Abstract
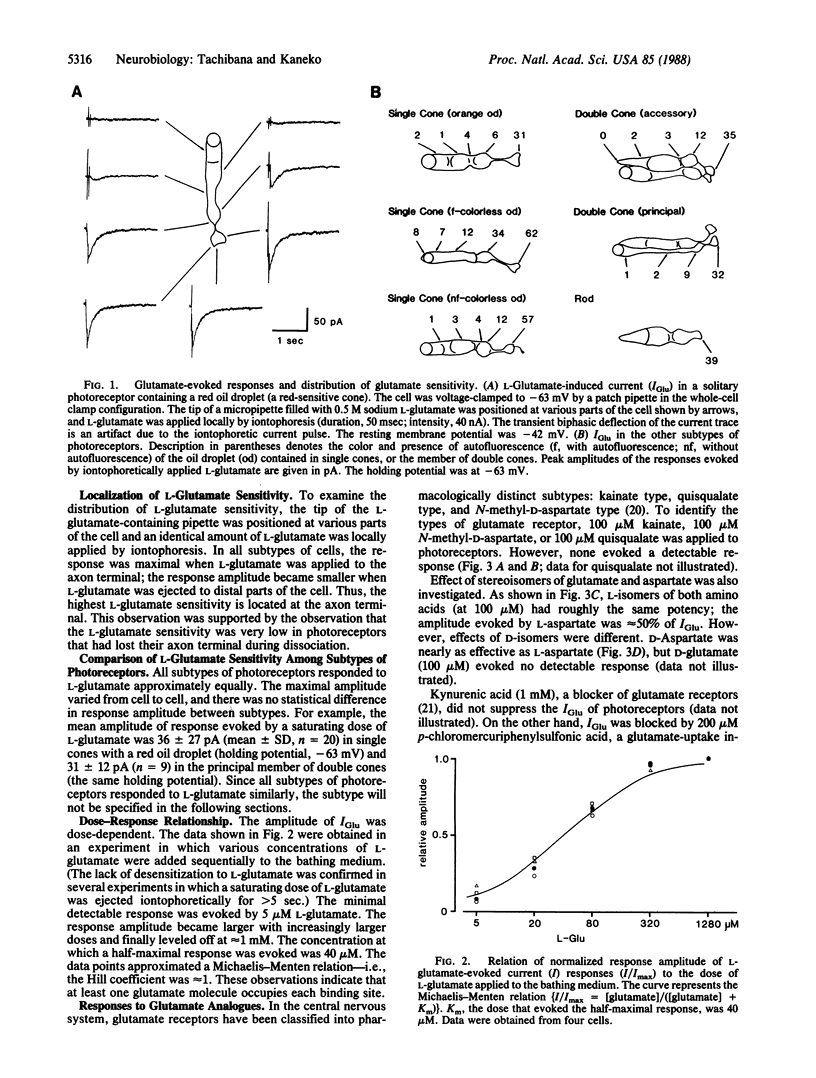
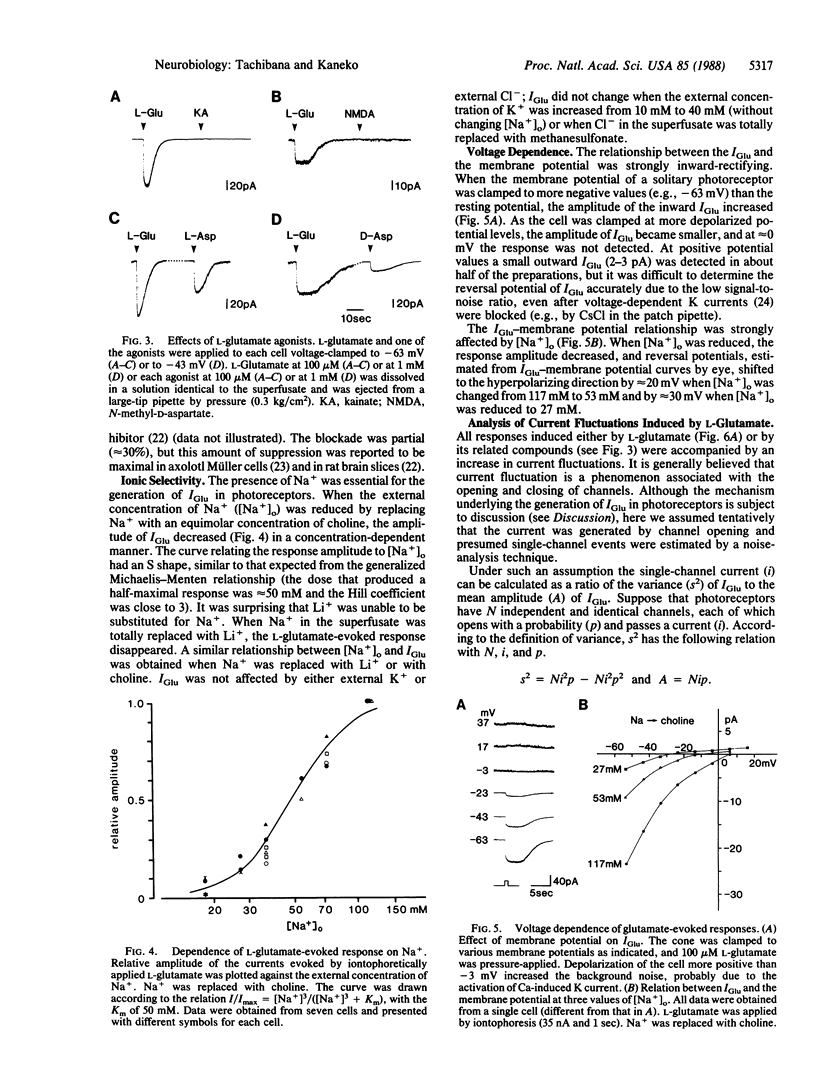
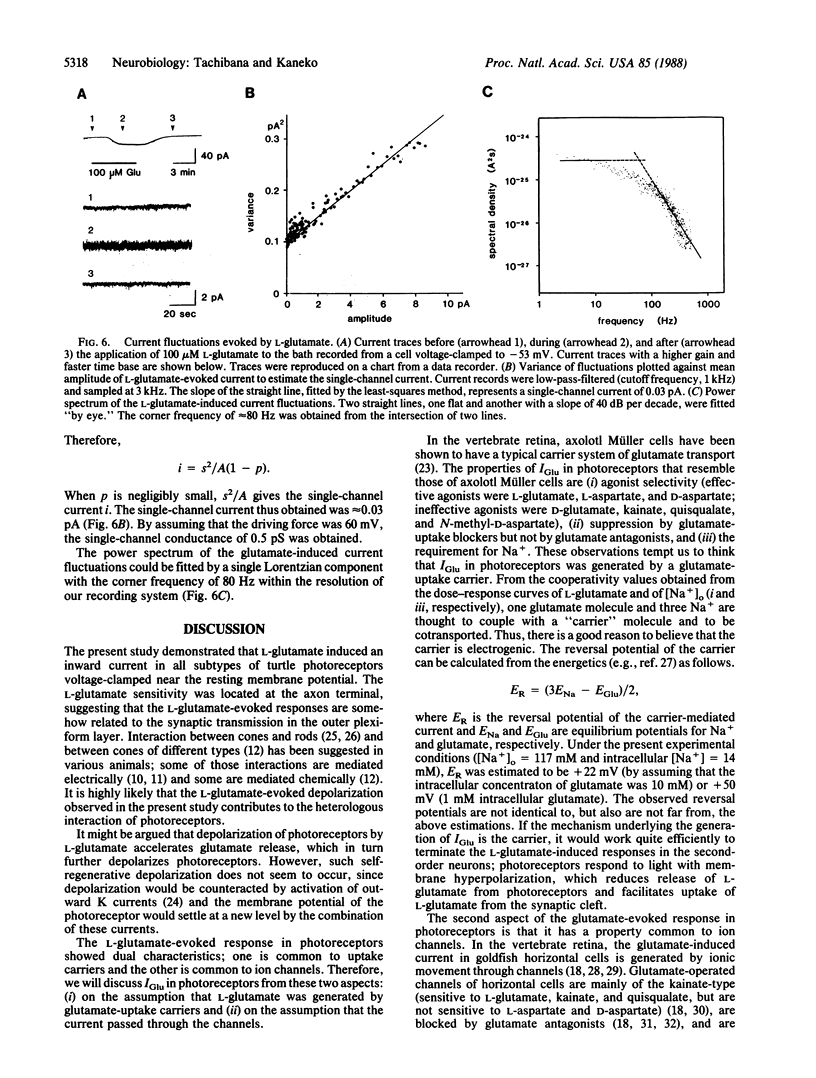
L-Glutamate is a leading candidate for the vertebrate photoreceptor transmitter. In addition to the signal transmission to second-order neurons, photoreceptors communicate with each other not only electrically but also chemically. In the present study, by using solitary turtle photoreceptors, we examined the possibility that L-glutamate mediates interreceptor communication. L-Glutamate evoked an inward current in all subtypes of photoreceptors voltage-clamped to the resting potential. The highest glutamate sensitivity was located at the axon terminal. Both stereoisomers of aspartate were effective, whereas kainate, quisqualate, N-methyl-D-aspartate, and D-glutamate were ineffective. The presence of Na+ was essential to response generation; even Li+ could not substitute for Na+. The relation between L-glutamate-induced current and the membrane voltage was strongly inward-rectifying. These results favor the hypothesis that the L-glutamate-induced response is generated by an electrogenic uptake carrier. However, L-glutamate-induced current was always accompanied by an increase in current fluctuations, a phenomenon commonly observed in ion channels but not expected for an uptake carrier. Although the underlying mechanism needs further elucidation, it seems likely that L-glutamate is a transmitter for communication between photoreceptors.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bader C. R., Bertrand D., Schwartz E. A. Voltage-activated and calcium-activated currents studied in solitary rod inner segments from the salamander retina. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:253–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balcar V. J., Johnston G. A. The structural specificity of the high affinity uptake of L-glutamate and L-aspartate by rat brain slices. J Neurochem. 1972 Nov;19(11):2657–2666. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brew H., Attwell D. Electrogenic glutamate uptake is a major current carrier in the membrane of axolotl retinal glial cells. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):707–709. doi: 10.1038/327707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervetto L., MacNichol E. F., Jr Inactivation of horizontal cells in turtle retina by glutamate and aspartate. Science. 1972 Nov 17;178(4062):767–768. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4062.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dacheux R. F., Miller R. F. Photoreceptor-bipolar cell transmission in the perfused retina eyecup of the mudpuppy. Science. 1976 Mar 5;191(4230):963–964. doi: 10.1126/science.175443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling J. E., Ripps H. Effect of magnesium on horizontal cell activity in the skate retina. Nature. 1973 Mar 9;242(5393):101–103. doi: 10.1038/242101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehinger B. [3H]-D-aspartate accumulation in the retina of pigeon, guinea-pig and rabbit. Exp Eye Res. 1981 Oct;33(4):381–391. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(81)80090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain G. L., Gold G. H., Dowling J. E. Receptor coupling in the toad retina. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:547–561. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain G. L. Interactions of rod and cone signals in the mudpuppy retina. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(3):735–769. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida A. T., Fain G. L. D-aspartate potentiates the effects of L-glutamate on horizontal cells in goldfish retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5890–5894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida A. T., Kaneko A., Tachibana M. Responses of solitary retinal horizontal cells from Carassius auratus to L-glutamate and related amino acids. J Physiol. 1984 Mar;348:255–270. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida A. T., Neyton J. Quisqualate and L-glutamate inhibit retinal horizontal-cell responses to kainate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1837–1841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A., Shimazaki H. Synaptic transmission from photoreceptors to bipolar and horizontal cells in the carp retina. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:537–546. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko A., Tachibana M. Effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid on isolated cone photoreceptors of the turtle retina. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:443–461. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasater E. M., Dowling J. E. Carp horizontal cells in culture respond selectively to L-glutamate and its agonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):936–940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marc R. E., Lam D. M. Uptake of aspartic and glutamic acid by photoreceptors in goldfish retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7185–7189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. M., Schwartz E. A. Evidence for the identification of synaptic transmitters released by photoreceptors of the toad retina. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:325–349. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Otsu K., Otsuka T. Effects of chemicals on receptors and horizontal cells in the retina. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):899–913. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normann R. A., Perlman I., Kolb H., Jones J., Daly S. J. Direct excitatory interactions between cones of different spectral types in the turtle retina. Science. 1984 May 11;224(4649):625–627. doi: 10.1126/science.6710161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsuka T. Relation of spectral types to oil droplets in cones of turtle retina. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):874–877. doi: 10.1126/science.4023716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsuka T. Spectral sensitivities of seven morphological types of photoreceptors in the retina of the turtle, Geoclemys reevesii. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Jul 8;237(2):145–154. doi: 10.1002/cne.902370202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. N., Stone T. W. An iontophoretic investigation of the actions of convulsant kynurenines and their interaction with the endogenous excitant quinolinic acid. Brain Res. 1982 Sep 9;247(1):184–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarantis M., Everett K., Attwell D. A presynaptic action of glutamate at the cone output synapse. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):451–453. doi: 10.1038/332451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. A. Cones excite rods in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1975 Apr;246(3):639–651. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz E. A. Electrical properties of the rod syncytium in the retina of the turtle. J Physiol. 1976 May;257(2):379–406. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter M. M., Miller R. F. Identification of a distinct synaptic glutamate receptor on horizontal cells in mudpuppy retina. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):96–97. doi: 10.1038/314096a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana M., Kaneko A. gamma-Aminobutyric acid acts at axon terminals of turtle photoreceptors: difference in sensitivity among cell types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7961–7964. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana M. Permeability changes induced by L-glutamate in solitary retinal horizontal cells isolated from Carassius auratus. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:153–167. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



