Abstract
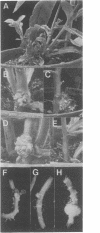
The isopentenyltransferase (ipt) gene associated with cytokinin biosynthesis in plants was cloned from a tumor-inducing plasmid carried by Agrobacterium tumefaciens and placed under the control of promoters of differing activities, the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter and the nopaline synthase promoter. These promoter-gene constructs were introduced into wounded Nicotiana stems, leaf pieces, and cucumber seedlings by A. tumefaciens infection. Shoots were observed in the infection site on all responding genotypes of Nicotiana plants infected with the 35S promoter construct (35S—ipt), whereas only 41% responded similarly to infection with the unmodified gene. Furthermore, shoots were observed 19 days after infection with the 35S—ipt gene but not until 28 to 45 days with the unaltered ipt gene. Shoots were more numerous (>40) on galls incited by 35S—ipt and were up to 6 times taller than shoots induced by the native gene. On Cucumis (cucumber), shoots were observed only on galls incited by the 35S—ipt construct. These galls were on the average 7.5 times larger than those incited by the nopaline synthase promoter construct (NOS—ipt) or the unmodified ipt gene. Zeatin and zeatinriboside concentrations averaged 23 times greater in the 35S—ipt transformed shoots than in ones transformed with the native ipt gene. These results suggest that a more active promoter on the ipt gene can enhance or change the morphogenic potential of transformed plant cells by increasing their endogenous cytokinin levels.
Keywords: isopentenyl transferase gene, Agrobacterium, phytohormones, Nicotiana, Cucumis
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1229–1231. doi: 10.1126/science.227.4691.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyoshi D. E., Klee H., Amasino R. M., Nester E. W., Gordon M. P. T-DNA of Agrobacterium tumefaciens encodes an enzyme of cytokinin biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5994–5998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyoshi D. E., Morris R. O., Hinz R., Mischke B. S., Kosuge T., Garfinkel D. J., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Cytokinin/auxin balance in crown gall tumors is regulated by specific loci in the T-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):407–411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amasino R. M., Miller C. O. Hormonal control of tobacco crown gall tumor morphology. Plant Physiol. 1982 Feb;69(2):389–392. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.2.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- An G., Watson B. D., Stachel S., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. New cloning vehicles for transformation of higher plants. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):277–284. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03626.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry G. F., Rogers S. G., Fraley R. T., Brand L. Identification of a cloned cytokinin biosynthetic gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4776–4780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M., Barnes W. M., Chilton M. D. Structure and transcription of the nopaline synthase gene region of T-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):369–385. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M. Binary Agrobacterium vectors for plant transformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8711–8721. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A., Herrera-Estrella L., Inzé D., Van Haute E., Van Montagu M., Schell J., Zambryski P. Introduction of genetic material into plant cells. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):815–821. doi: 10.1126/science.222.4625.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. M., Melitz D. K. Cytokinin biosynthesis in a cell-free system from cytokinin-autotrophic tobacco tissue cultures. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 1;107(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80452-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton M. D., Drummond M. H., Merio D. J., Sciaky D., Montoya A. L., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Stable incorporation of plasmid DNA into higher plant cells: the molecular basis of crown gall tumorigenesis. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):263–271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton M. D., Saiki R. K., Yadav N., Gordon M. P., Quetier F. T-DNA from Agrobacterium Ti plasmid is in the nuclear DNA fraction of crown gall tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4060–4064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamborg O. L. The effects of amino acids and ammonium on the growth of plant cells in suspension culture. Plant Physiol. 1970 Apr;45(4):372–375. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.4.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel D. J., Simpson R. B., Ream L. W., White F. F., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Genetic analysis of crown gall: fine structure map of the T-DNA by site-directed mutagenesis. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90368-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell J. T., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Identification of DNA sequences required for activity of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):810–812. doi: 10.1038/313810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooms G., Hooykaas P. J., Van Veen R. J., Van Beelen P., Regensburg-Tuïnk T. J., Schilperoort R. A. Octopine Ti-plasmid deletion mutants of agrobacterium tumefaciens with emphasis on the right side of the T-region. Plasmid. 1982 Jan;7(1):15–29. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ream L. W., Gordon M. P. Crown gall disease and prospects for genetic manipulation of plants. Science. 1982 Nov 26;218(4575):854–859. doi: 10.1126/science.218.4575.854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOOG F., MILLER C. O. Chemical regulation of growth and organ formation in plant tissues cultured in vitro. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1957;11:118–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders P. R., Winter J. A., Barnason A. R., Rogers S. G., Fraley R. T. Comparison of cauliflower mosaic virus 35S and nopaline synthase promoters in transgenic plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1543–1558. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder G., Waffenschmidt S., Weiler E. W., Schröder J. The T-region of Ti plasmids codes for an enzyme synthesizing indole-3-acetic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 16;138(2):387–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C. H., Carter G. H., Watson M. D., Shaw C. H. A functional map of the nopaline synthase promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7831–7846. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Larebeke N., Engler G., Holsters M., Van den Elsacker S., Zaenen I., Schilperoort R. A., Schell J. Large plasmid in Agrobacterium tumefaciens essential for crown gall-inducing ability. Nature. 1974 Nov 8;252(5479):169–170. doi: 10.1038/252169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson B., Currier T. C., Gordon M. P., Chilton M. D., Nester E. W. Plasmid required for virulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):255–264. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.255-264.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pater B. S., Klinkhamer M. P., Amesz P. A., de Kam R. J., Memelink J., Hoge J. H., Schilperoort R. A. Plant expression signals of the Agrobacterium T-cyt gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8267–8281. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]