Abstract
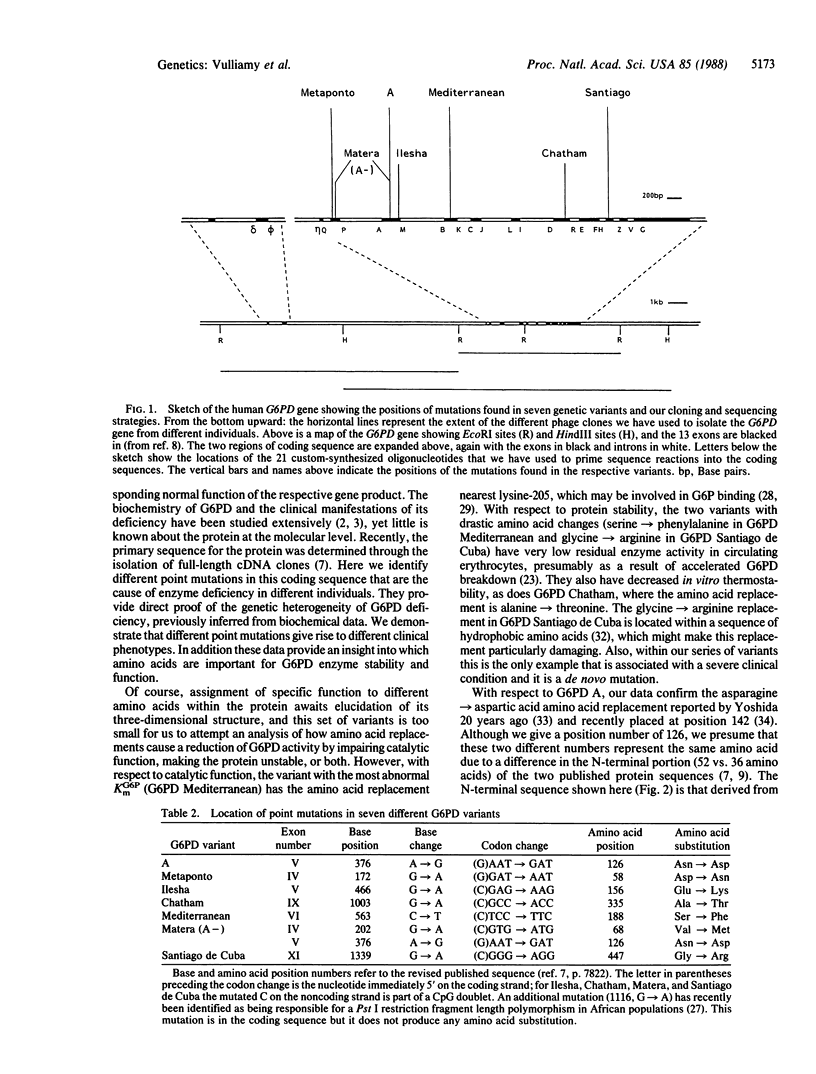
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD; EC 1.1.1.49) deficiency is a common genetic abnormality affecting an estimated 400 million people worldwide. Clinical and biochemical analyses have identified many variants exhibiting a range of phenotypes, which have been well characterized from the hematological point of view. However, until now, their precise molecular basis has remained unknown. We have cloned and sequenced seven mutant G6PD alleles. In the nondeficient polymorphic African variant G6PD A we have found a single point mutation. The other six mutants investigated were all associated with enzyme deficiency. In one of the commonest, G6PD Mediterranean, which is associated with favism among other clinical manifestations, a single amino acid replacement was found (serine----phenylalanine): it must be responsible for the decreased stability and the reduced catalytic efficiency of this enzyme. Single point mutations were also found in G6PD Metaponto (Southern Italy) and in G6PD Ilesha (Nigeria), which are asymptomatic, and in G6PD Chatham, which was observed in an Indian boy with neonatal jaundice. In G6PD "Matera," which is now known to be the same as G6PD A-, two separate point mutations were found, one of which is the same as in G6PD A. In G6PD Santiago, a de novo mutation (glycine----arginine) is associated with severe chronic hemolytic anemia. The mutations observed show a striking predominance of C----T transitions, with CG doublets involved in four of seven cases. Thus, diverse point mutations may account largely for the phenotypic heterogeneity of G6PD deficiency.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON A. C. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency in red blood cells of East Africans. Nature. 1960 May 14;186:531–532. doi: 10.1038/186531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babalola A. O., Beetlestone J. G., Luzzatto L. Genetic variants of human erythrocyte glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of variants A, B, and A- in relation to quaternary structure. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):2993–3002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballabio A., Parenti G., Carrozzo R., Sebastio G., Andria G., Buckle V., Fraser N., Craig I., Rocchi M., Romeo G. Isolation and characterization of a steroid sulfatase cDNA clone: genomic deletions in patients with X-chromosome-linked ichthyosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4519–4523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Schafer M., White R. Restriction sites containing CpG show a higher frequency of polymorphism in human DNA. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battistuzzi G., Esan G. J., Fasuan F. A., Modiano G., Luzzatto L. Comparison of GdA and GdB activities in Nigerians. A study of the variation of the G6PD activity. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Jan;29(1):31–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Pictet R., Rutter W. J. Analysis of the regions flanking the human insulin gene and sequence of an Alu family member. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4091–4109. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camardella L., Caruso C., Rutigliano B., Romano M., Di Prisco G., Descalzi-Cancedda F. Human erythrocyte glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Identification of a reactive lysyl residue labelled with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;171(3):485–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13815.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Urso M., Battistuzzi G., Luzzatto L. Genetic variants of human erythrocyte glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase: automated procedure for characterization by column chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1980 Oct;108(1):146–150. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90704-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Urso M., Luzzatto L., Perroni L., Ciccodicola A., Gentile G., Peluso I., Persico M. G., Pizzella T., Toniolo D., Vulliamy T. J. An extensive search for RFLP in the human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase locus has revealed a silent mutation in the coding sequence. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 May;42(5):735–741. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferraris A. M., Giuntini P., Galiano S., Gaetani G. F. 2-deoxy-glucose-6-phosphate utilization in the study of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase mosaicism. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Mar;33(2):307–313. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foroni L., Foldi J., Matutes E., Catovsky D., O'Connor N. J., Baer R., Forster A., Rabbitts T. H., Luzzatto L. Alpha, beta and gamma T-cell receptor genes: rearrangements correlate with haematological phenotype in T cell leukaemias. Br J Haematol. 1987 Nov;67(3):307–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1987.tb02352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Hidaka S., Sakaki Y. Sequence analysis of a KpnI family member near the 3' end of human beta-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7813–7827. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirono A., Beutler E. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA for human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase variant A(-). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3951–3954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery J., Hobbs L., Jörnvall H. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: characterization of a reactive lysine residue labeled with acetylsalicylic acid. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):666–671. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Hypervariable 'minisatellite' regions in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):67–73. doi: 10.1038/314067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Matthes H. W., Gait M. J., Brenner S. A new selective phage cloning vector, lambda 2001, with sites for XbaI, BamHI, HindIII, EcoRI, SstI and XhoI. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(1-2):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L., Battistuzzi G. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Adv Hum Genet. 1985;14:217-329, 386-8. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9400-0_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L. Genetics of red cells and susceptibility to malaria. Blood. 1979 Nov;54(5):961–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L. Regulation of the activity of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase by NADP+ and NADPH. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 12;146(1):18–25. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L. Studies of polymorphic traits for the characterization of populations. African populations south of the Sahara. Isr J Med Sci. 1973 Sep-Oct;9(9):1181–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luzzatto L., Usanga E. A., Bienzle U., Esan G. F., Fusuan F. A. Imbalance in X-chromosome expression: evidence for a human X-linked gene affecting growth of hemopoietic cells. Science. 1979 Sep 28;205(4413):1418–1420. doi: 10.1126/science.472761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOTULSKY A. G. Metabolic polymorphisms and the role of infectious diseases in human evolution. Hum Biol. 1960 Feb;32:28–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini G., Toniolo D., Vulliamy T., Luzzatto L., Dono R., Viglietto G., Paonessa G., D'Urso M., Persico M. G. Structural analysis of the X-linked gene encoding human glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1849–1855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04436.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modiano G., Battistuzzi G., Motulsky A. G. Nonrandom patterns of codon usage and of nucleotide substitutions in human alpha- and beta-globin genes: an evolutionary strategy reducing the rate of mutations with drastic effects? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1110–1114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morelli A., Benatti U., Gaetani G. F., De Flora A. Biochemical mechanisms of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1979–1983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER I. H., BOYER S. H., WATSON-WILLIAMS E. J., ADAM A., SZEINBERG A., SINISCALCO M. VARIATION OF GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE IN DIFFERENT POPULATIONS. Lancet. 1964 Apr 25;1(7339):895–899. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91626-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persico M. G., Viglietto G., Martini G., Toniolo D., Paonessa G., Moscatelli C., Dono R., Vulliamy T., Luzzatto L., D'Urso M. Isolation of human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) cDNA clones: primary structure of the protein and unusual 5' non-coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2511–2522. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takizawa T., Huang I. Y., Ikuta T., Yoshida A. Human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: primary structure and cDNA cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4157–4161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usanga E. A., Bienzle U., Cancedda R., Fasuan F. A., Ajayi O., Luzzatto L. Genetic variants of human erythrocyte glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase: new variants in West Africa characterized by column chromatography. Ann Hum Genet. 1977 Jan;40(3):279–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1977.tb00192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel F., Kopun M. Higher frequencies of transitions among point mutations. J Mol Evol. 1977 Apr 29;9(2):159–180. doi: 10.1007/BF01732746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A. A single amino Acid substitution (asparagine to aspartic Acid) between normal (b+) and the common negro variant (a+) of human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):835–840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssoufian H., Antonarakis S. E., Aronis S., Tsiftis G., Phillips D. G., Kazazian H. H., Jr Characterization of five partial deletions of the factor VIII gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3772–3776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssoufian H., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Phillips D. G., Aronis S., Tsiftis G., Brown V. A., Antonarakis S. E. Recurrent mutations in haemophilia A give evidence for CpG mutation hotspots. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):380–382. doi: 10.1038/324380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




