Abstract
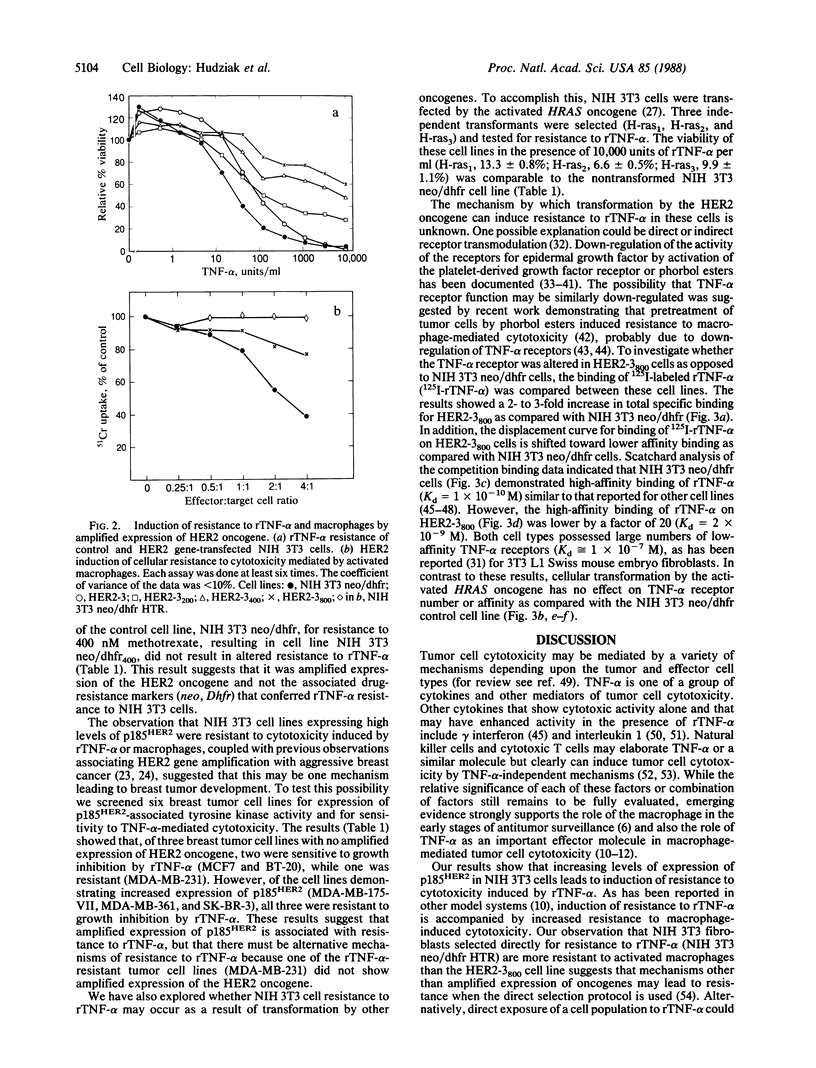
Functional characterization of oncogene products that induce cellular transformation has progressed rapidly in recent years. However, less is known about the mechanism(s) by which the transformed cells may escape destruction by host immune defenses and form tumors. A recently described oncogene that has an important association with aggressive human breast carcinoma is "HER2," for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2. The oncogene has also been called NGL and human c-erbB-2 (ERBB2). In this paper we show that amplification of HER2 oncogene expression can induce resistance of NIH 3T3 cells to the cytotoxic effects of recombinant tumor necrosis factor alpha (rTNF-alpha) or macrophages. Resistance is accompanied by an increased dissociation constant for rTNF-alpha binding to high-affinity receptors on the HER2-transformed NIH 3T3 cells. The resistance phenotype is independent of transformation since NIH 3T3 cells transformed by the activated human homologue of the Harvey-ras oncogene (HRAS) retain high-affinity binding sites for rTNF-alpha as well as sensitivity to its cytotoxic effects. These results suggest that HER2 may potentiate tumorigenesis by inducing tumor cell resistance to host defense mechanisms.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal B. B., Eessalu T. E. Effect of phorbol esters on down-regulation and redistribution of cell surface receptors for tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16450–16455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal B. B., Eessalu T. E., Hass P. E. Characterization of receptors for human tumour necrosis factor and their regulation by gamma-interferon. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):665–667. doi: 10.1038/318665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C., McCandless S., Tavernier J., Fiers W. Binding of human tumor necrosis factor to high affinity receptors on HeLa and lymphoblastoid cells sensitive to growth inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13395–13397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. The molecular genetics of cancer. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):305–311. doi: 10.1126/science.3541204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen-Pope D. F., Dicorleto P. E., Ross R. Interactions between the receptors for platelet-derived growth factor and epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):679–683. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Dicker P., Rozengurt E. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding to surface receptors by tumor promotors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 28;86(4):1037–1043. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90221-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capon D. J., Chen E. Y., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H., Goeddel D. V. Complete nucleotide sequences of the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene and its normal homologue. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):33–37. doi: 10.1038/302033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Gill G. N., Meisenhelder J., Cooper J. A., Hunter T. C-kinase phosphorylates the epidermal growth factor receptor and reduces its epidermal growth factor-stimulated tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2553–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Yang-Feng T. L., Liao Y. C., Chen E., Gray A., McGrath J., Seeburg P. H., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J., Francke U. Tyrosine kinase receptor with extensive homology to EGF receptor shares chromosomal location with neu oncogene. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1132–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.2999974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore P. P., Pierce J. H., Kraus M. H., Segatto O., King C. R., Aaronson S. A. erbB-2 is a potent oncogene when overexpressed in NIH/3T3 cells. Science. 1987 Jul 10;237(4811):178–182. doi: 10.1126/science.2885917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinman R., Henriksen-DeStefano D., Tsujimoto M., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor is an important mediator of tumor cell killing by human monocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):635–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Macrophages and metastasis--a biological approach to cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 1985 Oct;45(10):4714–4726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman M., Gunther G. Induction of tumor cell resistance to macrophage-mediated lysis by phorbol esters: a postbinding event. Cell Immunol. 1986 Jul;100(2):374–388. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudziak R. M., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Increased expression of the putative growth factor receptor p185HER2 causes transformation and tumorigenesis of NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7159–7163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwashita S., Fox C. F. Epidermal growth factor and potent phorbol tumor promoters induce epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation in a similar but distinctively different manner in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2559–2567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jadus M. R., Schmunk G., Djeu J. Y., Parkman R. Morphology and lytic mechanisms of interleukin 3-dependent natural cytotoxic cells: tumor necrosis factor as a possible mediator. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2774–2783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Kraus M. H., Aaronson S. A. Amplification of a novel v-erbB-related gene in a human mammary carcinoma. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):974–976. doi: 10.1126/science.2992089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus M. H., Popescu N. C., Amsbaugh S. C., King C. R. Overexpression of the EGF receptor-related proto-oncogene erbB-2 in human mammary tumor cell lines by different molecular mechanisms. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):605–610. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04797.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Cellular receptor for 125I-labeled tumor necrosis factor: specific binding, affinity labeling, and relationship to sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5756–5760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman L. B., Dinarello C. A., Llansa N. D., Fidler I. J. Natural and recombinant human interleukin 1-beta is cytotoxic for human melanoma cells. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):3098–3102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1: cytokines with multiple overlapping biological activities. Lab Invest. 1987 Mar;56(3):234–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Weinstein I. B. Mechanism of tumor promoter inhibition of cellular binding of epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5168–5172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis G. D., Aggarwal B. B., Eessalu T. E., Sugarman B. J., Shepard H. M. Modulation of the growth of transformed cells by human tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma. Cancer Res. 1987 Oct 15;47(20):5382–5385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. C., Steffen M., King F., Young J. D. Identification, isolation, and characterization of a novel cytotoxin in murine cytolytic lymphocytes. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Tumor cell instability, diversification, and progression to the metastatic phenotype: from oncogene to oncofetal expression. Cancer Res. 1987 Mar 15;47(6):1473–1487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell P. C. Mechanisms of tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1986 May;46(5):2203–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell P. C. The clonal evolution of tumor cell populations. Science. 1976 Oct 1;194(4260):23–28. doi: 10.1126/science.959840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Mason L. H., Mathieson B. J., Liang S. M., Flick D. A., Herberman R. B. Mediation of mouse natural cytotoxic activity by tumour necrosis factor. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):700–702. doi: 10.1038/321700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patek P. Q., Lin Y., Collins J. L. Natural cytotoxic cells and tumor necrosis factor activate similar lytic mechanisms. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1641–1646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J. S., Shepard H. M., Wilking H., Lewis G., Aggarwal B. B., Eessalu T. E., Gavin L. A., Grunfeld C. Interferons and tumor necrosis factors have similar catabolic effects on 3T3 L1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8313–8317. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters P. M., Ortaldo J. R., Shalaby M. R., Svedersky L. P., Nedwin G. E., Bringman T. S., Hass P. E., Aggarwal B. B., Herberman R. B., Goeddel D. V. Natural killer-sensitive targets stimulate production of TNF-alpha but not TNF-beta (lymphotoxin) by highly purified human peripheral blood large granular lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2592–2598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R., Epstein L. B. Tumour necrosis factor as immunomodulator and mediator of monocyte cytotoxicity induced by itself, gamma-interferon and interleukin-1. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):86–89. doi: 10.1038/323086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Collins M., Brown K. D., Pettican P. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding to mouse cultured cells by fibroblast-derived growth factor. Evidence for an indirect mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3680–3686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Collins M. Molecular aspects of growth factor action: receptors and intracellular signals. J Pathol. 1983 Nov;141(3):309–331. doi: 10.1002/path.1711410310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero V., Baglioni C. Synergistic anti-proliferative activity of interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):661–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoyab M., De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Biologically active phorbol esters specifically alter affinity of epidermal growth factor membrane receptors. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):387–391. doi: 10.1038/279387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
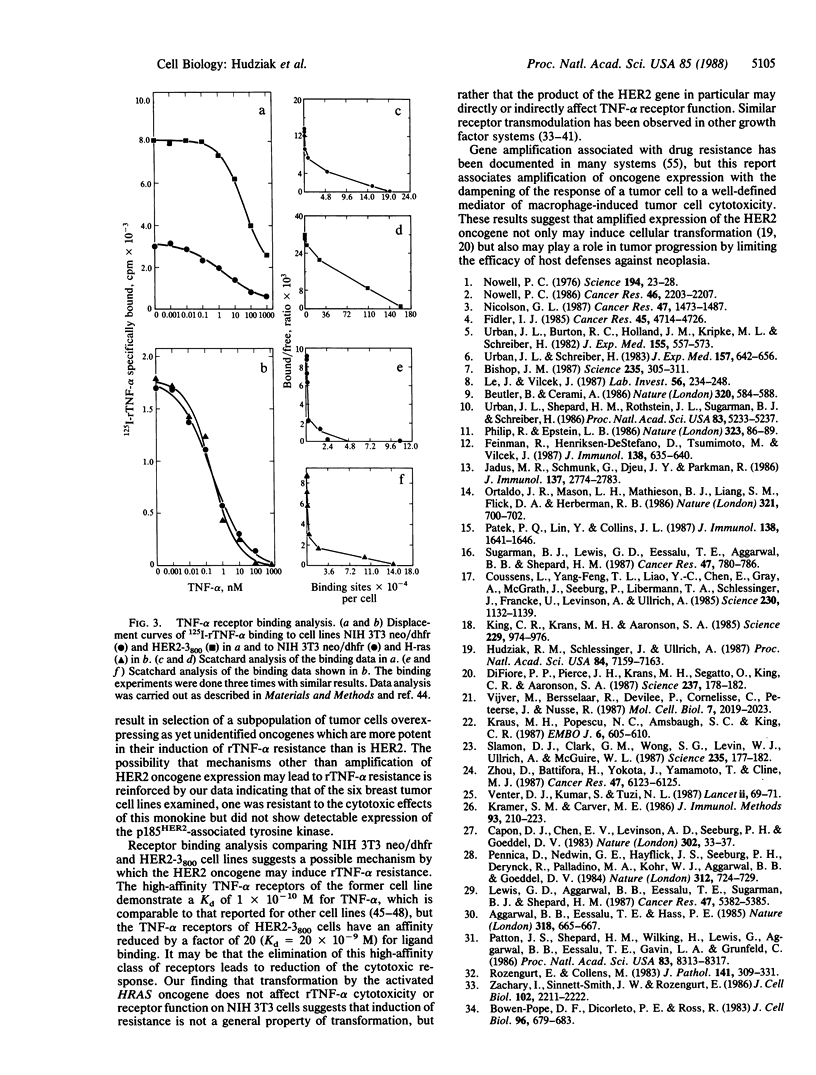
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M., Wong S. G., Levin W. J., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3798106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs D., Imamura K., Rodriguez C., Horiguchi J., Kufe D. W. Induction of tumor necrosis factor expression and resistance in a human breast tumor cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6563–6566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Gene amplification. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:447–491. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Aggarwal B. B., Hass P. E., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Shepard H. M. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3933111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Lewis G. D., Eessalu T. E., Aggarwal B. B., Shepard H. M. Effects of growth factors on the antiproliferative activity of tumor necrosis factors. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 1;47(3):780–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takehara K., LeRoy E. C., Grotendorst G. R. TGF-beta inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation: alteration of EGF binding and EGF-induced growth-regulatory (competence) gene expression. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):415–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90294-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto M., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor: specific binding and internalization in sensitive and resistant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7626–7630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unglaub R., Maxeiner B., Thoma B., Pfizenmaier K., Scheurich P. Downregulation of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) sensitivity via modulation of TNF binding capacity by protein kinase C activators. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1788–1797. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J. L., Burton R. C., Holland J. M., Kripke M. L., Schreiber H. Mechanisms of syngeneic tumor rejection. Susceptibility of host-selected progressor variants to various immunological effector cells. J Exp Med. 1982 Feb 1;155(2):557–573. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J. L., Schreiber H. Selection of macrophage-resistant progressor tumor variants by the normal host. Requirement for concomitant T cell-mediated immunity. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):642–656. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J. L., Shepard H. M., Rothstein J. L., Sugarman B. J., Schreiber H. Tumor necrosis factor: a potent effector molecule for tumor cell killing by activated macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5233–5237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Sinnett-Smith J. W., Rozengurt E. Early events elicited by bombesin and structurally related peptides in quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. I. Activation of protein kinase C and inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2211–2222. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D., Battifora H., Yokota J., Yamamoto T., Cline M. J. Association of multiple copies of the c-erbB-2 oncogene with spread of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 15;47(22):6123–6125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Vijver M., van de Bersselaar R., Devilee P., Cornelisse C., Peterse J., Nusse R. Amplification of the neu (c-erbB-2) oncogene in human mammmary tumors is relatively frequent and is often accompanied by amplification of the linked c-erbA oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):2019–2023. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]