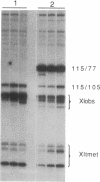
Abstract
The long-term stability of transcription complexes on 5S RNA genes has been demonstrated in vivo. Complexes on oocyte and somatic-type 5S RNA genes injected into Xenopus laevis oocyte nuclei are stable for at least 4 days. Tissue culture cells and mature erythrocytes have equivalent numbers of somatic 5S RNA genes programmed into transcription complexes, yet the former cell type has a greater than 50-fold higher cellular content of transcription factor IIIA (TFIIIA). Functional transcription complexes on somatic 5S RNA genes in nucleated erythrocytes of Xenopus are stable for weeks, perhaps months, even though a mature erythrocyte has less than two molecules of TFIIIA for each somatic 5S RNA gene. These findings strengthen our proposal that stable transcription complexes are a means of maintaining the differentiated state.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews M. T., Brown D. D. Transient activation of oocyte 5S RNA genes in Xenopus embryos by raising the level of the trans-acting factor TFIIIA. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90640-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Brown D. D., Jordan E. A nuclear extract of Xenopus laevis oocytes that accurately transcribes 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1077–1086. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription termination. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90522-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Stable transcription complexes of Xenopus 5S RNA genes: a means to maintain the differentiated state. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Gurdon J. B. High-fidelity transcription of 5S DNA injected into Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2064–2068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Schlissel M. S. A positive transcription factor controls the differential expression of two 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D. The role of stable complexes that repress and activate eucaryotic genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90366-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cizewski V., Sollner-Webb B. A stable transcription complex directs mouse ribosomal RNA synthesis by RNA polymerase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7043–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson S. G., Kurer V., Smith H. O. Sequence organization of a cloned tDNA met fragment from Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):713–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90253-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzarelli N. R., Gerrard S. P., Schlissel M., Brown D. D., Bogenhagen D. F. Purified RNA polymerase III accurately and efficiently terminates transcription of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):829–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90540-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Brown D. D. The transcription of 5 S DNA injected into Xenopus oocytes. Dev Biol. 1978 Dec;67(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. L., Gregori T. J. Cloning multiple copies of a DNA segment. Gene. 1981 May;13(4):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Tata J. R. Template-engaged and free RNA polymerases during Xenopus erythroid cell maturation. Dev Biol. 1978 Aug;65(2):496–507. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Hamer D. H., Roeder R. G. Stable transcription complex on a class III gene in a minichromosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):40–45. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Lienhard S., Jiricny J., De Robertis E. M. An enhancer-like sequence within the Xenopus U2 gene promoter facilitates the formation of stable transcription complexes. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):163–167. doi: 10.1038/316163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Roeder R. G. Selective and accurate transcription of the Xenopus laevis 5S RNA genes in isolated chromatin by purified RNA polymerase III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):44–48. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Related 5S RNA transcription factors in Xenopus oocytes and somatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J. Purification of nuclear factor I by DNA recognition site affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1398–1408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryrie I. J., Gallagher A. The yeast mitochondrial ATPase complex. Subunit composition and evidence for a latent protease contaminant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 11;545(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90108-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D., Engelke D., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. The binding of a transcription factor to deletion mutants of a 5S ribosomal RNA gene. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):665–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M. S., Brown D. D. The transcriptional regulation of Xenopus 5s RNA genes in chromatin: the roles of active stable transcription complexes and histone H1. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):903–913. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90425-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastry B. S., Honda B. M., Roeder R. G. Altered levels of a 5 S gene-specific transcription factor (TFIIIA) during oogenesis and embryonic development of Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11373–11382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Jackson I. J., Brown D. D. Domains of the positive transcription factor specific for the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90396-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas N., Maclean N. The erythroid cells of anaemic Xenopus laevis. I. Studies on cellular morphology and protein and nucleic acid synthesis during differentiation. J Cell Sci. 1975 Dec;19(3):509–520. doi: 10.1242/jcs.19.3.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A., Jared D. W., Dumont J. N., Sega M. W. Protein incorporation by isolated amphibian oocytes. 3. Optimum incubation conditions. J Exp Zool. 1973 Jun;184(3):321–333. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401840305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandelt C., Grummt I. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes is a prerequisite for ribosomal DNA transcription in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3795–3809. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Brown D. D. Differential 5S RNA gene expression in vitro. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):733–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Jordan E., Brown D. D. A bacteriophage RNA polymerase transcribes through a Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription complex without disrupting it. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woll W. W., Duffy J. J., Giese N. A., Lindell T. J. Nuclear isolation by a modified method of Hewish and Burgoyne: implications for the study of nuclear enzymology. Life Sci. 1981 Dec 28;29(26):2709–2719. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90530-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]