Abstract
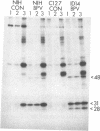
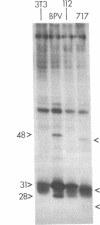
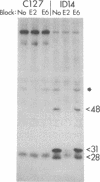
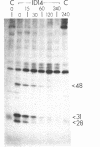
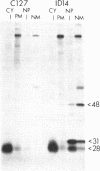
Genetic evidence suggests that the bovine papilloma virus type 1 (BPV) E2 open reading frame may encode at least two gene products involved in the regulation of viral gene expression. One, which is probably the full-length product, trans-activates transcription via an enhancer in the viral regulatory region. A second, containing sequences from the 3' end of the open reading frame, inhibits the trans-activating activity of the first product. We now report the identification and initial characterization of three E2-encoded proteins, with mobilities corresponding to 48, 31, and 28 kDa in cells transformed by the wild-type BPV. Pulse-chase experiments indicated that the 48-kDa protein had the longest half-life (40 min), but there was no indication that one species was the precursor of another. The 48-kDa species corresponds to the full-length trans-activating protein. The two smaller species contain only carboxyl-terminal determinants, and either or both could represent inhibitory E2 proteins. Subcellular fractionation localized all three E2 proteins to the nucleus. Consistent with the low rate of viral transcription in BPV-transformed cells, the 31-kDa presumptive repressor species was more abundant than the 48-kDa species.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Androphy E. J., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. Bovine papillomavirus E2 trans-activating gene product binds to specific sites in papillomavirus DNA. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):70–73. doi: 10.1038/325070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Androphy E. J., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R. Identification of the protein encoded by the E6 transforming gene of bovine papillomavirus. Science. 1985 Oct 25;230(4724):442–445. doi: 10.1126/science.2996134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Howley P. M. Differential promoter utilization by the bovine papillomavirus in transformed cells and productively infected wart tissues. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1027–1035. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Lampert M. A., Li A. C., Baluda M. A. Nuclear compartmentalization of the v-myb oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3017–3023. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciejek E. M., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Actively transcribed genes are associated with the nuclear matrix. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):607–609. doi: 10.1038/306607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douillard J. Y., Hoffman T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for screening monoclonal antibody production using enzyme-labeled second antibody. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:168–174. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretzky I., Shober R., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R. A quantitative in vitro focus assay for bovine papilloma virus. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R. Localization of the adenovirus E1Aa protein, a positive-acting transcriptional factor, in infected cells infected cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):829–838. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugen T. H., Cripe T. P., Ginder G. D., Karin M., Turek L. P. Trans-activation of an upstream early gene promoter of bovine papilloma virus-1 by a product of the viral E2 gene. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):145–152. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04732.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermonat P. L., Howley P. M. Mutational analysis of the 3' open reading frames and the splice junction at nucleotide 3225 of bovine papillomavirus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3889–3895. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3889-3895.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Spalholz B. A., Howley P. M. A transcriptional repressor encoded by BPV-1 shares a common carboxy-terminal domain with the E2 transactivator. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90663-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. C., Gilden R. V., Showalter S. D., Shah K. V. Identification of the human papillomavirus E2 protein in genital tract tissues. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):606–609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.606-609.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Dvoretzky I., Shober R., Law M. F., Engel L., Howley P. M. In vitro tumorigenic transformation by a defined sub-genomic fragment of bovine papilloma virus DNA. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):72–74. doi: 10.1038/287072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride A. A., Schlegel R., Howley P. M. The carboxy-terminal domain shared by the bovine papillomavirus E2 transactivator and repressor proteins contains a specific DNA binding activity. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):533–539. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskaluk C., Bastia D. The E2 "gene" of bovine papillomavirus encodes an enhancer-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1215–1218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. T., Vass W. C., Vousden K. H., Lowy D. R. E5 open reading frame of bovine papillomavirus type 1 encodes a transforming gene. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.1-6.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Wade-Glass M., Rabson M. S., Yang Y. C. The E5 transforming gene of bovine papillomavirus encodes a small, hydrophobic polypeptide. Science. 1986 Jul 25;233(4762):464–467. doi: 10.1126/science.3014660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Lambert P. F., Yee C. L., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus transcriptional regulation: localization of the E2-responsive elements of the long control region. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2128–2137. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2128-2137.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Yang Y. C., Howley P. M. Transactivation of a bovine papilloma virus transcriptional regulatory element by the E2 gene product. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):183–191. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenlund A., Zabielski J., Ahola H., Moreno-Lopez J., Pettersson U. Messenger RNAs from the transforming region of bovine papilloma virus type I. J Mol Biol. 1985 Apr 20;182(4):541–554. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Okayama H., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus contains multiple transforming genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1030–1034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]