Abstract
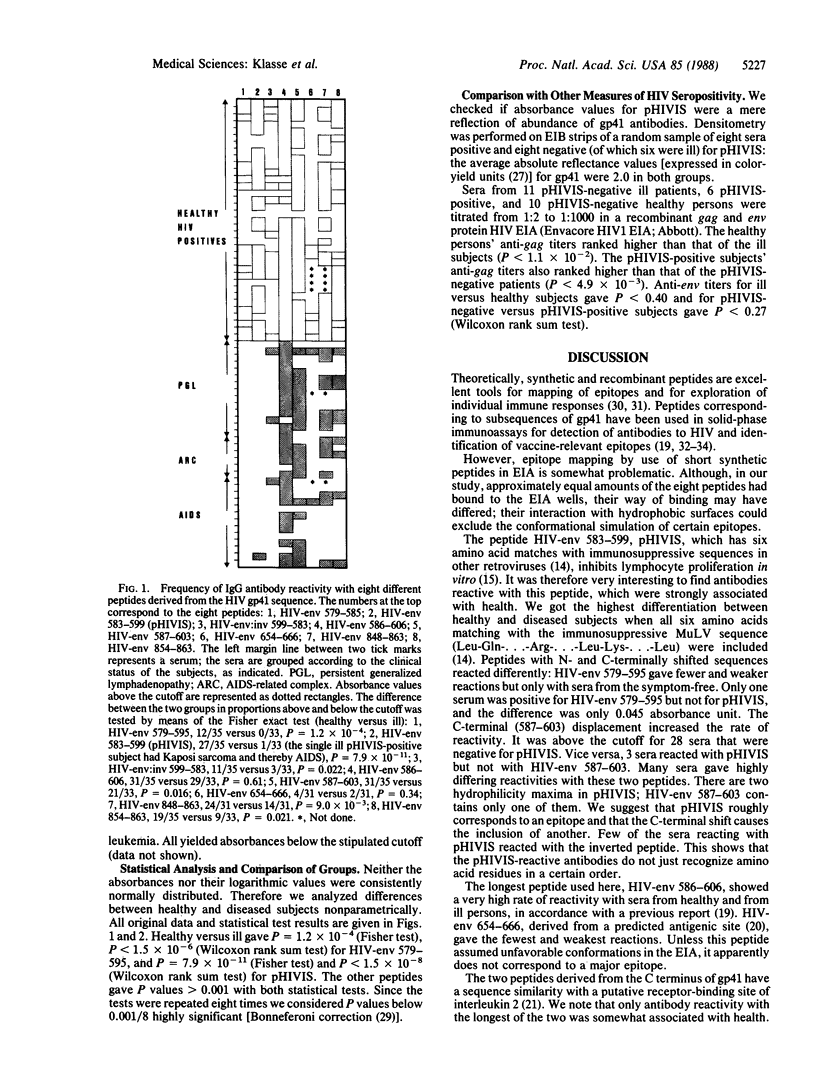
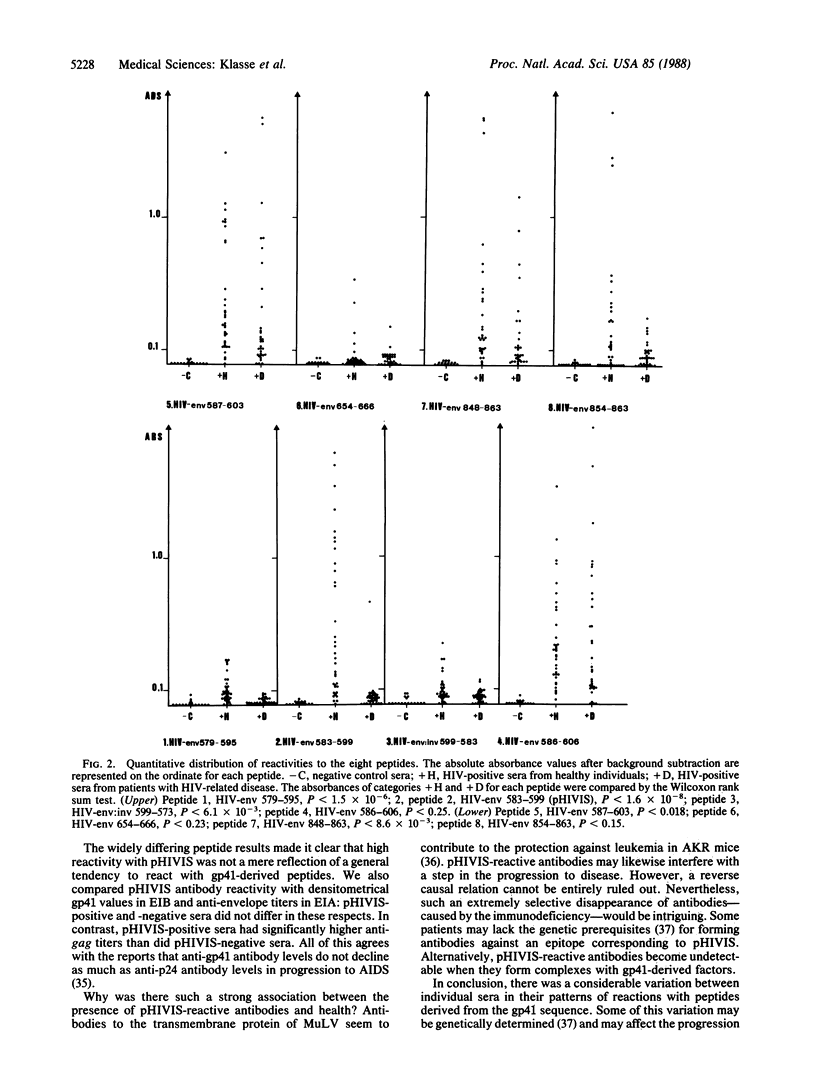
The IgG response to gp41 (envelope glycoprotein of Mr 41,000) of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) was studied with eight synthetic peptides derived from three different regions of the protein. We tested sera from 17 HIV-seronegative and 68 HIV-seropositive subjects in an enzyme immunoassay. No HIV antibody-negative serum reacted with any of the peptides. The peptide HIV-env 583-599 has a sequence similarity with immunosuppressive peptides derived from the transmembrane proteins of other retroviruses. Antibodies to this 17-mer (HIV-env 583-599; hereafter also referred to as pHIVIS, putative HIV immunosuppressive sequence) were detected in 27 of the 35 sera from healthy HIV-positive persons but only in 1 of the 33 sera from patients with HIV-related disease. Another 17-mer, displaced four amino acids N-terminally from pHIVIS, reacted with fewer of the sera from healthy seropositive subjects than pHIVIS but with no serum from ill seropositive patients. HIV-env 586-603, which shares two-thirds of its sequence with pHIVIS, reacted with the sera from nearly all subjects, regardless of clinical status. The remaining five peptides did not discriminate between healthy and ill seropositive subjects either but gave lower reactivity rates. HIV-positive sera thus exhibited distinct patterns of reactivity with subsequences of gp41. We have mapped two overlapping epitopes within a narrow part of gp41; antibodies to the most N-terminally located of the two--i.e., the pHIVIS-reactive antibodies--might counteract a possible immunosuppressive effect of gp41.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berzofsky J. A. Intrinsic and extrinsic factors in protein antigenic structure. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):932–940. doi: 10.1126/science.2410982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomberg J., Klasse P. J. Quantification of immunoglobulin on electrophoretic immunoblot strips as a tool for human immunodeficiency virus serodiagnosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jan;26(1):111–115. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.1.111-115.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomberg J., Nilsson I., Andersson M. Viral antibody screening system that uses a standardized single dilution immunoglobulin G enzyme immunoassay with multiple antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):1081–1091. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.1081-1091.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Classification system for human T-lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus infections. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1986 May 23;35(20):334–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Certa U., Bannwarth W., Stüber D., Gentz R., Lanzer M., Le Grice S., Guillot F., Wendler I., Hunsmann G., Bujard H. Subregions of a conserved part of the HIV gp41 transmembrane protein are differentially recognized by antibodies of infected individuals. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3051–3056. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04605.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciolo G. J., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S., Snyderman R. Inhibition of lymphocyte proliferation by a synthetic peptide homologous to retroviral envelope proteins. Science. 1985 Oct 25;230(4724):453–455. doi: 10.1126/science.2996136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciolo G., Hunter J., Silva J., Haskill J. S., Snyderman R. Inhibitors of monocyte responses to chemotaxins are present in human cancerous effusions and react with monoclonal antibodies to the P15(E) structural protein of retroviruses. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):831–844. doi: 10.1172/JCI110338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowl R., Ganguly K., Gordon M., Conroy R., Schaber M., Kramer R., Shaw G., Wong-Staal F., Reddy E. P. HTLV-III env gene products synthesized in E. coli are recognized by antibodies present in the sera of AIDS patients. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):979–986. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. G., Ratner L., Mitsuya H., Marselle L. M., Harper M. E., Broder S., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Infectious mutants of HTLV-III with changes in the 3' region and markedly reduced cytopathic effects. Science. 1986 Aug 8;233(4764):655–659. doi: 10.1126/science.3014663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler A. K., Twardzik D. R., Reed C. D., Weislow O. S., Hellman A. Inhibition of lymphocyte transformation by disrupted murine oncornavirus. Cancer Res. 1977 Dec;37(12):4529–4531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey K. Statistics in practice. Comparing the means of several groups. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 5;313(23):1450–1456. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512053132305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. T., Cianciolo G. J., Snyderman R., Argov S., Koren H. S. Inhibition of human natural killer cell activity by a synthetic peptide homologous to a conserved region in the retroviral protein, p15E. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):889–894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P. Protein surface analysis. Methods for identifying antigenic determinants and other interaction sites. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Apr 3;88(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90045-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy R. C., Henkel R. D., Pauletti D., Allan J. S., Lee T. H., Essex M., Dreesman G. R. Antiserum to a synthetic peptide recognizes the HTLV-III envelope glycoprotein. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1556–1559. doi: 10.1126/science.3006246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Masur H., Edgar L. C., Whalen G., Rook A. H., Fauci A. S. Abnormalities of B-cell activation and immunoregulation in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1983 Aug 25;309(8):453–458. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198308253090803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange J. M., Coutinho R. A., Krone W. J., Verdonck L. F., Danner S. A., van der Noordaa J., Goudsmit J. Distinct IgG recognition patterns during progression of subclinical and clinical infection with lymphadenopathy associated virus/human T lymphotropic virus. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Jan 25;292(6515):228–230. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6515.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurence J., Gottlieb A. B., Kunkel H. G. Soluble suppressor factors in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome and its prodrome. Elaboration in vitro by T lymphocyte-adherent cell interactions. J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;72(6):2072–2081. doi: 10.1172/JCI111172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurence J., Mayer L. Immunoregulatory lymphokines of T hybridomas from AIDS patients: constitutive and inducible suppressor factors. Science. 1984 Jul 6;225(4657):66–69. doi: 10.1126/science.6328662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson J. D., Feinberg M. B., Reyes G. R., Rabin L., Banapour B., Chakrabarti S., Moss B., Wong-Staal F., Steimer K. S., Engleman E. G. Induction of CD4-dependent cell fusion by the HTLV-III/LAV envelope glycoprotein. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):725–728. doi: 10.1038/323725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathes L. E., Olsen R. G., Hebebrand L. C., Hoover E. A., Schaller J. P. Abrogation of lymphocyte blastogenesis by a feline leukaemia virus protein. Nature. 1978 Aug 17;274(5672):687–689. doi: 10.1038/274687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathes L. E., Olsen R. G., Hebebrand L. C., Hoover E. A., Schaller J. P., Adams P. W., Nichols W. S. Immunosuppressive properties of a virion polypeptide, a 15,000-dalton protein, from feline leukemia virus. Cancer Res. 1979 Mar;39(3):950–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitani M., Cianciolo G. J., Snyderman R., Yasuda M., Good R. A., Day N. K. Suppressive effect on polyclonal B-cell activation of a synthetic peptide homologous to a transmembrane component of oncogenic retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):237–240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahwa S., Pahwa R., Good R. A., Gallo R. C., Saxinger C. Stimulatory and inhibitory influences of human immunodeficiency virus on normal B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9124–9128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahwa S., Pahwa R., Saxinger C., Gallo R. C., Good R. A. Influence of the human T-lymphotropic virus/lymphadenopathy-associated virus on functions of human lymphocytes: evidence for immunosuppressive effects and polyclonal B-cell activation by banded viral preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8198–8202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiher W. E., 3rd, Blalock J. E., Brunck T. K. Sequence homology between acquired immunodeficiency syndrome virus envelope protein and interleukin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9188–9192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson B., Fishleigh R. V., Morrison C. A. Prediction of HIV vaccine. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):395–395. doi: 10.1038/325395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S. M., Lane H. C., Higgins S. E., Folks T., Fauci A. S. Direct polyclonal activation of human B lymphocytes by the acquired immune deficiency syndrome virus. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1084–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.3016902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Goh W. C., Rosen C., Campbell K., Haseltine W. A. Role of the HTLV-III/LAV envelope in syncytium formation and cytopathicity. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):470–474. doi: 10.1038/322470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiel H. J., Schwarz H., Fischinger P., Bolognesi D., Schäfer W. Role of antibodies to murine leukemia virus p15E transmembrane protein in immunotherapy against AKR leukemia: a model for studies in human acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5893–5897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Allen P. M. The basis for the immunoregulatory role of macrophages and other accessory cells. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):551–557. doi: 10.1126/science.2437650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. J., Steel S., Wisniewolski R., Wang C. Y. Detection of antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type III by using a synthetic peptide of 21 amino acid residues corresponding to a highly antigenic segment of gp41 envelope protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6159–6163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. S. p-alkoxybenzyl alcohol resin and p-alkoxybenzyloxycarbonylhydrazide resin for solid phase synthesis of protected peptide fragments. J Am Chem Soc. 1973 Feb 21;95(4):1328–1333. doi: 10.1021/ja00785a602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




