Abstract
Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) regulates a variety of biological functions and is the principal lymphokine known to activate macrophages. In studies of the molecular mechanisms by which these cells are regulated by IFN-gamma, the transcriptional activation of an IFN-gamma-inducible gene, gamma.1, in human macrophage-like cell lines was examined. Transcription of this gene is rapidly induced by 0.1-1 unit of IFN-gamma. In addition, gamma.1 transcription is efficiently induced by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, which is known to activate protein kinase C (PKC). Both stimulators of gamma.1 transcription induce the translocation of PKC from the cytosol of a membrane fraction. Two selective inhibitors of PKC, H7 and sphingosine, suppressed not only the induction of gamma.1 mRNA but transcription of HLA-DR by IFN-gamma as well. These findings establish that PKC plays a significant role in the signal transduction pathway leading to transcriptional activation of some IFN-gamma-regulated genes of cells of the mononuclear phagocyte lineage.
Full text
PDF
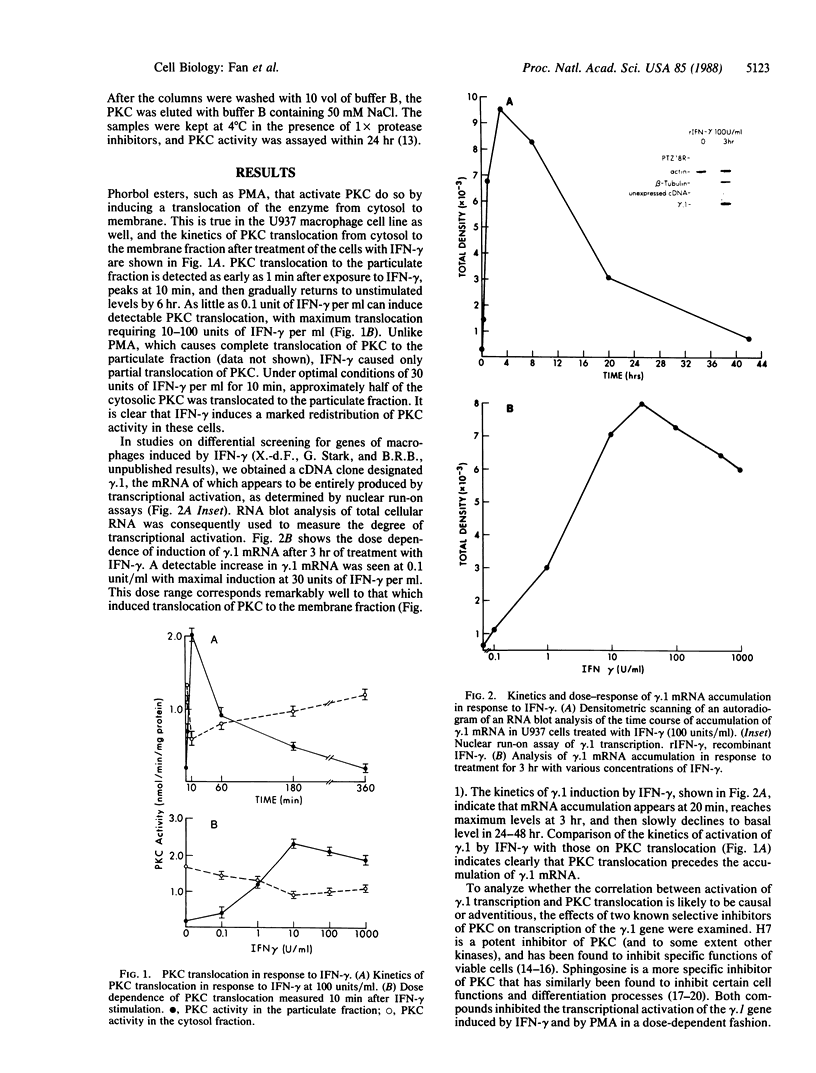
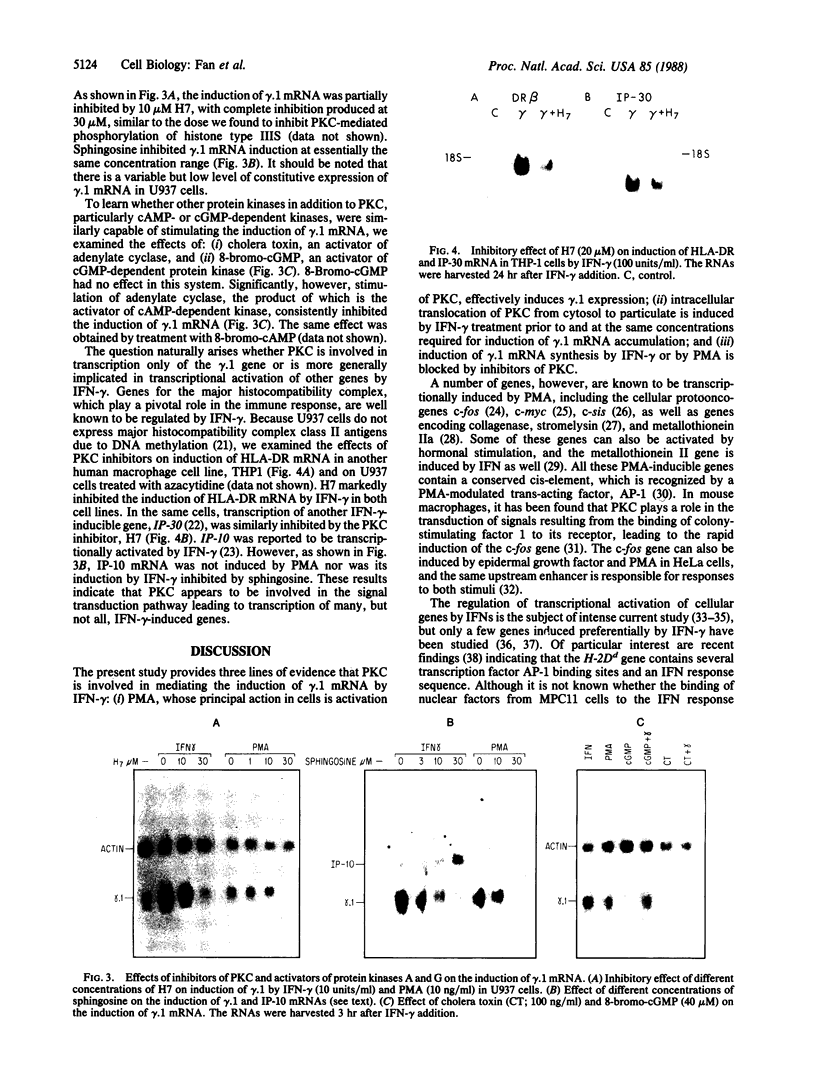

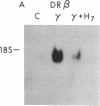
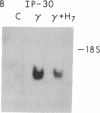
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Pöting A., Mallick U., Rahmsdorf H. J., Schorpp M., Herrlich P. Induction of metallothionein and other mRNA species by carcinogens and tumor promoters in primary human skin fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1760–1766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss J. M., Strominger J. L. Regulation of a transfected human class II major histocompatibility complex gene in human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9139–9143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branca A. A., Baglioni C. Evidence that types I and II interferons have different receptors. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):768–770. doi: 10.1038/294768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Neuberg M., Burckhardt J., Almendral J., Wallich R., Müller R. Involvement of common and cell type-specific pathways in c-fos gene control: stable induction of cAMP in macrophages. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90428-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colamonici O. R., Trepel J. B., Vidal C. A., Neckers L. M. Phorbol ester induces c-sis gene transcription in stem cell line K-562. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1847–1850. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Korman A. J., Wake C. T., Boss J. M., Kappes D. J., Fiers W., Ault K. A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Strominger J. L., Pober J. S. Immune interferon activates multiple class II major histocompatibility complex genes and the associated invariant chain gene in human endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch T. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G. c-fos sequence necessary for basal expression and induction by epidermal growth factor, 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate and the calcium ionophore. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3490–3502. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Stark G. R. alpha-Interferon-induced transcription of HLA and metallothionein genes containing homologous upstream sequences. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):637–639. doi: 10.1038/314637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M. Lysosphingolipids inhibit protein kinase C: implications for the sphingolipidoses. Science. 1987 Feb 6;235(4789):670–674. doi: 10.1126/science.3101176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Loomis C. R., Merrill A. H., Jr, Bell R. M. Sphingosine inhibition of protein kinase C activity and of phorbol dibutyrate binding in vitro and in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12604–12609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Hidaka H. Serotonin secretion from human platelets may be modified by Ca2+-activated, phospholipid-dependent myosin phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14321–14323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto S., Hidaka H. 1-(5-Isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methylpiperazine (H-7) is a selective inhibitor of protein kinase C in rabbit platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 30;125(1):258–264. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80362-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in transmembrane signalling. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:149–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyotaki C., Bloom B. R. Activation of murine macrophage cell lines. Possible involvement of protein kinases in stimulation of superoxide production. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):923–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korber B., Mermod N., Hood L., Stroynowski I. Regulation of gene expression by interferons: control of H-2 promoter responses. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1302–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.3125612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Peuch C. J., Ballester R., Rosen O. M. Purified rat brain calcium- and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6858–6862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J., Prensky W., Yip Y. K., Chang Z., Hoffman T., Stevenson H. C., Balazs I., Sadlik J. R., Vilcek J. Activation of human monocyte cytotoxicity by natural and recombinant immune interferon. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2821–2826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luster A. D., Ravetch J. V. Genomic characterization of a gamma-interferon-inducible gene (IP-10) and identification of an interferon-inducible hypersensitive site. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3723–3731. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luster A. D., Unkeless J. C., Ravetch J. V. Gamma-interferon transcriptionally regulates an early-response gene containing homology to platelet proteins. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):672–676. doi: 10.1038/315672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill A. H., Jr, Sereni A. M., Stevens V. L., Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M., Kinkade J. M., Jr Inhibition of phorbol ester-dependent differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemic (HL-60) cells by sphinganine and other long-chain bases. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12610–12615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Byrne G. I., Rothermel C. D., Cartelli D. M. Lymphokine enhances oxygen-independent activity against intracellular pathogens. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):234–239. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Prendergast T. J., Wiebe M. E., Stanley E. R., Platzer E., Remold H. G., Welte K., Rubin B. Y., Murray H. W. Activation of human macrophages. Comparison of other cytokines with interferon-gamma. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):600–605. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterlin B. M., Gonwa T. A., Stobo J. D. Expression of HLA-DR by a human monocyte cell line is under transcriptional control. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1984;1(3):191–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Chernajovsky Y., Dale T. C., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon response element of the human gene 6-16. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):85–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pure E., Luster A. D., Unkeless J. C. Cell surface expression of murine, rat, and human Fc receptors by Xenopus oocytes. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):606–611. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N., Evans B., Levy D., Fahey D., Knight E., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced transcription of a gene encoding a 15-kDa protein depends on an upstream enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6394–6398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D., Fellous M., Revel M. Preferential effect of gamma interferon on the synthesis of HLA antigens and their mRNAs in human cells. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):833–836. doi: 10.1038/299833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitham S. E., Murphy G., Angel P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Smith B. J., Lyons A., Harris T. J., Reynolds J. J., Herrlich P., Docherty A. J. Comparison of human stromelysin and collagenase by cloning and sequence analysis. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 15;240(3):913–916. doi: 10.1042/bj2400913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E., Olcott M. C., Bell R. M., Merrill A. H., Jr, Lambeth J. D. Inhibition of the oxidative burst in human neutrophils by sphingoid long-chain bases. Role of protein kinase C in activation of the burst. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12616–12623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., Maniatis T. Detection of factors that interact with the human beta-interferon regulatory region in vivo by DNAase I footprinting. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):611–618. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]