Abstract
A-type K+ currents are expressed in Xenopus oocytes injected with in vitro-synthesized transcripts from cDNAs for the Drosophila Shaker (Sh) locus. A single Sh gene product, possibly as a multimer, is sufficient for formation of functional A channels. Various Sh RNAs express A currents with distinct kinetic properties. An analysis of structure-function relationships shows that the conserved central region of Sh polypeptides determines ionic selectivity and overall channel behavior, whereas the divergent amino and carboxyl termini can modify channel kinetics. Alternative splicing of Sh gene transcripts may provide one mechanism for the generation of K+ channel diversity.
Full text
PDF
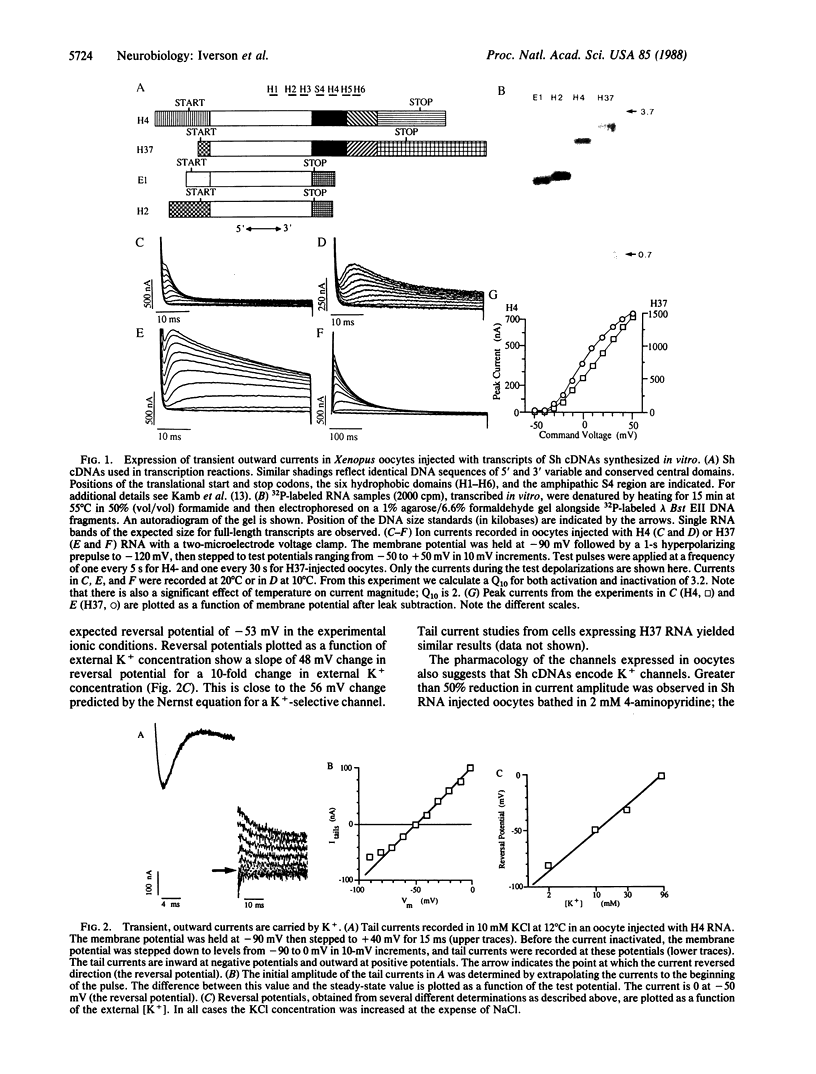



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumann A., Krah-Jentgens I., Müller R., Müller-Holtkamp F., Seidel R., Kecskemethy N., Casal J., Ferrus A., Pongs O. Molecular organization of the maternal effect region of the Shaker complex of Drosophila: characterization of an I(A) channel transcript with homology to vertebrate Na channel. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3419–3429. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02665.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Molecular properties of voltage-sensitive sodium channels. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:953–985. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R., Seetharamulu P. Molecular model of the action potential sodium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):508–512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamb A., Iverson L. E., Tanouye M. A. Molecular characterization of Shaker, a Drosophila gene that encodes a potassium channel. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90494-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Camardo J., Kandel E. R. Serotonin modulates a specific potassium current in the sensory neurons that show presynaptic facilitation in Aplysia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5713–5717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Ikeda T., Kayano T., Suzuki H., Takeshima H., Kurasaki M., Takahashi H., Numa S. Existence of distinct sodium channel messenger RNAs in rat brain. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):188–192. doi: 10.1038/320188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Diversity and ubiquity of K channels. Neuroscience. 1988 Jun;25(3):729–749. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salkoff L. B., Wyman R. J. Ion currents in Drosophila flight muscles. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:687–709. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salkoff L. Genetic and voltage-clamp analysis of a Drosophila potassium channel. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 1):221–231. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz T. L., Tempel B. L., Papazian D. M., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Multiple potassium-channel components are produced by alternative splicing at the Shaker locus in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):137–142. doi: 10.1038/331137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solc C. K., Zagotta W. N., Aldrich R. W. Single-channel and genetic analyses reveal two distinct A-type potassium channels in Drosophila. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1094–1098. doi: 10.1126/science.2437657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempel B. L., Papazian D. M., Schwarz T. L., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Sequence of a probable potassium channel component encoded at Shaker locus of Drosophila. Science. 1987 Aug 14;237(4816):770–775. doi: 10.1126/science.2441471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpe L. C., Schwarz T. L., Tempel B. L., Papazian D. M., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Expression of functional potassium channels from Shaker cDNA in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):143–145. doi: 10.1038/331143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. F., Haugland F. N. Voltage clamp analysis of membrane currents in larval muscle fibers of Drosophila: alteration of potassium currents in Shaker mutants. J Neurosci. 1985 Oct;5(10):2626–2640. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-10-02626.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




