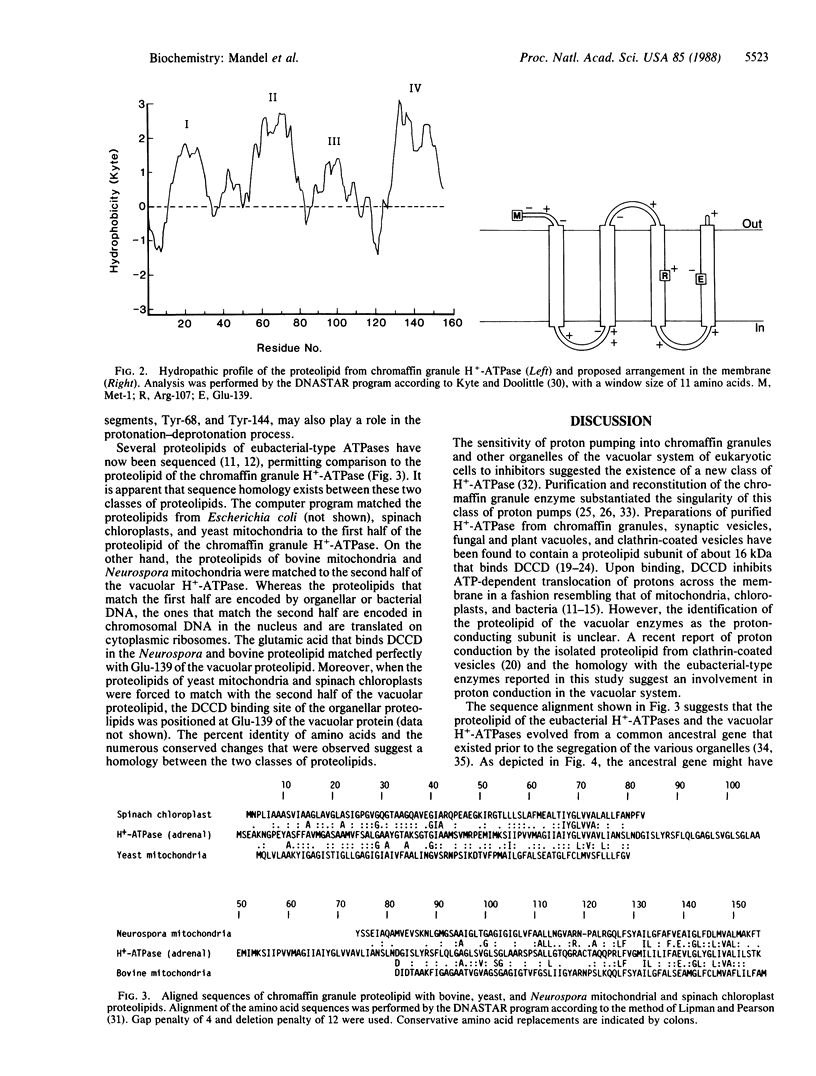
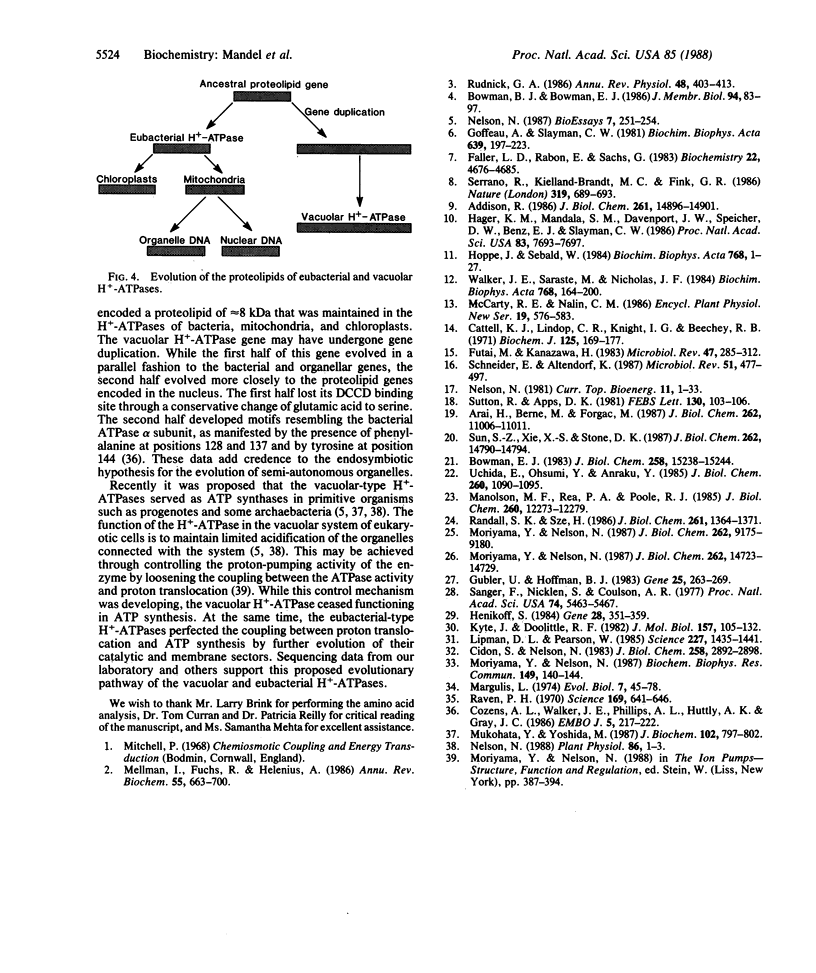
Abstract
Vacuolar H+-ATPases function in generating protonmotive force across the membranes of organelles connected with the vacuolar system of eukaryotic cells. This family of H+-ATPases is distinct from the two other families of H+-ATPases, the plasma membrane-type and the eubacterial-type. One of the subunits of the vacuolar H+-ATPase binds N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCD) and has been implicated in the proton-conducting activity of these enzymes. We have cloned and sequenced the gene encoding the DCCD-binding protein (proteolipid) of the H+-ATPase of bovine chromaffin granules. The gene encodes a highly hydrophobic protein of 15,849 Da. Hydropathy plots revealed four transmembrane segments, one of which contains a glutamic residue that is the likely candidate for the DCCD binding site. Sequence homology with the vacuolar proteolipid and with the proteolipids of eubacterial-type H+-ATPases was detected. The proteolipids from Escherichia coli, spinach chloroplasts, and yeast mitochondria matched better to the NH2-terminal part of the vacuolar protein. The proteolipids of bovine mitochondria and Neurospora mitochondria matched better to the COOH-terminal end of the vacuolar proteolipid. These findings suggest that the proteolipids of the vacuolar H+-ATPases were evolved in parallel with the eubacterial proteolipid, from a common ancestral gene that underwent gene duplication.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addison R. Primary structure of the Neurospora plasma membrane H+-ATPase deduced from the gene sequence. Homology to Na+/K+-, Ca2+-, and K+-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):14896–14901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai H., Berne M., Forgac M. Inhibition of the coated vesicle proton pump and labeling of a 17,000-dalton polypeptide by N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):11006–11011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman B. J., Bowman E. J. H+-ATPases from mitochondria, plasma membranes, and vacuoles of fungal cells. J Membr Biol. 1986;94(2):83–97. doi: 10.1007/BF01871190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman E. J. Comparison of the vacuolar membrane ATPase of Neurospora crassa with the mitochondrial and plasma membrane ATPases. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15238–15244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattell K. J., Lindop C. R., Knight I. G., Beechey R. B. The identification of the site of action of NN'-dicyclohexylcarbodi-imide as a proteolipid in mitochondrial membranes. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(1):169–177. doi: 10.1042/bj1250169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cidon S., Nelson N. A novel ATPase in the chromaffin granule membrane. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2892–2898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozens A. L., Walker J. E., Phillips A. L., Huttly A. K., Gray J. C. A sixth subunit of ATP synthase, an F(0) component, is encoded in the pea chloroplast genome. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):217–222. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04201.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faller L. D., Rabon E., Sachs G. Vanadate binding to the gastric H,K-ATPase and inhibition of the enzyme's catalytic and transport activities. Biochemistry. 1983 Sep 27;22(20):4676–4685. doi: 10.1021/bi00289a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futai M., Kanazawa H. Structure and function of proton-translocating adenosine triphosphatase (F0F1): biochemical and molecular biological approaches. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):285–312. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.285-312.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goffeau A., Slayman C. W. The proton-translocating ATPase of the fungal plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 30;639(3-4):197–223. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(81)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager K. M., Mandala S. M., Davenport J. W., Speicher D. W., Benz E. J., Jr, Slayman C. W. Amino acid sequence of the plasma membrane ATPase of Neurospora crassa: deduction from genomic and cDNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7693–7697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe J., Sebald W. The proton conducting F0-part of bacterial ATP synthases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 9;768(1):1–27. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(84)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manolson M. F., Rea P. A., Poole R. J. Identification of 3-O-(4-benzoyl)benzoyladenosine 5'-triphosphate- and N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-binding subunits of a higher plant H+-translocating tonoplast ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12273–12279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama Y., Nelson N. Internal anion binding site and membrane potential dominate the regulation of proton pumping by the chromaffin granule ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 30;149(1):140–144. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91615-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama Y., Nelson N. Nucleotide binding sites and chemical modification of the chromaffin granule proton ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14723–14729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama Y., Nelson N. The purified ATPase from chromaffin granule membranes is an anion-dependent proton pump. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9175–9180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukohata Y., Yoshida M. The H+-translocating ATP synthase in Halobacterium halobium differs from F0F1-ATPase/synthase. J Biochem. 1987 Oct;102(4):797–802. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N. Structure, Function, and Evolution of Proton-ATPases. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jan;86(1):1–3. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N. The vacuolar proton-ATPase of eukaryotic cells. Bioessays. 1987 Dec;7(6):251–254. doi: 10.1002/bies.950070605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall S. K., Sze H. Properties of the partially purified tonoplast H+-pumping ATPase from oat roots. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1364–1371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raven P. H. A multiple origin for plastids and mitochondria. Science. 1970 Aug 14;169(3946):641–646. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3946.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick G. ATP-driven H+ pumping into intracellular organelles. Annu Rev Physiol. 1986;48:403–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.48.030186.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E., Altendorf K. Bacterial adenosine 5'-triphosphate synthase (F1F0): purification and reconstitution of F0 complexes and biochemical and functional characterization of their subunits. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):477–497. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.477-497.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R., Kielland-Brandt M. C., Fink G. R. Yeast plasma membrane ATPase is essential for growth and has homology with (Na+ + K+), K+- and Ca2+-ATPases. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):689–693. doi: 10.1038/319689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. Z., Xie X. S., Stone D. K. Isolation and reconstitution of the dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-sensitive proton pore of the clathrin-coated vesicle proton translocating complex. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14790–14794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R., Apps D. K. Isolation of a DCCD-binding protein from bovine chromaffin-granule membranes. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jul 20;130(1):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80675-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida E., Ohsumi Y., Anraku Y. Purification and properties of H+-translocating, Mg2+-adenosine triphosphatase from vacuolar membranes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1090–1095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Gay N. J. The unc operon. Nucleotide sequence, regulation and structure of ATP-synthase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 6;768(2):164–200. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(84)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



