Abstract
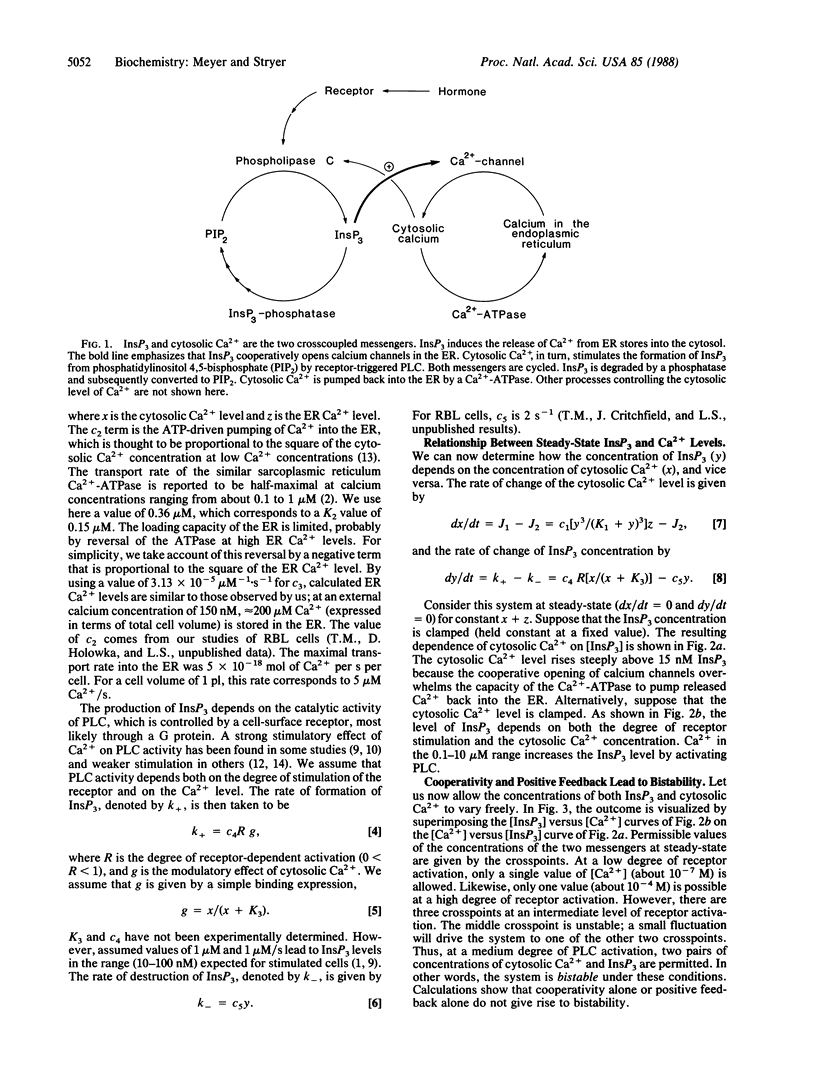
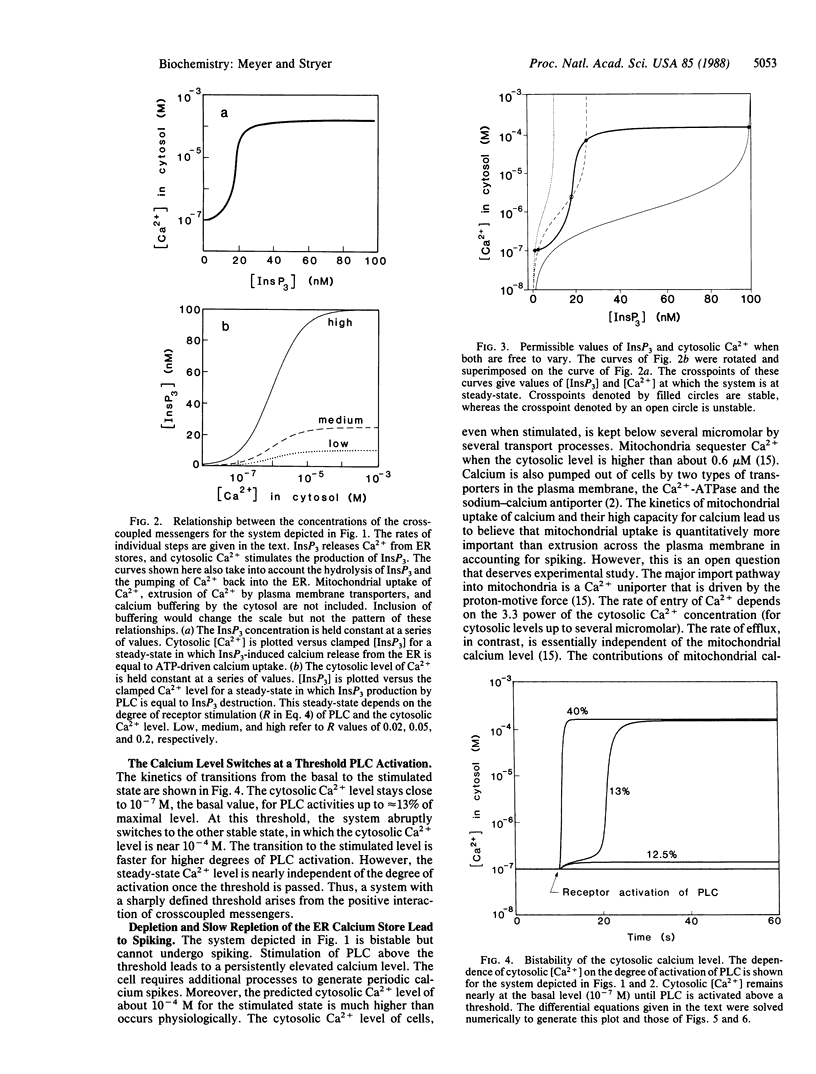
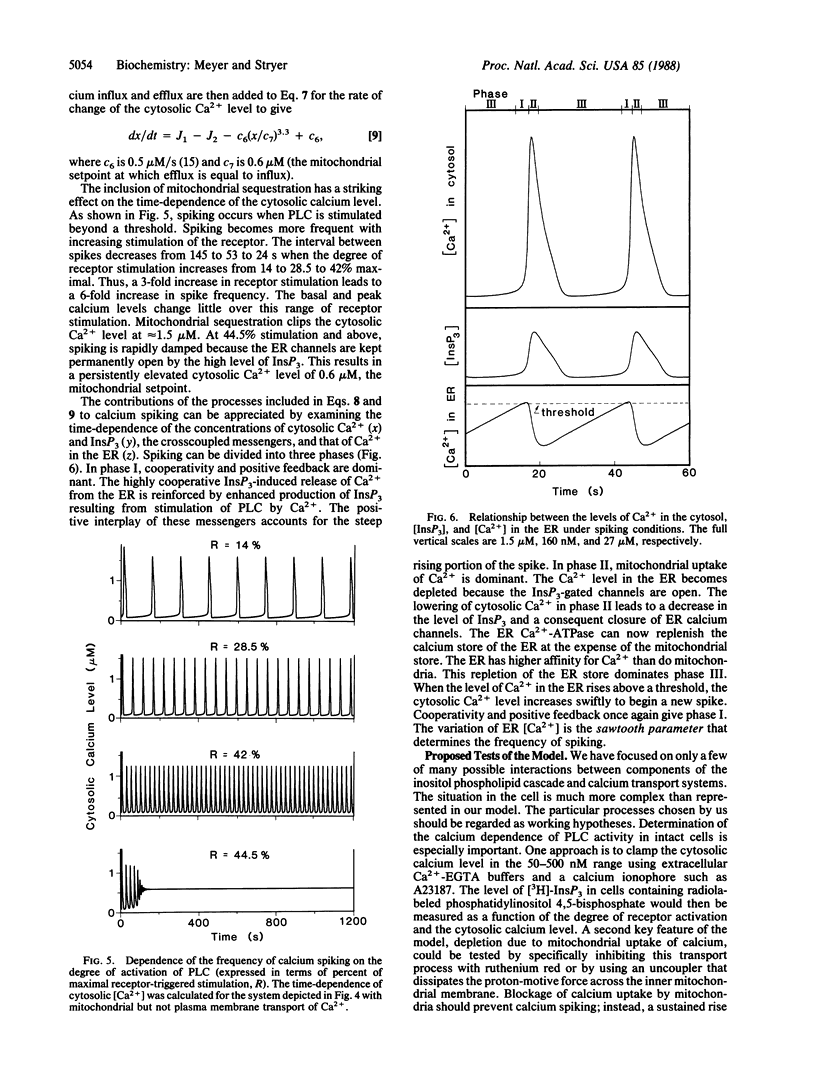
Many cells exhibit periodic transient increases in cytosolic calcium levels rather than a sustained rise when stimulated by a hormone or growth factor. We propose here a molecular model that accounts for periodic calcium spiking induced by a constant stimulus. Four elements give rise to repetitive calcium transients: cooperativity and positive feedback between a pair of reciprocally coupled (crosscoupled) messengers, followed by deactivation and then by reactivation. The crosscoupled messengers in our model are inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) and cytosolic calcium ions. The opening of calcium channels in the endoplasmic reticulum by the binding of multiple molecules of InsP3 provides the required cooperativity. The stimulation of receptor-activated phospholipase C by released calcium ions leads to positive feedback. InsP3 is destroyed by a phosphatase, and calcium ion is pumped back into the endoplasmic reticulum. These processes generate bistability: the cytosolic calcium concentration abruptly increases from a basal level to a stimulated level at a threshold degree of activation of phospholipase C. Spiking further requires slow deactivation and subsequent reactivation. In our model, mitochondrial sequestration of calcium ion prevents the cytosolic level from increasing above several micromolar and enables the system to return to the basal state. When the endoplasmic reticulum calcium store is refilled to a critical level by the Ca2+-ATPase pump, cooperative positive feedback between the InsP3-gated channel and phospholipase C begins again to give the next calcium spike. The time required for the calcium level in the endoplasmic reticulum to reach a threshold sets the interval between spikes. The amplitude, shape, and period of calcium spikes calculated for this model are like those observed experimentally.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E. Intracellular calcium homeostasis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:395–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G., Kurzmack M., Coan C., Lewis D. E. Cooperative calcium binding and ATPase activation in sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3025–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Connolly T. M., Deckmyn H., Ross T. S., Bross T. E., Ishii H., Bansal V. S., Wilson D. B. The metabolism of phosphoinositide-derived messenger molecules. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1519–1526. doi: 10.1126/science.3024320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T., Holowka D., Stryer L. Highly cooperative opening of calcium channels by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):653–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2452482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki S., Hashimoto N., Yoshimoto Y., Kishimoto T., Igusa Y., Hiramoto Y. Temporal and spatial dynamics of the periodic increase in intracellular free calcium at fertilization of golden hamster eggs. Dev Biol. 1986 Nov;118(1):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Almers W. Fast calcium transients in rat peritoneal mast cells are not sufficient to trigger exocytosis. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):51–53. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04176.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D., Akerman K. Mitochondrial calcium transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 1;683(1):57–88. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(82)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp P. E. Why are so many biological systems periodic? Prog Neurobiol. 1987;29(3):261–273. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(87)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renard D., Poggioli J., Berthon B., Claret M. How far does phospholipase C activity depend on the cell calcium concentration? A study in intact cells. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 15;243(2):391–398. doi: 10.1042/bj2430391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway E. B., Durham A. C. Oscillations of calcium ion concentrations in Physarum polycephalum. J Cell Biol. 1976 Apr;69(1):223–226. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth B. L. Modulation of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis in rat aorta by guanine nucleotides, calcium and magnesium. Life Sci. 1987 Aug 3;41(5):629–634. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90417-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Cho K. S., Lee K. Y., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G. Purification and characterization of two immunologically distinct phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases C from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12511–12518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel W., Winiger B. P., Mollard P., Vacher P., Wuarin F., Zahnd G. R., Wollheim C. B., Dufy B. Oscillations of cytosolic Ca2+ in pituitary cells due to action potentials. Nature. 1987 Oct 22;329(6141):719–721. doi: 10.1038/329719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Agonist-induced oscillations in cytoplasmic free calcium concentration in single rat hepatocytes. Cell Calcium. 1987 Feb;8(1):79–100. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(87)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Repetitive transient rises in cytoplasmic free calcium in hormone-stimulated hepatocytes. Nature. 1986 Feb 13;319(6054):600–602. doi: 10.1038/319600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



