Abstract
Rationale
S100A4/Mts1 is implicated in motility of human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (hPASMC), through an interaction with the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE).
Objective
We hypothesized that S100A4/Mts1-mediated hPASMC motility might be enhanced by loss of function of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptor (R) II, observed in pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH).
Methods and Results
Both S100A4/Mts1 (500ng/ml) and BMP-2 (10ng/ml) induce migration of hPASMCS in a novel co-dependent manner, in that the response to either ligand is lost with anti-RAGE or BMPRII siRNA. Phosphorylation of ERK is induced by both ligands and is required for motility by inducing MMP2 activity, but phosphoERK1/2 is blocked by anti-RAGE and not by BMPRII siRNA. In contrast, BMPRII siRNA, but not anti-RAGE, reduces expression of intracellular chloride channel 4 (CLIC4), a scaffolding molecule necessary for motility in response to S100A4/Mts1 or BMP-2. Reduced CLIC4 expression does not interfere with S100A4/Mts1 internalization or its interaction with myosin heavy chain IIA (MHCIIA), but does alter alignment of MHCIIA and actin filaments creating the appearance of vacuoles. This abnormality is associated with reduced peripheral distribution and/or delayed activation of RhoA and Rac1, small GTPases required for retraction and extension of lamellipodiae in motile cells.
Conclusions
Our studies demonstrate how a single ligand (BMP-2 or S100A4/Mts1) can recruit multiple cell surface receptors to relay signals that coordinate events culminating in a functional response, i.e., cell motility. We speculate that this carefully controlled process limits signals from multiple ligands, but could be subverted in disease.
Keywords: Bone morphogenetic protein, S100 protein, Vascular smooth muscle cells, Intracellular chloride channel, migration
Introduction
S100A4 (also known as Mts1, metastasin, p9Ka, pEL98, CAPL, calvasculin, Fsp-1, placental calcium-binding protein) belongs to the family of EF-hand calcium-binding proteins1. Increased expression of S100A4/Mts1 is observed in cancer cells and contributes to tumor cell motility and metastatic progression, through interaction with myosin heavy chain II2,. Our group has shown that S100A4/Mts1 also induces human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell (hPASMC) migration and proliferation by interacting with the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE)3. Migration and proliferation of hPASMC have been linked to the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH)4. This is in keeping with our previously reported finding that a small percentage of transgenic mice overexpressing S100A4/Mts1 develop occlusive pulmonary vascular changes5. We have also previously reported that expression of S100A4/Mts1 requires a co-operative interaction between the serotonin receptor and transporter3. This, too, is relevant to the pathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension, since heightened serotonin activity has been linked, both clinically and experimentally, to the pathogenesis of PAH6.
Mutations causing loss of function of BMPRII have been linked to >60% of cases of familial (F) PAH and 25% of cases of sporadic (I) PAH, but the penetrance is low7, 8, suggesting that other modifier genes and/or environmental factors may be important. Thus, understanding the interactions between signaling via BMPRII and other cell surface receptors, such as RAGE, via S100A4/Mts1 is helpful in uncovering factors that modify propensity to vascular disease in association with a BMPRII mutation.
Our studies reveal a previously unknown co-dependence between signals emanating from BMPRII and RAGE in mediating cell motility. Suppression of RAGE, but not BMPRII, resulted in loss of pERK and MMP2 activity, whereas loss of BMPRII but not RAGE reduced levels of the intracellular chloride channel 4 (CLIC4), a scaffolding protein previously implicated in motility9,10. Loss of CLIC4 resulted in impaired activation and distribution of the small GTPases RhoA and Rac1, necessary for cell retraction and extension of filapodiae and lamellipodiae during cell migration.
Material and Methods
Expanded Material and Methods are found in the online Supplement.
Cell Culture
Human PASMC were used between passages 5 and 9, and synchronized using a defined starvation medium. In some experiments, cells were pre-incubated with the phospho(p)ERK1/2-inhibitor PD 98059 at 25 and 100 μM, or with the MEK inhibitor U0126 10 μM or with a rabbit polyclonal anti-RAGE antibody.
Migration Assay Using a Modified Boyden Chamber
Cells were added to fibronectin-coated microporous inserts of 24 well plates, and the migratory stimulus was added to the well in the bottom of the chamber for 6h. The cells that had migrated to the bottom of the insert were fixed and stained with the Diff Quick Kit. The cells in three different fields (200-400×) at the center of each well were counted under the microscope.
Transfection with siRNA
To suppress expression of BMPRII and CLIC4 in hPASMC, we transfected siRNA SMARTpool® from Dharmacon (Lafayette, CO) and LipofectamineTM 2000 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) as described in the Supplement. Suppression of BMPRII and CLIC4 was documented 48h later both by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and by western immunoblot.
Western Immunoblotting and Phosphorylation Assays
Cell lysates were prepared and run under reducing conditions prior to transfer to a nitrocellulose membrane. The membrane was blocked and the blots were incubated with polyclonal antibodies against human CLIC4, S100A4/Mts1 or His tag. Densitometry was carried out using the quantity one software by Biorad (Hercules, CA).
cDNA Microarray Analysis
Microarray analysis of cDNAs obtained from hPASMCS, data acquisition and analysis were performed as previously described11 comparing genes that were similarly up or down regulated >2 fold by S100A4/Mts1 and BMP-2 and blocked by BMPRII siRNA but not by anti-RAGE.
Quantitative TaqMan Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (q-RT-PCR)
RNA was isolated by Trizol (Invitrogen) and reverse transcribed using Superscript III (Invitrogen). RT-PCR was performed on a 7900HT Sequence Detection System with TaqMan pre-verified Assays-on-Demand gene expression probes (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) for BMPRII (assay ID Hs 01556128_m1), CLIC4 (assay ID Hs 00983246_g1), using the absolute quantification method with β2-microglobulin (assay ID Mm 01269327_g1) as the endogenous control.
Immunocytochemistry
Human PASMCs were seeded on collagen I coated 4-chamber slides fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde. We used, a polyclonal rabbit and monoclonal goat CLIC4 antibody, a polyclonal rabbit myosin heavy chain IIA (MHCIIA) antibody, a mouse monoclonal Rac1 and a rabbit polyclonal α smooth muscle actin antibody. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Images were acquired with a Leica microscope using Openlab 3.1.4 software (Improvision, Coventry, UK).
Luminescence Caspase 3/7 apoptosis assay
In PASMCs 48 hours after transfection with control RNAi, BMPRII RNAi and CLIC4 RNAi, Caspase 3/7 activity was assessed with Luminescence Caspase-Glo® 3/7 Assay (Promega, Madison, WI, G8091) in a 96 well plate as described in the kit.
Rac1 and RhoA and Cd42 Pulldown Assays
Both Rac1, RhoA and Cd42 activation were assayed after stimulation with recombinant S100A4/Mts1, using kits for Rac1 and RhoA (Upstate technology, Temecula, NY) and for Cdc42 (EZ-DetectTM Cdc42 Activation kit, Pierce, Rockford, IL).
Gelatin Zymography
To assess matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) activity, electrophoresis was carried out on an 8% SDS-PAGE co-polymerized with gelatin and stained with 0.05% Coomassie brilliant blue and de-stained in 5% ethanol with 7.5% acetic acid. Areas of proteolysis were quantified using the public JAVA image-processing program, NIH Image/ImageJ.
Statistical Analysis
The number of experiments carried out for each determination is given in the Figure legends. All quantitative results are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni post-hoc test or Dunnett's when comparisons involved ≥3 groups. A p value of <0.05 was considered significant.
Results
S100A4/Mts1 or BMP-2 Induced hPASMC Migration Requires RAGE and BMPRII
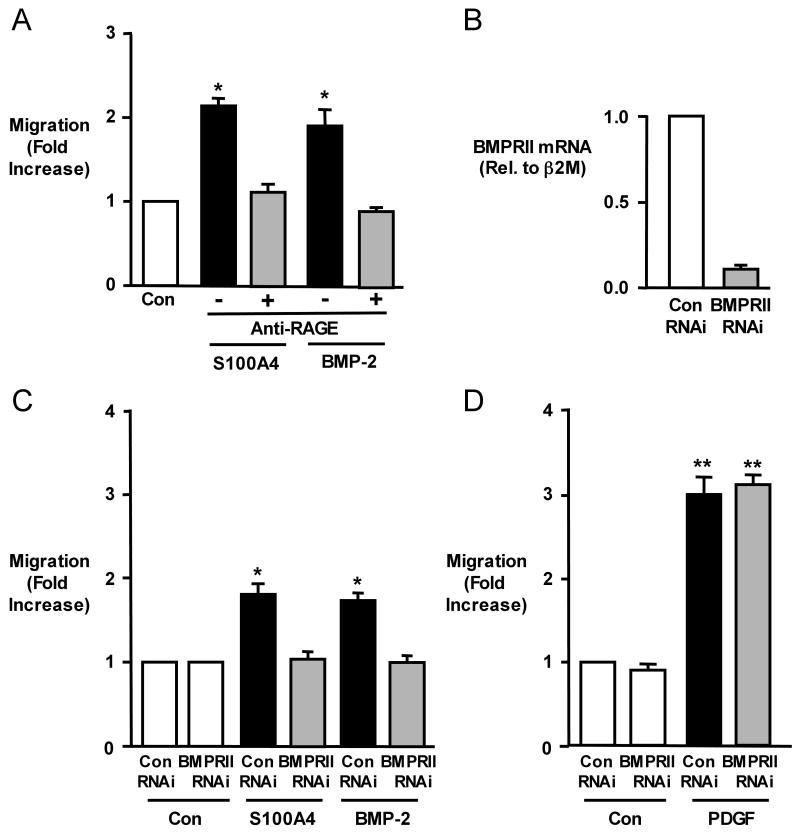
Stimulation of hPASMCs with recombinant S100A4/Mts1 (500ng/ml) or with BMP-2 (10ng/ml) resulted in a 2-fold increase in migration compared to unstimulated (control) cells as assessed in Boyden chambers at 6h. While we expected that the S100A4/Mts1 migratory response of hPASMC would be blocked by anti-RAGE, the same was true for BMP-2 mediated hPAMSC migration (Figure 1A). Similarly, when we reduced the levels of BMPRII mRNA and protein12 with siRNA to 20% of those in hPASMC transfected with control siRNA (Figure 1B), the migratory response to both BMP-2 and to S100A4/Mts1 was repressed (Figure 1C). We previously published that in cells from the same harvests, the reduction in BMPRII protein by siRNA was associated with reduced phosphorylation of Smad 1/512. The migratory response to the motogen PDGF-BB was not influenced by knocking down BMPRII (Figure 1D) or by anti-RAGE3.
Figure 1. S100A4/Mts1 and BMP-2 Mediated Migration of hPASMCs is Blocked by anti-RAGE and BMPRIIsi.
(A) Migration of hPASMCs using a modified Boyden chamber 6h without (Con) or after stimulation with S100A4 (500ng/ml) or BMP-2 (10ng/ml) ± anti-RAGE blocking antibody (1:1000; preincubation 30min). (B) Quantitative RT-PCR for BMPRII following control(con) RNAi or BMPRII RNAi. (C) Migration of hPASMCs in response to S100A4 and BMP-2 after reducing BMPRII levels by BMPRII RNAi to 20% compared to Con RNAi. (D) Migration of hPASMCs in response to PDGF-BB(PDGF) 20ng/ml using Con RNAi or BMPRII RNAi. Bars represent mean±SEM, n=6 in each group; *p<0.001, vs. control (A) or con RNAi (C, D).
pERK1/2 is Necessary but not Sufficient for S100A4/Mts1 and BMP-2 Induced hPASMC Migration
In a search for common or complementary signaling mechanisms activated via RAGE or BMPRII in response to either S100A4/Mts1 or BMP-2, we identified pERK1/2 (Figure 2A). Other signaling molecules involved in migration (JNK, p38, Smads) were not induced by both ligands (data not shown). Blockade of pERK1/2 with the specific MAP kinase inhibitor PD98059 at 25 and 100 μM or with the MEK inhibitor U0126 10μM, abrogated the migratory response to both BMP-2 and S100A4/Mts1 (Figure 2B). Interestingly, pERK1/2 was blocked by anti-RAGE but not by BMPRII siRNA, suggesting that both BMP-2 and S100A4/Mts1 activate pERK through RAGE (Figure 2C). In addition, cells that were treated with BMPRII siRNA and stimulated with BMP-2 showed ERK phosphorylation that could be blocked with anti-RAGE, indicating that BMP-2 can induce pERK in a BMPRII independent manner via RAGE (Figure 2D). However, it also implies that, with loss of BMPRII, neither BMP-2 nor S100A4/Mts1 mediated pERK is sufficient to induce the migratory response of hPASMC. We therefore set out to determine downstream targets of BMPRII important in migration that were influenced by stimulation with both S100A4/Mts1 and BMP-2.
Figure 2. Phosphorylation of ERK, induced by S100A4/Mts1 and BMP-2, is necessary for migration of PASMCs downstream of RAGE, but is not BMPRII, dependent.
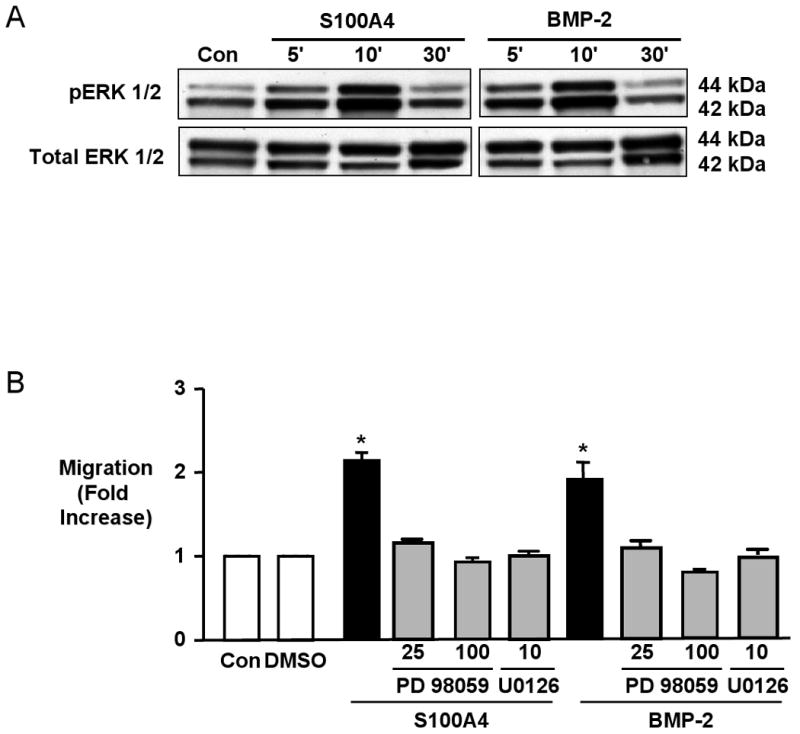
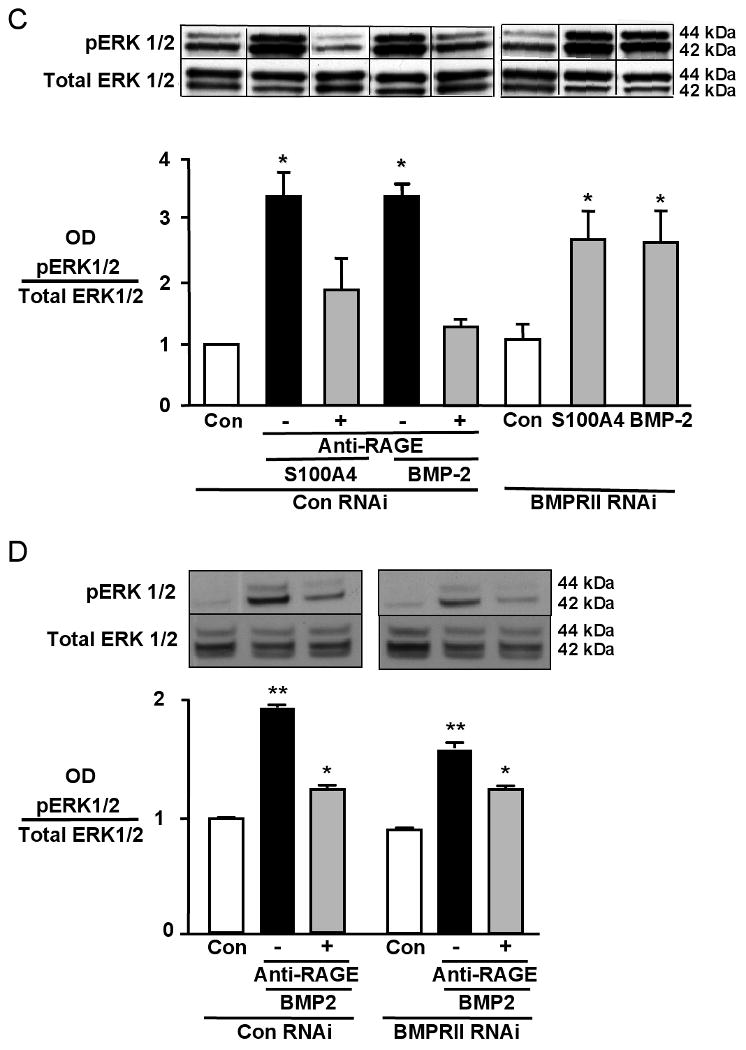
(A) Western immunoblot showing pERK1/2 (kDa 42/44) relative to total ERK1/2 in response to S100A4 and BMP-2. (B) Migration assays ± 30-minute preincubation with MAPK inhibitor PD 98059 (25 μM,100μM) and MEK inhibitor U0126 (10μM). DMSO as vehicle control for PD 98059. (C, D) Western immunoblot and densitometry of pERK1/2 over total ERK1/2 ± anti-RAGE ± BMPRII RNAi, un-stimulated (Con) or following stimulation with BMP-2 and S100A4 for 10 minutes. Each value is normalized to total ERK on the same blot but lanes are non-consecutive, indicated by the lines between them (C). Bars represent mean±SEM, for n=6 in B, and n=3 in C. *p<0.001 vs. Con. Experiments in C and D reflect differences in the magnitude of change in cells from different harvests.
Chloride Intracellular Channel (CLIC)4 Expression Depends on BMPRII and is Necessary for S100A4/Mts1- and BMP-2-Mediated Migration of hPASMCs
To identify BMPRII-dependent gene transcripts, we used Stanford cDNA microarrays11 to mine for mRNAs in hPASMC that were altered by BMPRII siRNA but not by anti-RAGE in response to BMP-2 and S100A4/Mts1 stimulation for 6h.
Of all 14,500 annotated genes on the array, 23 were BMPRII-dependent genes meaning that they were similarly expressed after S100A4/Mts1 and BMP-2 stimulation and had a similar alteration in expression pattern with BMPRII siRNA but not the RAGE antibody. Of those, 6 genes have been previously associated with motility (tenascin C, fibrillin I, myosin light chain polypeptide kinase, alpha tubulin, Ras-GTPase activating protein, and CLIC4 (chloride intracellular channel 4). Of those 6 genes, CLIC4 showed the greatest alteration in expression with loss of BMPRII (4-fold reduction). Confirmation of this reduction in gene expression was verified by qRT-PCR (Figure 3A). Knockdown of CLIC4 following pretreatment with BMPRII siRNA was dependent on a ligand-receptor interaction, as knocking down of BMPRII in the absence of ligand stimulation, did not reduce CLIC4 levels (Figure 3A). Migration assays were carried out to test the functional importance of these findings, comparing the response of hPASMCs following knockdown of BMPRII or CLIC4 after transfection with siRNA. We documented a reduction in CLIC4 mRNA to 20% of the values obtained with control siRNA (Figure 3B) as well as a comparable decrease in CLIC4 protein (Figure 3C). We show in Figure 3D that migration of hPASMC in response to S100A4/Mts1 or BMP-2 was abrogated by CLIC4siRNA. As with BMPRII siRNA, the migratory response to PDGF-BB was not influenced by CLIC4 siRNA (Online Figure 1).
Figure 3. CLIC4 lies downstream of BMPRII, not RAGE, and is necessary in S100A4/Mts1 and BMP-2 induced migration of hPASMCs.
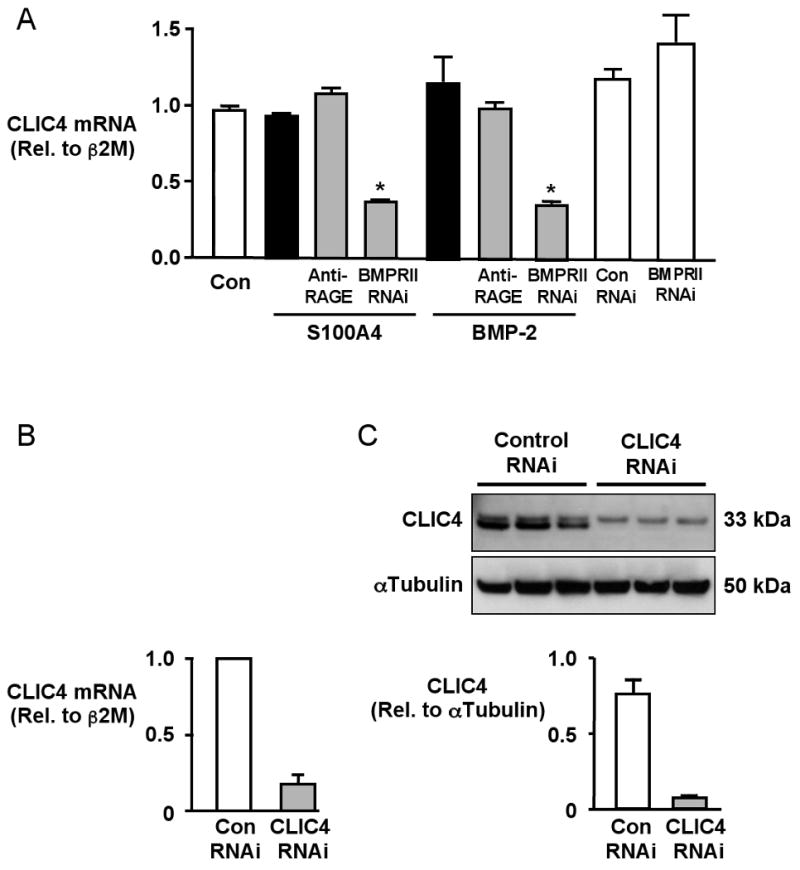
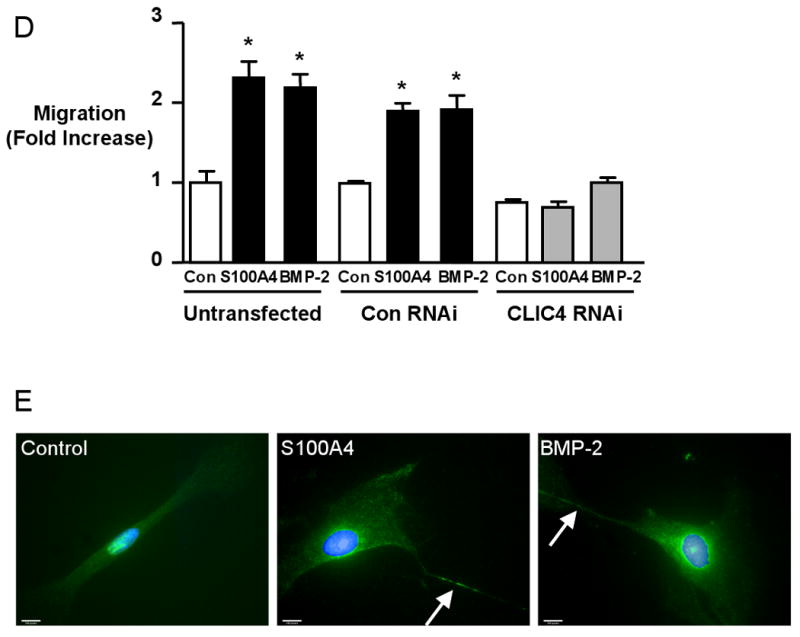
(A) Quantitative RT-PCR of CLIC4 mRNA normalized to β2 Microglobulin (β2M) mRNA in hPASMCs without stimulation and following S100A4 and BMP-2 for 6h ± 30min pretreatment with anti-RAGE (1:1000) or 48h after transfection with BMPRII RNAi (80% knock-down) or CLIC4 RNAi (B). (C) Western immunoblot and densitometry show a reduction in protein to less than 10% after CLIC4 RNAi. (D) Relative migration ± stimulation with S100A4 or BMP-2 of hPASMC transfected with Con or CLIC4 RNAi. Bars represent mean±SEM for n=3 in A and n=4 in C. *p<0.001 vs. control unstimulated. (E) Immunolocalization of CLIC4 in hPASMCs under control conditions and following 2h stimulation with S100A4 and BMP-2. CLIC4, localized with a primary antibody and a secondary antibody conjugated to fluorescein (FITC) exhibits some nuclear staining under control conditions. In response to stimulation with BMP-2 and S100A4, CLIC4 staining becomes increasingly perinuclear and diffusely cytoplasmic, and localizes to the cell membrane, particularly in filopodiae (arrow). Nuclei counterstained with DAPI. (Bars represent 10μm).
Previous reports described the localization of CLIC4 in multiple subcellular compartments13-15. We observed by immunocytochemistry that there is some nuclear staining of CLIC4 under conditions of serum starvation, but as early as 10 min after stimulation of hPASMCs with S100A4/Mts1 or BMP-2, CLIC4 moves to a perinuclear and cytoplasmic location and concentrates at or near cell membranes as well as in filopodiae (Figure 3E). We therefore set out to determine why maintaining normal CLIC4 levels and pERK1/2 are necessary for hPASMC migration.
CLIC4 and pERK Do not Influence S100A4/Mts1 Uptake or Binding to MHCIIA
We investigated whether CLIC4 and/or pERK might be required for internalization of S100A4/Mts1 or for binding of S100A4/Mts1 to MHCIIA, processes implicated in motility. His-tagged S100A4/Mts1 uptake into the cell did not depend upon CLIC4 (Online Figure 2A). In addition, blockade of pERK1/2 had no effect on rS100A4/Mts1 uptake (Online Figure 2B). Binding of S100A4/Mts1 to MCHIIA16,2 was also neither dependent on pERK 1/2 (Online Figure 2C) nor on CLIC4 (data not shown).
Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP) 2 Activity Depends on pERK1/2, not on CLIC4
Previous studies have shown that pERK is necessary for MMP2 mediated motility in aortic smooth muscle cells17. We observed in hPASMC that S100A4/Mts1 mediates pro-MMP2 activity, in a pERK dependent manner in that the response is lost in cells pretreated with the inhibitor PD98059 (Figure 4). We observed primarily an increase in pro-MMP-2, as both the amount and any alteration in the active form of MMP-2 was difficult to appreciate by zymography. This observation is consistent with that of other investigators using cytokines to stimulate MMP-2 activity in SMCs 18. In contrast, reducing CLIC4 by siRNA did not alter pro-MMP2 activity, in response to S100A4/Mts1 (Figure 4).
Figure 4. Inhibition of pERK not CLIC4 Reduces S100A4/Mts1-induced MMP-2.
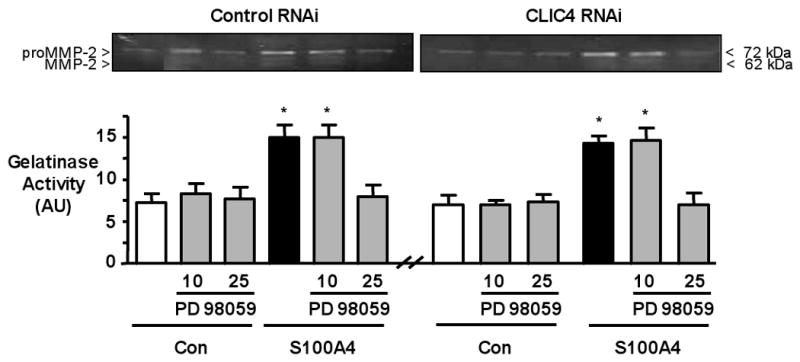
Representative gelatin zymography (top) and densitometry from three different experiments (bottom) carried out on conditioned media of cells in the Boyden chambers following 6h under control conditions or after stimulation with S100A4. Cells transfected with Con or with CLIC4 RNAi ± PD 98059. The pro-form of MMP2 is prominent whereas the active form is faint. Bars represent Mean±SEM of n=3 experiments. *p<0.05 vs. unstimulated control.
Loss of CLIC4 Causes Accumulation of MHCIIA Around Vacuolar Structures
Following transfection of cells with either BMPRII siRNA or with CLIC4 siRNA but not control siRNA, changes in the cytoskeleton were observed related to the alignment of MHCIIA (Figure 5A-D). Loss of CLIC4 resulted in disruption of the linear pattern of myosin staining and caused accumulation of MHCIIA around vacuolar structures. The vacuolar structures are also apparent by staining with an α smooth muscle actin antibody (Online Figure 3). Quantification shows that 50-60% of cells with knockdown in BMPRII or CLIC4 show vacuole formation, in contrast to 2-3% of cells after transfection with control siRNA (Online Figure 5). Cell survival assays measuring caspase 3/7 activity don't show differences between transfected and non-transfected cells, suggesting that the vacuole appearing structures do not reflect cell damage (Figure 5E). We confirmed CLIC4 localization not only in the cell body but also extending to cell processes such as lamellipodiae and filopodiae (arrows). In addition, we demonstrated by immunocytochemistry that CLIC4 staining is markedly reduced in BMPRII RNAi and CLIC4 RNAi treated cells and that the homogeneous distribution of CLIC4 is interrupted by the vacuolar structures (Figure 5F).
Figure 5. Loss of CLIC4 induces a vacuolar phenotype with accumulation of MHCIIA around vacuoles.
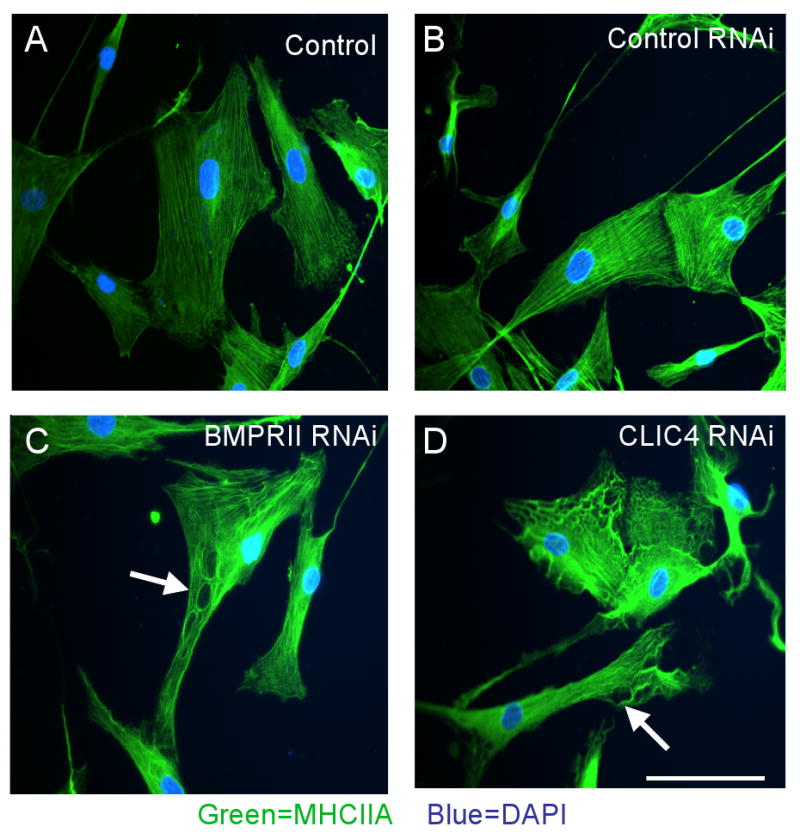
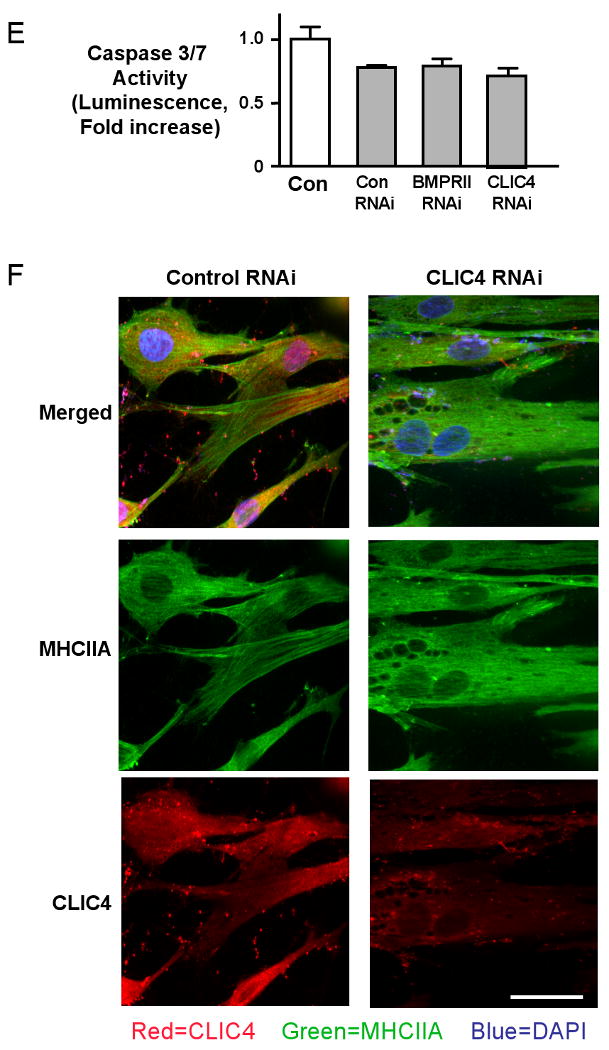
Immunofluorescence of MHCIIA in hPASMC stimulated with 500 ng/ml 6XHis-tagged S100A4/Mts1 for 10 min using a primary antibody against MHCIIA and a secondary antibody linked to fluorescein (FITC) under (A) untransfected conditions, following transfection with (B) control siRNA, (C) BMPRII siRNA, and (D) CLIC4 siRNA. Reducing CLIC4 either by BMPRII RNAi or CLIC4 RNAi interrupts linear alignment of MHCIIA (FITC) around what appear to be vacuoles (arrows in C and D). (E) Luminescent assay for caspase-3/7 activities in Control, BMPRII and CLIC4 RNAi treated cells. No significant differences between siRNA treated and control non-transfected cells are seen (Bar represents mean±SEM of n=6). F. Immunofluorescence of MHCIIA (FITC) and CLIC4 (rhodamine) in hPASMC under (A) untransfected control conditions and (B) following CLIC4 RNAi. Nuclear counterstain DAPI. (Bars = 50 μM).
CLIC4 Delays and Alters S100A4/Mts1 Induced RhoA and Rac1 Activation
Stimulation of hPASMC migration with both BMP-2 (not shown) and S100A4/Mts1 resulted in rapid activation of RhoA and Rac1 (Figure 6A, B). In contrast, suppression of CLIC4 with siRNA resulted in delayed Rac1 (Figure 6A) and RhoA activities (Figure 6B). We stained cells for Rac1 to assess changes in localization and interestingly have found that the distribution of Rac1 is altered after BMPRII and CLIC4 knockdown. In non-transfected or control RNAi cells, Rac1 is located both at the periphery and in the perinuclear region in response to S100A4, whereas with BMPRII or CLIC4 RNAi, the perinuclear localization persists but peripheral staining for Rac1 is markedly reduced (see arrows) (Figure 6C). These data support altered small GTPase signaling in response to down-regulation of CLIC4.
Figure 6. Suppression of CLIC4 Alters S100A4/Mts1 activation of RhoA and Rac1.
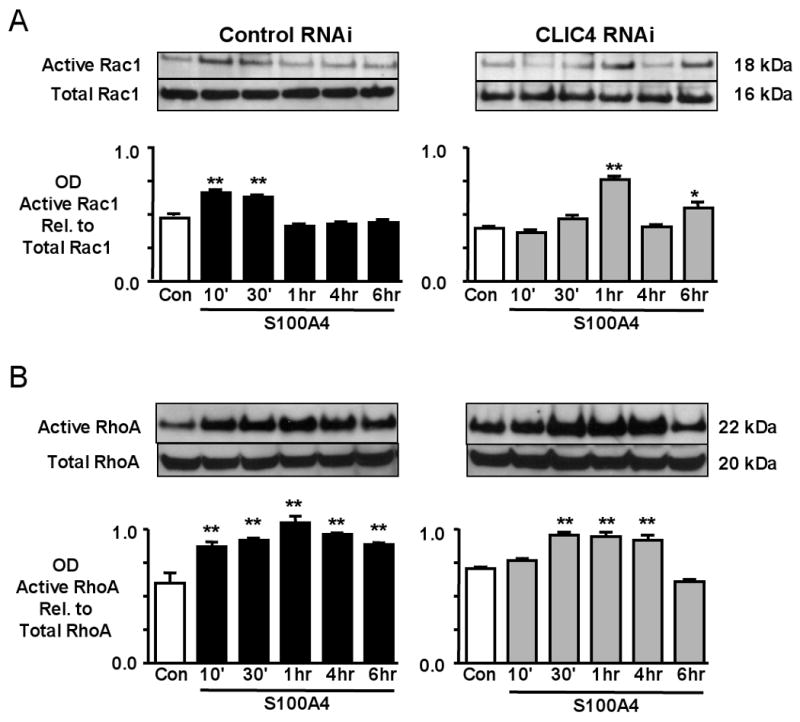
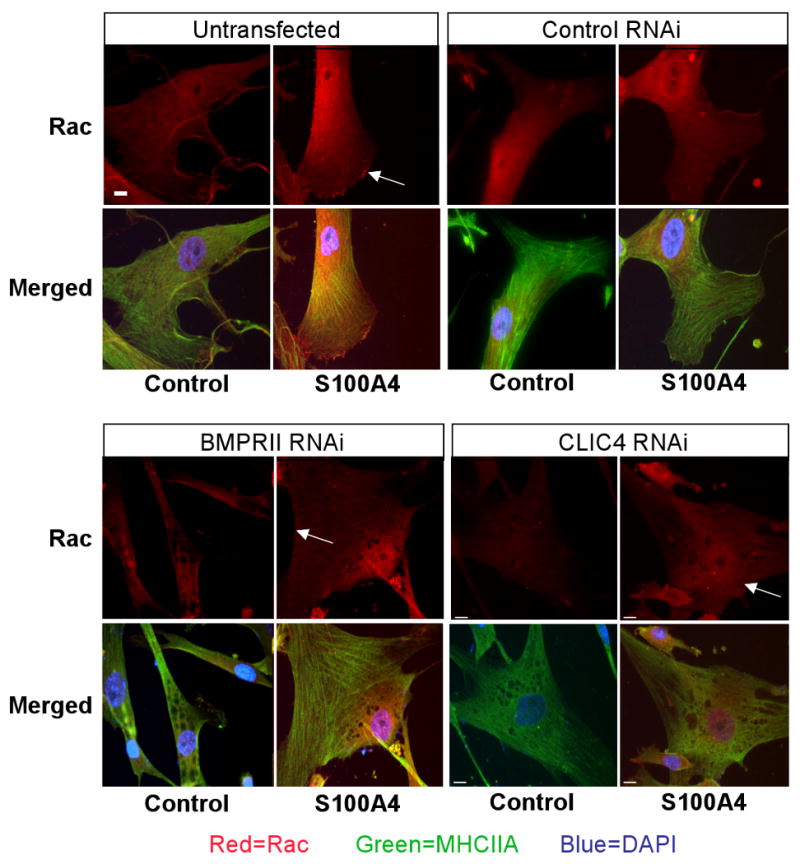
Western immunoblotting and densitometry of (A) active Rac1/total Rac1, and (B) active RhoA/total RhoA, from hPASMC lysates 10min to 6h after stimulation with S100A4/Mts1. (C) Immunofluorescence of MHCIIA and Rac1 in hPASMC stimulated with S100A4/Mts1 for 10 min using a primary antibody against MHCIIA and Rac1 and a secondary antibody linked to fluorescein (FITC) and rhodamine (red) under untransfected control conditions, and following transfection with non-targeting siRNA, BMPRII siRNA, and CLIC4 RNAi. Reducing CLIC4 either by BMPRII siRNA or CLIC4 siRNA reduces peripheral distribution of Rac1. Bars represent mean±SEM from n=3 experiments, *p<0.01, **p<0.001 vs. unstimulated control.
In assessing the role of Cdc42 we found that total Cdc42 is increased after CLIC4 siRNA vs. control RNAi independent of S100A4/Mts1 stimulation. Active to total Cdc42 in response to S100A4/Mts1 stimulation, is not significantly affected by CLIC4 vs. control siRNA (Online Figure 4).
Discussion
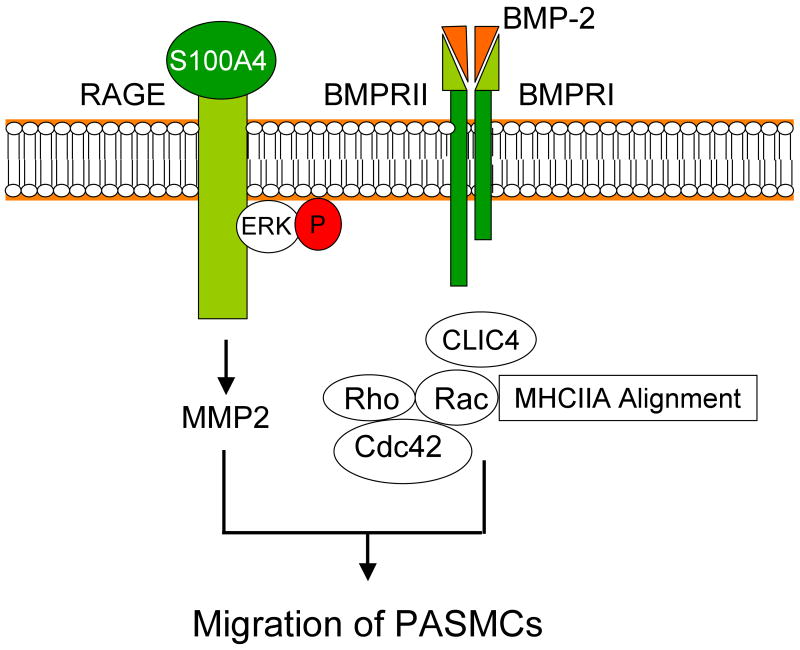
We propose a novel co-dependence between RAGE and BMPRII and indicate how a single ligand (BMP-2 or S100A4/Mts1) can recruit additional cell surface receptors to relay signals necessary to orchestrate a functional response, in this case to coordinate cytoskeletal changes with MMP activity and Rho/Rac activation required for cell motility (Figure 7). We speculate that this carefully controlled process limits signals from multiple ligands, but could be subverted in disease.
Figure 7. Model of interdependent RAGE-S100A4/Mts1 and BMPRII/BMP-2 signaling in hPASMCS migration.
The S100A4/Mts1 receptor RAGE is necessary for phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and subsequent MMP2 activity, whereas BMPRII is required to maintain CLIC4 levels. In turn, sustaining CLIC4 is necessary for proper activation of Rac1 and RhoA and subsequent cytoskeletal rearrangements required for hPASMC migration.
S100A4/Mts1 was described as a protein differentially regulated in metastatic breast cancer and subsequent experimental animal and clinical studies established this protein as a ‘metastasis’ factor in a variety of cancers19. Our previous studies indicated that RAGE is the receptor for S100A4/Mts13 and work by others showed that S100A4/Mts1 internalization and binding to MHCIIA mediates cell motility2. That BMP-2 is also a motogen is consistent with studies previously reported in human aortic smooth muscle cells20. However, in rat aortic smooth muscle cells BMP-2 and BMP-4 were shown to suppress motility but in those studies, the BMPs were only used in conjunction with serum or PDGF mediated motility, and in very high doses of 100ng/ml21. BMP-2 promotes mesenchymal cell migration in association with atrioventricular valvulogenesis22 and also induces migration of neural crest cells23
That S100A4/Mts1-RAGE signals depended upon cross-talk with BMPRII is a novel finding, but cross talk between RAGE and Smad 2/3 signals both in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells as well as in mesangial cells have been related to diabetic vascular disease and nephropathy24. In unpublished work from our laboratory, we have shown that BMP-2 mediates motility of endothelial cells in a pSmad 1/5 dependent manner.
It has been suggested that the S100 proteins may have interactions with proteins other than RAGE through the hinge domain, so it is possible that S100A4/Mts1 could interact with BMPRII or with some other receptor that recruits BMPRII, such as BMPRIA or BMPRIB. This is because blocking RAGE does not abrogate S100A4/Mts1 mediated processes that depend upon BMPRII such as maintaining CLIC4 levels. Since S100A proteins can interact with lipid rafts25 and since BMPRII exists in lipid rafts26 it is possible that there is a direct association at the level of the cell membrane. Conversely it is possible that BMP-2 interacts with RAGE or recruits RAGE in a non-BMPRII dependent manner, i. e., through BMPRIA or BMPRIB and an Activin type II receptor27 since the absence of BMPRII does not repress BMP-2 mediated pERK1/2 in contrast to pre-treatment with anti-RAGE. Since pERK is known to bind RAGE28, it is perhaps not surprising that S100A4/Mts1 and BMP-2 mediated motility is pERK dependent. To further substantiate the role of RAGE in mediating the pERK signal we have made multiple attempts to reduce RAGE expression using a variety of RAGE siRNAs and transfection strategies, but could not successfully knockdown RAGE in PASMC.
In addition to regulating MHCIIA mediated motility, S100A4/Mts1 also induces MMP2 activity, which is essential for vascular SMC migration17. RAGE and MMP2 activity have been implicated in restenosis29 and in atherosclerosis30, S100A4/Mts1 is thought to be a marker of intimal SMC31 and mediates cancer cell invasiveness through MMP232.
Our observation that BMPRII is necessary to maintain levels of CLIC4 is novel and unexpected as was the further observation that reduced levels of CLIC4 are sufficient to suppress motility. These findings are consistent with the association of CLIC4 with a signaling complex required for motility of spermatozoa9. On the other hand, up-regulation of CLIC4 during conversion of fibroblasts to myofibroblasts correlates with reduced motility10. Thus, the exact role of CLIC4 in cell motility may depend on a particular signaling pathway, cell type, or biological context. CLIC4 is found in lipid rafts33 and acts as a scaffolding protein for protein kinases and phosphatases14, and may play a key role in microtubule dynamics, particularly since it localizes with the centrosome of the cell during division and at the apical junctions of polarized epithelial cells. Most recently, CLIC4 has been shown to associate with G-protein coupled receptors such as the histamine H3 receptor35, suggesting that CLIC4 could play a role in expression/presentation of receptors at the cell surface. We have shown hat peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR) gamma is downstream of BMP-212 signaling in SMC, and loss of PPAR beta/delta also decreases CLIC436.
We observed mal-alignment of myosin with loss of BMPRII or CLIC4 giving the appearance of ‘fenestrations’ or vacuoles in the cytoskeleton. Although nuclear CLIC4 is associated with apoptosis15, it is possible that loss of cytoplasmic CLIC4, leads to autophagy and that these vacuolar structures represent autophagosomes36 induced as a cell survival mechanism. Alternatively, the vacuoles could represent some stage of intracellular lumen formation, since reduction of CLIC4 and a C. elegans CLIC, EXC-4, have been linked to defects in lumen/tube formation in endothelial cells and intracellular secretory canals, respectively37. Based on these findings, our data indicate that the cytoskeletal changes and intracellular vacuoles are indeed induced by loss of CLIC4. We suggest that this leads to delayed activity of Rac1 and RhoA and alterations in the localization of Rac1, and this impairs migration, since these GTPases are critical regulators of cytoskeletal dynamics and play key roles in cell retraction and extension of filopodiae38. Alternatively, reduced activity of RhoA and Rac1 might reflect loss of the function of CLIC4 act as a scaffolding molecule14, suggesting that CLIC4 may permit timely activation and translocation of these GTPases. CLICs can interact directly or indirectly with members of the ERM (ezrin-radixin-moesin) family of membrane-cytoskeletal linkers13, proteins reported to be involved in regulation of signaling by Rho family GTPases. Interestingly we could not show a significant change in Cdc42 activation yet total Cdc42 seems to be increased with CLIC4 RNAi.
Recent studies in cultured hPASMC, by our group indicate that loss of BMPRII function increases proliferation in response to agonists such as PDGF-BB12. Since loss of BMPRII function reduces motility, it is possible that migration is less important than proliferation in the pathogenesis of occlusive lesions in PAH. Alternatively, additional modifications are necessary for loss of function of BMPRII to result in both heightened proliferation and migration, for example, up-regulation of RAGE or heightened activity of other mito/motogens such as PDGF-BB that are unimpeded by reduced BMPRII. This would be in keeping with the low penetrance39 of disease in patients with loss of function of BMPRII and with the relatively mild phenotype in mice with haploinsufficiency of BMPRII6.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to Dr. Michal Roof for help with the Figures and with editorial review of our manuscript.
Funding Sources: Postdoctoral Fellowship from the American Heart Association/Pulmonary Hypertension Association to E.S.; Postdoctoral Fellowship from the Institut National de la Sante et de la Recherché Medicale (INSERM) to C.G.; Postdoctoral Fellowship from the American Lung Association to V.P.; Postdoctoral fellowships from the Sigrid Juselius Foundation, Instrumentarium Foundation, the Finnish Foundation for Cardiovascular Research and the Academy of Finland to T-P.A.; NHLBI National Research Service Award T32-HL007708-14 to J.M.B.; British Heart Foundation Project Grant PG/06/125/1633 to A.L.; The Ohio University Office of Research and Sponsored Programs to M.B.; and National Institutes of Health (1-R01-HL074186-01) and the Dwight and Vera Dunlevie Endowed Professorship to M.R.
Non-Standard Abbreviations and Acronyms
- RAGE
Receptor for Advanced Gycation end-products
- CLIC4
Chloride Intracellular Channel 4
- PASMC
Pulmonary Artery Smooth Muscle Cell
- siRNA
short interference RNA
- BMP-2
Bone morphogenetic protein 2
- PCR
Polymerase chain reaction
Footnotes
Disclosures: The authors declare that no conflict of interest exists.
Literature
- 1.Tarabykina S, Griffiths TR, Tulchinsky E, Mellon JK, Bronstein IB, Kriajevska M. Metastasis-associated protein S100A4: spotlight on its role in cell migration. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2007;7:217–228. doi: 10.2174/156800907780618329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Li ZH, Bresnick AR. The S100A4 metastasis factor regulates cellular motility via a direct interaction with myosin-IIA. Cancer Res. 2006;66:5173–5180. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lawrie A, Spiekerkoetter E, Martinez EC, Ambartsumian N, Sheward WJ, MacLean MR, Harmar AJ, Schmidt AM, Lukanidin E, Rabinovitch M. Interdependent serotonin transporter and receptor pathways regulate S100A4/Mts1, a gene associated with pulmonary vascular disease. Circ Res. 2005;97:227–235. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000176025.57706.1e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jones PL, Cowan KN, Rabinovitch M. Tenascin-C, proliferation and subendothelial fibronectin in progressive pulmonary vascular disease. Am J Pathol. 1997;150:1349–1360. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Greenway S, van Suylen RJ, Du Marchie Sarvaas G, Kwan E, Ambartsumian N, Lukanidin E, Rabinovitch M. S100A4/Mts1 produces murine pulmonary artery changes resembling plexogenic arteriopathy and is increased in human plexogenic arteriopathy. Am J Pathol. 2004;164:253–262. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63115-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Long L, MacLean MR, Jeffery TK, Morecroft I, Yang X, Rudarakanchana N, Southwood M, James V, Trembath RC, Morrell NW. Serotonin increases susceptibility to pulmonary hypertension in BMPR2-deficient mice. Circ Res. 2006;98:818–827. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000215809.47923.fd. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lane KB, Machado RD, Pauciulo MW, Thomson JR, Phillips JA, 3rd, Loyd JE, Nichols WC, Trembath RC. Heterozygous germline mutations in BMPR2, encoding a TGF-beta receptor, cause familial primary pulmonary hypertension. The International PPH Consortium. Nat Genet. 2000;26:81–84. doi: 10.1038/79226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Deng Z, Morse JH, Slager SL, Cuervo N, Moore KJ, Venetos G, Kalachikov S, Cayanis E, Fischer SG, Barst RJ, Hodge SE, Knowles JA. Familial primary pulmonary hypertension (gene PPH1) is caused by mutations in the bone morphogenetic protein receptor-II gene. Am J Hum Genet. 2000;67:737–744. doi: 10.1086/303059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Myers K, Somanath PR, Berryman M, Vijayaraghavan S. Identification of chloride intracellular channel proteins in spermatozoa. FEBS Lett. 2004;566:136–140. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.04.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ronnov-Jessen L, Villadsen R, Edwards JC, Petersen OW. Differential expression of a chloride intracellular channel gene, CLIC4, in transforming growth factor-beta1-mediated conversion of fibroblasts to myofibroblasts. Am J Pathol. 2002;161:471–480. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)64203-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Merklinger SL, Wagner RA, Spiekerkoetter E, Hinek A, Knutsen RH, Kabir MG, Desai K, Hacker S, Wang L, Cann GM, Ambartsumian NS, Lukanidin E, Bernstein D, Husain M, Mecham RP, Starcher B, Yanagisawa H, Rabinovitch M. Increased fibulin-5 and elastin in S100A4/Mts1 mice with pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res. 2005;97:596–604. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000182425.49768.8a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hansmann G, de Jesus Perez VA, Alastalo TP, Alvira CM, Guignabert C, Bekker JM, Schellong S, Urashima T, Wang L, Morrell NW, Rabinovitch M. An antiproliferative BMP-2/PPARgamma/apoE axis in human and murine SMCs and its role in pulmonary hypertension. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:1846–1857. doi: 10.1172/JCI32503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Berryman M, Bretscher A. Identification of a novel member of the chloride intracellular channel gene family (CLIC5) that associates with the actin cytoskeleton of placental microvilli. Mol Biol Cell. 2000;11:1509–1521. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.5.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Berryman MA, Goldenring JR. CLIC4 is enriched at cell-cell junctions and colocalizes with AKAP350 at the centrosome and midbody of cultured mammalian cells, Cell Motil. Cytoskeleton. 2003;56:159–172. doi: 10.1002/cm.10141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fernandez-Salas E, Suh KS, Speransky VV, Bowers WL, Levy JM, Adams T, Pathak KR, Edwards LE, Hayes DD, Cheng C, Steven AC, Weinberg WC, Yuspa SH. mtCLIC/CLIC4, an organellular chloride channel protein, is increased by DNA damage and participates in the apoptotic response to p53. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:3610–3620. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.11.3610-3620.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Li ZH, Spektor A, Varlamova O, Bresnick AR. Mts1 regulates the assembly of nonmuscle myosin-IIA. Biochemistry. 2003;42:14258–14266. doi: 10.1021/bi0354379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kenagy RD, Hart CE, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Clowes AW. Primate smooth muscle cell migration from aortic explants is mediated by endogenous platelet-derived growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor acting through matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9. Circulation. 1997;96:3555–3560. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.96.10.3555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Growcott EJ, Spink KG, Ren X, Afzal S, Banner KH, Wharton J. Phosphodiesterase type 4 expression and anti-proliferative effects in human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Respir Res. 2006;7:9. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-7-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ambartsumian N, Grigorian M, Lukanidin E. Genetically modified mouse models to study the role of metastasis-promoting S100A4(mts1) protein in metastatic mammary cancer. J Dairy Res. 2005;72(Spec No):27–33. doi: 10.1017/s0022029905001093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Willette RN, Gu JL, Lysko PG, Anderson KM, Minehart H, Yue T. BMP-2 gene expression and effects on human vascular smooth muscle cells. J Vasc Res. 1999;36:120–125. doi: 10.1159/000025634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Maciel TT, Melo RS, Schor N, Campos AH. Gremlin promotes vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008;44:370–379. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.10.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Inai K, Norris RA, Hoffman S, Markwald RR, Sugi Y. BMP-2 induces cell migration and periostin expression during atrioventricular valvulogenesis. Dev Biol. 2007 doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.12.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Correia AC, Costa M, Moraes F, Bom J, Novoa A, Mallo M. Bmp2 is required for migration but not for induction of neural crest cells in the mouse. Dev Dyn. 2007;236:2493–2501. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Li JH, Huang XR, Zhu HJ, Oldfield M, Cooper M, Truong LD, Johnson RJ, Lan HY. Advanced glycation end products activate Smad signaling via TGF-beta-dependent and independent mechanisms: implications for diabetic renal and vascular disease. Faseb J. 2004;18:176–178. doi: 10.1096/fj.02-1117fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nacken W, Sorg C, Kerkhoff C. The myeloid expressed EF-hand proteins display a diverse pattern of lipid raft association. FEBS Lett. 2004;572:289–293. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.07.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ramos M, Lame MW, Segall HJ, Wilson DW. The BMP type II receptor is located in lipid rafts, including caveolae, of pulmonary endothelium in vivo and in vitro. Vascul Pharmacol. 2006;44:50–59. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2005.09.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yu PB, Beppu H, Kawai N, Li E, Bloch KD. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type II receptor deletion reveals BMP ligand-specific gain of signaling in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:24443–24450. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M502825200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ishihara K, Tsutsumi K, Kawane S, Nakajima M, Kasaoka T. The receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE) directly binds to ERK by a D-domain-like docking site. FEBS Lett. 2003;550:107–113. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00846-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sakaguchi T, Yan SF, Yan SD, Belov D, Rong LL, Sousa M, Andrassy M, Marso SP, Duda S, Arnold B, Liliensiek B, Nawroth PP, Stern DM, Schmidt AM, Naka Y. Central role of RAGE-dependent neointimal expansion in arterial restenosis. J Clin Invest. 2003;111:959–972. doi: 10.1172/JCI17115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cipollone F, Iezzi A, Fazia M, Zucchelli M, Pini B, Cuccurullo C, De Cesare D, De Blasis G, Muraro R, Bei R, Chiarelli F, Schmidt AM, Cuccurullo F, Mezzetti A. The receptor RAGE as a progression factor amplifying arachidonate-dependent inflammatory and proteolytic response in human atherosclerotic plaques: role of glycemic control. Circulation. 2003;108:1070–1077. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000086014.80477.0D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Brisset AC, Hao H, Camenzind E, Bacchetta M, Geinoz A, Sanchez JC, Chaponnier C, Gabbiani G, Bochaton-Piallat ML. Intimal smooth muscle cells of porcine and human coronary artery express S100A4, a marker of the rhomboid phenotype in vitro. Circ Res. 2007;100:1055–1062. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000262654.84810.6c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pazzaglia L, Ponticelli F, Magagnoli G, Magagnoli G, Gamberi G, Ragazzini P, Balladelli A, Picci P, Benassi M. Activation of metalloproteinases-2 and -9 by interleukin-1alpha in S100A4-positive liposarcoma cell line: correlation with cell invasiveness. Anticancer Res. 2004;24:967–972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Suginta W, Karoulias N, Aitken A, Ashley RH. Chloride intracellular channel protein CLIC4 (p64H1) binds directly to brain dynamin I in a complex containing actin, tubulin and 14-3-3 isoforms. Biochem J. 2001;359:55–64. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3590055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Maeda K, Haraguchi M, Kuramasu A, Sato T, Ariake K, Sakagami H, Kondo H, Yanai K, Fukunaga K, Yanagisawa T, Sukegawa J. CLIC4 interacts with histamine H3 receptor and enhances the receptor cell surface expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008 doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.02.071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Adamkiewicz J, Kaddatz K, Rieck M, Wilke B, Muller-Brusselbach S, Muller R. Proteomic profile of mouse fibroblasts with a targeted disruption of the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-beta/delta gene. Proteomics. 2007;7:1208–1216. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200601003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Berry KL, Bulow HE, Hall DH, Hobert O. A C. elegans CLIC-like protein required for intracellular tube formation and maintenance. Science. 2003;302:2134–2137. doi: 10.1126/science.1087667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yamada S, Nelson WJ. Localized zones of Rho and Rac activities drive initiation and expansion of epithelial cell-cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 2007;178:517–527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200701058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Machado RD, James V, Southwood M, Harrison RE, Atkinson C, Stewart S, Morrell NW, Trembath RC, Aldred MA. Investigation of second genetic hits at the BMPR2 locus as a modulator of disease progression in familial pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circulation. 2005;111:607–613. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000154543.07679.08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.