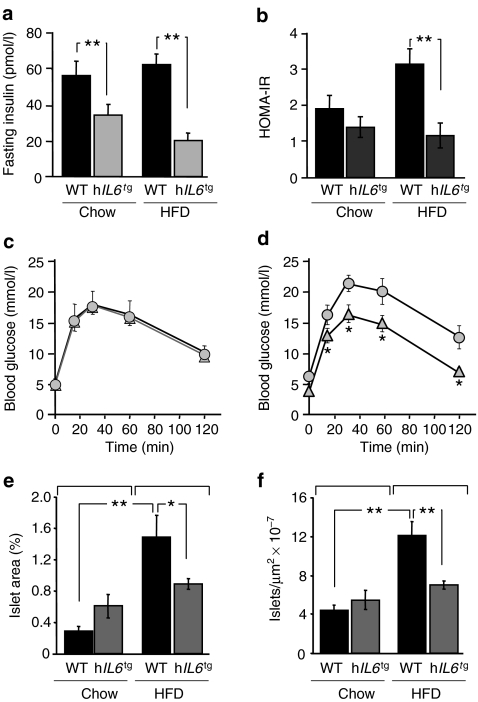
Glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in hIL6tgmice
Although acute treatment of C57BL/6J mice with IL6 causes insulin resistance and hyperinsulinaemia, fasting insulin was unexpectedly low in chow- and HFD-fed hIL6 tg mice (Fig. 2a). The HOMA2 (http://software.informer.com/getfree-homa2-calculator-download/) of insulin resistance confirmed that HFD-fed wild-type mice developed insulin resistance, whereas HFD-fed hIL6 tg mice remained insulin-sensitive (Fig. 2b). Moreover, glucose tolerance in HFD-fed hIL6 tg mice was indistinguishable from that in chow-fed wild-type and hIL6 tg mice, whereas the HFD caused glucose intolerance in wild-type mice (Fig. 2c, d). Consistent with the expected compensatory response to insulin resistance, beta cell mass and islet density increased significantly in HFD-fed wild-type mice; however, beta cell mass in hIL6 tg mice on chow or HFD was indistinguishable from that in chow-fed wild-type and hIL6 tg mice (Fig. 2e, f). Thus, hIL6 prevented diet-induced insulin resistance and compensatory beta cell growth in hIL6 tg mice.
Fig. 2.
Glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in hIL6 tg mice. a Fasting serum insulin levels (n = 10) at 24 weeks. b HOMA index of insulin resistance (IR). c Glucose tolerance test of 24-week-old male mice fed a chow (n = 15) diet or d HFD (n = 10). Circles, wild-type; triangles, hIL6 tg. e Percent of pancreas area that consisted of islets (n = 4 animals per group). f The number of islets per μm2 (n = 4 animals per group). Data are expressed as average ± SEM. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 for wild-type vs hIL6 tg mice
Hepatic metabolism and signalling in hIL6tgmice
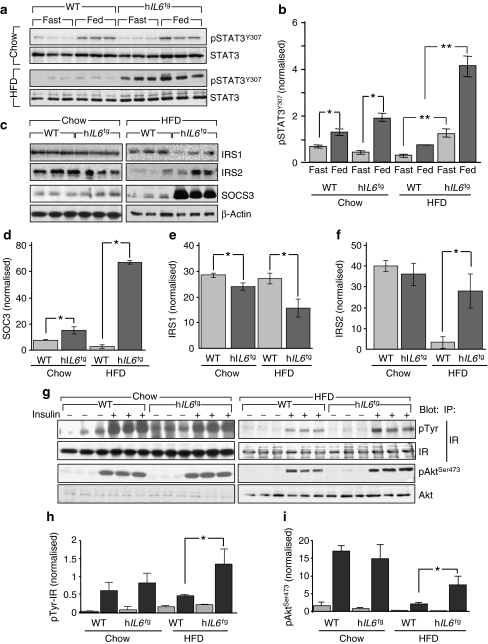
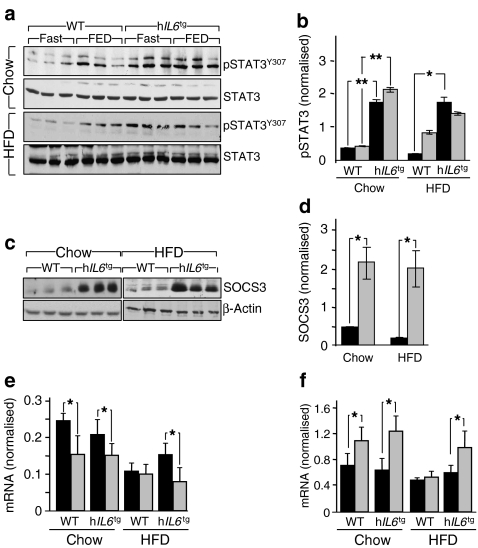
IL6 has contradictory effects upon hepatic glucose metabolism due at least in part to the opposing action of hepatic STAT3 signalling. Under ordinary conditions, STAT3 mediates the suppressive effect of IL6 on hepatic glucose production [32]. However, during obesity IL6 inhibits peripheral insulin signalling by stimulating STAT3 to SOCS3 signalling [33]. In the present study, postprandial STAT3 phosphorylation increased in chow-fed wild-type and hIL6 tg mice; however, STAT3 phosphorylation was barely detected in HFD-fed wild-type mice (Fig. 3a, b). Basal and postprandial STAT3 phosphorylation increased significantly in HFD-fed hIL6 tg mice, consistent with the improved glucose tolerance under these conditions (Fig. 3a).
Fig. 3.
Hepatic metabolism and signalling in hIL6 tg mice. a Western blot analysis and b quantification of pSTAT3 normalised to STAT3 in liver of wild-type and hIL6 tg mice aged 24 weeks and maintained on chow and HFD. c Western blot analysis of IRS1, IRS2 and SOCS3 normalised to β-actin in liver of mice as above (a), with bar graph quantification for SOCS3 (d), IRS1 (e) and IRS2 (f). g Insulin receptor (IR) level and tyrosine and Aktser473 phosphorylation in mice as above (a), but aged 17 weeks and on chow and HFD stimulated with insulin by i.v. injection. h, i Quantification of blot (g). Light grey, no insulin; dark grey, insulin. Results, where applicable, were normalised to loading controls and are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 6. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 for wild-type mice vs hIL6 tg mice
As expected, liver SOCS3 levels were related to STAT3 phosphorylation. Compared with chow-fed wild-type mice, SOCS3 increased in chow-fed hIL6 tg mice, decreased in HFD-fed wild-type mice and increased tenfold in HFD-fed hIL6 tg mice (Fig. 3c, d). The postprandial IRS1 concentration decreased significantly in the liver of chow-fed and HFD-fed hIL6 tg mice, which correlated with increased SOCS3 concentration as previously described (Fig. 3c, e) [33]. By comparison, hIL6 had no effect on liver IRS2 concentrations in chow-fed mice, whereas it prevented loss of IRS2 in HFD-fed hIL6 tg mice (Fig. 3d, f). Thus changes in IRS1 and IRS2 concentrations were poor predictors of the effect of hIL6 upon systemic glucose homeostasis and peripheral insulin sensitivity.
The insulin receptor mediates tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS1 and IRS2, which directly activates the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase to Akt cascade in all cells. Insulin stimulated equally insulin receptor phosphorylation and AktSer473 phosphorylation in liver of chow-fed wild-type and hIL6 tg mice; however, insulin-stimulated insulin receptor phosphorylation in HFD-fed hIL6 tg mice was significantly stronger than in HFD-fed wild-type mice (Fig. 3g, h). Consistent with these results, insulin-stimulated AktSer473 phosphorylation in HFD-fed hIL6 tg mice was also increased compared with HFD-fed wild-type mice (Fig. 3g, i). This pattern of insulin receptor and Akt phosphorylation might explain in part the positive effect of hIL6 upon insulin sensitivity in hIL6 tg mice.
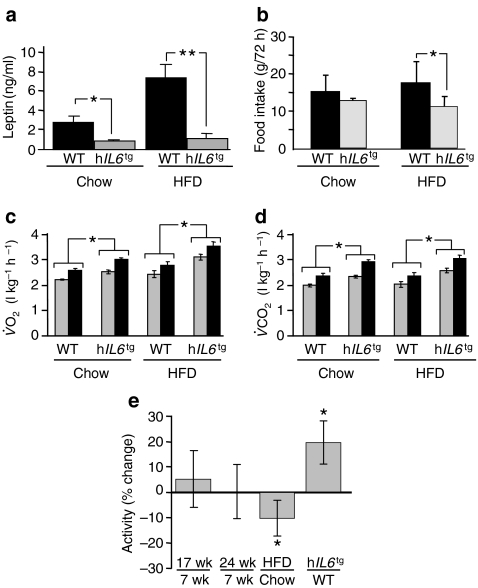
Energy balance in hIL6 tg mice Excess food intake relative to energy expenditure promotes obesity, a process in which leptin plays an important regulatory role [34]. At 6 months of age, wild-type and hIL6 tg mice were monitored for 72 h in the comprehensive lab animal monitoring system. Food intake by chow-fed wild-type and hIL6 tg mice was indistinguishable, whereas circulating leptin decreased significantly in the latter (Fig. 4a, b). These results suggest that chow-fed hIL6 tg mice were more sensitive to leptin than wild-type mice. Compared with chow-fed wild-type mice, leptin increased significantly in HFD-fed wild-type mice, while food intake in both groups was indistinguishable, suggesting that wild-type mice developed leptin resistance on HFD (Fig. 4a, b). By comparison, leptin decreased sevenfold in HFD-fed hIL6 tg mice, while food intake decreased. Since adipose mass was equal in hIL6 tg mice on chow or HFD (Fig. 1e), these results suggest that hIL6 promotes leptin sensitivity in hIL6 tg mice.
Fig. 4.
Energy balance in hIL6
tg mice. a Serum leptin concentrations (n = 10–12) in 24-week-old wild-type and hIL6
tg mice maintained on chow diet or HFD. b Male mice at 24 weeks of age were monitored for 72 h in the comprehensive lab animal monitoring system (n = 10 mice per group) to assess food intake, c oxygen consumption ( ) and d carbon dioxide production (
) and d carbon dioxide production ( ). Significance (*p < 0.05) was determined by generalised linear model. e Locomotor activity of mice aged 7, 17 and 24 weeks during the light and dark cycles was analysed by logistic regression (SPSS) of the beam breaks classified above or below the median of 96 breaks in a 5-min test interval. Values for change relative to the control are mean ± SEM. All other values (a–d) are means ± SEM. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 for wild-type vs hIL6
tg mice. Wk, weeks
). Significance (*p < 0.05) was determined by generalised linear model. e Locomotor activity of mice aged 7, 17 and 24 weeks during the light and dark cycles was analysed by logistic regression (SPSS) of the beam breaks classified above or below the median of 96 breaks in a 5-min test interval. Values for change relative to the control are mean ± SEM. All other values (a–d) are means ± SEM. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 for wild-type vs hIL6
tg mice. Wk, weeks
Regardless of diet, the hIL6 tg mice consumed more oxygen and expelled more CO2 than wild-type mice during the light and dark phases (Fig. 4c, d). They also displayed 20% more voluntary movement than wild-type controls, when controlling for age, time of day and diet (Fig. 4e). Thus, diet-induced obesity was probably avoided in hIL6 tg mice by a combination of reduced food intake and increased activity and energy expenditure, which was associated with increased leptin sensitivity.
Central regulation of feeding behaviour in hIL6tgmice
Intracerebral IL6 injections can prevent obesity in Il6 −/− mice, suggesting that IL6 might affect central regulation of nutrient homeostasis [26]. We investigated the STAT3 to SOCS3 signalling cascade in the hypothalamus of wild-type and hIL6 tg mice, where this pathway plays an important role in regulating expression of Pomc and Agrp [35]. Compared with wild-type mice and regardless of diet, STAT3 phosphorylation was significantly increased in fasted hIL6 tg mice; however, feeding increased STAT3 phosphorylation only in HFD-fed wild-type mice (Fig. 5a, b). Consistent with these results, chow- and HFD-fed hIL6 tg mice displayed a significant tenfold increase in hypothalamic SOCS3 protein compared with wild-type mice (Fig. 5c, d).
Fig. 5.
Central regulation of feeding behaviour in hIL6 tg mice. a Western blot analysis of pSTAT3, normalised to STAT3, in hypothalamus of wild-type and hIL6 tg mice aged 24 weeks and on chow or HFD (16 h fasting [Fast] and 4 h refeeding [FED]), with b quantification as mean ± SEM (n = 6). Black bars, fasted; grey bars, fed. c Western blot analysis of SOCS3 normalised to β-actin in the hypothalamus of wild-type and hIL6 tg mice aged 24 weeks and on chow or HFD, with d quantification as mean ± SEM (n = 6). Black bars, wild-type; grey bars, hIL6 tg. e Levels of Agrp mRNA and (f) of Pomc mRNA from hypothalamus of wild-type and hIL6 tg mice, as determined by semi-quantitative RT–PCR. Mice were 24 weeks old and maintained on chow or HFD (24 h fasted, black bars; 8 h feeding, grey bars), n = 6, values means ± SEM. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 for wild-type mice vs hIL6 tg mice
We used semi-quantitative RT–PCR to determine whether hIL6 altered expression of Agrp and Pomc. As expected, feeding suppressed expression of the former and increased expression of the latter in chow-fed wild-type and hIL6 tg mice (Fig. 5e, f). By comparison, expression of Agrp and Pomc was reduced and insensitive to feeding in HFD-fed wild-type mice, whereas expression in HFD-fed hIL6 tg mice responded normally to feeding (Fig. 5e, f). Thus, hIL6 had multiple effects in the hypothalamus of mice on HFD; these effects were consistent with increased energy utilisation, reduced food intake and changes in peripheral glucose homeostasis.
The effect of human IL6 in ob/ob mice
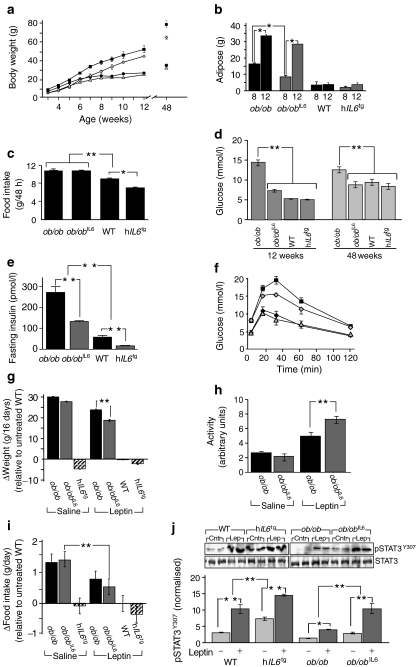
Ob/ob mice are hyperphagic, obese and develop severe insulin resistance that progresses to diabetes; however, peripheral injections of leptin can restore nutrient homeostasis [36]. We created ob/ob IL6 mice to determine whether hIL6 could restore nutrient homeostasis without leptin. As expected, ob/ob mice on a chow diet were heavier than wild-type mice between 4 and 12 weeks of age (Fig. 6a). Until 7 weeks, both hIL6 tg and ob/ob IL6 mice had reduced body mass compared with wild-type mice (Fig. 6a). However, at 8 weeks the ob/ob IL6 mice were slightly heavier than wild-type and hIL6 tg mice, gaining weight until the ob/ob IL6 mice were only 3.3 ± 0.3 g (p < 0.0001) lighter than ob/ob mice at 12 weeks of age (Fig. 6a). DEXA analysis showed that ob/ob IL6 mice accumulated less adipose mass than ob/ob mice at 8 weeks of age, whereas the adipose mass was indistinguishable by 12 weeks (Fig. 6b). Compared with wild-type and hIL6 tg mice, food intake during a 48 h period was significantly greater and indistinguishable in ob/ob and ob/ob IL6 mice (Fig. 6c). By 48 weeks, the ob/ob mice were heavier than ob/ob IL6 mice (ob/ob 78 g, ob/ob IL6 65 g; p < 0.05), whereas wild-type and hIL6 tg mice had identical weights (wild-type 34.7 g, hIL6 tg 32.8 g; p = 0.7) (Fig. 6a). Thus, hIL6 largely failed to restore nutrient homeostasis in ob/ob IL6 mice.
Fig. 6.
Effect of human IL6 in ob/ob mice. a Average body weights of male ob/ob (black squares), ob/ob IL6 (grey rhombs), wild-type (black circles) and hIL6 tg (grey triangles) mice (n = 6–8) on chow diet. p < 0.001 for ob/ob IL6 vs ob/ob; p = 0.7 for wild-type vs hIL6 tg. b Adipose mass determined by DEXA of mice at 8 and 12 weeks of age (n = 6–8). c Food intake (average ± SEM, n = 6) of 12-week-old male mice maintained on a chow diet. d Fed blood glucose at 12 and 48 weeks of age; e fasting circulating insulin concentration; and f glucose tolerance test (key as above [a]). Blood glucose was plotted at the indicated time intervals after intraperitoneal injection of 0.75 g of d-glucose/kg body weight. g Body weight relative to chow-fed wild-type mice was determined over 16 days. h Spontaneous activity determined in the comprehensive lab animal monitoring system. i Daily food intake (mean ± SEM) relative to untreated wild-type mice was determined over 16 days. Significant differences in body weight (g) and food intake (i) were determined by generalised linear model with the presence or absence of leptin injections, hIL6 transgene or the ob/ob genotype were used as categorical predictors, as the initial body weight and day of measurement were fixed at 4.82 and 42.1 g, respectively. j Western blot analysis of pSTAT3, normalised to STAT3, in hypothalamus of ob/ob, ob/ob IL6, wild-type and hIL6 tg mice, with quantification by bar graph. Values are mean ± SEM; significant differences were determined by a generalised linear model, using the Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01
Despite the fact that the adipose mass was equal in ob/ob and ob/ob IL6 mice at 12 weeks, the fed blood glucose and fasted insulin concentrations were reduced 50% in the latter (Fig. 6d, e). Despite this, ob/ob and ob/ob IL6 mice were diabetic, as their fasting blood glucose and glucose tolerance were dysregulated compared with wild-type and hIL6 tg mice (Fig. 6f). By 48 weeks of age, fed blood glucose was indistinguishable in wild-type, hIL6 tg and ob/ob IL6 mice, and significantly lower than in ob/ob mice (Fig. 6d). Thus, hIL6 promotes glucose homeostasis in old obese ob/ob IL6 mice.
To directly establish the effect of hIL6 upon leptin action, we injected leptin intraperitoneally into 12-week-old chow-fed mice. A typical daily dose of leptin (1 mg/kg body weight) decreased food intake and body weight of ob/ob and ob/ob IL6 mice (data not shown). To better distinguish the effect of leptin in these two groups, we injected a low dose of leptin (0.1 mg/kg) daily for 16 days. Compared with ob/ob mice, low-dose leptin significantly decreased body weight and increased locomotor activity of obese ob/ob IL6 mice; however, low-dose leptin had no effect in chow-fed wild-type or hIL6 tg mice, and was too low to significantly reduce food consumption by ob/ob mice (Δfood = −0.5±0.3 g, p > 0.05) (Fig. 6g–i). Low-dose leptin did, however, significantly reduce food consumption by ob/ob IL6 mice (Δfood = −1.0±0.2 g/day, p < 0.001) (Fig. 6i). To establish whether hIL6 increases central leptin signalling, we compared STAT3 phosphorylation in the hypothalamus of 1-year-old wild-type, hIL6 tg, ob/ob and ob/ob IL6 mice at 2 h after a single low-dose leptin injection. Compared with wild-type mice, basal and leptin-stimulated STAT3 phosphorylation was significantly increased in hIL6 tg mice, but significantly decreased in ob/ob mice (Fig. 6j). Remarkably, basal and leptin-stimulated STAT3 phosphorylation in ob/ob IL6 mice was indistinguishable from that in wild-type mice (Fig. 6j). These results support the hypothesis that circulating hIL6 augments central leptin signalling and action, revealing the principle mechanism by which hIL6 promotes nutrient homeostasis in hIL6 tg mice.
Discussion
Despite evidence of pleotropic and contradictory actions of IL6 upon glucose tolerance in rodent models and human studies, our experiments show clearly that overexpression of hIL6 in brain and lung of hIL6 tg mice reduces daily food consumption and promotes energy expenditure. Consistent with the reduced adiposity, circulating insulin decreases and glucose tolerance improves, confirming that hIL6 promotes systemic insulin sensitivity, especially in animals on HFD. Moreover, circulating leptin and daily food consumption decreases, suggesting that hIL6 improves central leptin sensitivity or action.
Previous reports have shown that central leptin signalling requires IL6-mediated signals for a normal response. Thus Il6 −/− mice slowly develop obesity while circulating leptin increases, and obese Il6 −/− mice do not respond to intracranial leptin injections [26]. By contrast, circulating leptin decreases significantly in hIL6 tg mice on chow or HFD. Since leptin signalling is required in the hypothalamus to suppress appetite and promote energy expenditure, hIL6 apparently augments leptin action: otherwise the hIL6 tg mice would consume more food and accumulate adipose mass [23]. In our study, only ob/ob IL6 mice responded significantly to low-dose leptin injections with greater locomotor activity accompanied by decreased body weight and food consumption. Thus our results support the hypothesis that life-long hIL6 promotes central leptin signalling, which prevents diet-induced obesity in mice.
The signalling subunit gp130 of the IL6 receptor complex is similar structurally to the intracellular tail of the signalling-isoform of the leptin receptor, isoform b (LepRb) [37]. Consistent with the shared regulation of STAT3 phosphorylation by leptin and IL6, Pomc and Agrp expression in our study was nearly normal in hIL6 tg mice on a HFD. However, the effect of hIL6 upon Pomc and Agrp regulation appears to occur through its effects upon leptin signalling, as ob/ob and ob/ob IL6 mice were equally hyperphagic.
STAT3 to SOCS3 signalling is stimulated by leptin in the hypothalamus and throughout the body by numerous factors including IL6, IFN-γ, IL10, CNTF (ciliary neurotrophic factor) and other gp130 signalling cytokines [2]. However, the leptin response increased while SOCS3 production also increased in the hypothalamus of lean hIL6 tg mice, suggesting that SOCS3 does not inexorably block the leptin signal. Direct comparison of hypothalamic STAT3 phosphorylation in ob/ob and ob/ob IL6 mice shows that hIL6 weakly promoted STAT3 phosphorylation in the absence of leptin. Thus, hIL6 largely promotes the leptin-stimulated STAT3 to SOCS3 cascade, which maintains the normal relation between leptin and SOCS3.
We posit that IL6 receptor α-neurons are separate from LepRb-neurons, since hIL6 failed to normalise body weight or food intake in ob/ob IL6 mice. However, IL6 receptor α-neurons might converge upon a common efferent circuit, ordinarily regulated by LepRb neurons, to augment leptin signalling in ob/ob mice or wild-type mice on the HFD. A similar relation appears to exist between CNTF receptor neurons and LepRb neurons [2]. LepRb and the CNTF receptor share structural homology and can activate similar signalling pathways in the hypothalamus. In the absence of CNTF receptor, CNTF can activate gp130 through a homodimer of IL6 receptor and leukaemia inhibitory factor receptor (LIFR) [38]. CNTF can ameliorate obesity by circumventing diet-induced leptin resistance [39]. It remains to be investigated whether CNTF mediates any of the central effects of IL6.
Cell-based experiments suggest that the IL6-stimulated STAT3 to SOCS3 cascade causes hepatic insulin resistance by inhibiting insulin receptor signalling and increasing IRS1 degradation [10]. In parallel with increasing SOCS3 concentrations, IRS1 concentrations in the present study decreased in the postprandial liver of hIL6 tg mice; however, hIL6 prevented the near complete loss of insulin-stimulated insulin receptor autophosphorylation and the downstream phosphorylation of IRS2 and Aktser473 in animals on HFD, a finding consistent with improved systemic glucose tolerance. Recently, the negative effect of SOCS3 on insulin action has been questioned, since liver-specific Stat3 −/− mice with low SOCS3 concentrations were unable to suppress hepatic glucose production [32]. The strongest effect of mIL6 upon liver metabolism might depend upon hypothalamic STAT3 signalling, which mediates the normalising effect of leptin on hepatic insulin action in rats on a HFD [35]. Intracerebral ventricular insulin infusion has been shown to increase levels of mIL6 in the liver, which can increase hepatic STAT3 and through that suppress expression of gluconeogenic enzymes [32]. Thus hepatic IL6 to STAT3 signalling triggered by brain insulin action could play an important role in nutrient homeostasis. However, in animals on a chow diet hIL6 might not be sufficient, because STAT3 phosphorylation did not increase in fasted hIL6 tg mice, while increasing equally in wild-type and hIL6 tg mice. Whereas the HFD inhibited hepatic STAT3 phosphorylation in our study, hIL6 strongly promoted basal and postprandial STAT3 phosphorylation. Thus a postprandial signal, perhaps initiated by insulin and/or leptin in the hypothalamus, appears to be essential for hepatic STAT3 phosphorylation.
The question of whether IL6 has positive or negative effects on metabolism is the subject of continuing controversy [8]. The hypothesis that IL6 induces insulin resistance is challenged by findings that regular physical exercise increases insulin sensitivity while promoting production and release of IL6 from contracting skeletal muscle [40, 41]. IL6 can also increase peripheral insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in muscle [17, 42]. Here, however, hIL6 had no effect on AMPK phosphorylation or activity in hIL6 tg mice (data not shown). Further investigation regarding a potential of AMPK to mediate some of the effects of hIL6 is required.
The relation between IL6 and leptin in the central nervous system might play an important role on the effect of exercise upon nutrient homeostasis. Moderate exercise promotes peripheral insulin sensitivity and suppresses weight gain [43]. Human IL6 secretion from skeletal muscle is dramatically increased during and after exercise [44]. Our results are consistent with the hypothesis that the effect of exercise upon nutrient homeostasis and insulin sensitivity might be mediated through central effects of muscle-derived IL6 in promoting central leptin signalling.
Our results are consistent with the hypothesis that decreased fat mass in hIL6 tg mice, especially those on HFD, arises through increased energy expenditure. Thus oxygen consumption, CO2 production and physical activity were increased in the hIL6 tg mice. These data are consistent with previous reports that a single intracranial injection of IL6 increases oxygen consumption and energy expenditure by rats [22, 26].
Chronic cerebral expression of mIL6, using an IL6 transgene under the control of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) promoter, activates the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, which increases corticosterone concentrations in stressed mice [45]. However, in our experiments, plasma corticosterone concentrations were barely increased in unstressed hIL6 tg mice compared with control mice and increased equally in both mice during stress (data not shown). However, as in our hIL6 tg mice, the plasma leptin concentration was reduced in GFAP-IL6 transgenic mice [45]. Since circulating IL6 was not elevated in those GFAP-IL6 mice, those results support the hypothesis that hIL6 promotes leptin action in the central nervous system.
Previous reports have shown that transgenic IL6 causes various pathologies of the immune system that can be fatal to mice [46, 47]. Human IL6 in C57BL/6J mice under the control of human immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer develop mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis with massive IgG1 plasmacytosis [48]. MTI/IL6 transgenic mice expressing murine IL6 constitutively in the liver developed progressive kidney damage and died between 12 and 20 weeks of age [49]. Hepatic inflammation occurs in transgenic mouse secreting mIL6 from muscle [14]. Despite the above, our hIL6 tg mice with circulating hIL6 secreted from brain and lung never displayed hepatic inflammation, acute inflammatory response or systemic inflammation. Perhaps the sites of IL6 secretion are critical for its systemic effect. In any case, hIL6 tg mice provide a unique system to investigate the role of hIL6 in central and peripheral nutrient homeostasis.
In summary, hIL6 protects mice from insulin resistance and obesity. Since this effect was not observed in ob/ob mice, hIL6 apparently augments central leptin action without substituting for leptin. Due to its immunoreactive nature, IL6 might never be a successful therapeutic treatment strategy; however, prolonged treatment with IL6 homologues with high accessibility to the central nervous system might show therapeutic promise in anti-obesity therapy.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
(PDF 19 kb)
(PDF 52 kb)
(PDF 85 kb)
(PDF 222 kb)
(PDF 134 kb)
(PDF 49 kb)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by American Diabetes Association grant 105RA143 and NIH ROI grant DK038712 to M. F. White. The authors thank A. Parlow, National Pituitary Program (NIDDK) for kindly providing us with the recombinant mouse leptin.
Duality of interest
The authors declare that there is no duality of interest associated with this manuscript.
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Abbreviations
- AMPK
AMP-activated protein kinase
- CNTF
Ciliary neurotrophic factor
- DEXA
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
- GFAP
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- HFD
High-fat diet
- hIL6
Human IL6
- hIL6tg mice
Mice with sustained circulating human IL6 secreted predominantly from brain and lung
- LepRb
Leptin receptor, isoform b
- mIL6
Murine IL6
- SOCS3
Suppressor of cytokine signalling
- STAT3
Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3
References
- 1.Glund S, Krook A. Role of interleukin-6 signalling in glucose and lipid metabolism. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2008;192:37–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2007.01779.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Febbraio MA. gp130 receptor ligands as potential therapeutic targets for obesity. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:841–849. doi: 10.1172/JCI30453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gabay C. Interleukin-6 and chronic inflammation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(Suppl 2):S3. doi: 10.1186/ar1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature. 2006;444:860–867. doi: 10.1038/nature05485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Vozarova B, Weyer C, Hanson K, Tataranni PA, Bogardus C, Pratley RE. Circulating interleukin-6 in relation to adiposity, insulin action, and insulin secretion. Obes Res. 2001;9:414–417. doi: 10.1038/oby.2001.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Carey AL, Bruce CR, Sacchetti M, et al. Interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha are not increased in patients with type 2 diabetes: evidence that plasma interleukin-6 is related to fat mass and not insulin responsiveness. Diabetologia. 2004;47:1029–1037. doi: 10.1007/s00125-004-1403-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Petersen AM, Pedersen BK. The role of IL-6 in mediating the anti-inflammatory effects of exercise. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2006;57(Suppl 10):43–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pedersen BK, Febbraio MA. Muscle as an endocrine organ: focus on muscle-derived interleukin-6. Physiol Rev. 2008;88:1379–1406. doi: 10.1152/physrev.90100.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Senn JJ, Klover PJ, Nowak IA, Mooney RA. Interleukin-6 induces cellular insulin resistance in hepatocytes. Diabetes. 2002;51:3391–3399. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.51.12.3391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Senn JJ, Klover PJ, Nowak IA, et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 (SOCS-3), a potential mediator of interleukin-6-dependent insulin resistance in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:13740–13746. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M210689200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kim HJ, Higashimori T, Park SY, et al. Differential effects of interleukin-6 and -10 on skeletal muscle and liver insulin action in vivo. Diabetes. 2004;53:1060–1067. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.4.1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Klover PJ, Zimmers TA, Koniaris LG, Mooney RA. Chronic exposure to interleukin-6 causes hepatic insulin resistance in mice. Diabetes. 2003;52:2784–2789. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.52.11.2784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Klover PJ, Clementi AH, Mooney RA. Interleukin-6 depletion selectively improves hepatic insulin action in obesity. Endocrinology. 2005;146:3417–3427. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-1468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Franckhauser S, Elias I, Rotter SV, et al. Overexpression of Il6 leads to hyperinsulinaemia, liver inflammation and reduced body weight in mice. Diabetologia. 2008;51:1306–1316. doi: 10.1007/s00125-008-0998-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.van Hall G, Steensberg A, Sacchetti M, et al. Interleukin-6 stimulates lipolysis and fat oxidation in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:3005–3010. doi: 10.1210/jc.2002-021687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Petersen EW, Carey AL, Sacchetti M, et al. Acute IL-6 treatment increases fatty acid turnover in elderly humans in vivo and in tissue culture in vitro. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2005;288:E155–E162. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00257.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Carey AL, Steinberg GR, Macaulay SL, et al. Interleukin-6 increases insulin-stimulated glucose disposal in humans and glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation in vitro via AMP-activated protein kinase. Diabetes. 2006;55:2688–2697. doi: 10.2337/db05-1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Trujillo ME, Sullivan S, Harten I, Schneider SH, Greenberg AS, Fried SK. Interleukin-6 regulates human adipose tissue lipid metabolism and leptin production in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:5577–5582. doi: 10.1210/jc.2004-0603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pedersen BK, Bruunsgaard H, Ostrowski K, et al. Cytokines in aging and exercise. Int J Sports Med. 2000;21(Suppl 1):S4–S9. doi: 10.1055/s-2000-1444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pedersen BK, Fischer CP. Physiological roles of muscle-derived interleukin-6 in response to exercise. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2007;10:265–271. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e3280ebb5b3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Starkie R, Ostrowski SR, Jauffred S, Febbraio M, Pedersen BK. Exercise and IL-6 infusion inhibit endotoxin-induced TNF-alpha production in humans. FASEB J. 2003;17:884–886. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-0670fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wallenius K, Wallenius V, Sunter D, Dickson SL, Jansson JO. Intracerebroventricular interleukin-6 treatment decreases body fat in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;293:560–565. doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00230-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Myers MG, Cowley MA, Munzberg H. Mechanisms of leptin action and leptin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol. 2007;70:537–556. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.70.113006.100707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Takahashi N, Patel HR, Qi Y, Dushay J, Ahima RS. Divergent effects of leptin in mice susceptible or resistant to obesity. Horm Metab Res. 2002;34:691–697. doi: 10.1055/s-2002-38251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Spiegelman BM, Flier JS. Obesity and the regulation of energy balance. Cell. 2001;104:531–543. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wallenius V, Wallenius K, Ahren B, et al. Interleukin-6-deficient mice develop mature-onset obesity. Nat Med. 2002;8:75–79. doi: 10.1038/nm0102-75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lieskovska J, Guo D, Derman E. IL-6-overexpression brings about growth impairment potentially through a GH receptor defect. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2002;12:388–398. doi: 10.1016/S1096-6374(02)00079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Withers DJ, Burks DJ, Towery HH, Altamuro SL, Flint CL, White MF. Irs-2 coordinates Igf-1 receptor-mediated beta-cell development and peripheral insulin signalling. Nat Genet. 1999;23:32–40. doi: 10.1038/12631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dong X, Park S, Lin X, Copps K, Yi X, White MF. Irs1 and Irs2 signaling is essential for hepatic glucose homeostasis and systemic growth. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:101–114. doi: 10.1172/JCI25735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Han CY, Chiba T, Campbell JS, et al. Reciprocal and coordinate regulation of serum amyloid A vs apolipoprotein A-I and paraoxonase-1 by inflammation in murine hepatocytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:1806–1813. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000227472.70734.ad. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Migita K, Miyashita T, Maeda Y, et al. An active metabolite of leflunomide, A77 1726, inhibits the production of serum amyloid A protein in human hepatocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2005;44:443–448. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Inoue H, Ogawa W, Asakawa A, et al. Role of hepatic STAT3 in brain-insulin action on hepatic glucose production. Cell Metab. 2006;3:267–275. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lebrun P, Van Obberghen E. SOCS proteins causing trouble in insulin action. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2008;192:29–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2007.01782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Myers MG., Jr Leptin receptor signaling and the regulation of mammalian physiology. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2004;59:287–304. doi: 10.1210/rp.59.1.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Buettner C, Pocai A, Muse ED, Etgen AM, Myers MG, Jr, Rossetti L. Critical role of STAT3 in leptin's metabolic actions. Cell Metab. 2006;4:49–60. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.04.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Seufert J, Kieffer TJ, Habener JF. Leptin inhibits insulin gene transcription and reverses hyperinsulinemia in leptin-deficient ob/ob mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:674–679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ernst M, Jenkins BJ. Acquiring signalling specificity from the cytokine receptor gp130. Trends Genet. 2004;20:23–32. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2003.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Schuster B, Kovaleva M, Sun Y, et al. Signaling of human ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) revisited. The interleukin-6 receptor can serve as an alpha-receptor for CTNF. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:9528–9535. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M210044200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Steinberg GR, Watt MJ, Fam BC, et al. Ciliary neurotrophic factor suppresses hypothalamic AMP-kinase signaling in leptin-resistant obese mice. Endocrinology. 2006;147:3906–3914. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-1587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Febbraio MA, Hiscock N, Sacchetti M, Fischer CP, Pedersen BK. Interleukin-6 is a novel factor mediating glucose homeostasis during skeletal muscle contraction. Diabetes. 2004;53:1643–1648. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.53.7.1643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Steensberg A, van Hall G, Osada T, Sacchetti M, Saltin B, Klarlund PB. Production of interleukin-6 in contracting human skeletal muscles can account for the exercise-induced increase in plasma interleukin-6. J Physiol. 2000;529(Pt 1):237–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00237.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ruderman NB, Keller C, Richard AM, et al. Interleukin-6 regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Potential role in the systemic response to exercise and prevention of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes. 2006;55(Suppl 2):S48–S54. doi: 10.2337/db06-S007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Flores MB, Fernandes MF, Ropelle ER, et al. Exercise improves insulin and leptin sensitivity in hypothalamus of Wistar rats. Diabetes. 2006;55:2554–2561. doi: 10.2337/db05-1622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Pedersen BK. IL-6 signalling in exercise and disease. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007;35:1295–1297. doi: 10.1042/BST0351295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Raber J, O'Shea RD, Bloom FE, Campbell IL. Modulation of hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal function by transgenic expression of interleukin-6 in the CNS of mice. J Neurosci. 1997;17:9473–9480. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-24-09473.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Suematsu S, Matsuda T, Aozasa K, et al. IgG1 plasmacytosis in interleukin 6 transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86:7547–7551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hirano T, Suematsu S, Matsusaka T, Matsuda T, Kishimoto T. The role of interleukin 6 in plasmacytomagenesis. Ciba Found Symp. 1992;167:188–196. doi: 10.1002/9780470514269.ch12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Katsume A, Miyai T, Suzuki H, et al. Interleukin-6 overexpression cannot generate serious disorders in severe combined immunodeficiency mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1997;82:117–124. doi: 10.1006/clin.1996.4278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Fattori E, Della RC, Costa P, et al. Development of progressive kidney damage and myeloma kidney in interleukin-6 transgenic mice. Blood. 1994;83:2570–2579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(PDF 19 kb)
(PDF 52 kb)
(PDF 85 kb)
(PDF 222 kb)
(PDF 134 kb)
(PDF 49 kb)