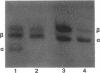
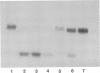
Abstract
The mechanism of hybrid-arrested translation by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides has been investigated with the rabbit reticulocyte lysate system. The oligonucleotides studied were directed against different regions of mouse alpha- or beta-globin mRNAs. Freshly prepared reticulocyte lysates were found to contain 1-2% of the level of RNase H in nucleated cells. This level of activity was sufficient to cleave nearly 100% of the targeted mRNA at the site of hybridization with a complementary oligodeoxynucleotide in 1 hr under conditions of active translation. Using poly(rA).oligo(dT) as a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme, hybrid arrest by oligodeoxynucleotides complementary to the sequence spanning the initiation codon or to a sequence in the coding region was found to be due entirely to cleavage of mRNA by RNase H. Hybridization of oligodeoxynucleotides adjacent to the cap site of beta-globin mRNA, but not the alpha-globin mRNA, also inhibited protein synthesis directly. Even in this case, however, cleavage of the mRNA by RNase H was the predominant pathway of inhibition.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agris C. H., Blake K. R., Miller P. S., Reddy M. P., Ts'o P. O. Inhibition of vesicular stomatitis virus protein synthesis and infection by sequence-specific oligodeoxyribonucleoside methylphosphonates. Biochemistry. 1986 Oct 7;25(20):6268–6275. doi: 10.1021/bi00368a065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake K. R., Murakami A., Miller P. S. Inhibition of rabbit globin mRNA translation by sequence-specific oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6132–6138. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake K. R., Murakami A., Spitz S. A., Glave S. A., Reddy M. P., Ts'o P. O., Miller P. S. Hybridization arrest of globin synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates and cells by oligodeoxyribonucleoside methylphosphonates. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6139–6145. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave C., Loreau N., Thuong N. T., Toulmé J. J., Hélène C. Enzymatic amplification of translation inhibition of rabbit beta-globin mRNA mediated by anti-messenger oligodeoxynucleotides covalently linked to intercalating agents. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4717–4736. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cazenave C., Loreau N., Toulmé J. J., Hélène C. Anti-messenger oligodeoxynucleotides: specific inhibition of rabbit beta-globin synthesis in wheat germ extracts and Xenopus oocytes. Biochimie. 1986 Sep;68(9):1063–1069. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)80180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelissen A. W., Verspieren M. P., Toulmé J. J., Swinkels B. W., Borst P. The common 5' terminal sequence on trypanosome mRNAs: a target for anti-messenger oligodeoxynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5605–5614. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dash P., Lotan I., Knapp M., Kandel E. R., Goelet P. Selective elimination of mRNAs in vivo: complementary oligodeoxynucleotides promote RNA degradation by an RNase H-like activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7896–7900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan J. M., Waxman L., Goldberg A. L. Red blood cells contain a pathway for the degradation of oxidant-damaged hemoglobin that does not require ATP or ubiquitin. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5705–5713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrick L. M., Dembure P. P., Garrick M. D. Interaction between the synthesis of alpha and beta globin. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Oct 15;58(2):339–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02380.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goossens M., Kan Y. Y. DNA analysis in the diagnosis of hemoglobin disorders. Methods Enzymol. 1981;76:805–817. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)76159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Pines O., Inouye M. The role of antisense RNA in gene regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:569–597. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta K. C. Antisense oligodeoxynucleotides provide insight into mechanism of translation initiation of two Sendai virus mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7492–7496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberkern R. C., Cantoni G. L. Studies on a calf thymus ribonuclease specific for ribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybrids. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 19;12(13):2389–2395. doi: 10.1021/bi00737a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeuptle M. T., Frank R., Dobberstein B. Translation arrest by oligodeoxynucleotides complementary to mRNA coding sequences yields polypeptides of predetermined length. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1427–1448. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izant J. G., Weintraub H. Constitutive and conditional suppression of exogenous and endogenous genes by anti-sense RNA. Science. 1985 Jul 26;229(4711):345–352. doi: 10.1126/science.2990048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabat D., Chappell M. R. Competition between globin messenger ribonucleic acids for a discriminating initiation factor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2684–2690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki E. S. Quantitative hybridization-arrest of mRNA in Xenopus oocytes using single-stranded complementary DNA or oligonucleotide probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 11;13(13):4991–5004. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.13.4991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson T. G., Ray B. K., Dodds J. T., Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Merrick W. C., Betsch D. F., Weith H. L., Thach R. E. Influence of 5' proximal secondary structure on the translational efficiency of eukaryotic mRNAs and on their interaction with initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):13979–13989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaitre M., Bayard B., Lebleu B. Specific antiviral activity of a poly(L-lysine)-conjugated oligodeoxyribonucleotide sequence complementary to vesicular stomatitis virus N protein mRNA initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber S. A., Cash F. E., Shakin S. H. Translationally associated helix-destabilizing activity in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15597–15602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher L. J., 3rd, Dolnick B. J. Specific hybridization arrest of dihydrofolate reductase mRNA in vitro using anti-sense RNA or anti-sense oligonucleotides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Feb 15;253(1):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90654-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Hunt T. The use of single-stranded DNA and RNase H to promote quantitative 'hybrid arrest of translation' of mRNA/DNA hybrids in reticulocyte lysate cell-free translations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6433–6451. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., Magarian C., Borun T. W. Resolution of hemoglobin subunits by electrophoresis in acid urea polyacrylamide gels containing Triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):506–518. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. C., Aurelian L., Reddy M. P., Miller P. S., Ts'o P. O. Antiviral effect of an oligo(nucleoside methylphosphonate) complementary to the splice junction of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early pre-mRNAs 4 and 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2787–2791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stavrianopoulos J. G., Chargaff E. Purification and properties of ribonuclease H of calf thymus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1959–1963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson M. L., Zamecnik P. C. Inhibition of Rous sarcoma viral RNA translation by a specific oligodeoxyribonucleotide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):285–288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada K., Sawai Y., Saito J., Sato F. Change of ribonuclease H activity from rat liver nuclei by thioacetamide: preferential increase in the activity of magnesium-dependent ribonuclease H. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Nov 14;85(1):280–286. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(78)80040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walder J. A., Eder P. S., Engman D. M., Brentano S. T., Walder R. Y., Knutzon D. S., Dorfman D. M., Donelson J. E. The 35-nucleotide spliced leader sequence is common to all trypanosome messenger RNA's. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):569–571. doi: 10.1126/science.3523758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamecnik P. C., Stephenson M. L. Inhibition of Rous sarcoma virus replication and cell transformation by a specific oligodeoxynucleotide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):280–284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]