Abstract
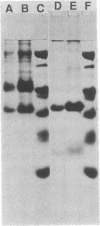
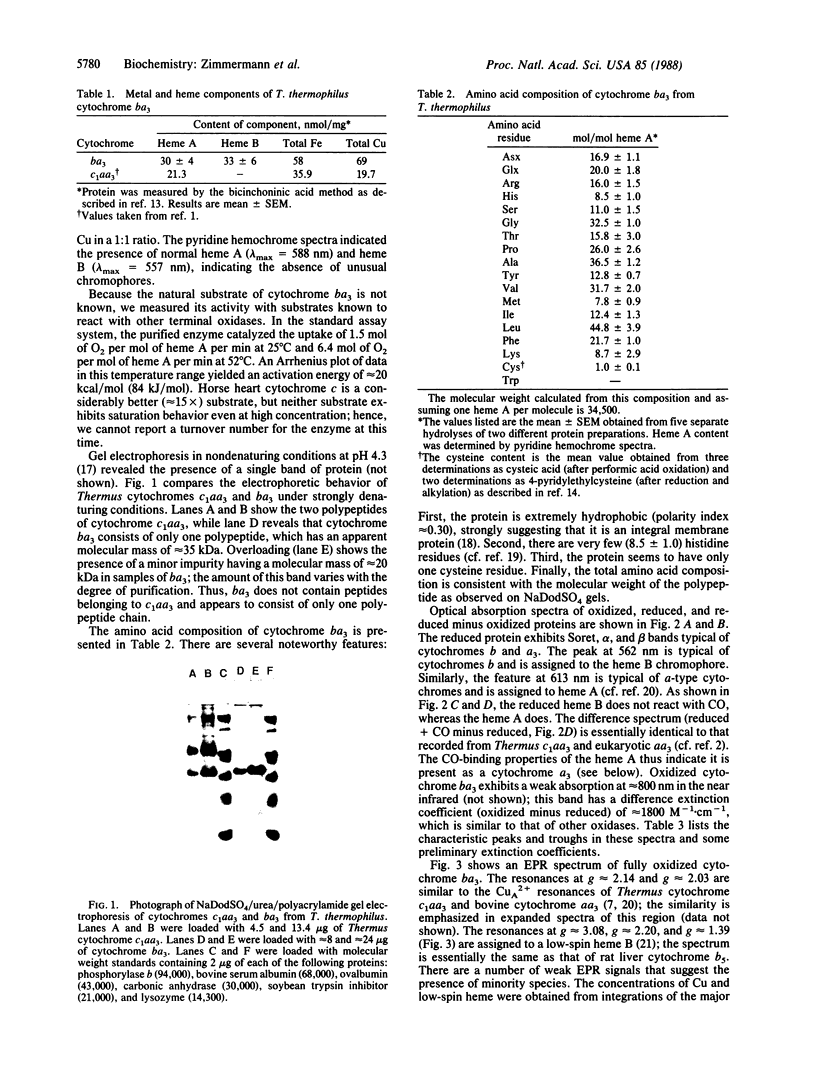
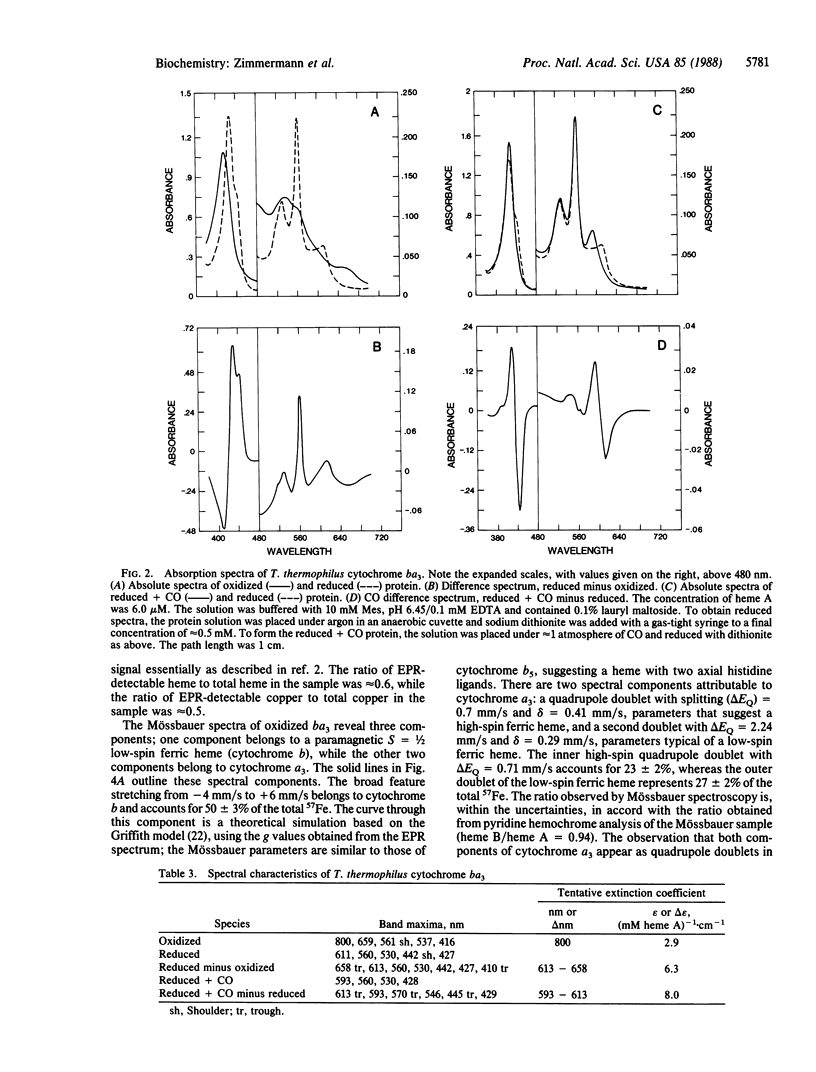
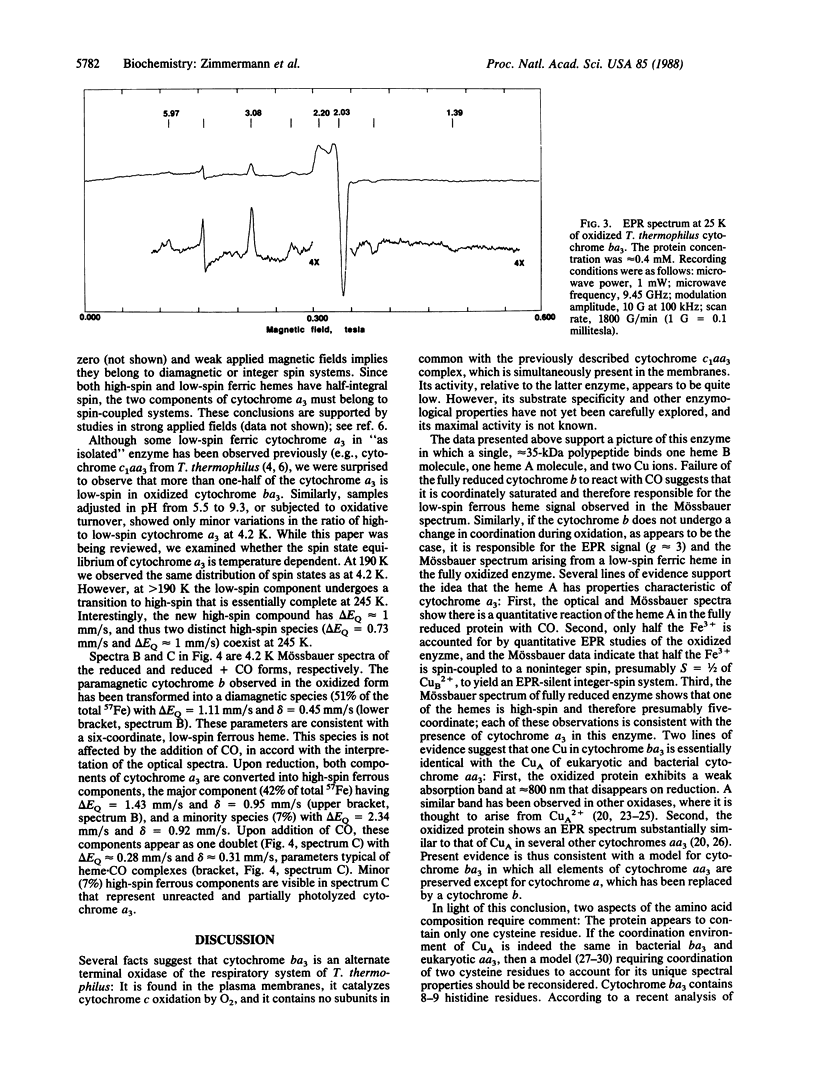
We describe an alternate terminal oxidase found in the plasma membrane of Thermus thermophilus and designate it cytochrome ba3. The enzyme consists of a single approximately equal to 35-kDa polypeptide that binds one heme B molecule, one heme A molecule, and two Cu ions. Optical spectra suggest the presence of cytochrome b, cytochrome a3, and CuA in this protein. Quantitative EPR and Mössbauer studies of the oxidized protein indicate the presence of one low-spin ferric heme, which is assigned to cytochrome b. Mössbauer studies of the reduced protein show the presence of one low-spin ferrous heme, assigned to cytochrome b, and a predominant high-spin ferrous heme that reacts quantitatively with CO to yield an additional low-spin ferrous heme. The latter Fe atom is associated with the heme A and is designated cytochrome a3. The EPR spectrum of the oxidized protein also reveals the presence of a CuA-type center that accounts for half the total Cu. The remainder of the Cu would appear to be present as CuB that is magnetically coupled to the heme A. Amino acid analyses of cytochrome ba3 show the presence of eight to nine histidine residues and one cysteine residue.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beinert H., Shaw R. W., Hansen R. E., Hartzell C. R. Studies on the origin of the near-infrared (800-900 nm) absorption of cytochrome c oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 8;591(2):458–470. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90176-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boelens R., Wever R. Redox reactions in mixed-valence cytochrome c oxidase. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 28;116(2):223–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80649-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downer N. W., Robinson N. C. Characterization of a seventh different subunit of beef heart cytochrome c oxidase. Similarities between the beef heart enzyme and that from other species. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2930–2936. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fee J. A., Choc M. G., Findling K. L., Lorence R., Yoshida T. Properties of a copper-containing cytochrome c1aa3 complex: a terminal oxidase of the extreme thermophile Thermus thermophilus HB8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):147–151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fee J. A., Kuila D., Mather M. W., Yoshida T. Respiratory proteins from extremely thermophilic, aerobic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986;853(2):153–185. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(86)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelles J., Blair D. F., Chan S. I. The proton-pumping site of cytochrome c oxidase: a model of its structure and mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986;853(3-4):205–236. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(87)90002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George-Nascimento C., Poyton R. O. Further analysis of the polypeptide subunits of yeast cytochrome c oxidase. Isolation and characterization of subunits III, V, and VII. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9363–9370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm L., Saraste M., Wikström M. Structural models of the redox centres in cytochrome oxidase. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2819–2823. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02578.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent T. A., Münck E., Dunham W. R., Filter W. F., Findling K. L., Yoshida T., Fee J. A. Mössbauer study of a bacterial cytochrome oxidase: cytochrome c1aa3 from Thermus thermophilus. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12489–12492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelberg H. K., Nicholls P. Kinetic studies on the interaction of TMPD with cytochrome c and cytochrome c oxidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Sep;133(2):327–335. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90461-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig B. Heme aa3-type cytochrome c oxidases from bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec;594(2-3):177–189. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(80)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münck E. Mössbauer spectroscopy of proteins: electron carriers. Methods Enzymol. 1978;54:346–379. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)54023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole R. K. Bacterial cytochrome oxidases. A structurally and functionally diverse group of electron-transfer proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 15;726(3):205–243. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(83)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusnak F. M., Münck E., Nitsche C. I., Zimmermann B. H., Fee J. A. Evidence for structural heterogeneities and a study of exchange coupling. Mössbauer studies of cytochrome c1aa3 from Thermus thermophilus. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16328–16332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens T. H., Martin C. T., Wang H., Brudvig G. W., Scholes C. P., Chan S. I. The nature of CuA in cytochrome c oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12106–12113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudzuki T., Wilson D. F. The oxidation-reduction potentials of the hemes and copper of cytochrome oxidase from beef heart. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Jul;145(1):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Fee J. A. Potentiometric study of cytochrome c1aa3 from Thermus thermophilus. J Inorg Biochem. 1985 Mar-Apr;23(3-4):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0162-0134(85)85036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Fee J. A. Studies on cytochrome c oxidase activity of the cytochrome c1aa3 complex from Thermus thermophilus. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1031–1036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida T., Lorence R. M., Choc M. G., Tarr G. E., Findling K. L., Fee J. A. Respiratory proteins from the extremely thermophilic aerobic bacterium, Thermus thermophilus. Purification procedures for cytochromes c552, c555,549, and c1aa3 and chemical evidence for a single subunit cytochrome aa3. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):112–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]