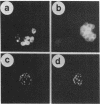
Abstract
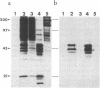
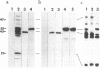
We describe the isolation and cloning of two integral membrane protein antigens of Plasmodium falciparum. The antigens were isolated by Triton X-114 temperature-dependent phase separation, electrophoretically transferred to nitrocellulose, and used to affinity-purify monospecific human antibodies. These antibodies were used to isolate the corresponding cDNA clones from a phage lambda gt11-Amp3 cDNA expression library. Clone Ag512 corresponds to a Mr 55,000 merozoite rhoptry antigen, and clone Ag513 corresponds to a Mr 45,000 merozoite surface antigen. Both proteins can be biosynthetically labeled with [3H]glucosamine and [3H]myristic acid, suggesting that they may be anchored in membranes via a glycosylphosphatidylinositol moiety. Similarities in the C-terminal sequences of the Mr 45,000 merozoite surface antigen and the Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoproteins provides further evidence that this antigen has a glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor.
Full text
PDF

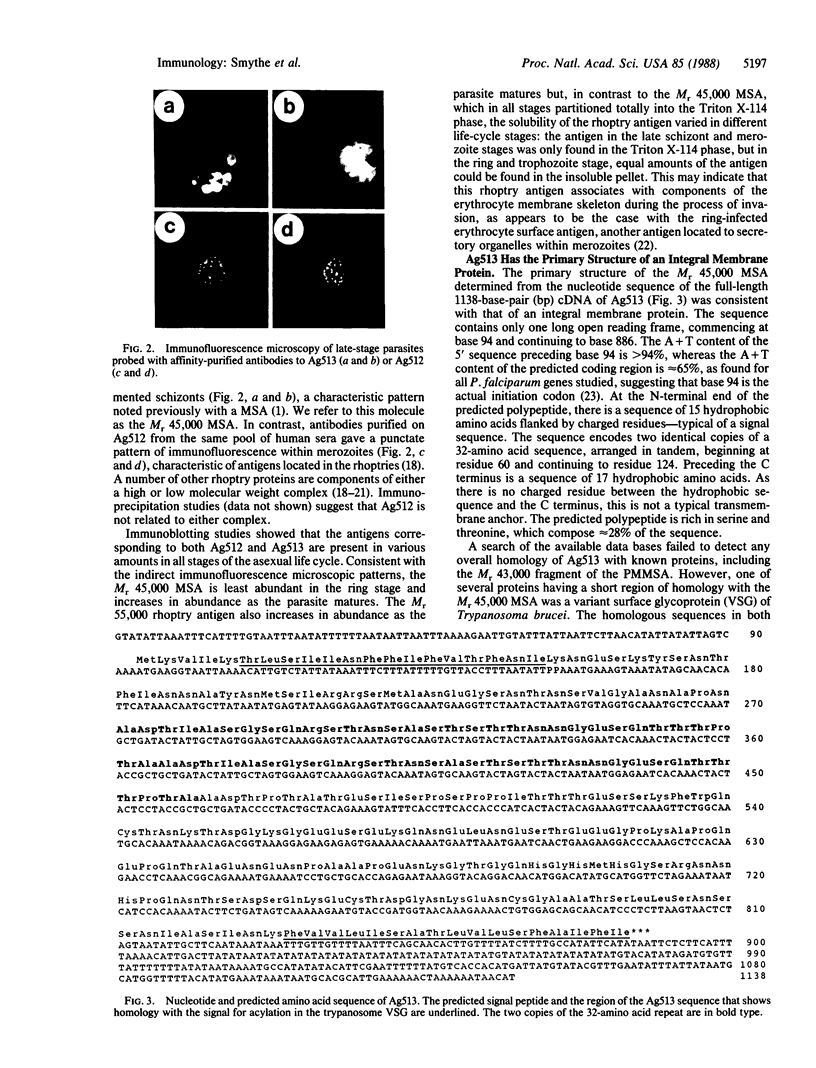


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aikawa M., Miller L. H., Johnson J., Rabbege J. Erythrocyte entry by malarial parasites. A moving junction between erythrocyte and parasite. J Cell Biol. 1978 Apr;77(1):72–82. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardeshir F., Flint J. E., Richman S. J., Reese R. T. A 75 kd merozoite surface protein of Plasmodium falciparum which is related to the 70 kd heat-shock proteins. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):493–499. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister L. H., Mitchell G. H., Butcher G. A., Dennis E. D. Lamellar membranes associated with rhoptries in erythrocytic merozoites of Plasmodium knowlesi: a clue to the mechanism of invasion. Parasitology. 1986 Apr;92(Pt 2):291–303. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000064064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall J. A., Mitchell G. F. Identification of a particular antigen from a parasite cDNA library using antibodies affinity purified from selected portions of Western blots. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Feb 12;86(2):217–223. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90456-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco A. E., Culvenor J. G., Coppel R. L., Crewther P. E., McIntyre P., Favaloro J. M., Brown G. V., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Putative glycophorin-binding protein is secreted from schizonts of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Feb;23(1):91–102. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Stace J. D., Alpers M. P., Mitchell G. F. Immunoprecipitation of biosynthetically-labelled proteins from different Papua New Guinea Plasmodium falciparum isolates by sera from individuals in the endemic area. Parasite Immunol. 1981 Winter;3(4):283–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1981.tb00407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown G. V., Culvenor J. G., Crewther P. E., Bianco A. E., Coppel R. L., Saint R. B., Stahl H. D., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Localization of the ring-infected erythrocyte surface antigen (RESA) of Plasmodium falciparum in merozoites and ring-infected erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):774–779. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell G. H., Miller L. H., Hudson D., Franco E. L., Andrysiak P. M. Monoclonal antibody characterization of Plasmodium falciparum antigens. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Nov;33(6):1051–1054. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P., Lamont G., Elliott T., Kidson C., Brown G., Mitchell G., Stace J., Alpers M. Plasmodium falciparum strains from Papua New Guinea: culture characteristics and drug sensitivity. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1980 Dec;11(4):435–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel R. L., Favaloro J. M., Crewther P. E., Burkot T. R., Bianco A. E., Stahl H. D., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F., Brown G. V. A blood stage antigen of Plasmodium falciparum shares determinants with the sporozoite coat protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5121–5125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crewther P. E., Bianco A. E., Brown G. V., Coppel R. L., Stahl H. D., Kemp D. J., Anders R. F. Affinity purification of human antibodies directed against cloned antigens of Plasmodium falciparum. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Feb 12;86(2):257–264. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90462-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dame J. B., Williams J. L., McCutchan T. F., Weber J. L., Wirtz R. A., Hockmeyer W. T., Maloy W. L., Haynes J. D., Schneider I., Roberts D. Structure of the gene encoding the immunodominant surface antigen on the sporozoite of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):593–599. doi: 10.1126/science.6204383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donelson J. E., Rice-Ficht A. C. Molecular biology of trypanosome antigenic variation. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Jun;49(2):107–125. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.2.107-125.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epping R. J., Goldstone S. D., Ingram L. T., Upcroft J. A., Ramasamy R., Cooper J. A., Bushell G. R., Geysen H. M. An epitope recognised by inhibitory monoclonal antibodies that react with a 51 kilodalton merozoite surface antigen in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Feb;28(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90173-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Williams A. F. Cell-surface anchoring of proteins via glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol structures. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:285–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldar K., Ferguson M. A., Cross G. A. Acylation of a Plasmodium falciparum merozoite surface antigen via sn-1,2-diacyl glycerol. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):4969–4974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R., Osland A., Hyde J. E., Simmons D. L., Hope I. A., Scaife J. G. Processing, polymorphism, and biological significance of P190, a major surface antigen of the erythrocytic forms of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Apr;11:61–80. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder A. A., Freeman R. R. Biosynthesis and processing of a Plasmodium falciparum schizont antigen recognized by immune serum and a monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1982 Nov 1;156(5):1528–1538. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.5.1528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder A. A., Freeman R. R. The three major antigens on the surface of Plasmodium falciparum merozoites are derived from a single high molecular weight precursor. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):624–629. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder A. A., Freeman R. R., Uni S., Aikawa M. Isolation of a Plasmodium falciparum rhoptry protein. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Mar;14(3):293–303. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder A. A., Lockyer M. J., Odink K. G., Sandhu J. S., Riveros-Moreno V., Nicholls S. C., Hillman Y., Davey L. S., Tizard M. L., Schwarz R. T. Primary structure of the precursor to the three major surface antigens of Plasmodium falciparum merozoites. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):270–273. doi: 10.1038/317270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Mackay M., Hyde J. E., Goman M., Scaife J. The gene for an exported antigen of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 25;13(2):369–379. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. F., Stanley H. A., Campbell G. H., Reese R. T. Proteins responsible for a punctate fluorescence pattern in Plasmodium falciparum merozoites. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Nov;33(6):1055–1059. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara A., Hou Y., Jacobson K. The Thy-1 antigen exhibits rapid lateral diffusion in the plasma membrane of rodent lymphoid cells and fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1290–1293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Coppel R. L., Cowman A. F., Saint R. B., Brown G. V., Anders R. F. Expression of Plasmodium falciparum blood-stage antigens in Escherichia coli: detection with antibodies from immune humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3787–3791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan J., Perkins M., Ravetch J. V. A tandemly repeated sequence determines the binding domain for an erythrocyte receptor binding protein of P. falciparum. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90834-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Coppel R. L., McIntyre P., Langford C. J., Woodrow G., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. Variation in the precursor to the major merozoite surface antigens of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jan 15;27(2-3):291–301. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramasamy R. Studies on glycoproteins in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Identification of a myristilated 45kDa merozoite membrane glycoprotein. Immunol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;65(Pt 5):419–424. doi: 10.1038/icb.1987.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roger N., Dubremetz J. F., Delplace P., Fortier B., Tronchin G., Vernes A. Characterization of a 225 kilodalton rhoptry protein of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jan 15;27(2-3):135–141. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saul A., Battistutta D. Codon usage in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jan 1;27(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D., Woollett G., Bergin-Cartwright M., Kay D., Scaife J. A malaria protein exported into a new compartment within the host erythrocyte. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):485–491. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04779.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley H. A., Howard R. F., Reese R. T. Recognition of a Mr 56K glycoprotein on the surface of Plasmodium falciparum merozoites by mouse monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3439–3444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. J., Schulman S., Vanderberg J. P. Rhoptry secretion of membranous whorls by Plasmodium falciparum merozoites. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Jan;35(1):37–44. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]